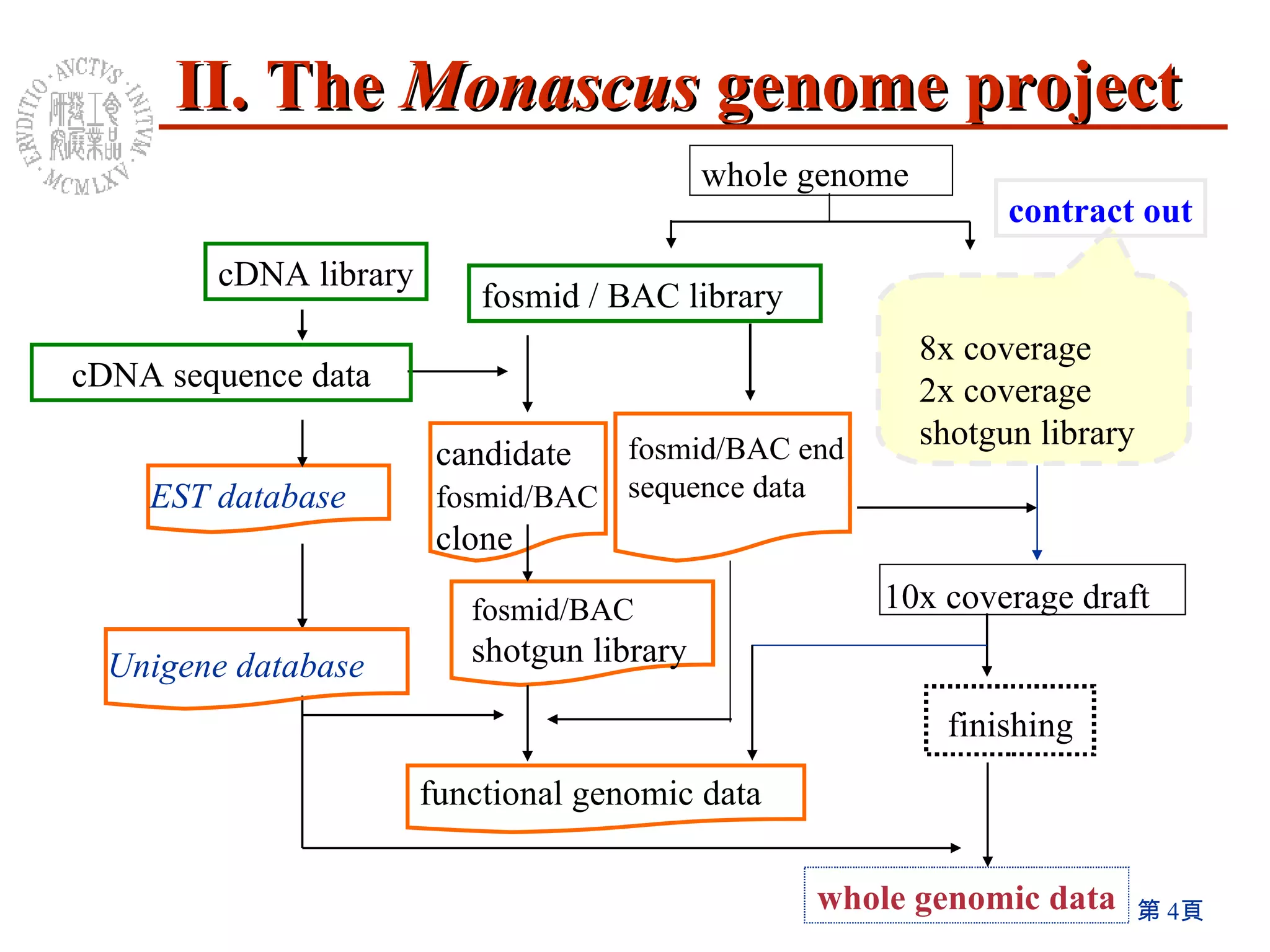
