- The document examines the inhibition effect of the antibiotic drug amoxicillin on the corrosion of reinforced steel samples immersed in a simulated concrete pore solution containing chloride ions.
- Potentiodynamic polarization measurements showed that as the concentration of amoxicillin increased, the corrosion potential shifted positively, corrosion current density and corrosion rate decreased, and inhibition efficiency increased, indicating amoxicillin forms a protective film on the steel surface.
- After 7 days, measurements showed the lowest corrosion current density, corrosion rate, and highest inhibition efficiency of 95.03% at a 2.5g/L concentration of amoxicillin, demonstrating it maintains effective corrosion inhibition of reinforced steel in the presence of

![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 –
6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 99-107 © IAEME
100
Keywords: Amoxicillin Drug, Reinforced Steel, Organic Corrosion Inhibitor, Corrosion Inhibition
Simulated Pore Solution.
1. INTRODUCTION
Organic inhibitors are commonly used to inhibit the corrosion of reinforced steel in concrete
[1-12]. The most effective inhibitors are the organic compound that contain aromatic rings,
π-electrons and hetro atoms such as sulphur, nitrogen, oxygen and phosphorus in their structures
which allow the adsorption of compound on the steel surface. This compound interact with the
anodic and or chathodic reaction, blocking the active sites by removing water molecule and forming
protective barrier over the steel surface resulting a decrease in the corrosion rate[13].
Most of organic inhibitors are expensive, toxic and have negative effect on the environment,
this properties restrict its use to inhibit the metal corrosion. Thus it is important and necessary to
develop low cost and environmentally safe corrosion inhibitors [14, 15]. Drugs are nontoxic, cheap,
negligible negative effects on environment, so it suggested to replace the traditional toxic corrosion
inhibitors. GokhanGece (2011) review from literatures the use of many types of drugs as corrosion
inhibitors of various metals [16]. Research efforts have been done recently on the use of antibacterial
drugs as corrosion inhibitors for carbon steel and aluminum in acidic and alkaline media [17, 18, 19].
Amoxicillin have been proved as a good steel corrosion inhibitor in acidic media but no
research work in alkaline media have been performed. Kumeret al (2013) investigated the effect of
amoxicillin on the corrosion of mild steel in HCL and H2SO4 solution and they was shown that
amoxicillin act as a mixed type inhibitor [20, 21]. However no reports are available for the corrosion
inhibition of concrete reinforced steel employing amoxicillin as corrosion inhibitor. Amoxicillin is
an N-S heterocyclic compound containing five oxygen atoms, three nitrogen atoms and one sulphur
atom as shown in figure 1 [21], this properties enable it to be an effective inhibitor.
Figure 1: Amoxicillin structure
Concrete pore solution is an alkaline solution pH = 13.5 [22]. In this paper experimental
study was done to examine the inhibition effect of amoxicillin on the corrosion of reinforced steel in
simulated chloride contaminated concrete pore solution (SCP) consisting of 2% KOH solution
containing 3% NaCl ( PH= 13.4) using potentiodynamic polarization technique.
2. EXPERIMENTAL WORK
2.1 Reinforced steel samples Preparation
The steel rebar was purchased from local supplier which is currently used as concrete
reinforcement. For potentiodynamic polarization tests, steel discs of 10 mm diameter were cut from
steel bar and then braded with abrasive grinder machine.
2.2 Inhibitor
Amoxicillin drug was purchased from medicine shop as a trade name Acamoxil500 capsule
made in Iraq and was used directly without any additional purification.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140506015-140703094045-phpapp01/85/20120140506015-2-320.jpg)
![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 –
6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 99-107 © IAEME
101
2.3 Solutions preparation
Potassium hydroxide KOH, Sodium chloride NaCl (analytical grade) was purchased from
local supplier, in order to use in this work. KOH solution was prepared by stirring appropriate
amount of solid KOH substance in de-ionized water to obtain 2% KOH solution to simulate the
alkalinity of concrete pore solution. 3% NaCl was added to this solution to form chloride
contaminated SCP solution (control solution PH = 13.46). 0.6 gm, 1.25 gm and 2.5 gm amoxicillin
were added to each liter of control solution to form three amoxicillin inhibitor solutions. In this study
four different solutions were prepared, the first one SCP solution (control solution) and the other
three solutions were the amoxicillin inhibitor solutions.
