Embed presentation
Download to read offline
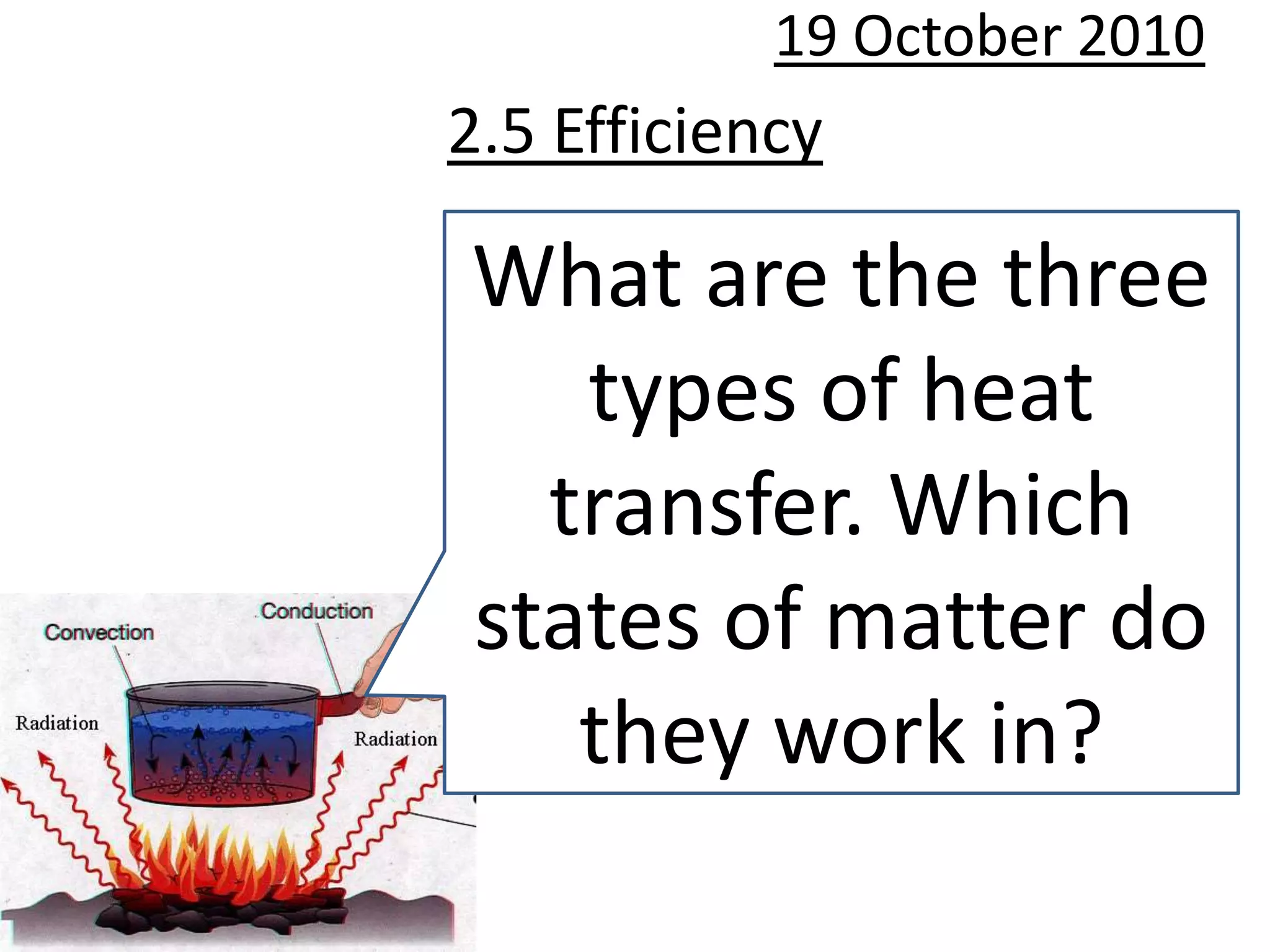

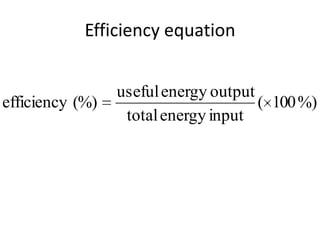





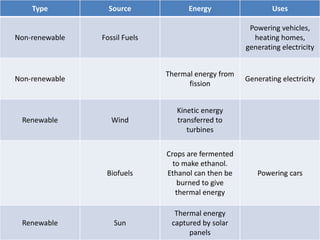
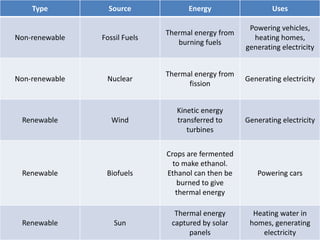

This document discusses the efficiency of energy transformations and calculations. It defines efficiency as the ratio of useful energy output to total energy input. An example is provided where a desk lamp with 100J input and 5J output has an efficiency of 5%. The document also mentions the three types of heat transfer that work across different states of matter and encourages activities to identify energy waste and calculate efficiency from input/output data.