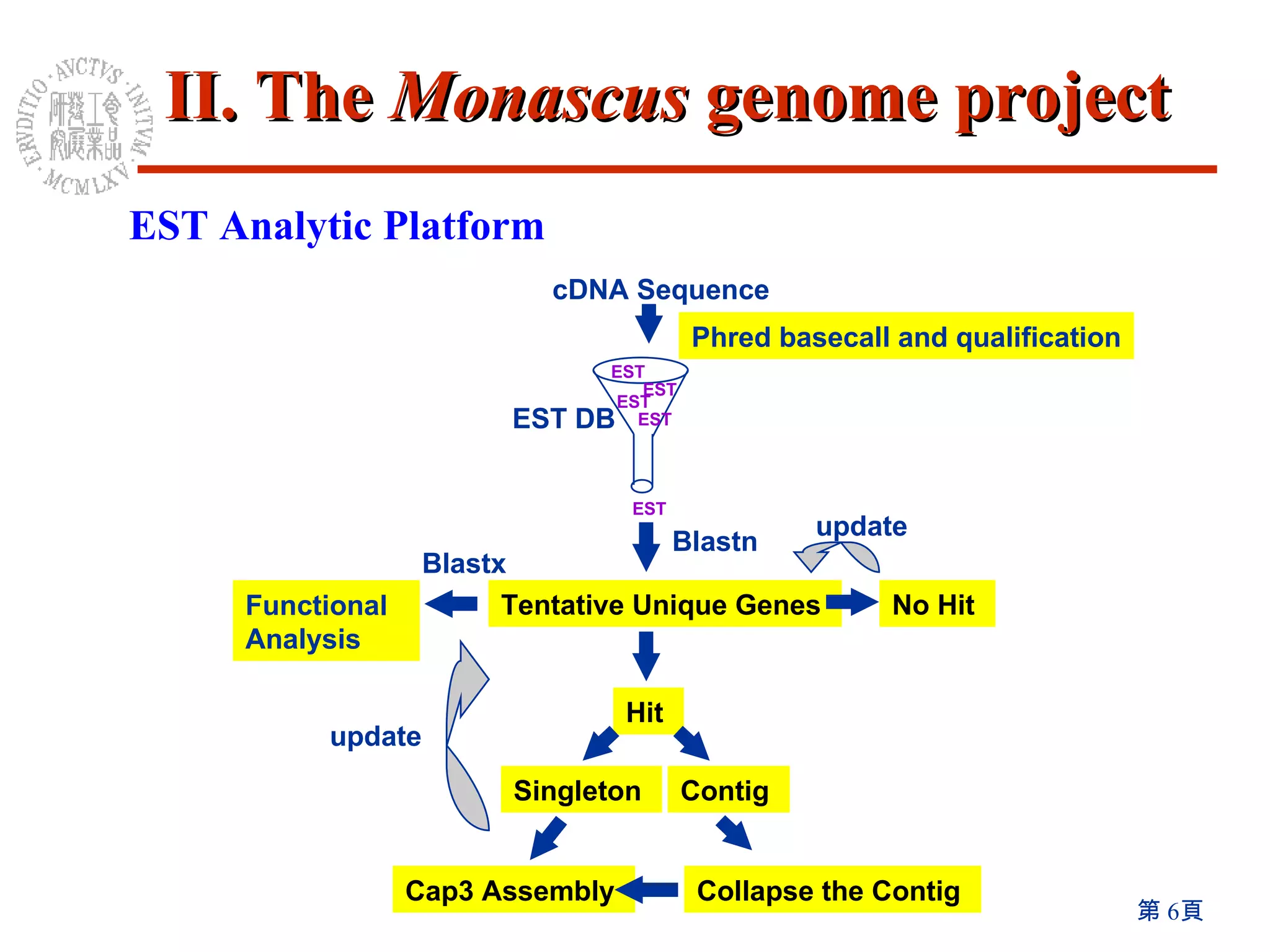
