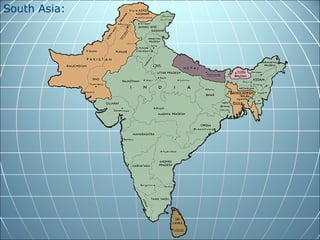
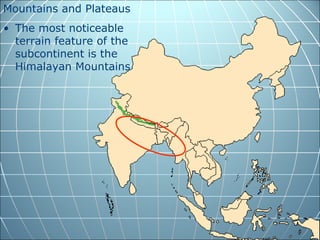
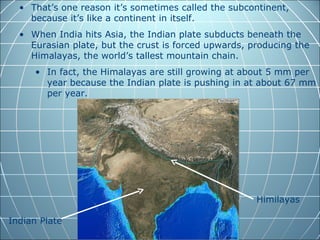
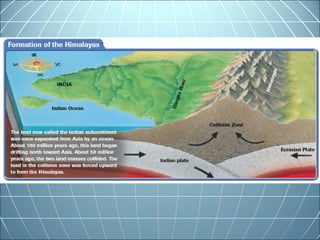
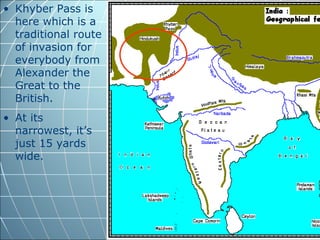
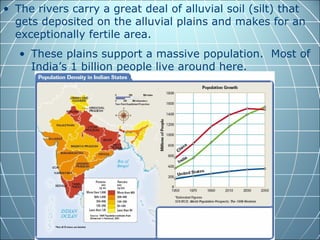
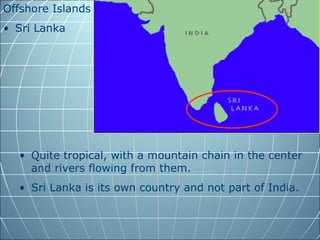
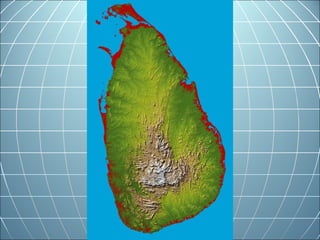
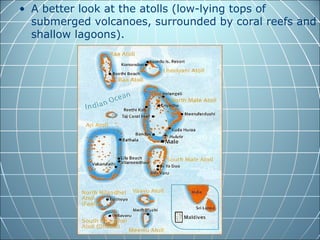
India is the largest country in South Asia. A subcontinent is a large landmass that is distinct from but connected to a larger landmass. Over 1 billion people live in India. The Himalayas mountain range serves as the border between the Indian subcontinent and China. The Hindu Kush mountains lie at the west end of the Himalayas. An archipelago is a group of islands. An atoll is a low-lying ring-shaped coral reef surrounding a lagoon.