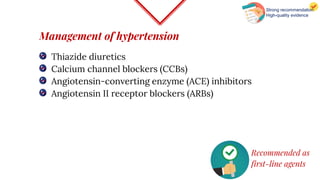
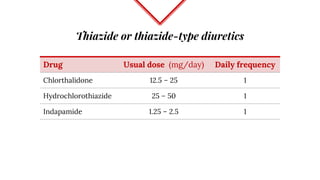
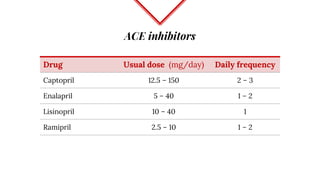
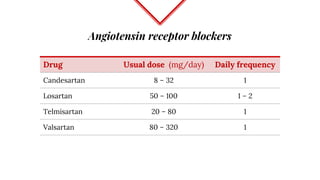
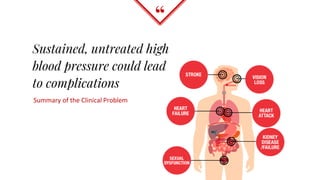
Untreated high blood pressure can lead to serious health complications. The 2017 guidelines from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association recommend evaluating and diagnosing hypertension based on multiple blood pressure readings on separate occasions. Once diagnosed, lifestyle changes and medication are recommended for management. First-line drug options include thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, and ARBs. The guidelines aim to help prevent disability and death from hypertension-related conditions like heart disease and stroke.













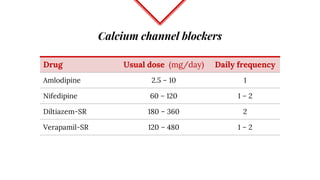
![Pharmacotherapy for hypertension
Drug-therapy is recommended for:
o Patients with clinical CVD
o (or) an estimated 10-year atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD) risk of
10% or higher patients who have a SBP ≥ 130mmHg or a
DBP ≥ 80mmHg
Strong recommendation
High-quality evidence
[for SBP] and expert
opinion [for DBP]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017hypertensionguidelines-drchaithanyamalalur-171222015502/85/2017-hypertension-guidelines-18-320.jpg)
![Pharmacotherapy for hypertension
For patients with no history of CVD and an ASCVD risk of less
than 10%, BP-lowering medication is recommended:
for patients who have an SBP of ≥ 140mmHg
or a DBP of ≥ 90mmHg
Strong recommendation
High-quality evidence
[for SBP] and expert
opinion [for DBP]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017hypertensionguidelines-drchaithanyamalalur-171222015502/85/2017-hypertension-guidelines-19-320.jpg)