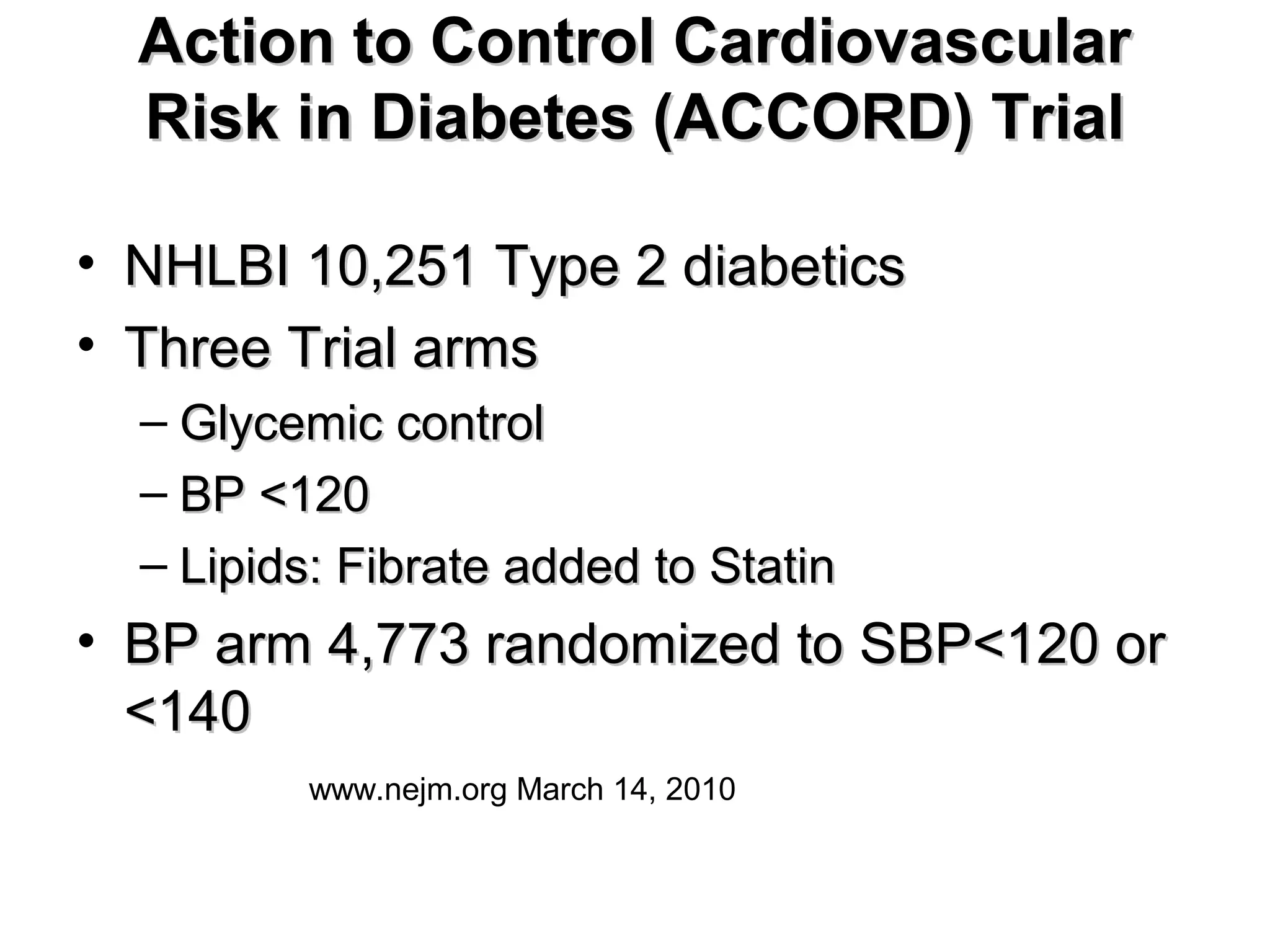
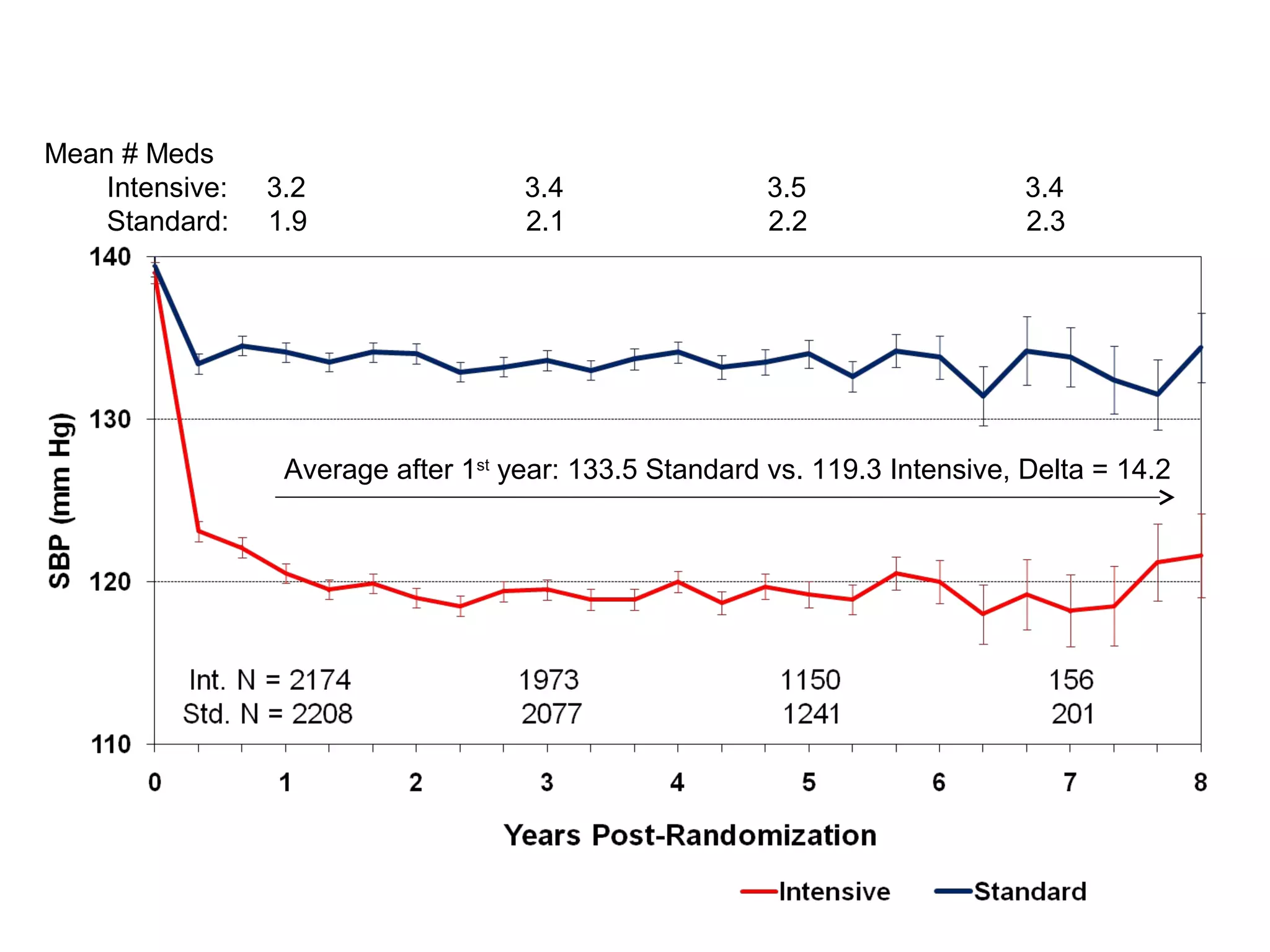
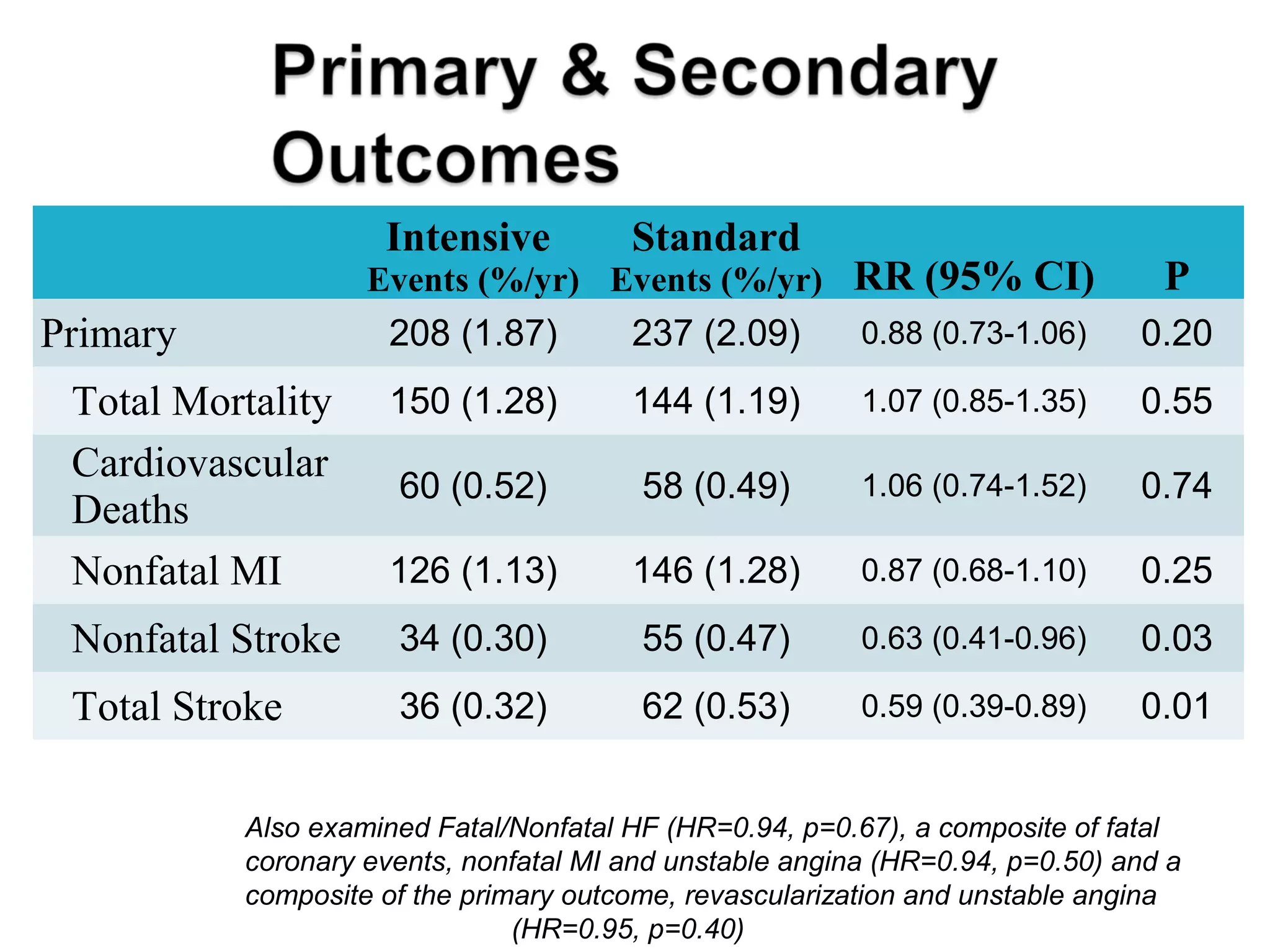
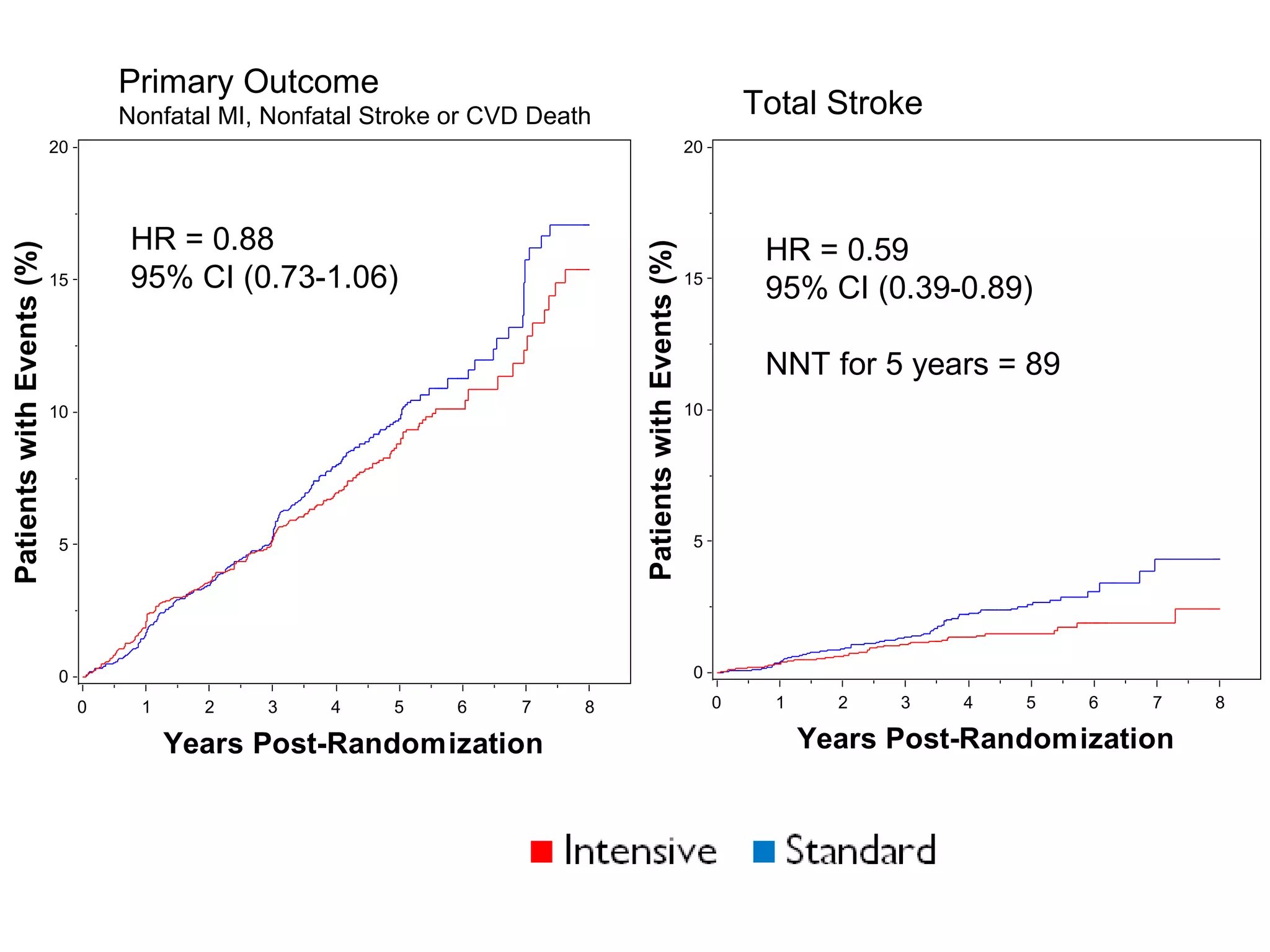
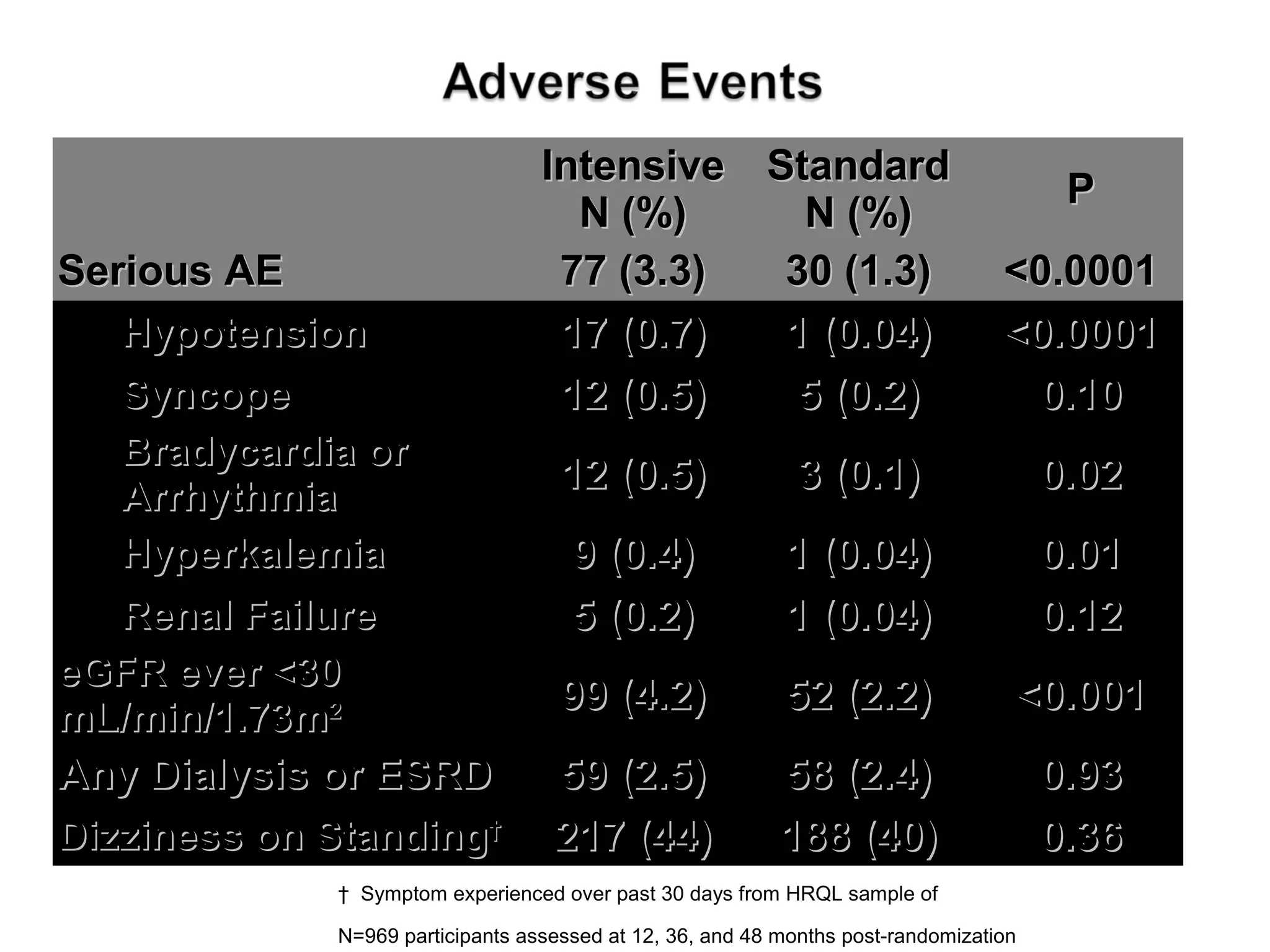
