Embed presentation
Download to read offline

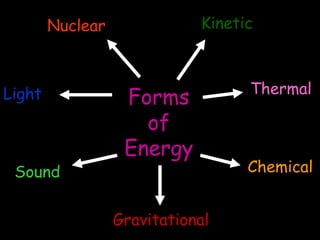



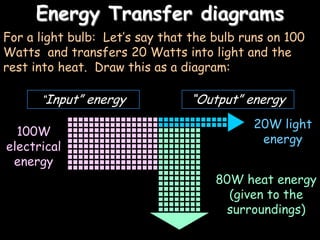
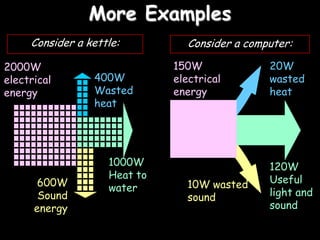

1. Energy can change forms as it is transferred. A light bulb takes in electrical energy and outputs light energy and heat energy. 2. Not all energy input is useful output - some is always wasted. For a light bulb, heat is wasted energy transferred to the surroundings. 3. Efficiency measures useful energy out versus energy in as a percentage. A light bulb that outputs 80J of light from 100J of electrical input has an efficiency of 80%.






