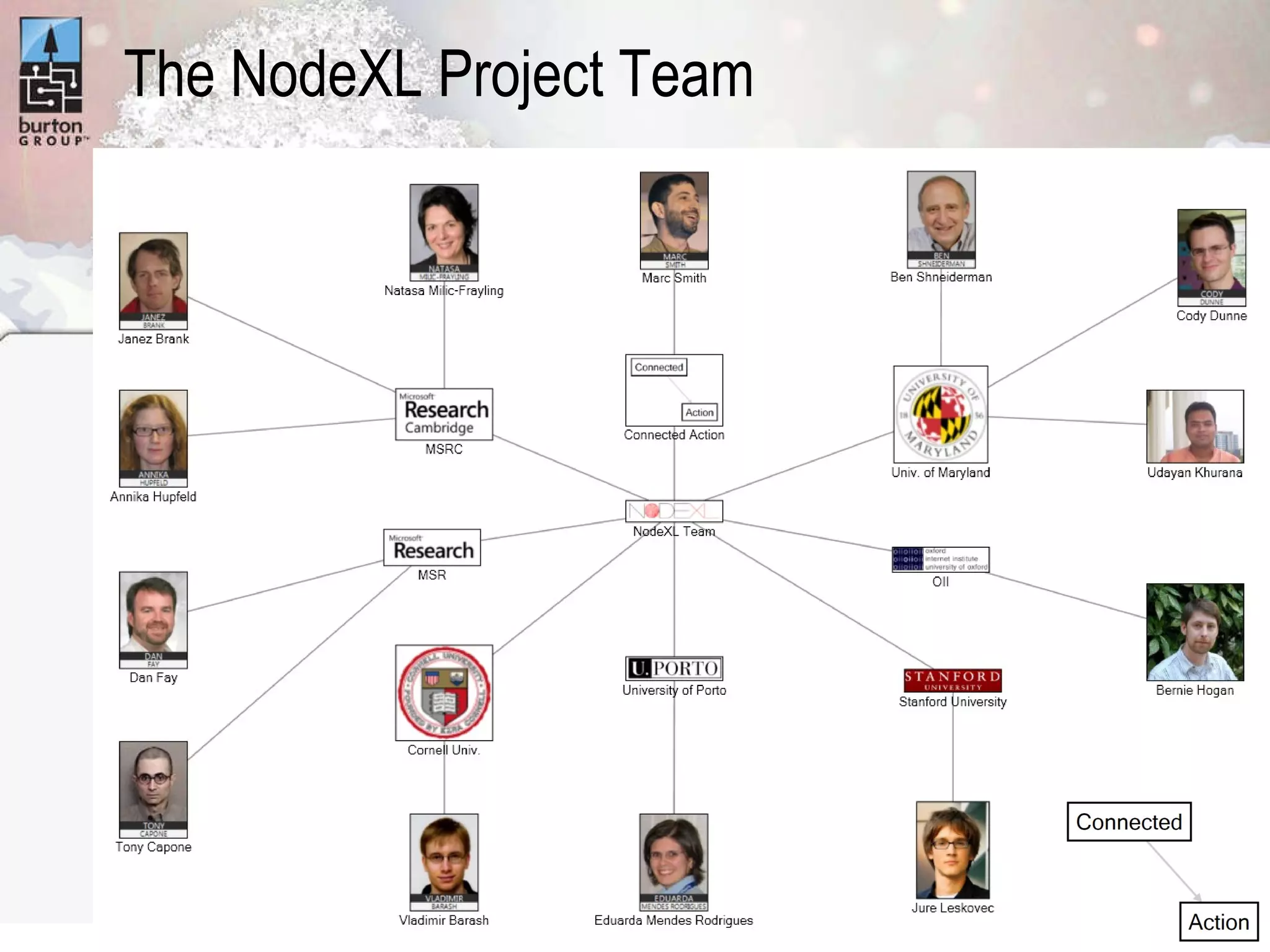
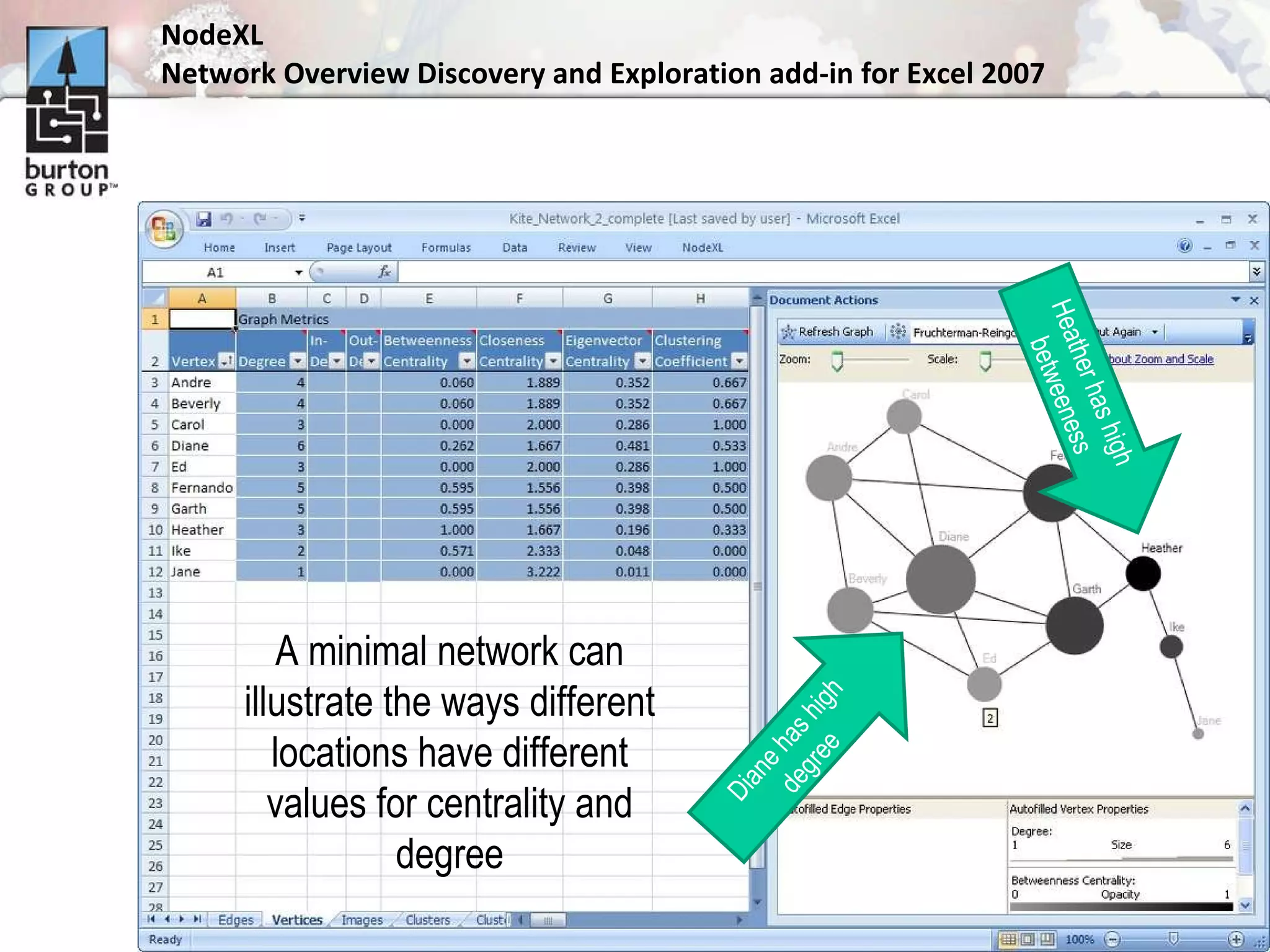
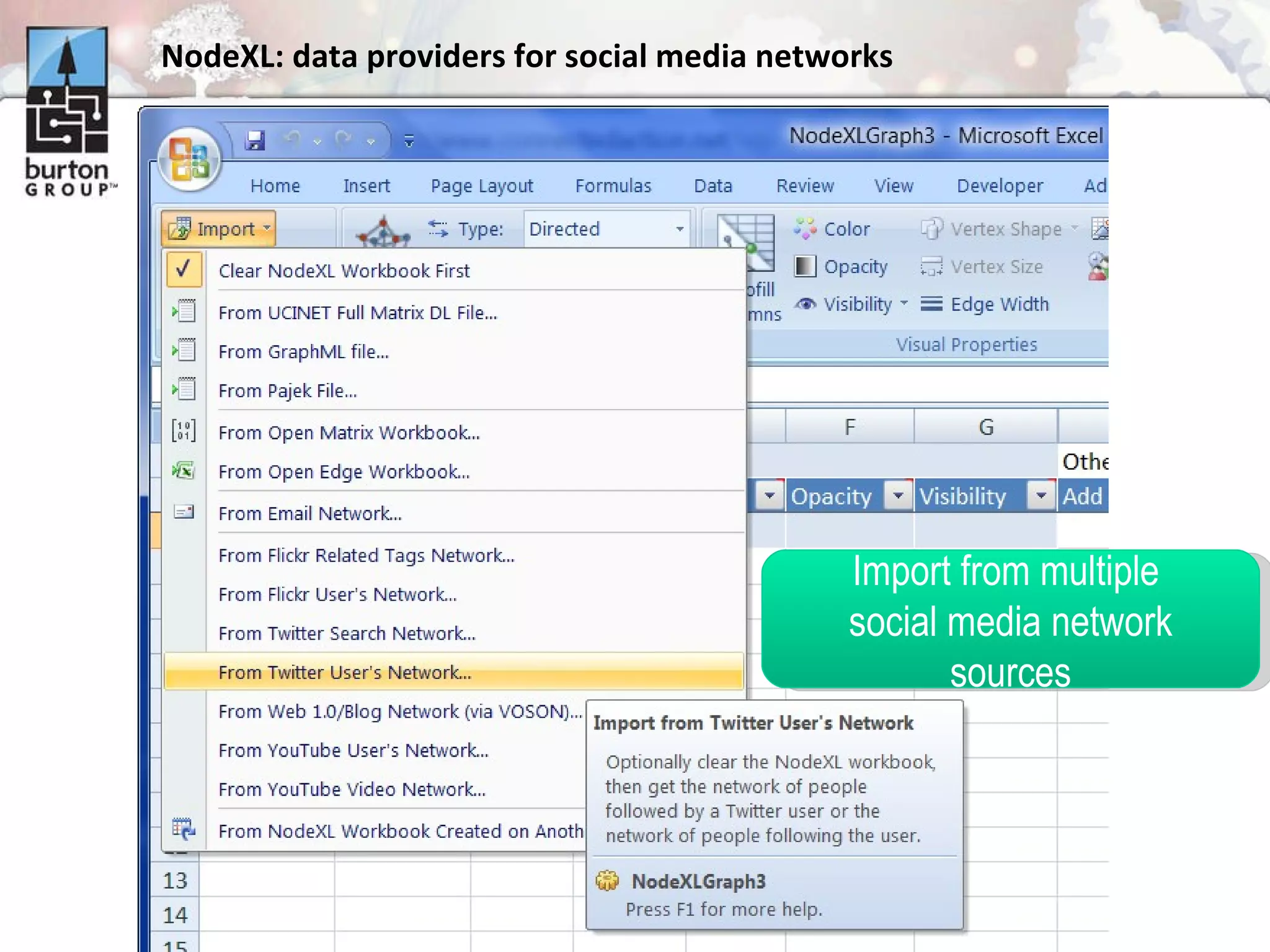
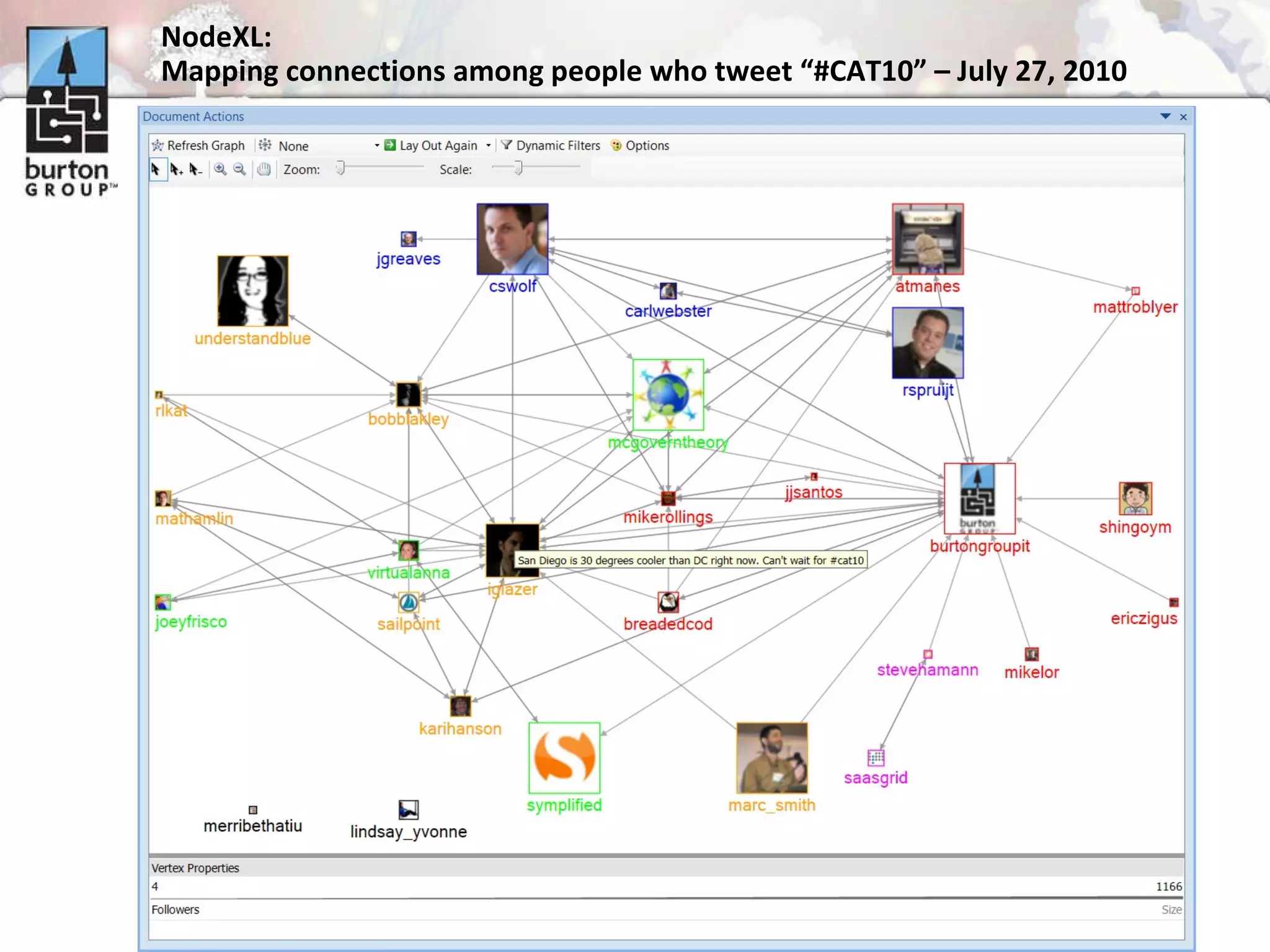
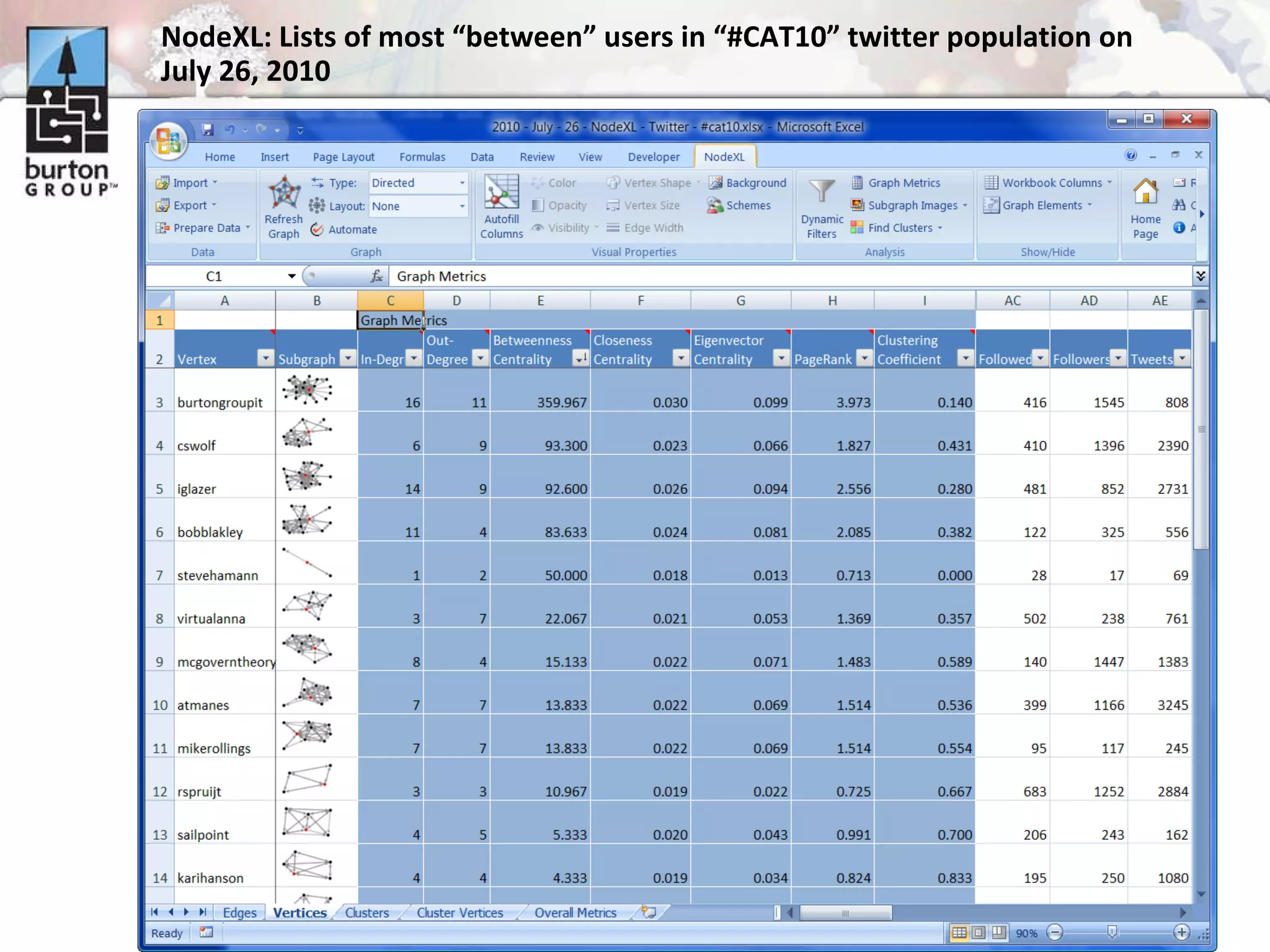
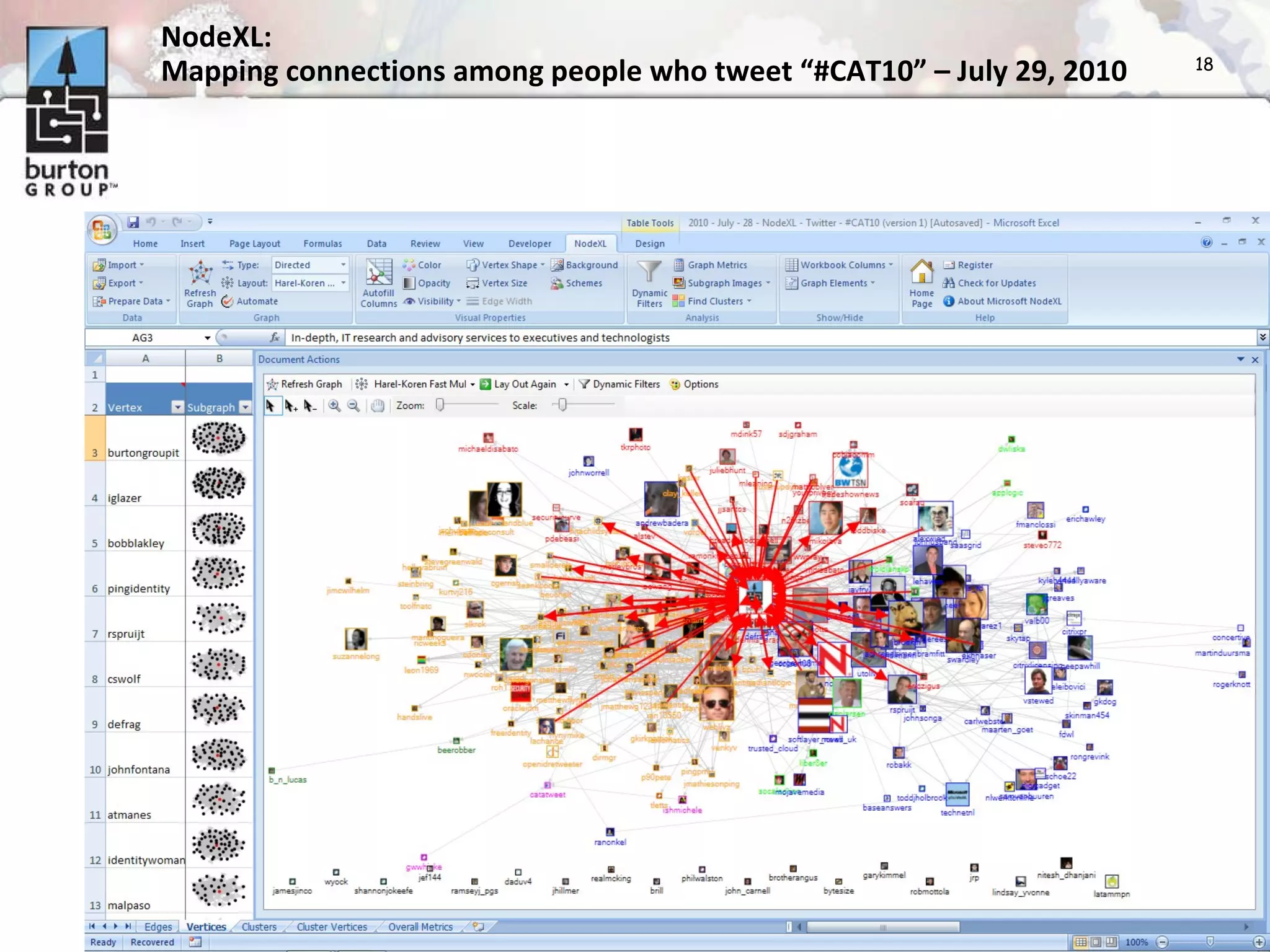
