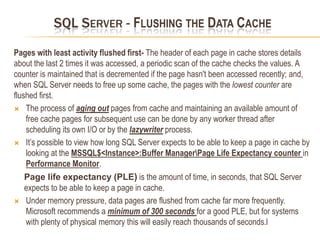
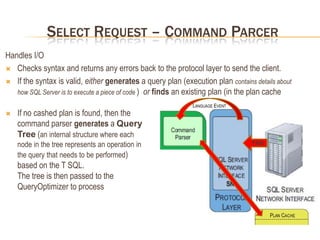
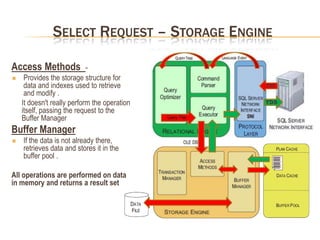
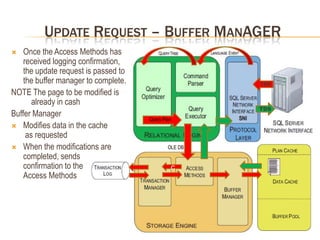
This document summarizes key differences between front-end applications like Access and the SQL Server backend. It also provides overviews of SQL Server transactions, server architecture including protocols and components, how select and update requests are processed, and uses of dynamic management views.