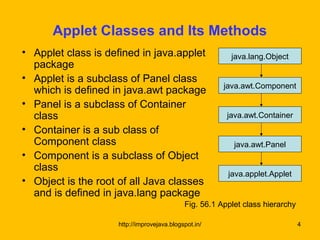
The document discusses applet classes, methods, and architecture. It explains that applet is a subclass of Panel and Component classes, and provides methods for running applets. The document also describes how applets are event-driven programs that wait for and respond to user interactions like mouse clicks or key presses by calling event handlers.