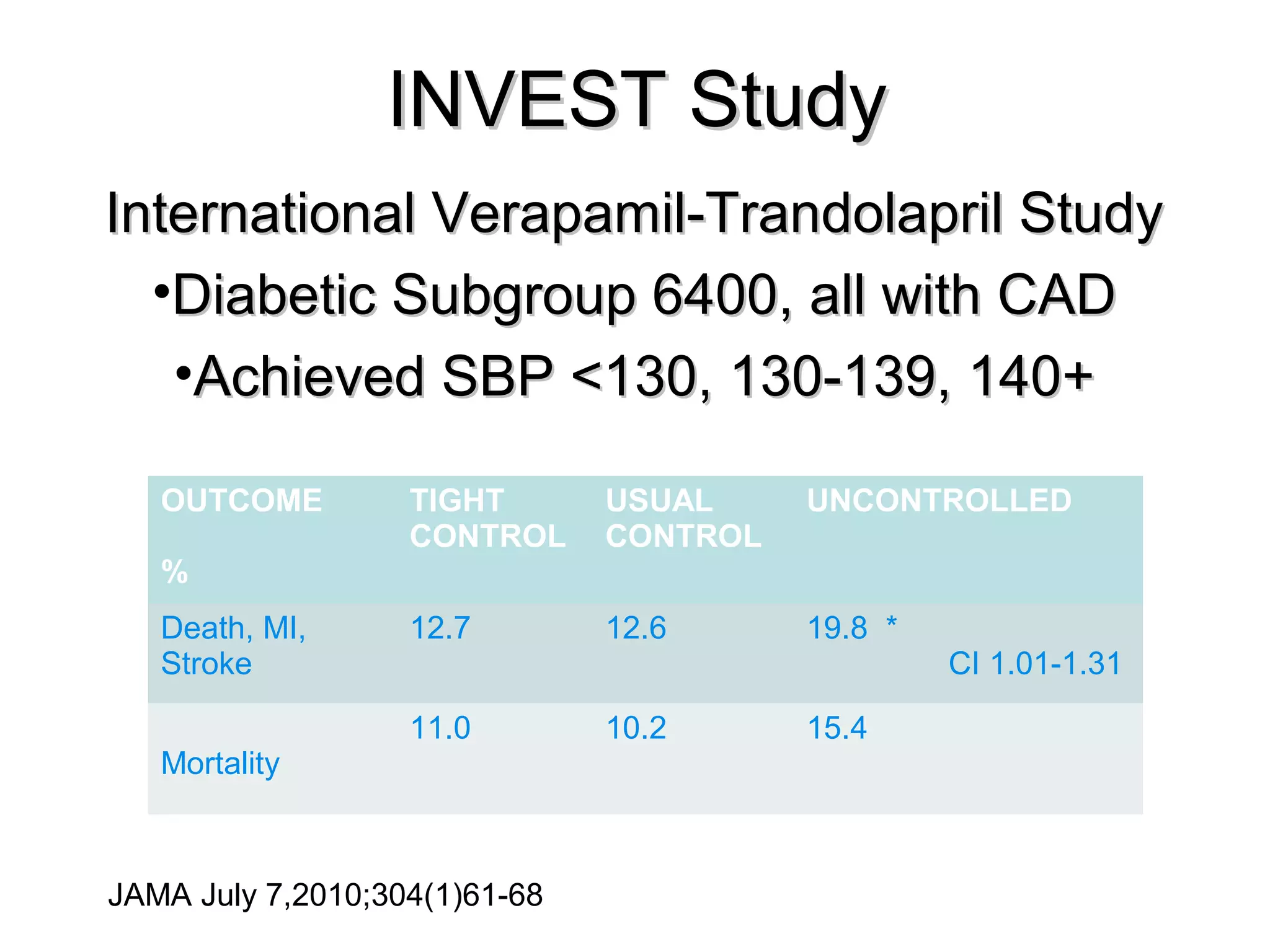
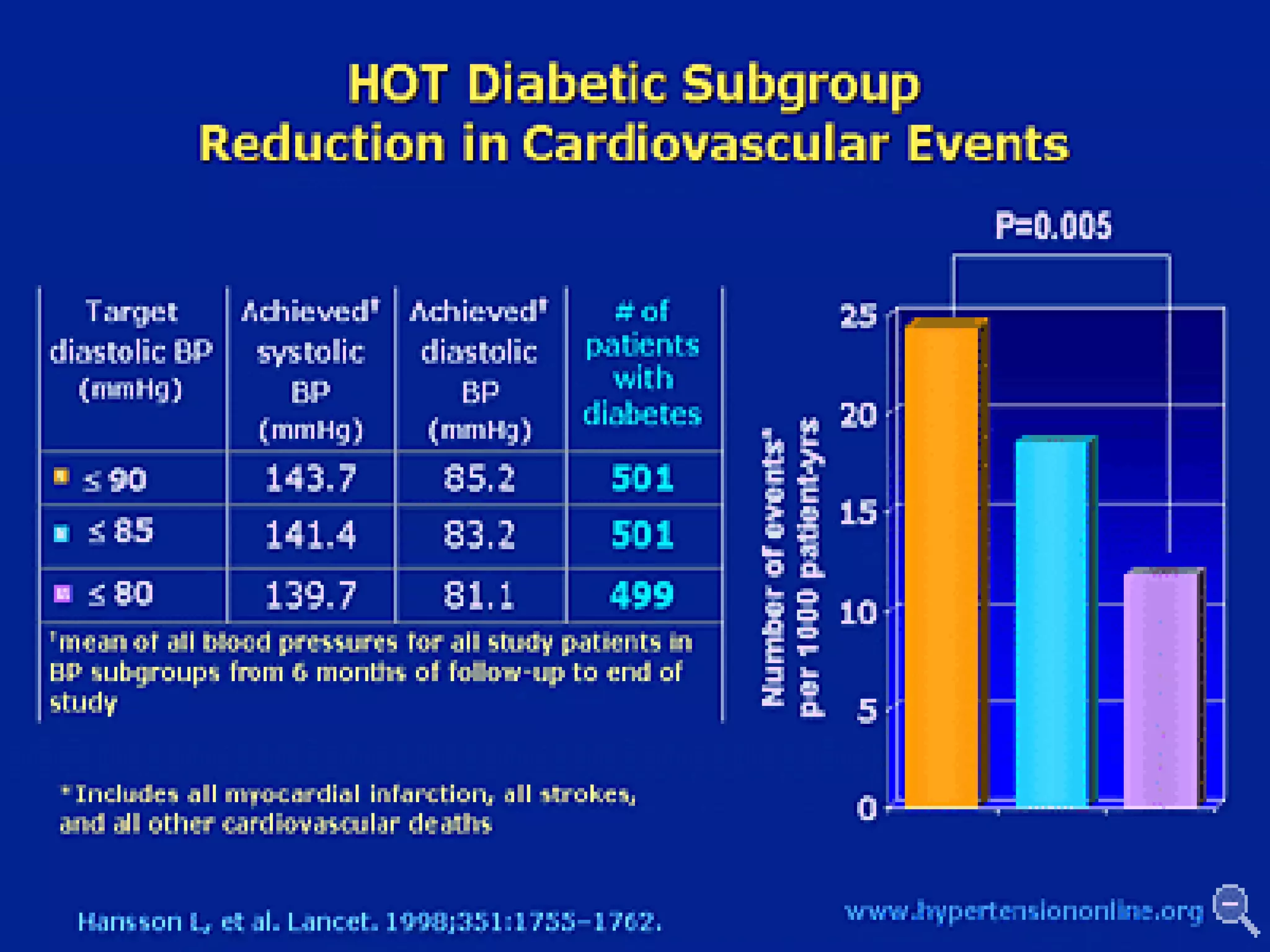
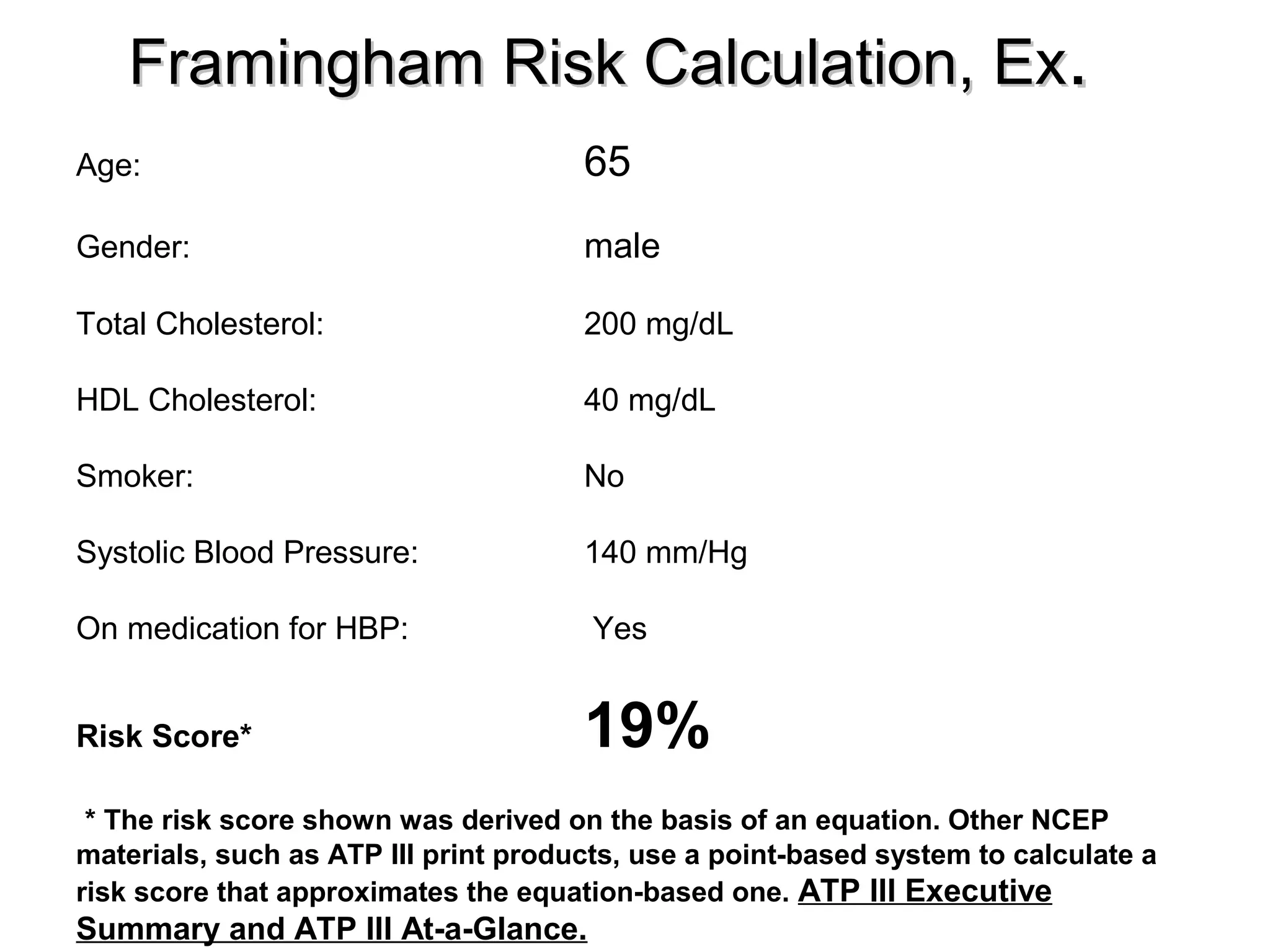
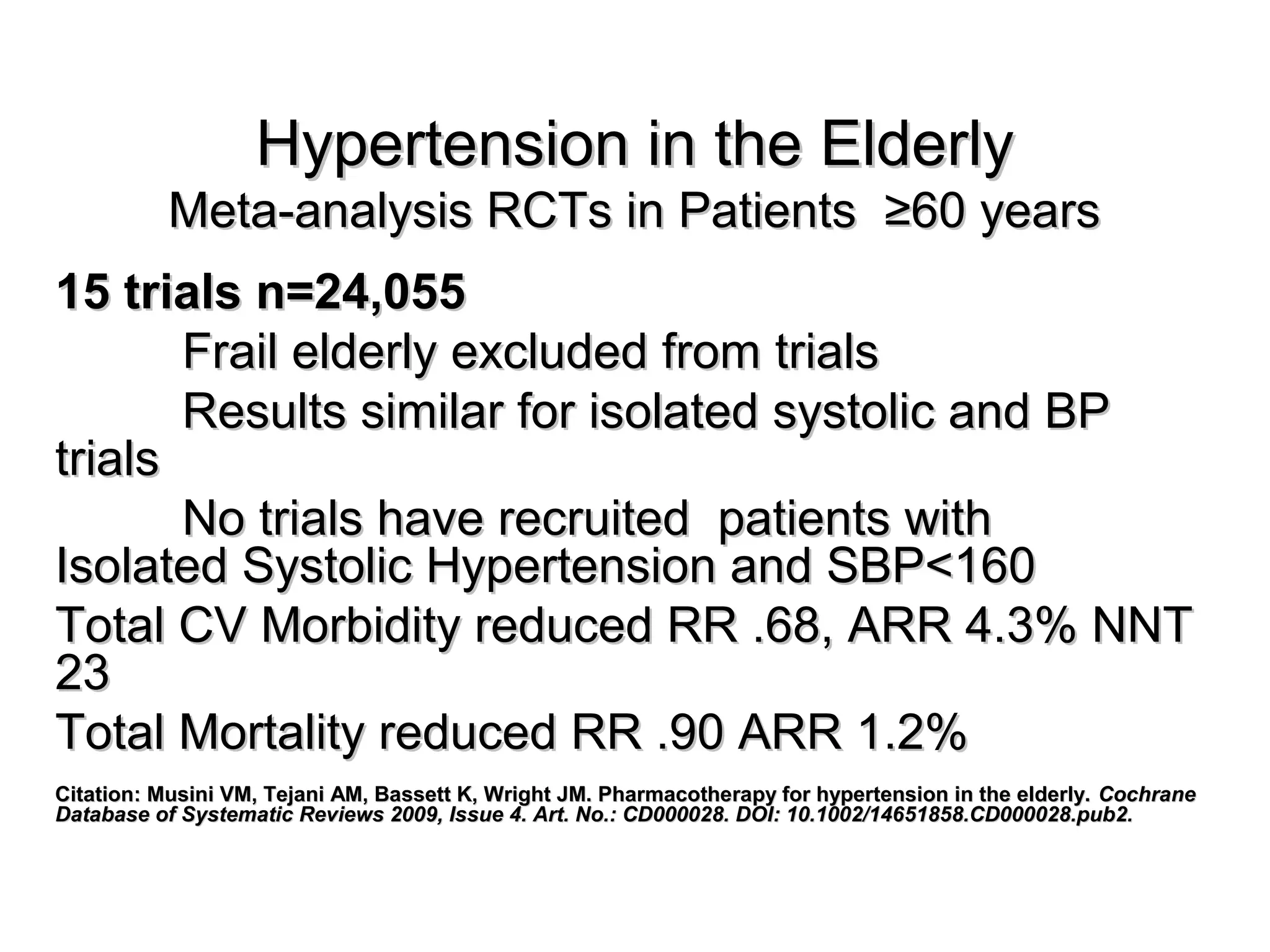
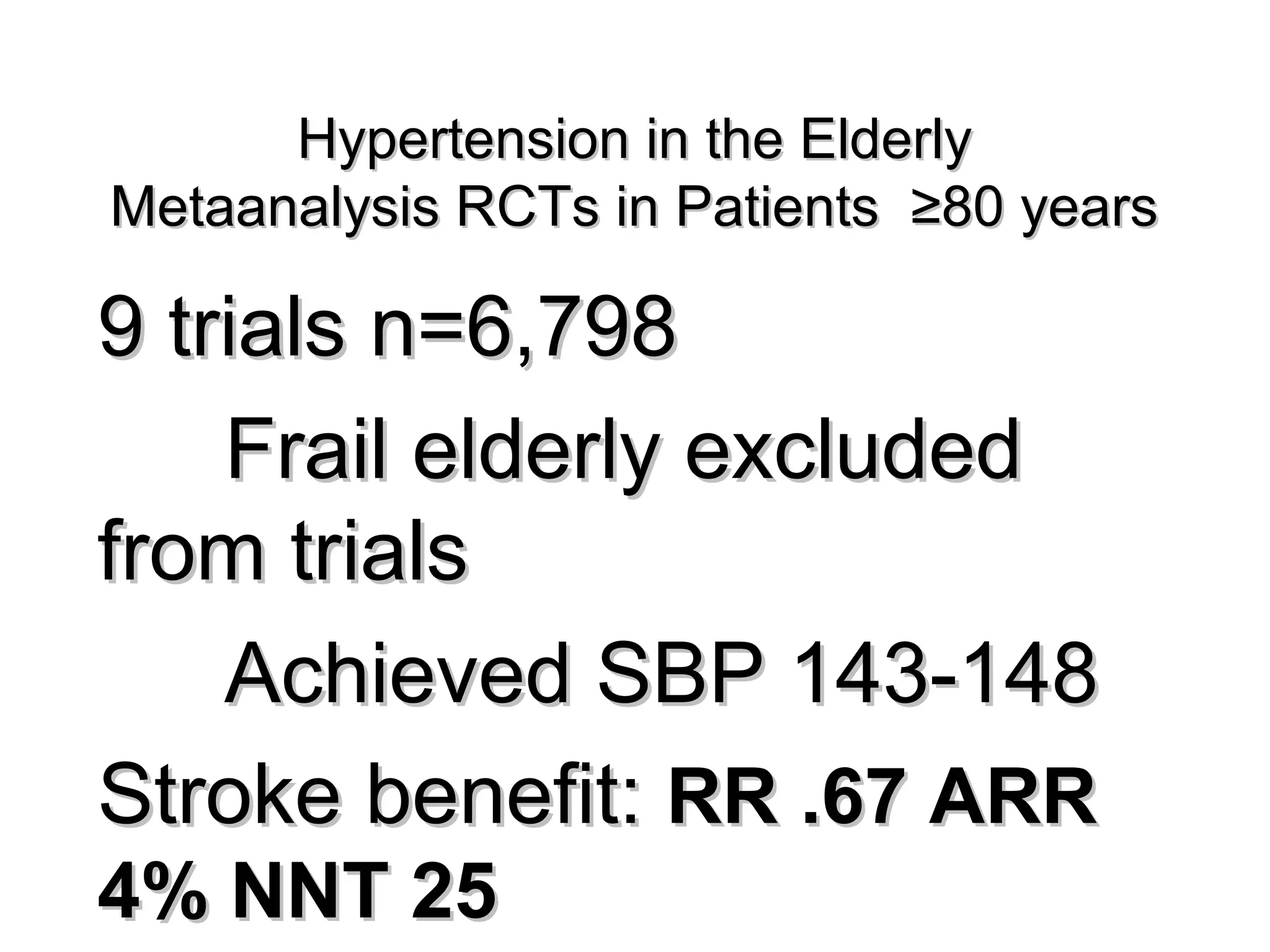
