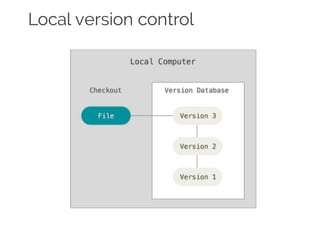
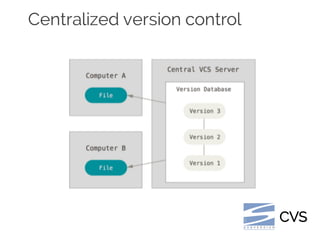
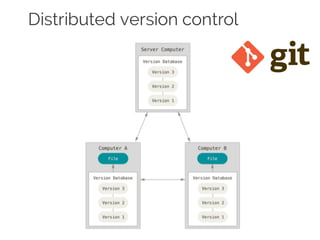
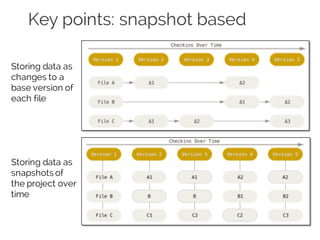
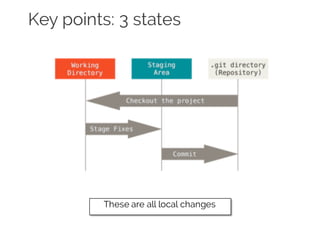
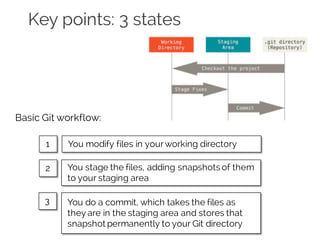
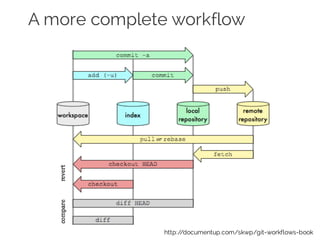
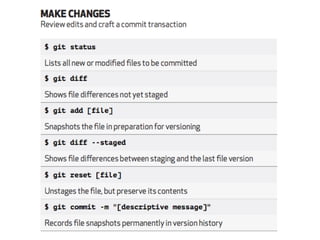
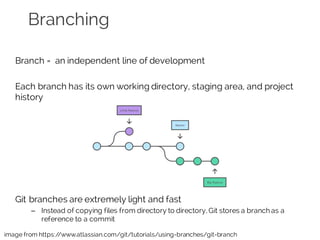
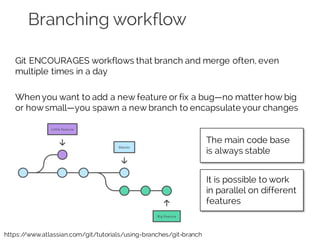
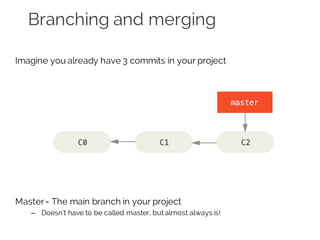
The document details collaborative software development using Git, emphasizing key concepts such as version control, branching, and workflows. It explains Git's distributed architecture, its snapshot-based data storage, and the integrity checks via checksums, alongside practical commands for managing branches and merging workflows. Additionally, it provides guidance on using GitHub for online repository storage and includes a laboratory exercise for practical application.




















![Lab
1. Register to GitHub
2. fork this repo: https://github.com/iivanoo/rest-biter
3. create a Python script your_name.py
4. in the script, add a simple function definition that does something
(even just a print statement)
5. in restBiter.py add:
– an import statement for importing your Python script of step 4
– a statement for calling the function defined in your Python script
6. test the main function by running the script in the terminal:
python restBiter.py http://www.google.com 2 0 500 1000
7. do commit and push your changes to your repo
8. [optional] open a newpull request to merge your changes with the
original repo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04secollaborativedevelopment-151120174340-lva1-app6891/85/2015-2016-Collaborative-software-development-with-Git-39-320.jpg)