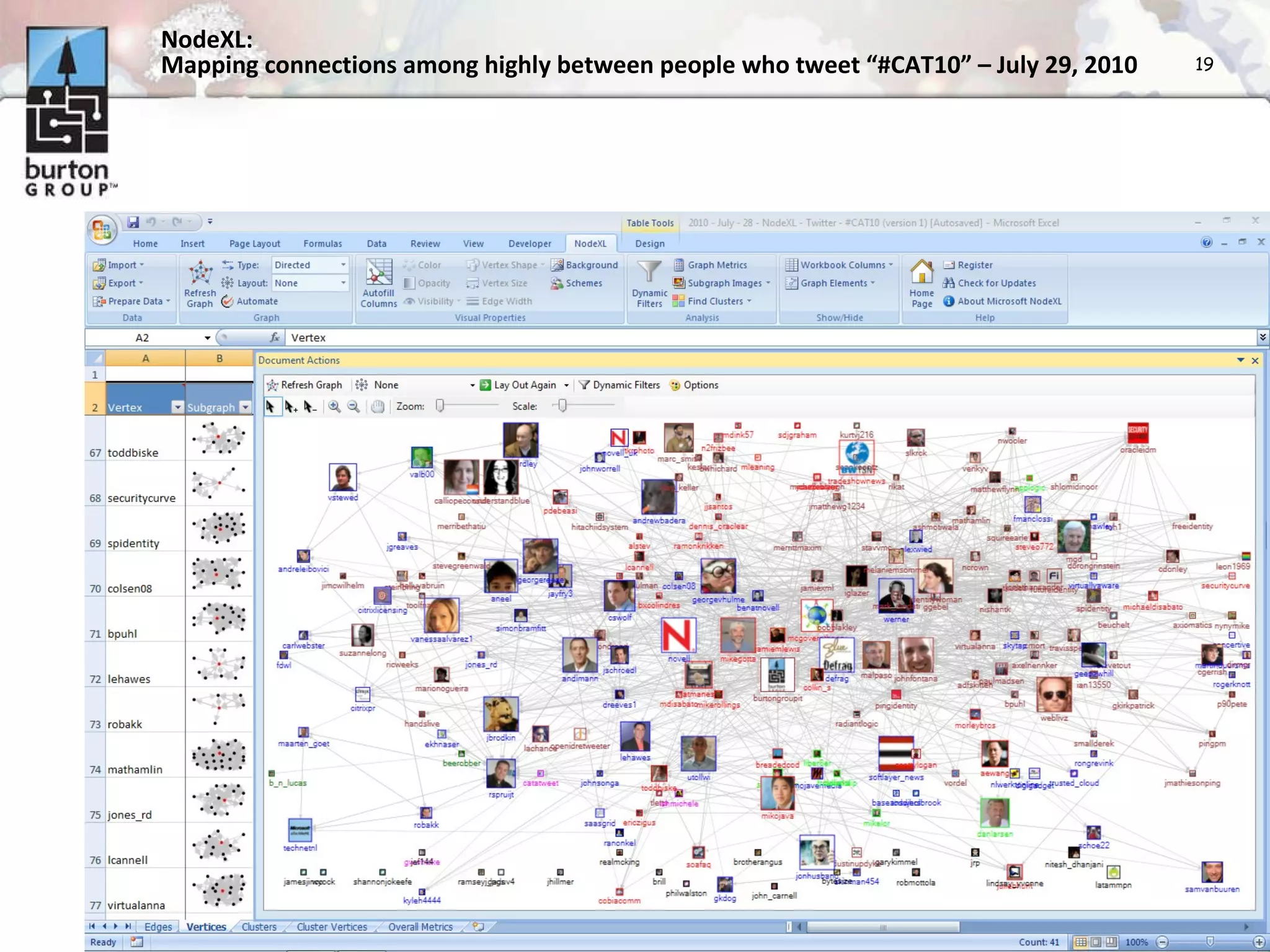
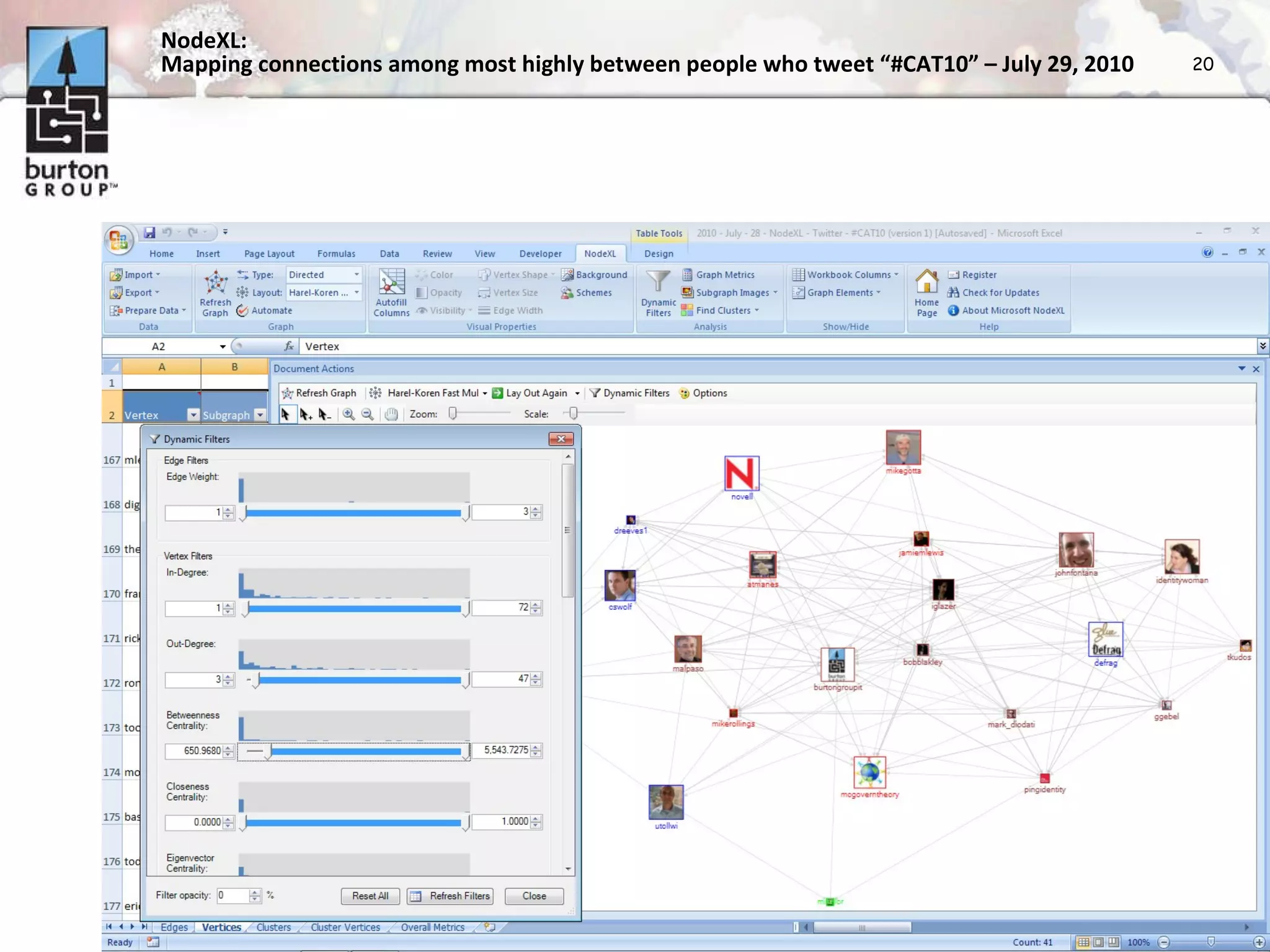
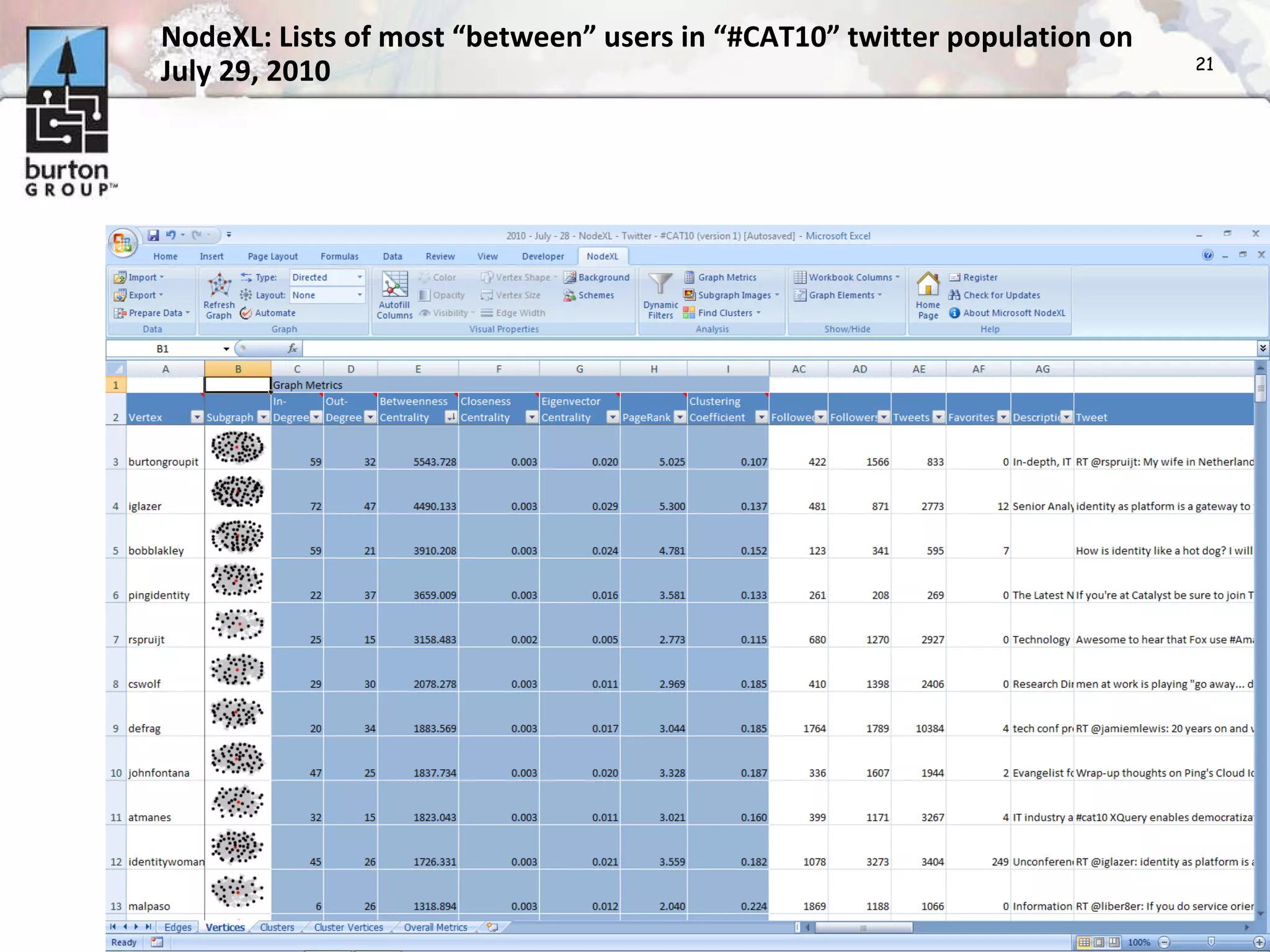
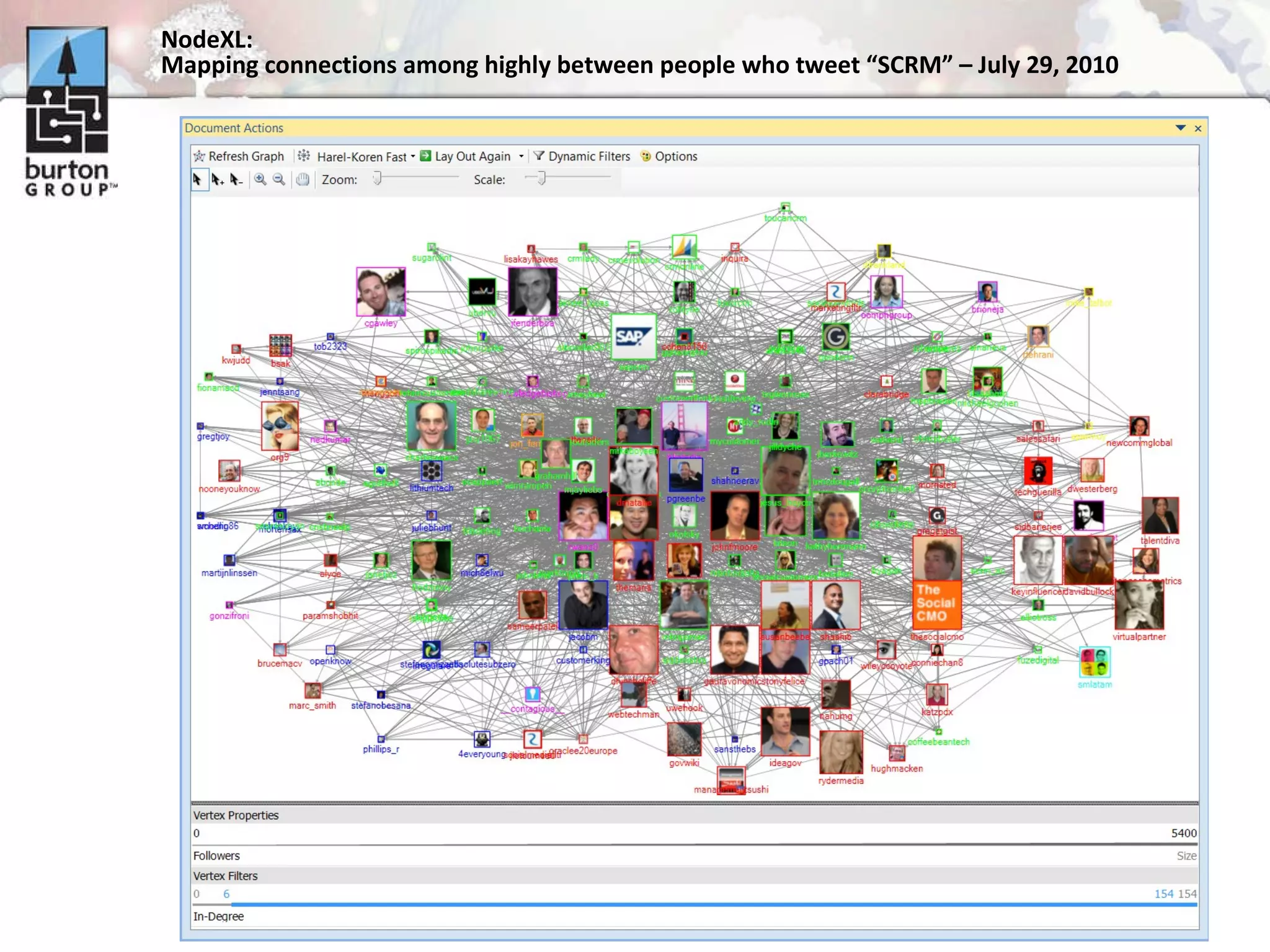
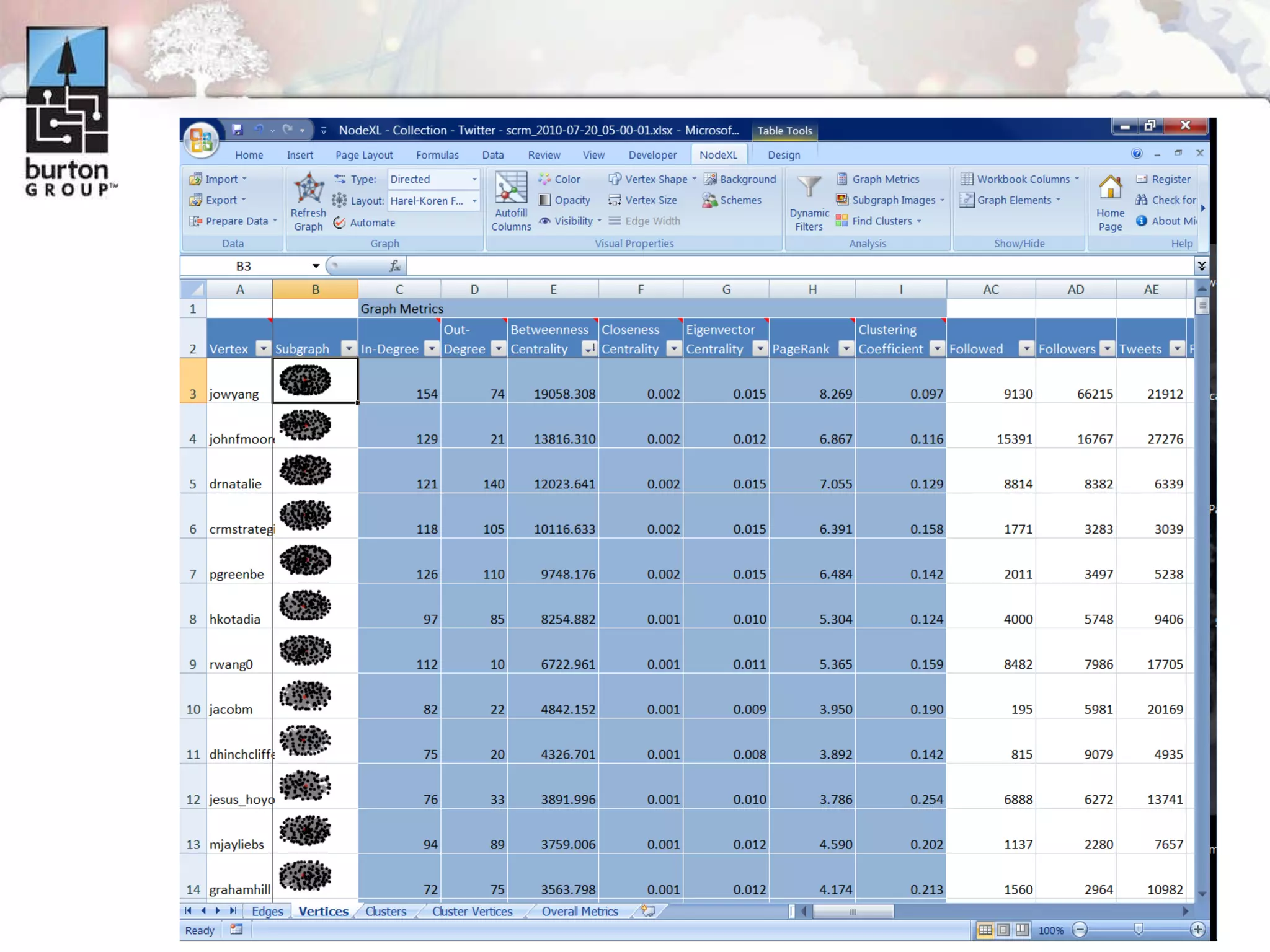
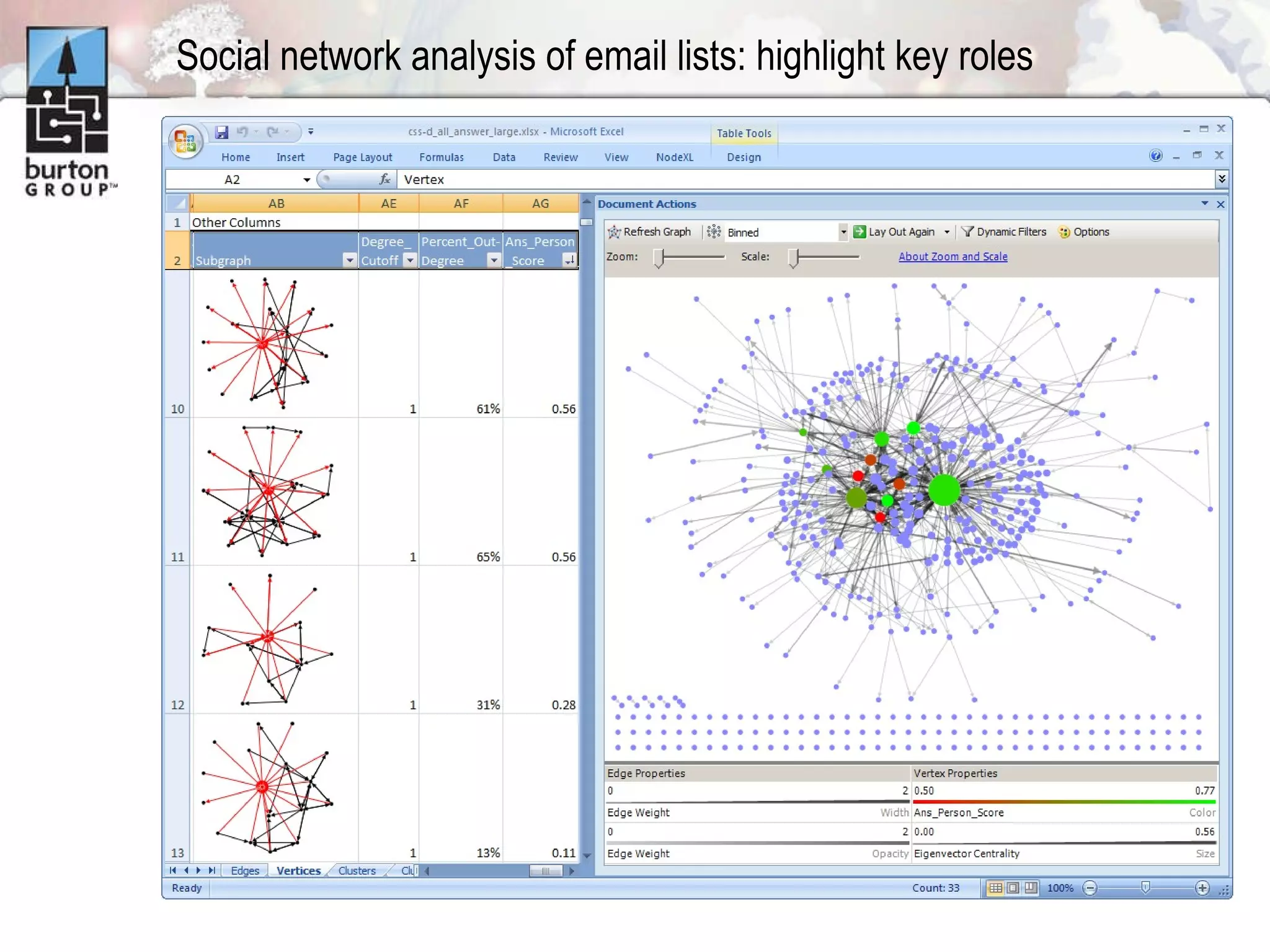