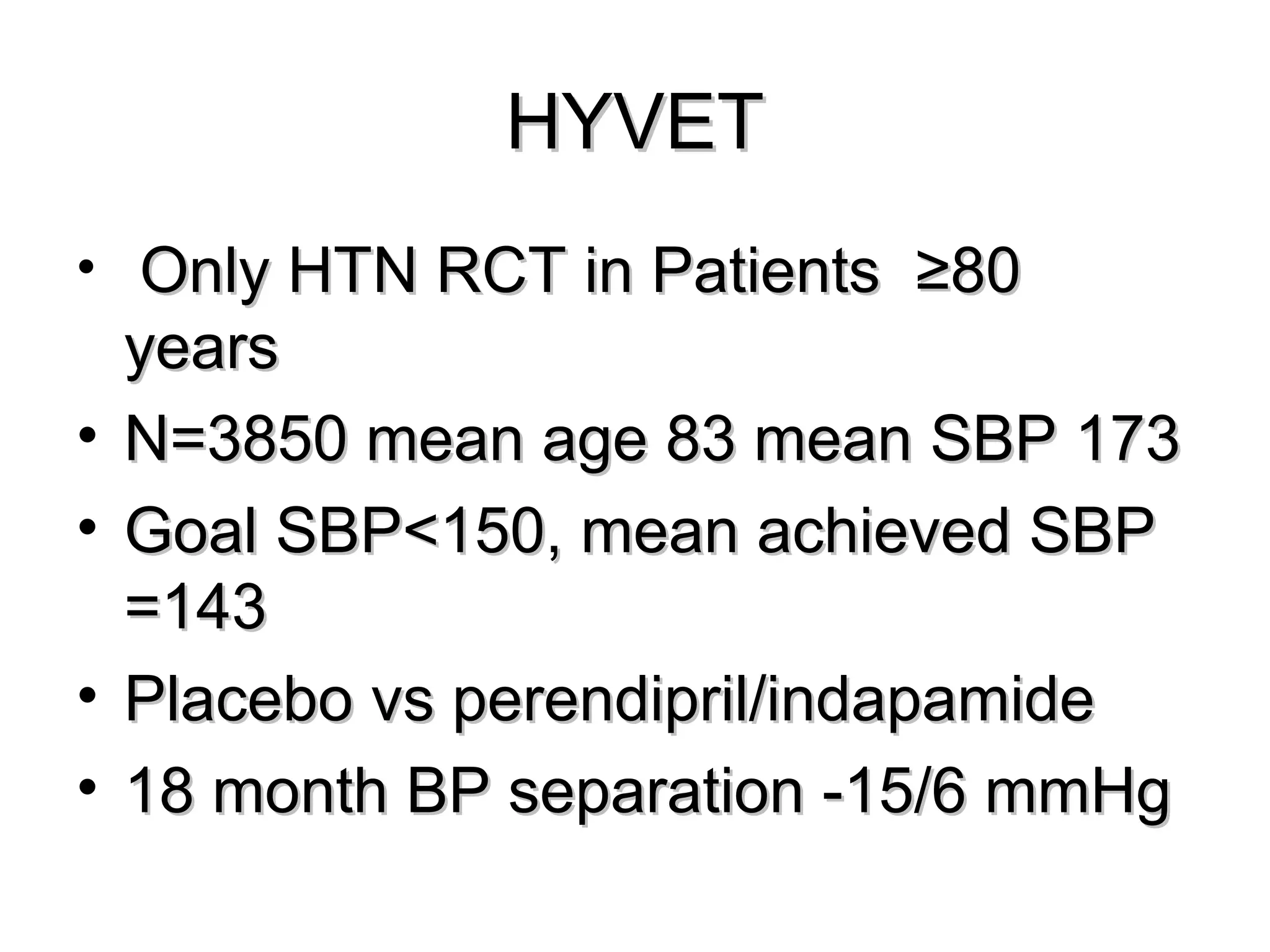
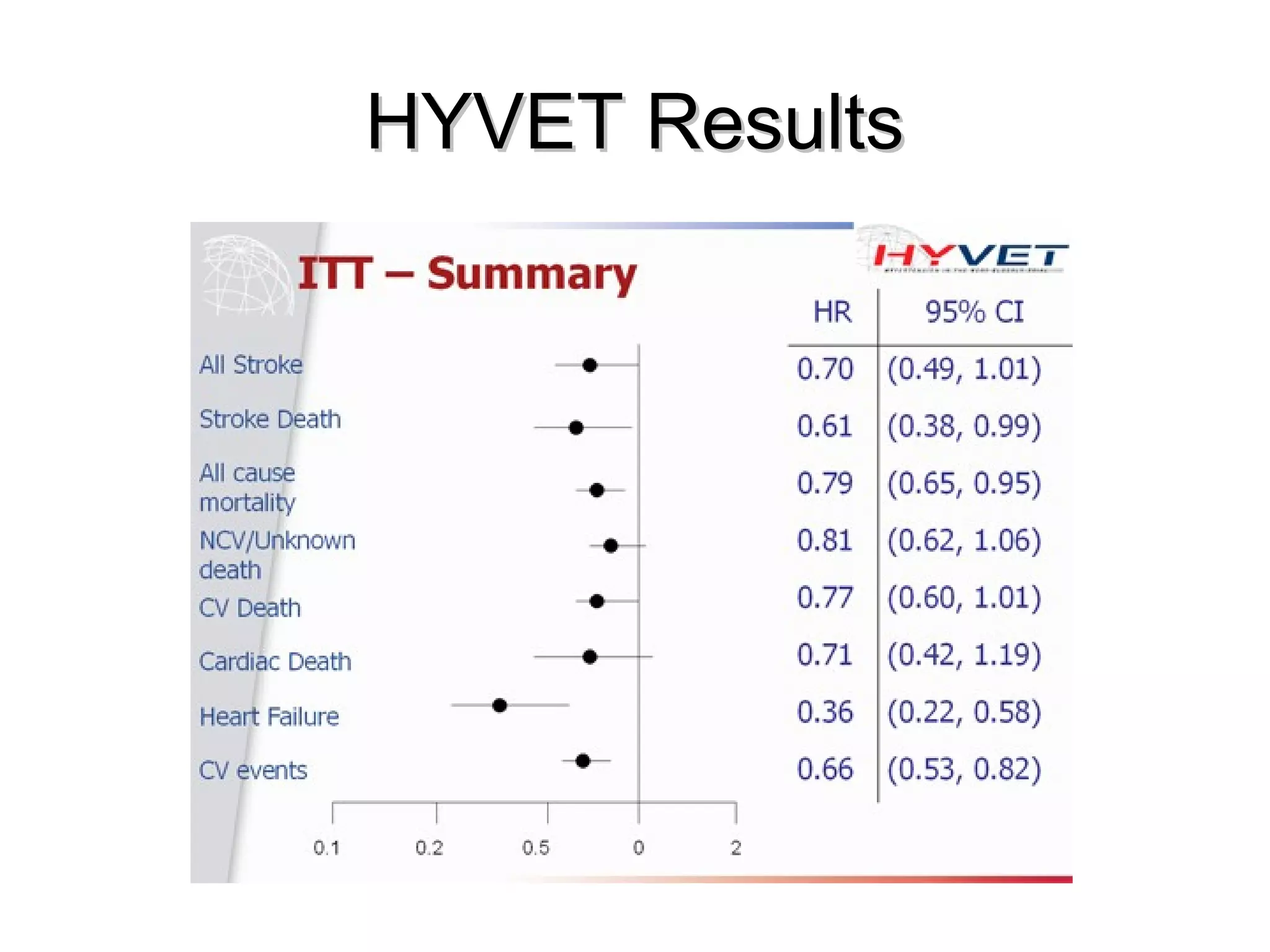
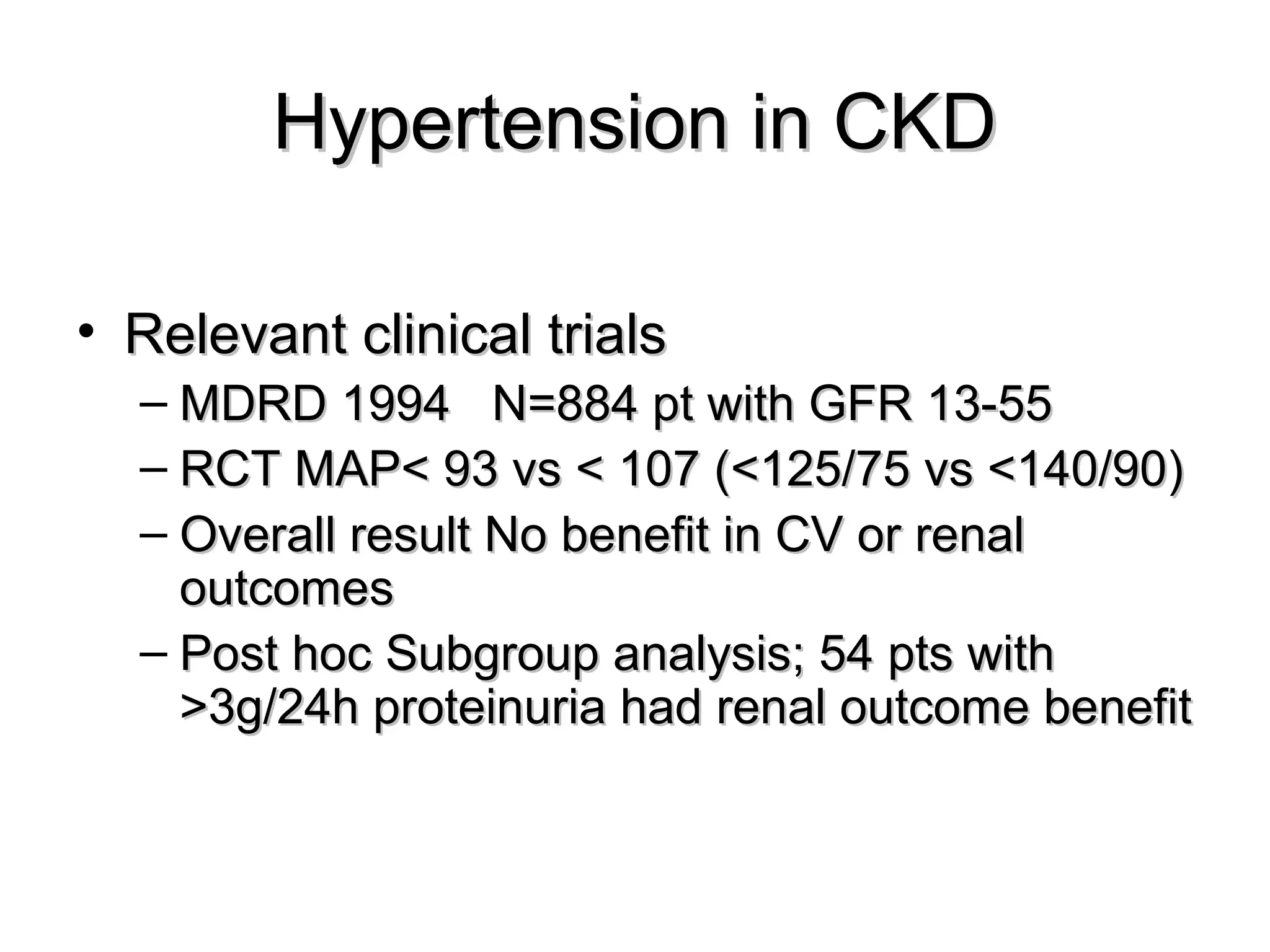
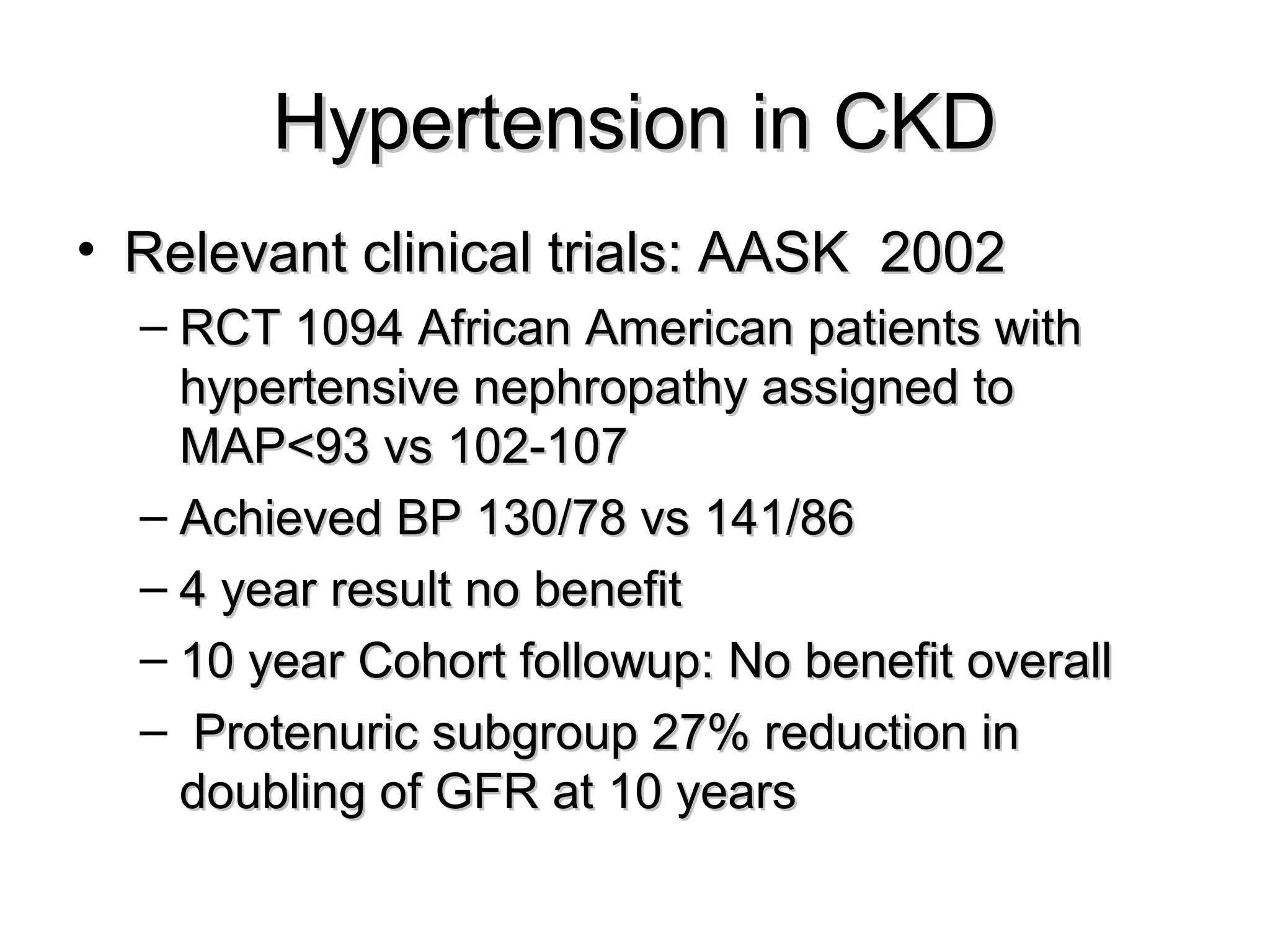
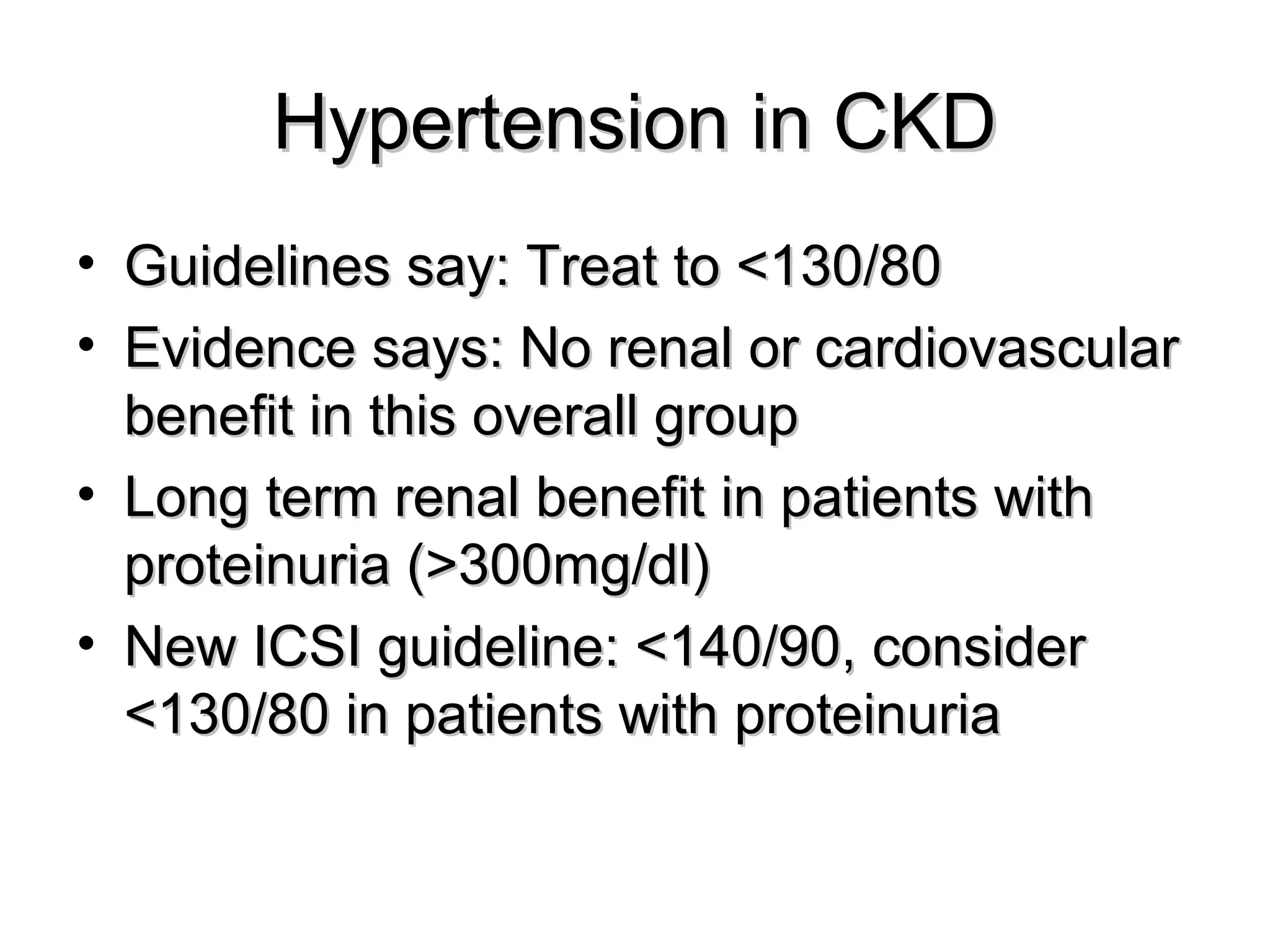