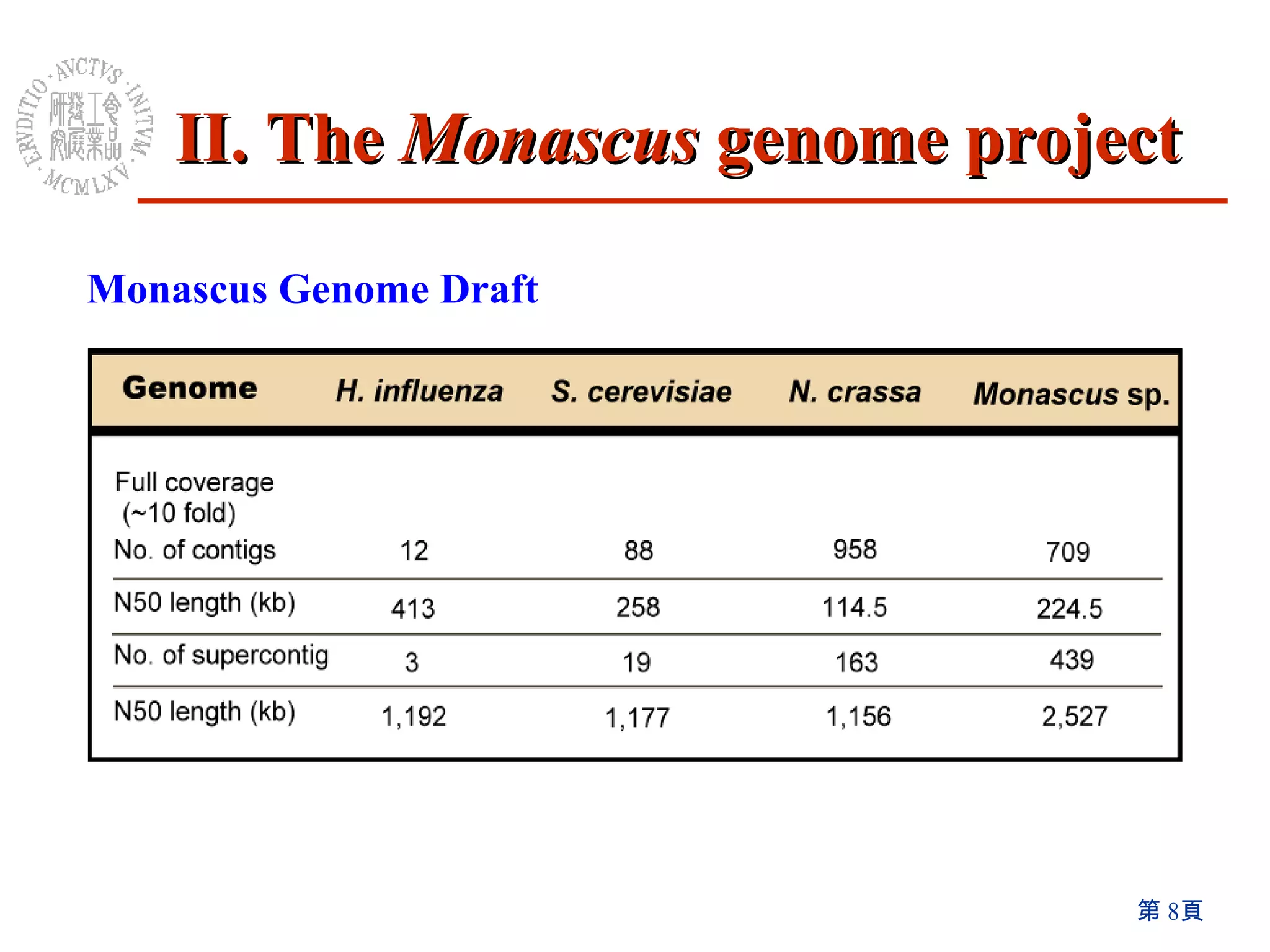