2.4 Polarization measurements
Experiments were carried out in SCP solution .Fixed concentrations of amoxicillin inhibitor
and corroding sodium chloride were used in these experiments. Corrosion rates and inhibition
efficiency were estimated using potentiodynamic polarization technique. Polarization measurements
were carried out with Wenking M Lab PotentiostatGalvanostat instrument (GERMAN origin) under
potentiodynamic conditions. This instrument itself is having programs to evaluate corrosion
parameters such as corrosion current (Icorr), corrosion potential (Ecorr), anodic Tafel slope (ba) and
cathodicTafel slope (bc). Three electrode cell consist of a specimens as a working electrode,
Platinum wire as a counter electrode and Ag/AgCl electrode as a reference electrode was used in this
experiment. The working electrode was rebar steel disk axially embedded in a Teflon holder to offer
a flat disc shaped exposed surface area of 0.785 cm2
. The steel discs were mechanically braded with
different grades of emery papers, degreased with acetone then rinsed with distilled water and dried
before each test. Control specimen was immersed in SCP solution and the other specimens immersed
in SCP solution containing amoxicillin at concentrations of 0.6 g/l, 1.25 g/l,2.5 g/l respectively. The
initial tests were performed at zero hour and one day of immersion. The final tests were performed
after 7 days of immersion to verify the stability of passive film in presence of corrosive chloride ions.
By changing the electrode potential automatically ± 200 mV around the open circuit potential
at a scan rate of 1 mV/s potentiodynamic polarization curves were conducted. From Tafel plot
corrosion parameters such as Ecorr, Icorr, ba and bc were recorded. Corrosion rate (mmpy),
corrosion inhibition efficiency (IE %) was calculated and reported using the following equations
[23].
Corrosion rate (mmpy) = 3.2 x Icor x equivalent weight / density
IE % = (Io - I) / Io× 100
Where:
Equivalent weight of steel = 27.93 gm,
Steel density = 7.8 gm/ cm3
,
Icor = current density mA/ cm2
IE = inhibition efficiency
Io and I are the corrosion current density without and with the inhibitor respectively.
2.5 Optical microscope image
5 mm diameter disc were cut from steel bar, braded with abrasive grinder machine and then
polished by polishing machine till mirror surface. The samples were immediately rinse in acetone
and air dried. Digital optical microscope was used to examine the specimens surface after two days
immersion in both inhibited and uninhibited solutions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140506015-140703094045-phpapp01/85/20120140506015-3-320.jpg)
![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 –
6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 99-107 © IAEME
102
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Potentiodynamic polarization
Polarization curves of reinforced steel samples in chloride contaminated SCP solution
containing various concentration of amoxicillin inhibitor after zero hr. immersion are shown in
figures 2. Corrosion current (Icor), corrosion potential (Ecor), anodic Tafel slope (ba) and
cathodicTafel slope (bc) were measured from Tafel plots. Corrosion parameters such as corrosion
rate (CR), inhibition efficiency (IE %) calculated using potentiodynamic polarization are
summarized in table 1.
The table shows that the Icor and CR values of reinforced steel samples immersed in
amoxicillin inhibitor decreased with increasing amoxicillin concentration compared with control
sample. The results explain that Icor of steel sample immersed in control solution is 13.08 µA/cm2
and it decreased to 1.89 µA/cm2
for sample immersed in 2.5 g/l amoxicillin solution. Corrosion rate
of steel sample in control solution is 0.153 mmpy and it decreased in the presence of amoxicillin till
it reach 0.022 mmpy for sample immersed in solution containing 2.5 g/l amoxicillin These results
explain that the adsorption of inhibitor on reinforced steel increases with increase in inhibitor
concentration .