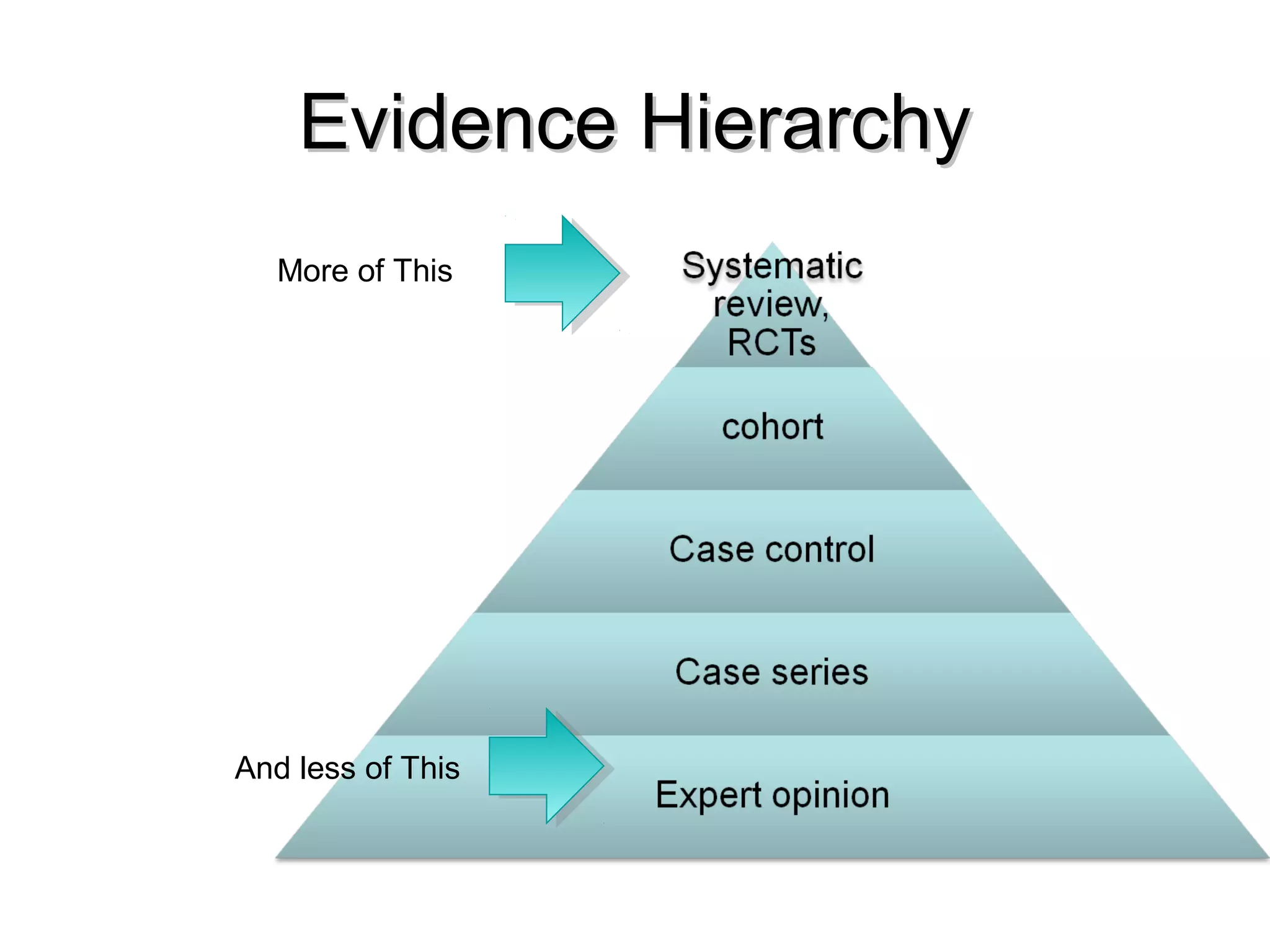
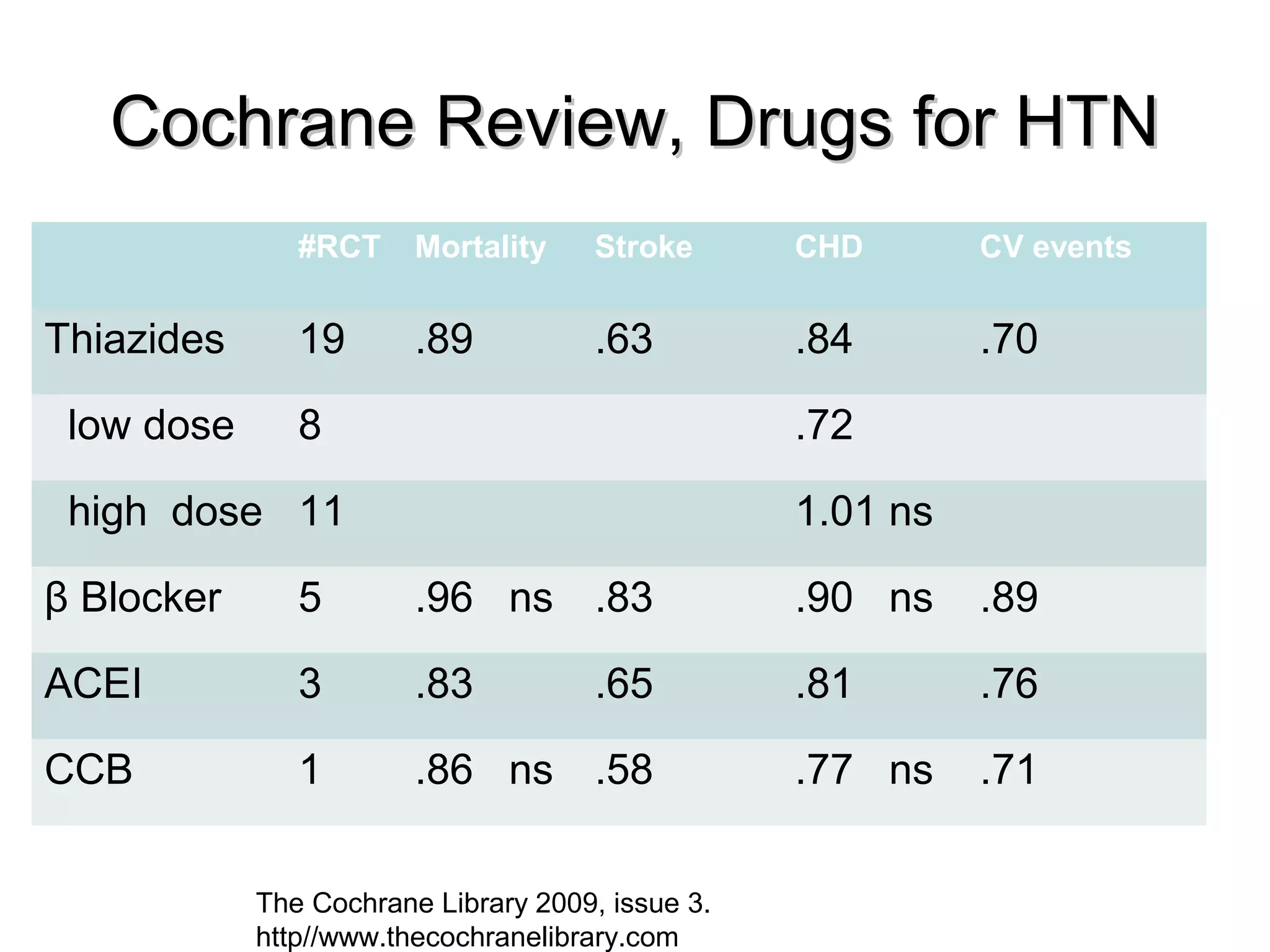
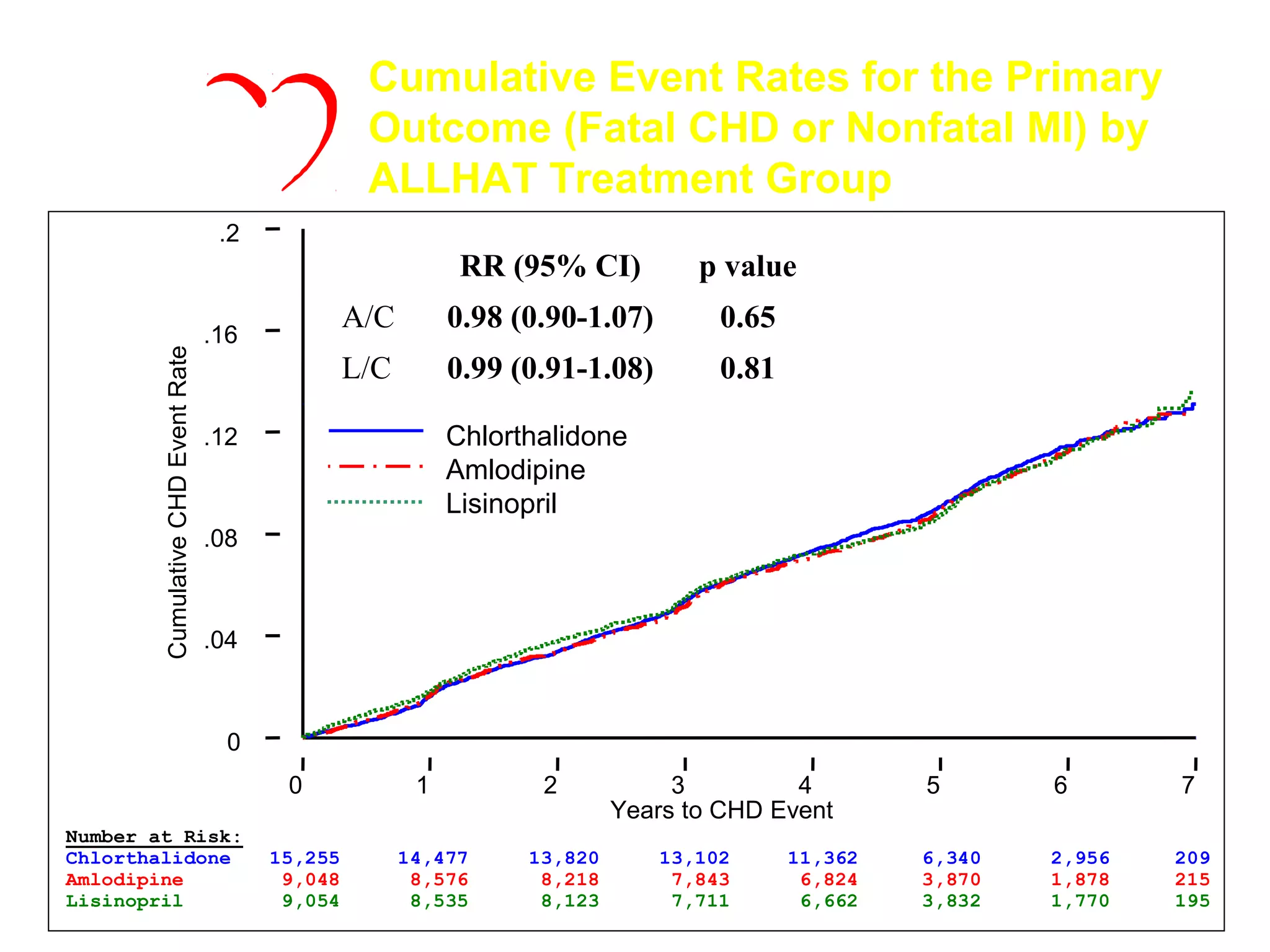
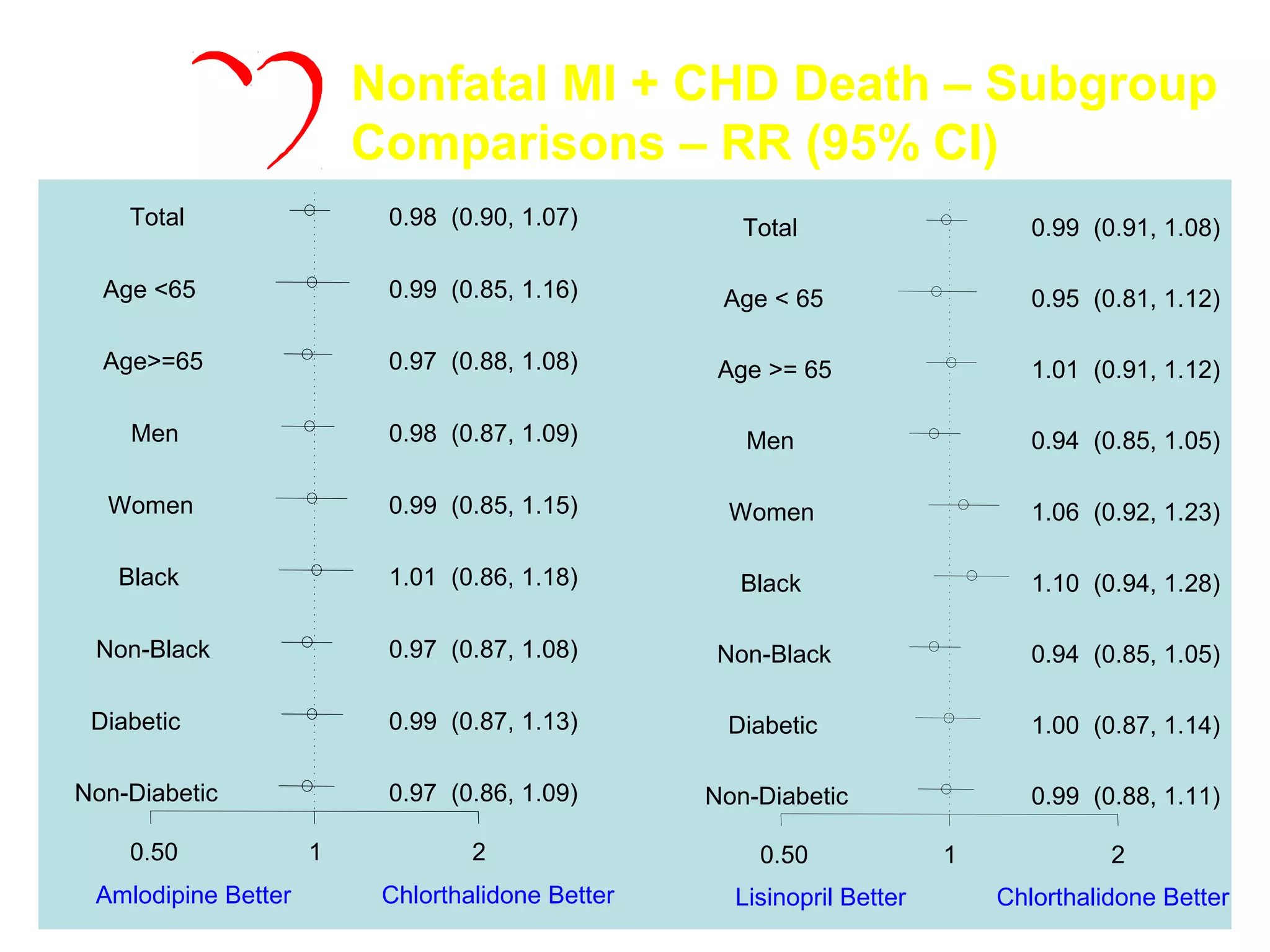
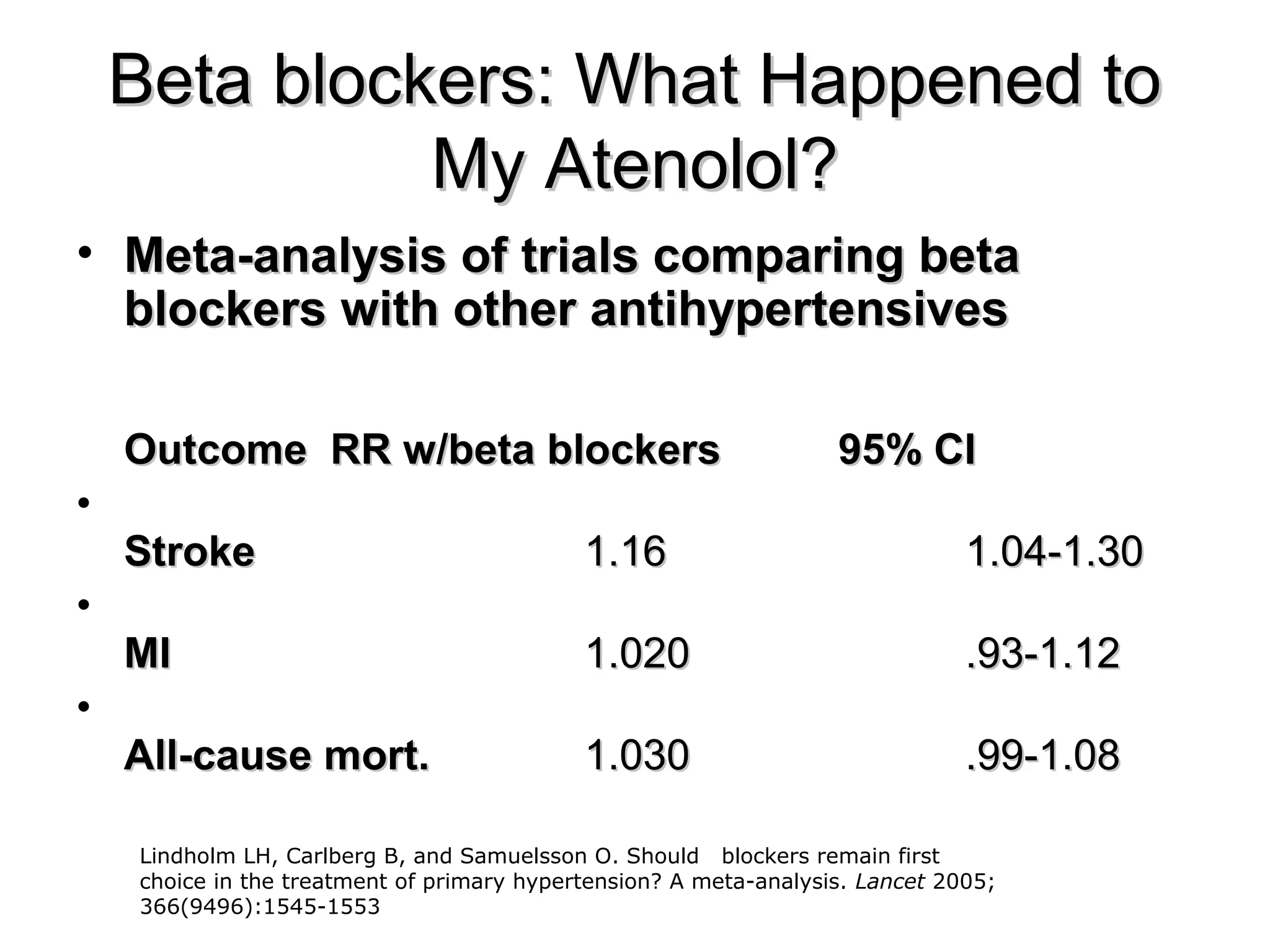