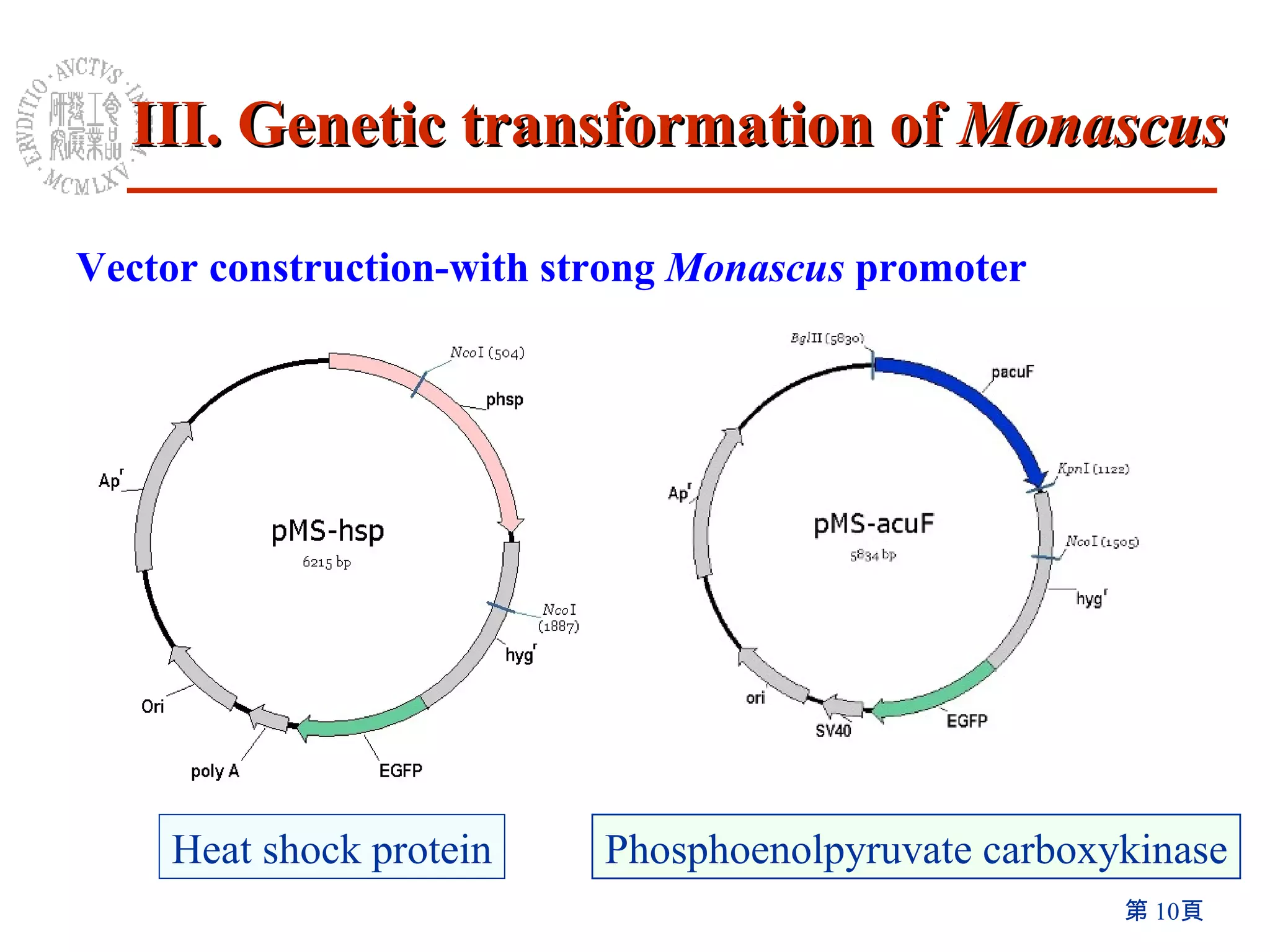