Furthermore it is clear from the table that the reinforced steel corrosion potential immersed in
SCP solution (control solution) was (- 452.2 mV Ag- AgCl) and it shifted toward the more positive
direction and a decrease in Icor in presence of amoxicillin in SCP solution, which is an indication on
the formation of protective film on the steel surface [24] . The table shows that the increasing in
inhibitor concentration decreased values of Icor and values of Tafel slopes ba and bc in indefinite
form Indicating that the amoxicillin acted under mixed type control [25]. Inhibition efficiency (IF)
increased with increasing antibiotic concentration. The maximum inhibition efficiency of 85.47%
was achieved at 2.5 g/l concentration.
Figure 2: Tafel polarization curves of the reinforced steel after zero hour immersion in the SCP
solutions without and with various concentrations of amoxicillin inhibitor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140506015-140703094045-phpapp01/85/20120140506015-4-320.jpg)
![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 –
6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 99-107 © IAEME
104
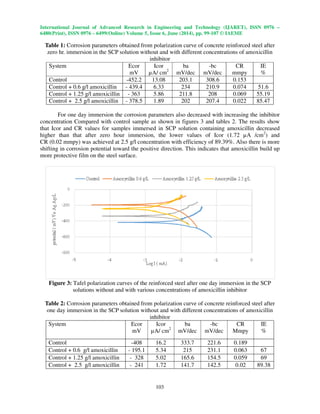
After 7 days of immersion of reinforced steel in SCP solution containing various amount of
amoxicillin inhibitor, the corrosion parameters values were decreased higher than the values of one
day immersion as shown in figure 4 and table 3. Table 3 informations explain that the Icor was
decreased to 0.83 µA/ cm2
and CR was decreased to 0.0096 mmpy and inhibition efficiency to
95.03 % in addition to Ecor also decreased toward more positive direction. This is an indication that
amoxicillin maintained stable protective film on the steel surface even in the presence of chloride
ions. According to table 4, this results reveal that amoxicillin has ability to be a good green corrosion
inhibitor for reinforced steel in concrete.
Figure 4: Tafel polarization curves of the reinforced steel after 7 days immersion in the SCP
solutions without and with various concentrations of amoxicillin inhibitor
Table 3 :Corrosion parameters obtained from polarization curve of concrete reinforced steel after 7
days immersion in the SCP solution without and with different concentrations of amoxicillin
inhibitor
System Ecor
mV
Icor
µA/ cm2
ba
mV/dec
- bc
mV/dec
CR
mmpy
IE
%
Control - 446.2 16.7 346.8 289.9 0.195
Control + 0.6 g/l amoxicillin -383 2.94 167.9 140.2 0.0343 82.4
Control + 1.25 g/l amoxicillin - 362 1.24 161.5 110..2 0.0146 92.6
Control + 2.5 g/l amoxicillin - 325 0.83 125.6 66.1 0.0096 95.03
3.2 Optical microscope image
Figure 5 shows the optical micrograph of reinforced steel discs surface immersed in control
solution and in control solution containing various concentration of amoxicillin. Observations of
micrograph (a) showed that the surface of steel sample immersed in control solution was rough and
damaged due to the direct chloride attack. Micrograph (b) and (c) showed that the surface roughness
was decreased due to the formation of a thin layer of inhibitor molecules that decreased the
dissolution of reinforced steel, micrograph (d) showed that the film formed cover large surface area
of steel and become thicker due to the increase in the inhibitor concentration ( 2.5 g/l ) [26].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140506015-140703094045-phpapp01/85/20120140506015-6-320.jpg)
![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 –
6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 99-107 © IAEME
105
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 5: Optical micrographs of reinforced steel surface after two days of immersion in
(a) Control sample, (b) 0.6 g/l amoxicillin sample, (c) 1.25 g/l amoxicillin sample,
(d) 2.5 g/l amoxicillin
4. CONCLUSION
The following conclusions can be drawn from this work:
a) Amoxicillin acts as a good green inhibitor for the corrosion of concrete reinforced steel.
b) The inhibition efficiency of amoxicillin increases with increasing inhibitor concentration.
c) After 7 days of immersion in test solutions the inhibitor showed maximum inhibition
efficiency of 95.03% at 2.5 g/l concentration.
d) Lower corrosion rate of 0.0096 mmpy at 2.5 g/l concentration.
e) Potentiodynamic polarization reveal that amoxicillin is a mixed type inhibitor.
f) Optical microscope images of reinforced steel samples enhanced the formation of protective
film on steel surface and the film formed at the surface of steel rebar immersed in 2.5 g/l
amoxicillin was thicker than that formed on steel surface immersed in the others solutions.
g) Studies with actual concrete specimens are needed to know the effect of amoxicillin on the
compression strength of the concrete.