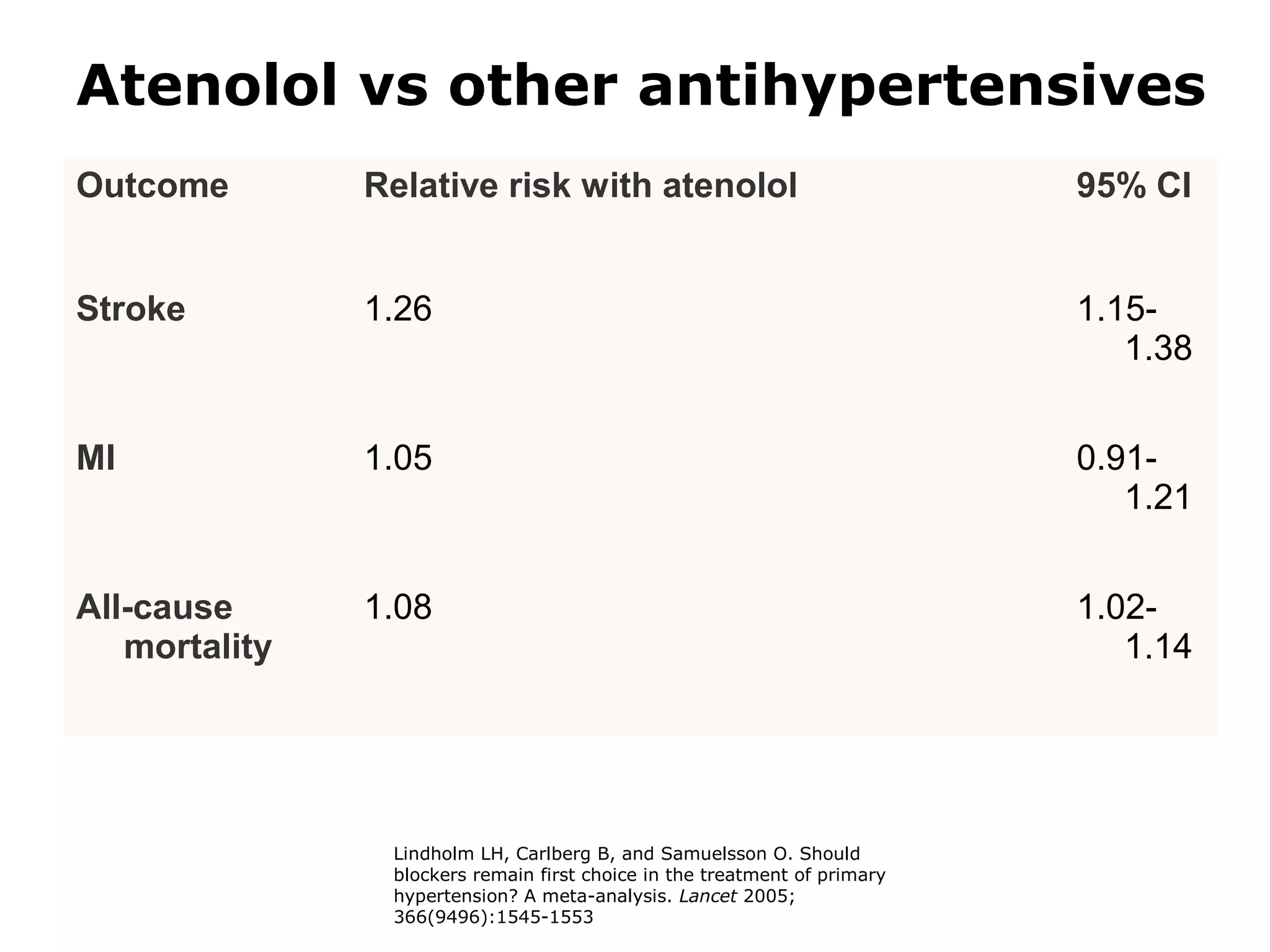
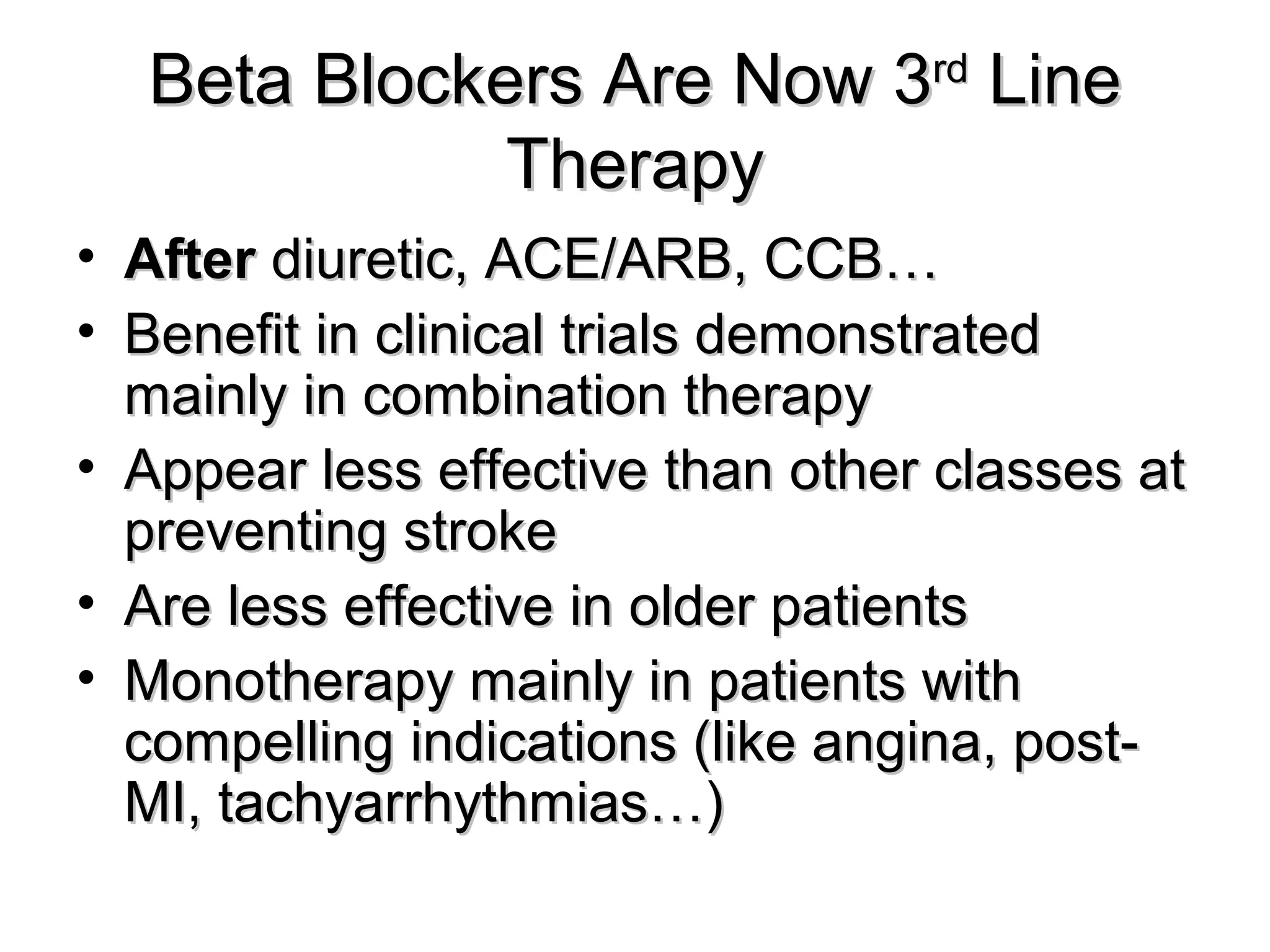
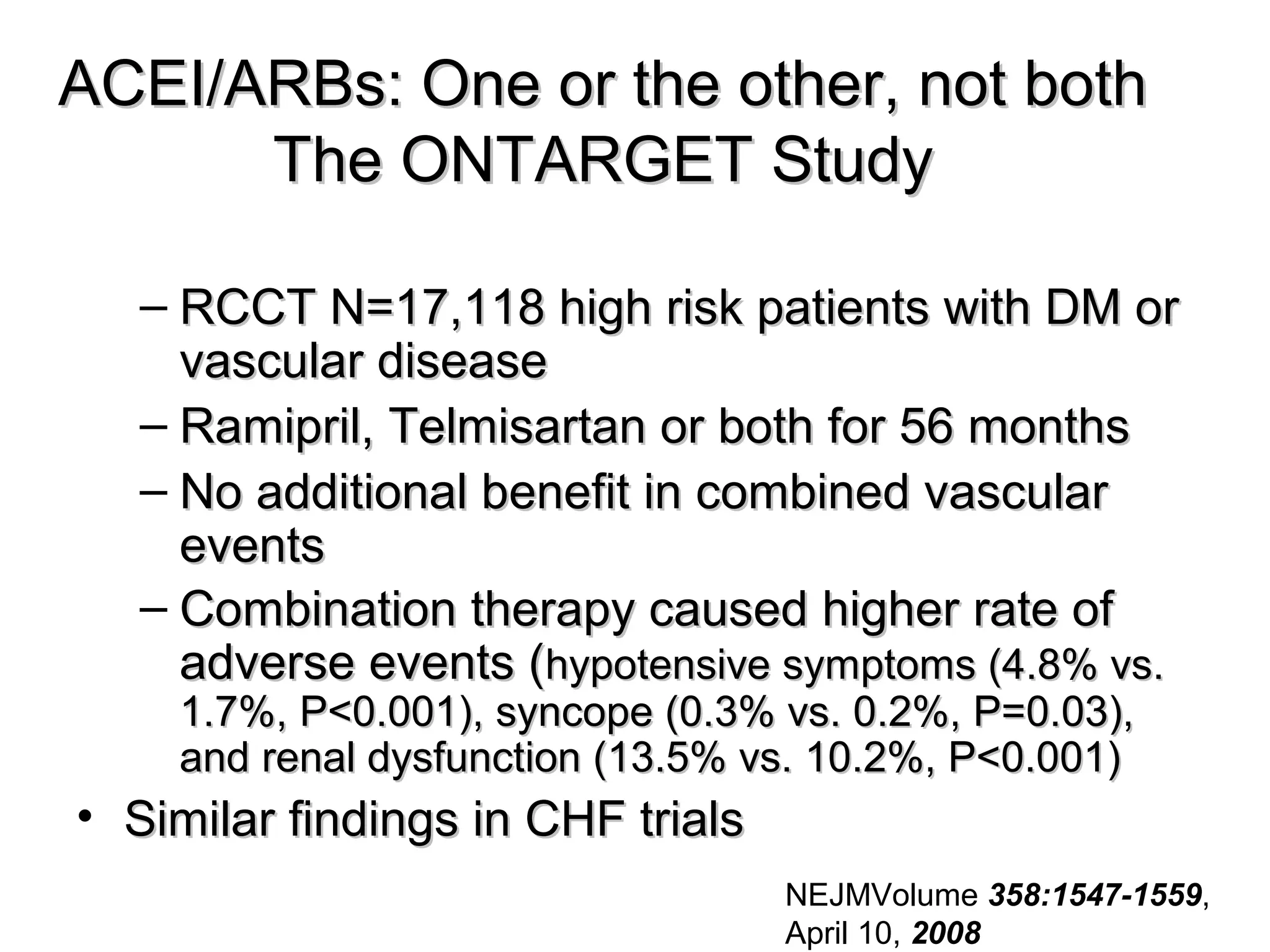
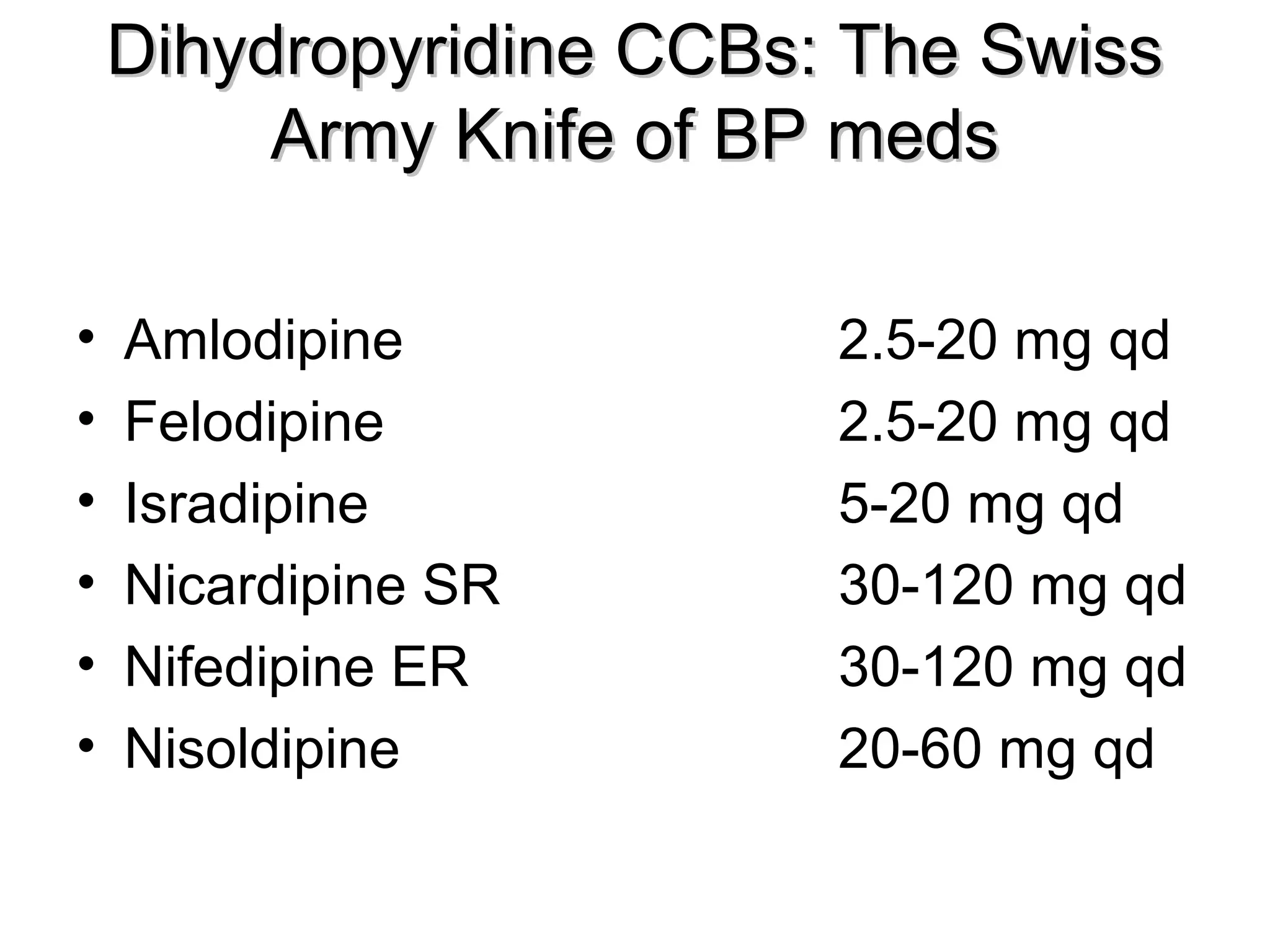
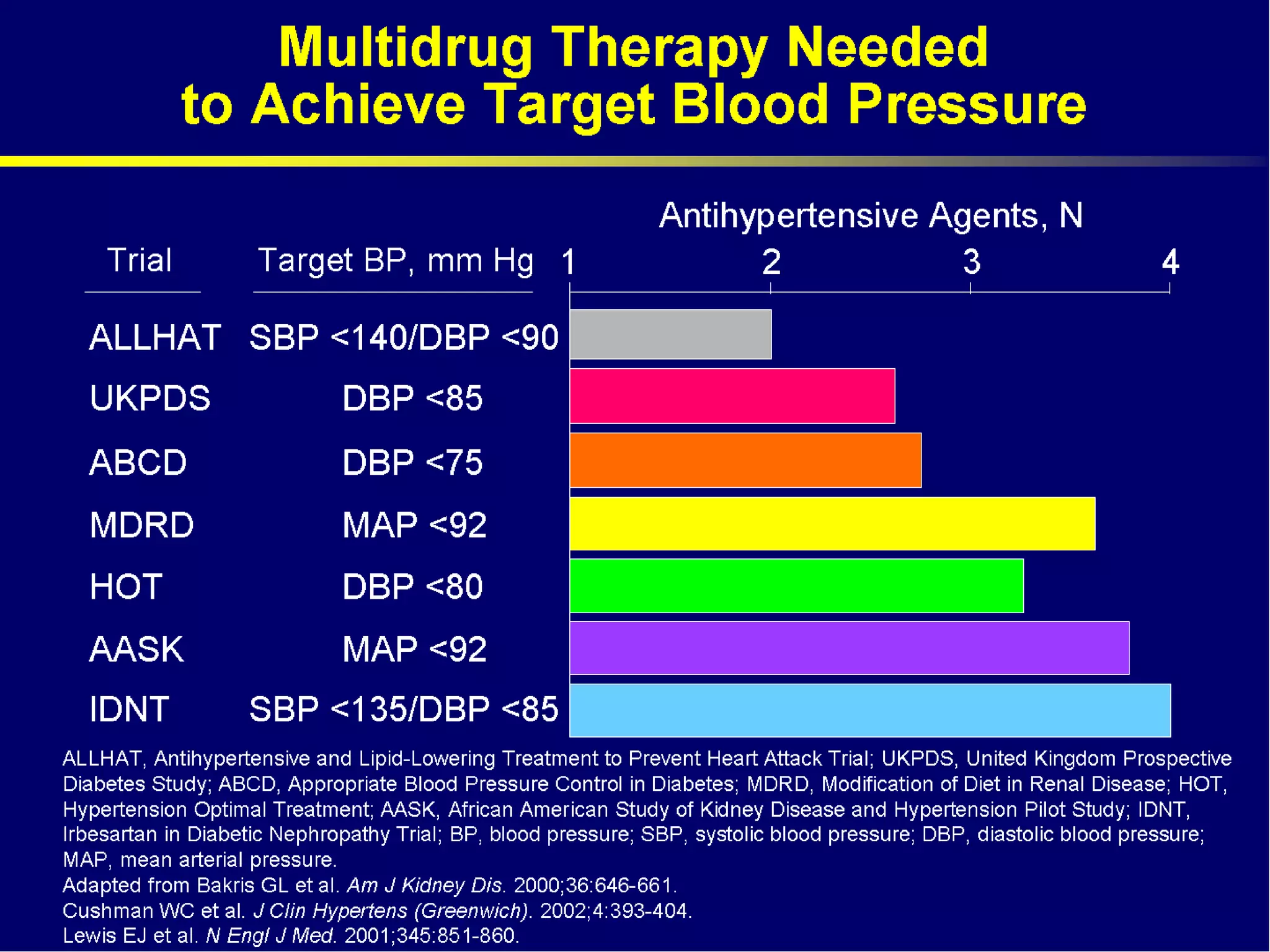