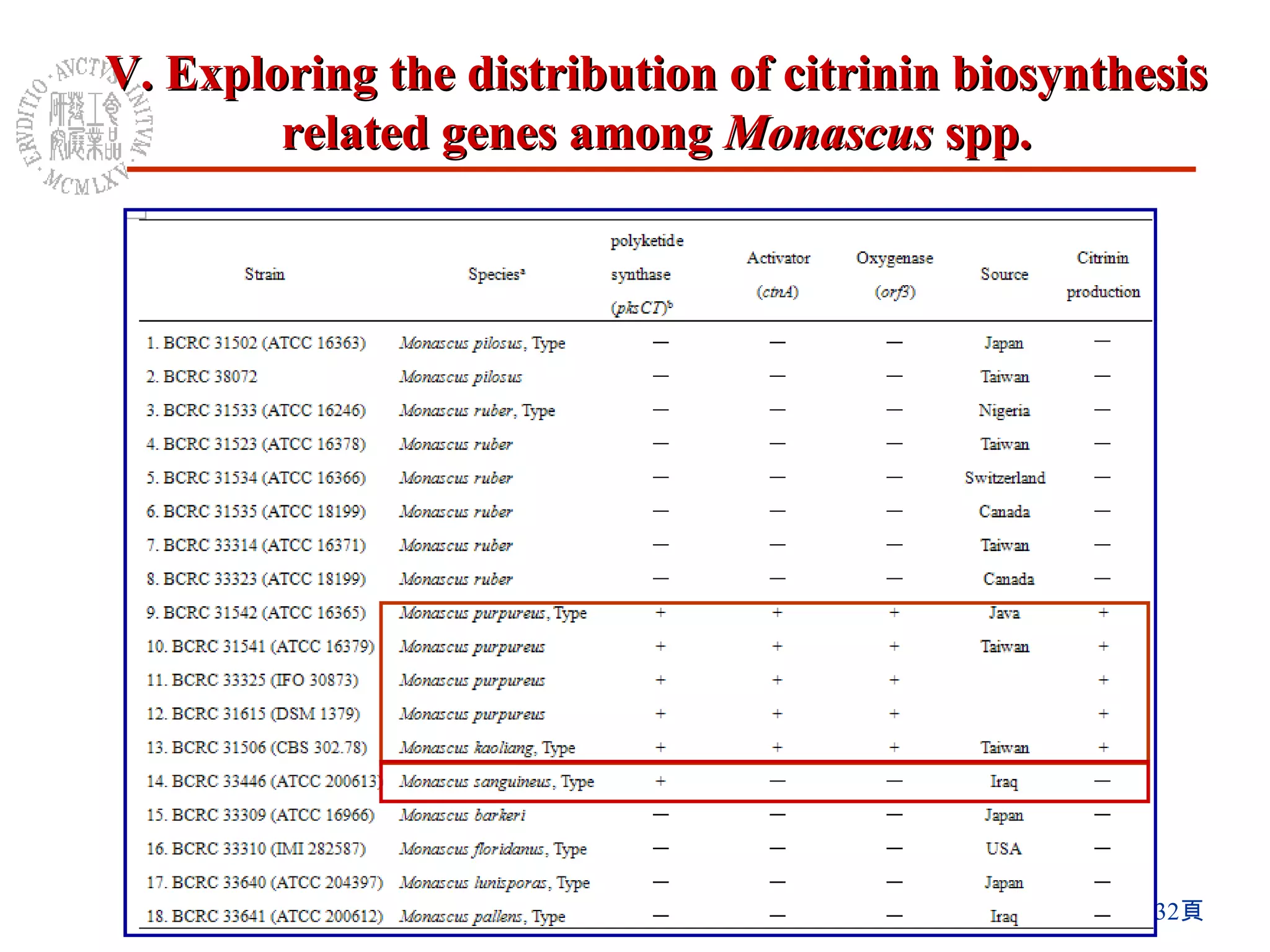