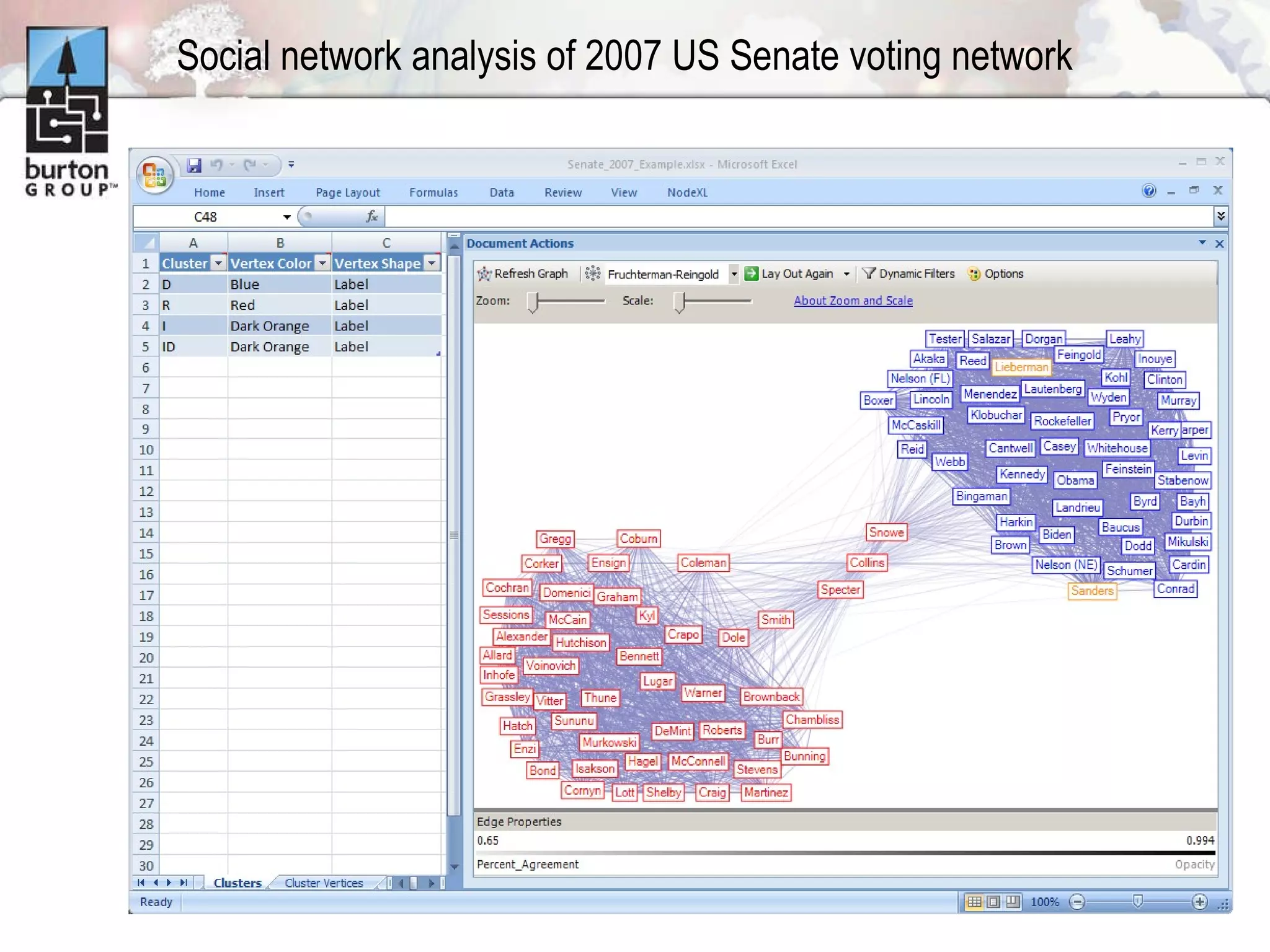
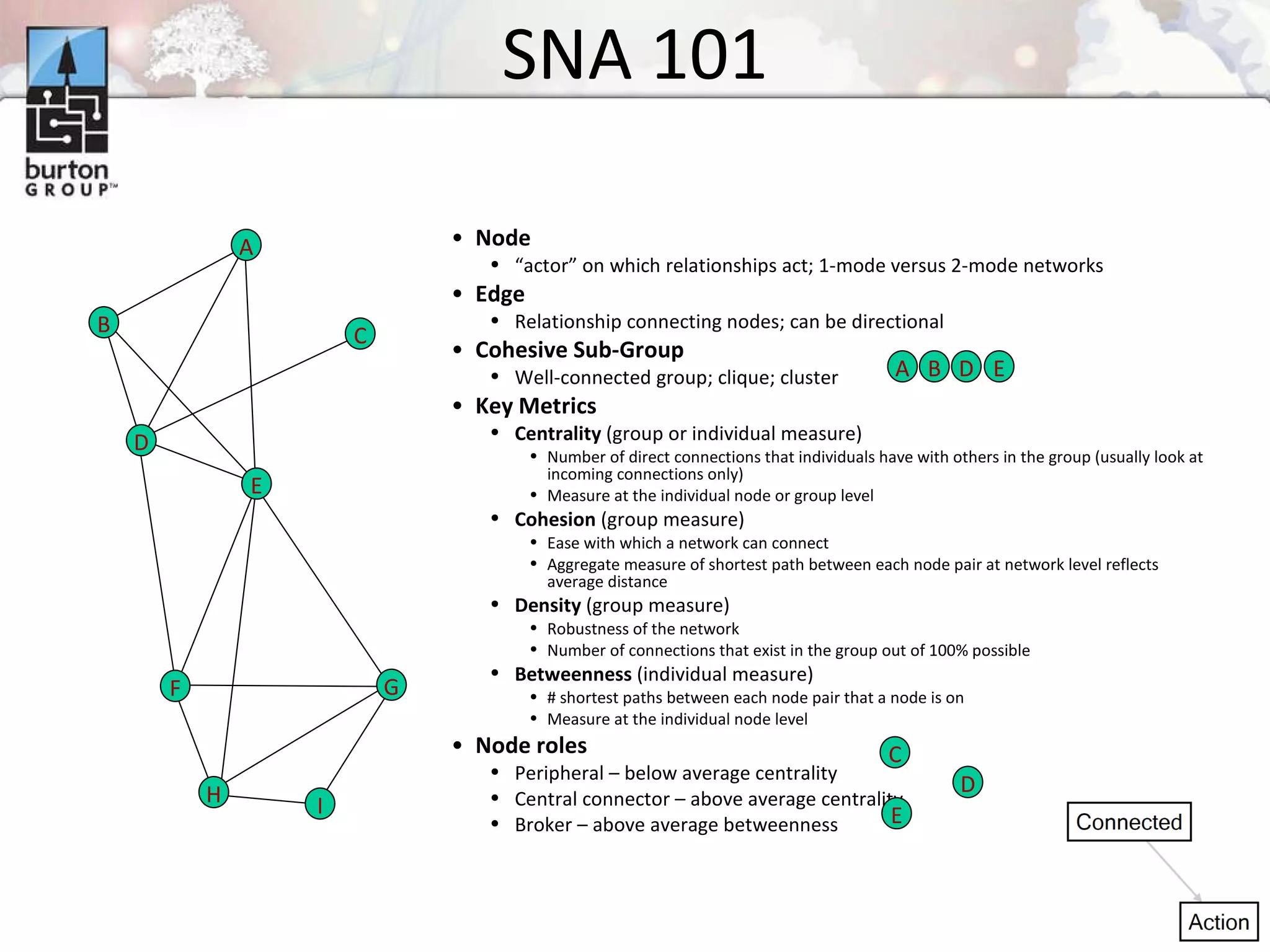
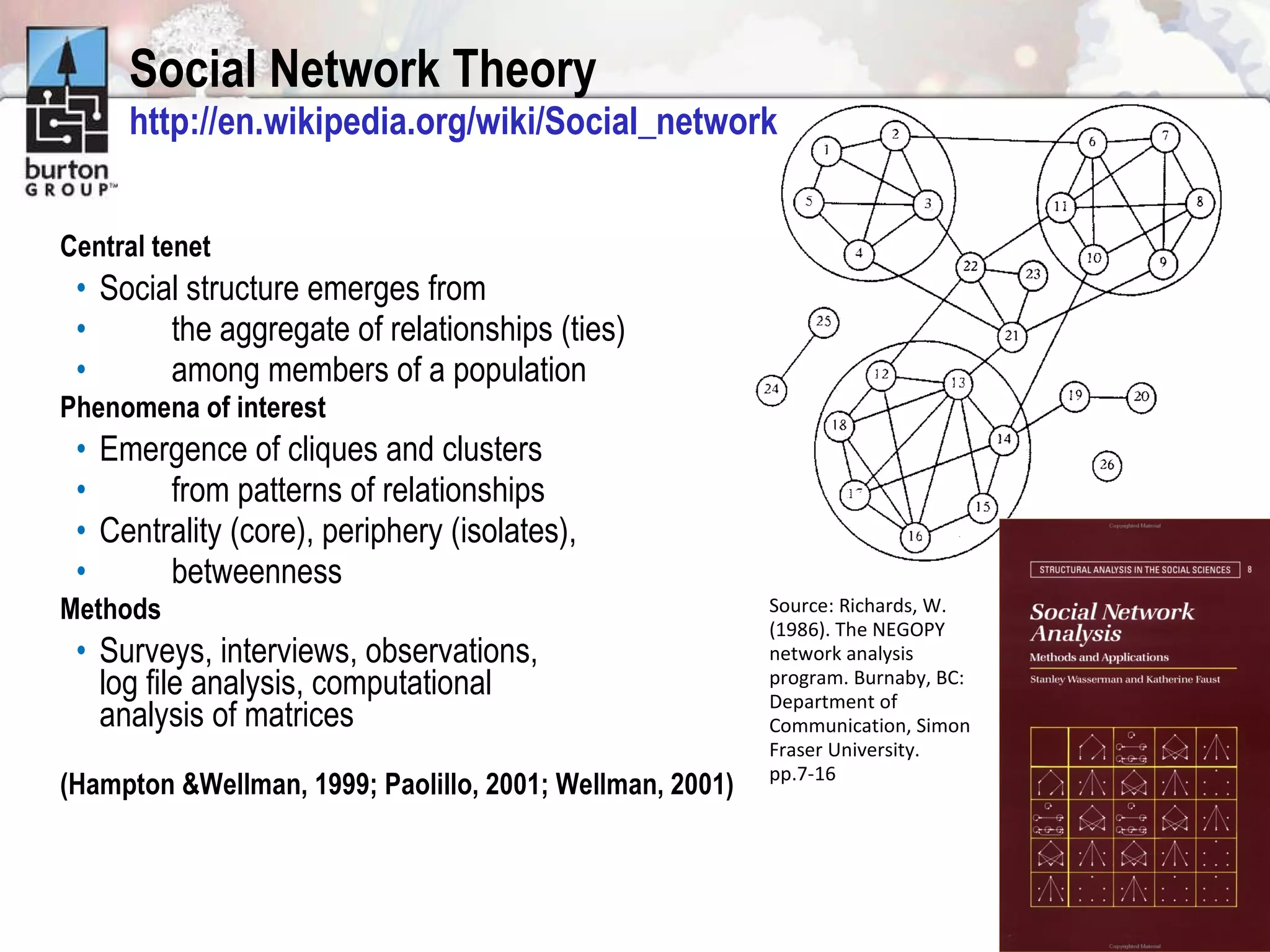
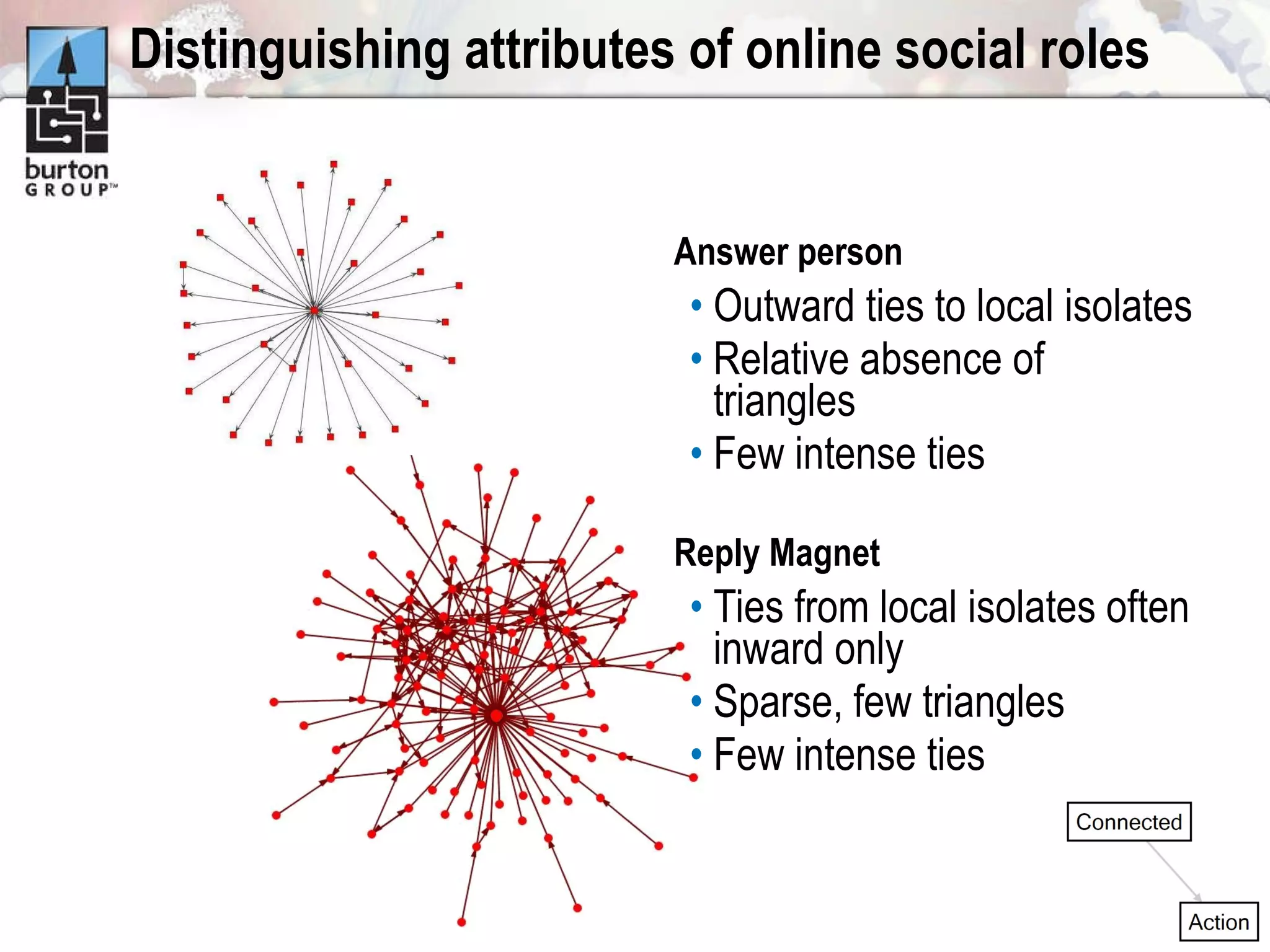
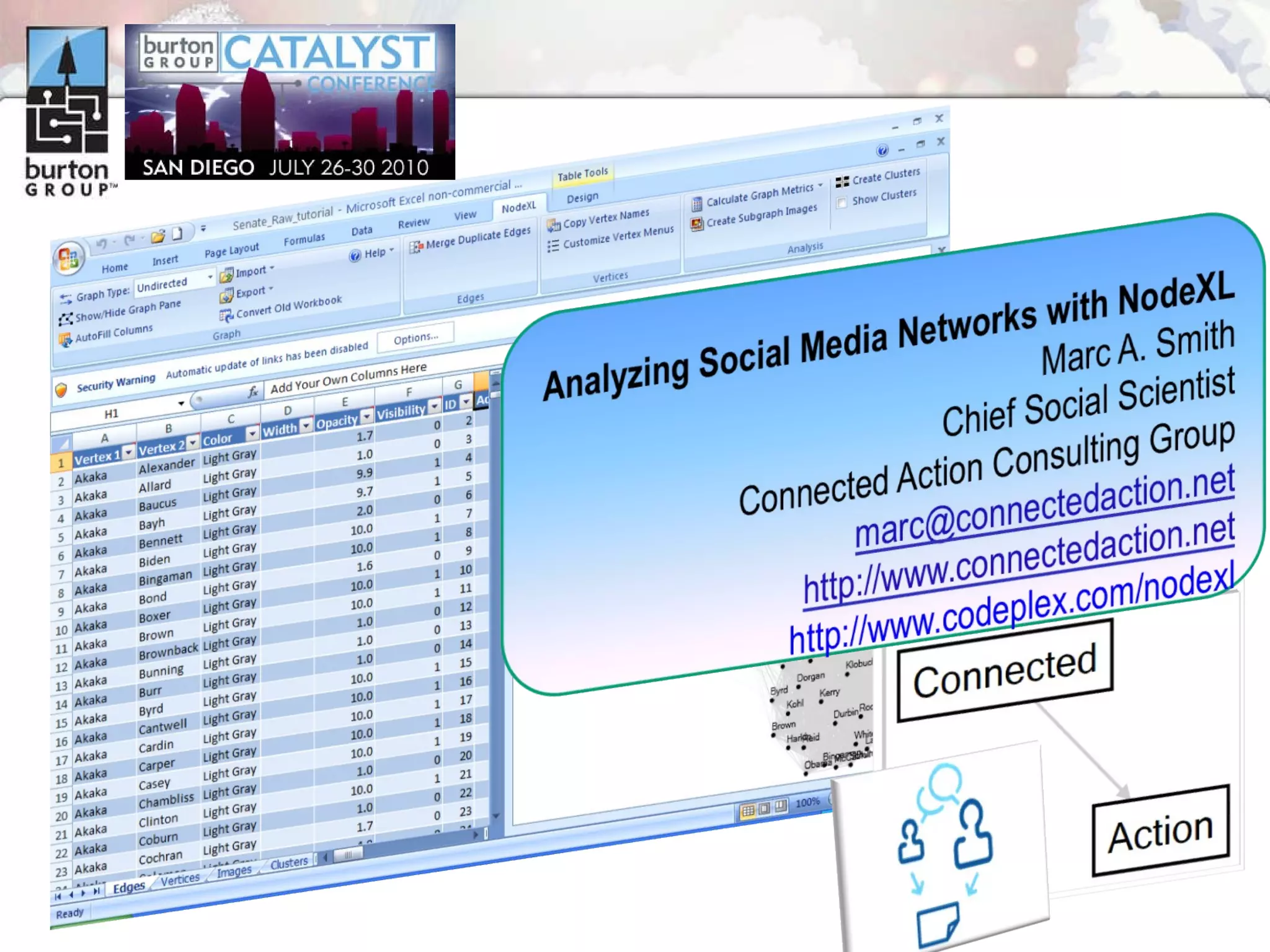
The document discusses trends in social networking and social network analysis (SNA) led by Dr. Marc A. Smith, highlighting his background and the Connected Action Consulting Group's focus on applying social science methods to social media. Key topics include the implications of SNA for IT organizations, privacy risks, and case studies on various social media platforms. It also outlines a tutorial for analyzing social media networks using the NodeXL tool, and anticipates future implications with the rise of social media data.
![Trends In Social Networking Thursday – 29 July, 2010 Mike Gotta Research VP Collaboration & Content [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cana10socnettrendsgottasmith-100729171556-phpapp02/75/2010-Catalyst-Conference-Trends-in-Social-Network-Analysis-1-2048.jpg)


![Trends In Social Networking Dr. Marc A. Smith Chief Social Scientist, Connected Action Consulting Group [email_address] http://www.connectedaction.net http://nodexl.codeplex.com http://twitter.com/marc_smith http://www.smrfoundation.org/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cana10socnettrendsgottasmith-100729171556-phpapp02/75/2010-Catalyst-Conference-Trends-in-Social-Network-Analysis-4-2048.jpg)