REFERENCES
[1] A.del Valle-Moreno (2010), “Efficiency of an amine-ester based corrosion inhibitor for
concrete” Superficies Vacío 23(S) 188-192.
[2] AymanAbabneh et al (2009), “Effect of Benzotriazole Derivatives on Steel Corrosion in
Solution Simulated Carbonated Concrete”, Jordan Journal of Civil Engineering, Volume 3,
No. 1, pp 91-102.
[3] O. motosho O. A.PP et al (2011), “Aniline effect on concrete steel rebar degradation in saline
and sulfate media”, AgricEngInt: CIGR Journal Vol. 13, No.2, pp1-10.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140506015-140703094045-phpapp01/85/20120140506015-7-320.jpg)
![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 –
6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 99-107 © IAEME
106
[4] J. Cai et al (2012), ” Influence of Alkyl Chain Length of 1, 3-Bis-Dialkylamino-2- Propanol
on the Adsorption and Corrosion Behavior of Steel Q235 in Simulated Concrete Pore
Solution”, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 7, pp 10894 - 10908.
[5] M.A. Ameer et al (2010), “Inhibition effect of newly synthesized heterocyclic organic
molecules on corrosion of steel in alkaline medium containing Chloride”, International
Journal of Hydrogen, 35, pp 11387 – 11396.
[6] Solmaz R et al (2008). “Citric acid as natural corrosion inhibitor for aluminum protection.
Corrosion Engineering Science and Technology”, 43(2), pp 186-191.
[7] Amin M.A et al (2010), “A study of the inhibition of iron corrosion in HCl solutions by some
amino acids”, Corrosion Science 52(5), pp 1684-1695.
[8] Sami Ben Aoun (2013), “Highly Efficient Corrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel in Aggressive
Acidic Media with a Pyridazinium-based Ionic Liquid”, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 8, pp 10788
- 10804.
[9] Abdulrahman A. S et al (2011), “Corrosion inhibitors for steel reinforcement in concrete: A
review, Scientific Research and Essays”, Vol. 6(20), pp. 4152-4162.
[10] M. Anwar Sathiq et al (2011),” Adsorption and Corrosion Inhibition Effect of
N-(l-Morpholinobenzyl) urea on Mild Steel in Acidic Medium”, E-Journal of Chemistry,
8(2), pp. 621-628.
[11] S.A.Abd El–Maksoud (2008), “The Effect of Organic Compounds on the Electrochemical
Behaviour of Steel in Acidic Media. A review”, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 3, pp 528 – 555.
[12] M. Manivannan et al (2011). “Inestigation of Inhibitive Action of Urea – Zn+2 System in the
Corrosion Control of Carbon Steel in Sea Water”, International Journal of Engineering
Science and Technology (IJEST) Vol. 3 No.11, pp 8048 -8060.
[13] S. Har. Kumer and S. Karthikeyan (2012),”Inhibition of mild steel corrosion in hydrolic acid
solution by cloxacillin”, J. Mater. Enviro. Sci., 3(5), pp 925-934.
[14] R.T. Loto et al (2012), “Corrosion inhibition of thiourea and thiadiazole derivatives: A
Review” J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 3 (5) pp 885-894.
[15] D.G. Ladha et al (2013), “Investigation of Cumin (CuminumCyminum) extract as an eco-
friendly green corrosion inhibitor for pure aluminium in acid medium”, J. Mater. Environ.
Sci. 4 (5), pp 701-708.
[16] GokhanGece (2011), “Drugs: A review of promising novel corrosion inhibitors”, Corrosion
Science 53, pp 3873–3898.
[17] S. Hari Kumar and S. Karthikeyan (2012), “Inhibition of mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric
acid solution by cloxacillin drug”, J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 3 (5), pp 925-934.