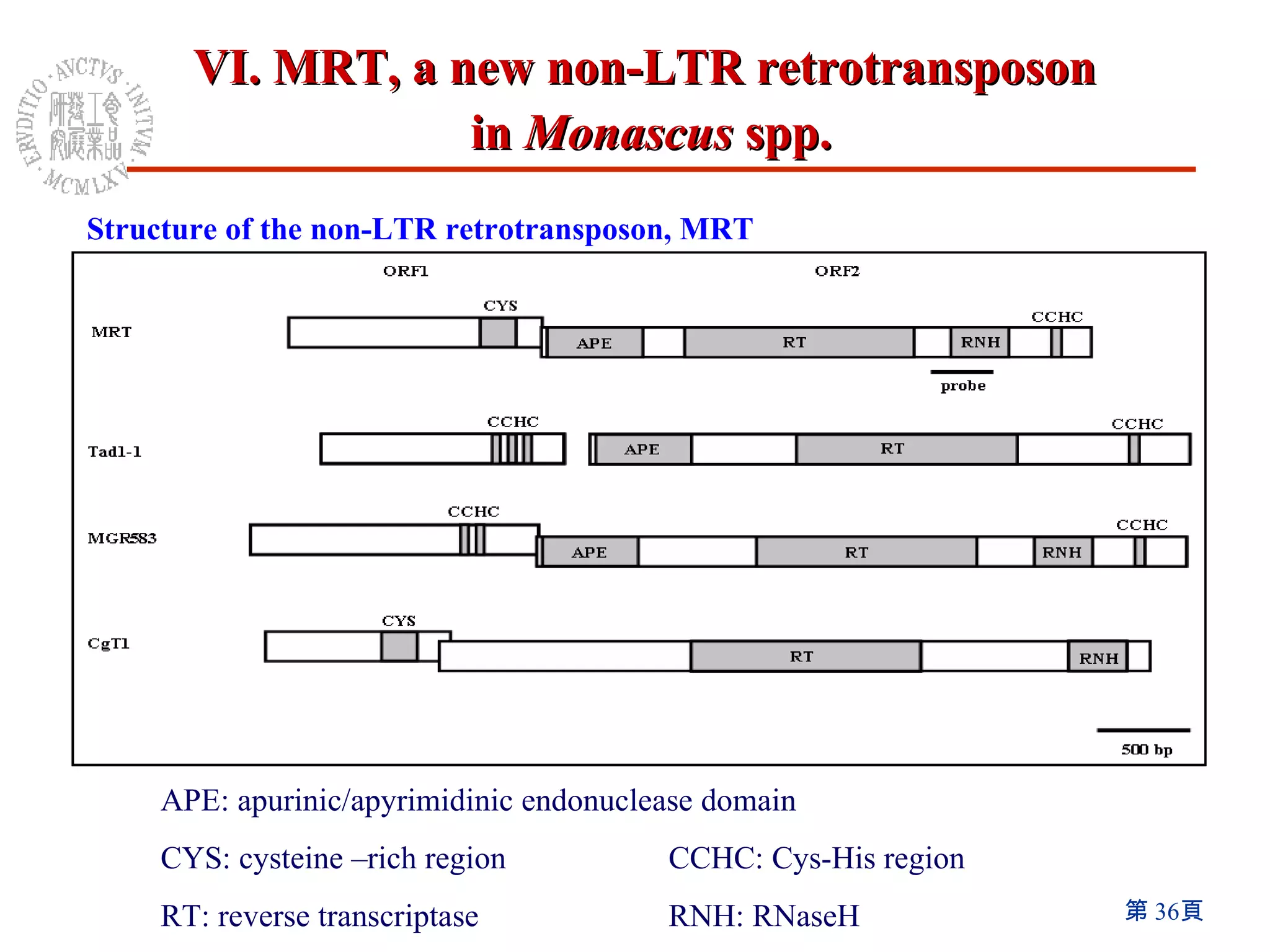
