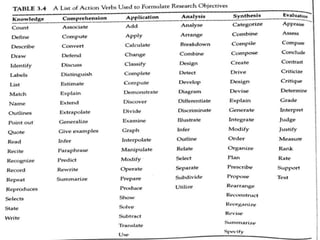
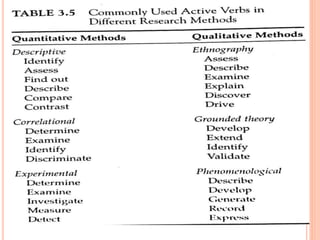
The document discusses the formulation of a research problem statement and objectives. It describes the multi-step process for selecting a research area and delimiting the specific research topic. Guidelines are provided for evaluating research problems based on substantive, methodological, stylistic, ethical, and practical issues. An example of a well-formulated research problem includes the design, variable(s), population, and setting. Research objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound to focus the research and avoid collecting unwanted information. Both general objectives and specific objectives are needed, with the latter being more narrow in scope. Objectives should be stated concisely using action verbs.