[18] Imran Naqvi et al (2011, “Cefixime: A drug as Efficient Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in
Acidic Media. Electrochemical and Thermodynamic Studies, “Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6,
pp 146 - 161.
[19] Ashish Kumar Singh et al (2011),“ Cefacetrile as Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in Acidic
Media” Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6, pp 5689 - 5700.
[20] S. Hari Kumar 1, S. Karthikeyan (2013),” Amoxicillin as an efficient green corrosion
inhibitor for mild steel in 1M sulphuric acid “, J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 4 (5), pp 675-984
[21] S. Hari Kumar et al ( 2012 ) ,” Inhibition Effect of Amoxicillin drug on the Corrosion of
Mild Steel in 1N Hydrochloric acid Solution”, International Journal of Chem Tech Research
Vol.4, No.3, pp 1077-1084.
[22] Amir Poursaee (2010), “Corrosion of steel bars in saturated Ca(OH)2 and concrete pore
solution” Concrete Research Letters Vol. 1(3) , pp 90-97.
[23] M. Vishnudevan (2012),” Synergistic influence of nitrite on inhibition of mild steel Corrosion
in chloride contaminated alkaline solution”, Iranian Journal of Materials Science &
Engineering 9(4), pp17-27.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140506015-140703094045-phpapp01/85/20120140506015-8-320.jpg)
![International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 –
6480(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6499(Online) Volume 5, Issue 6, June (2014), pp. 99-107 © IAEME
107
[24] Pandiarajan M. et al (2014), “Corrosion Inhibition by Potassium Chromate-Zn2+ System for
Mild Steel in Simulated Concrete Pore Solution”, Res. J. Chem. Sci., Vol. 4(2), pp 49-55.
[25] S. Karthikeyan et al (2012), “The Inhibitive Action of Tolyl-3,3 Dimethyl Thiourea on the
Corrosion of Mild Steel in Brine Water”, J. Surface Sci. Technol., Vol 28, No. 3-4,
pp. 101-110.
[26] Gunavathy, S.C. Murugavel (2013), “Corrosion inhibition study of bract extract of Musa
acuminate in florescence on mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium”, IOSR Journal of
Applied Chemistry, Volume 5, Issue 2, PP 29-35.
[27] Hameed Hussein Alwan, “Adsorption Mechanism for Corrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel
on HCl Solution by Ampicillin Sodium Salt”, International Journal of Advanced Research in
Engineering & Technology (IJARET), Volume 4, Issue 7, 2013, pp. 236 - 246, ISSN Print:
0976-6480, ISSN Online: 0976-6499.
[28] Nadir Mohamed Abdulreda, “Corrosion Inhibition of Carbon Steel in Nacl and Hcl Solutions
by Vitamin C”, International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering & Technology
(IJARET), Volume 5, Issue 4, 2014, pp. 38 - 45, ISSN Print: 0976-6480, ISSN Online:
0976-6499.
[29] Abdulrasoul Salih Mahdi, “Urea Fertilizer as Corrosion Inhibitor for Reinforced Steel in
Simulated Chloride Contaminated Concrete Pore Solution”, International Journal of
Advanced Research in Engineering & Technology (IJARET), Volume 5, Issue 5, 2014,
pp. 30 - 39, ISSN Print: 0976-6480.
[30] Sanad A.M. and Hassan H.A., “Effect of Corrosion on Concrete Reinforcement Mechanical
and Physical Properties”, International Journal of Civil Engineering & Technology (IJCIET),
Volume 4, Issue 3, 2013, pp. 176 - 184, ISSN Print: 0976-6308, ISSN Online: 0976-6316.
[31] Behrouz Mohebimoghaddam and S.Hossein Dianat, “Evaluation of the Corrosion and
Strength of Concrete Exposed to Sulfate Solution”, International Journal of Civil Engineering
& Technology (IJCIET), Volume 3, Issue 2, 2012, pp. 198 - 206, ISSN Print: 0976-6308,
ISSN Online: 0976-6316.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20120140506015-140703094045-phpapp01/85/20120140506015-9-320.jpg)