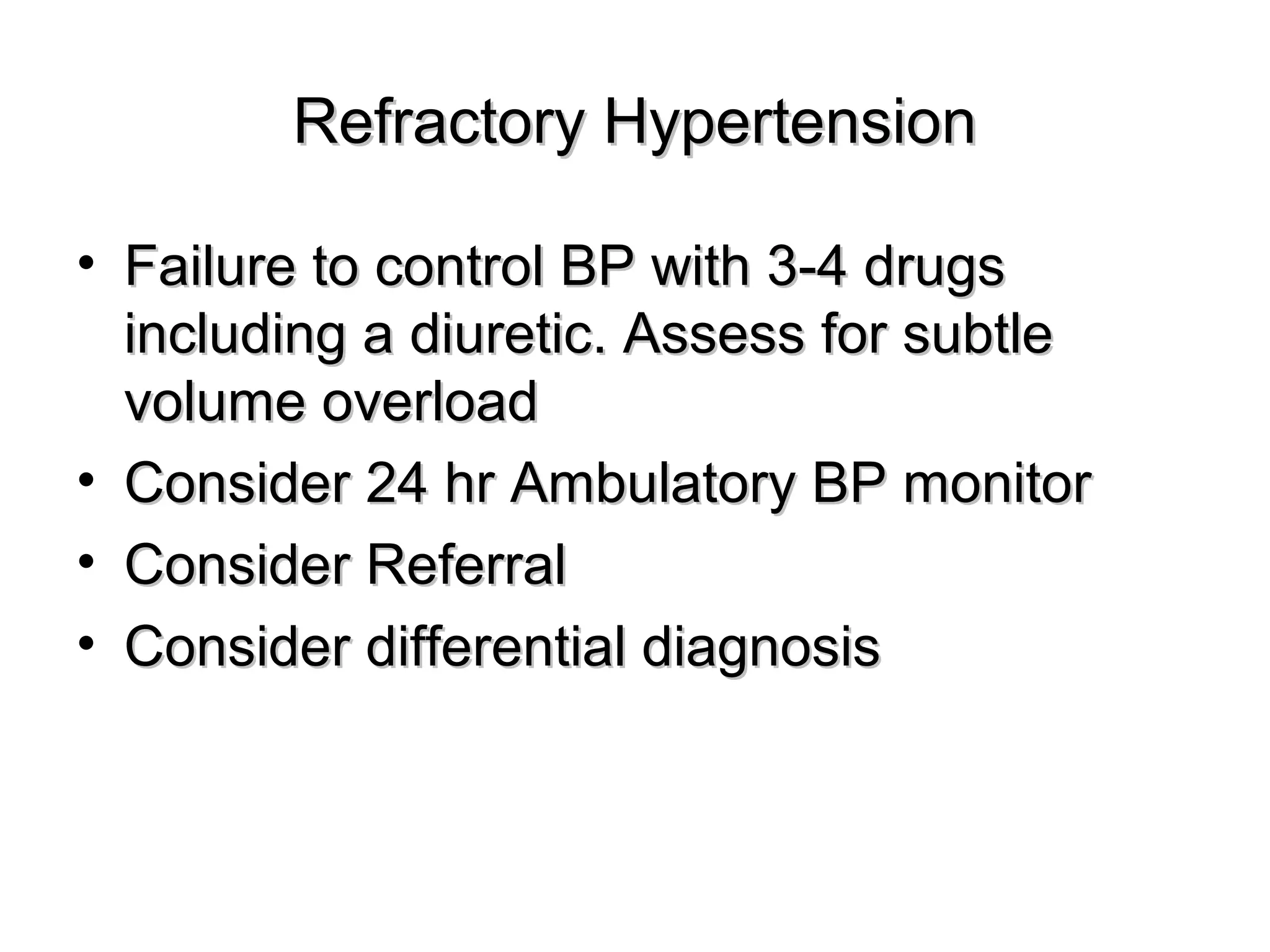
This document discusses evidence-based treatment strategies for hypertension. It summarizes recent clinical trials that have evaluated optimal blood pressure goals for different populations, such as those with diabetes or coronary artery disease. The document notes that while guidelines recommend lower blood pressure targets for certain high-risk groups, some trials have found no clear cardiovascular benefit and even potential harm from overly intensive control. It emphasizes using the hierarchy of evidence and balancing clinical evidence with patient preferences in individualizing treatment.