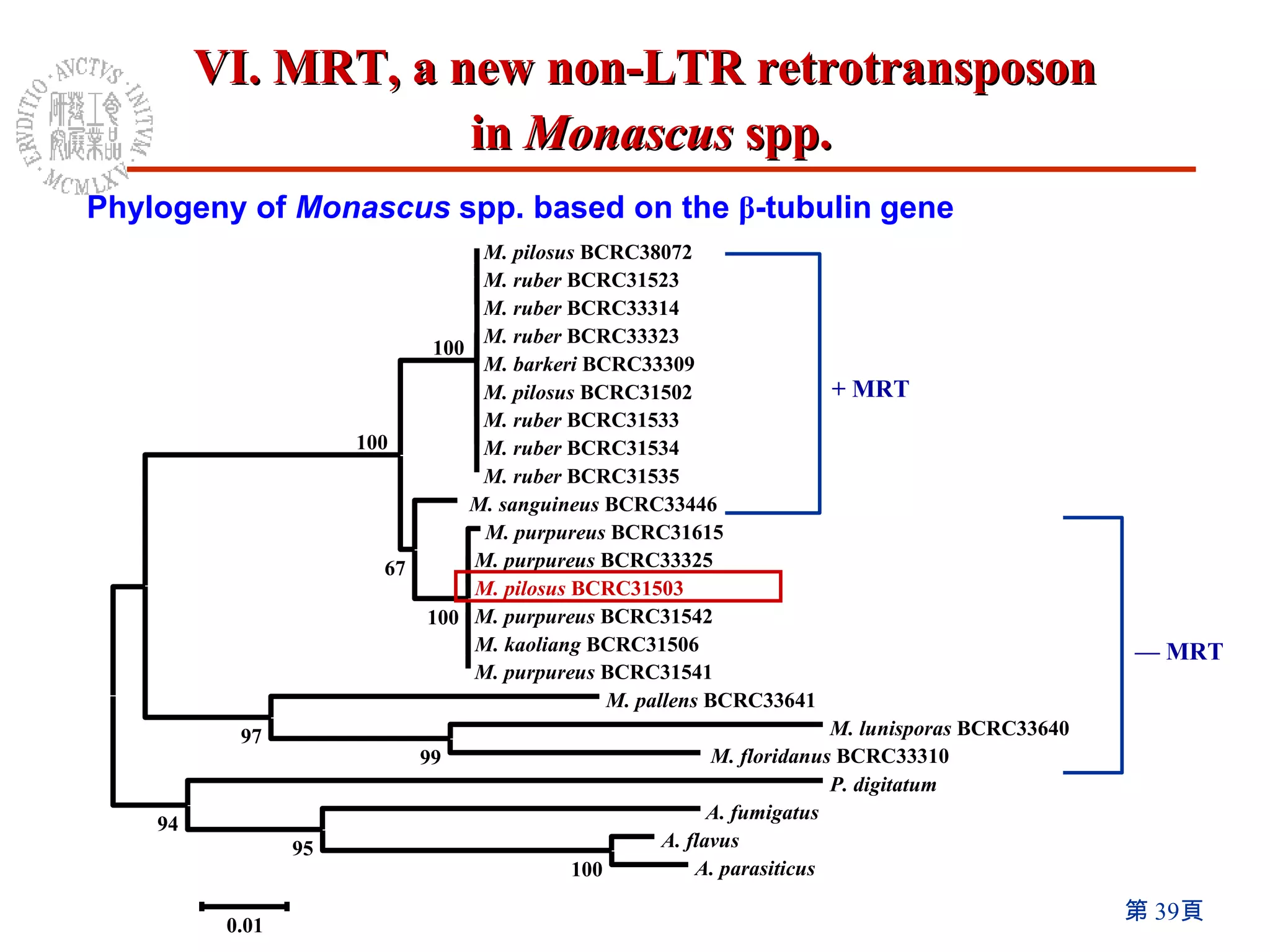
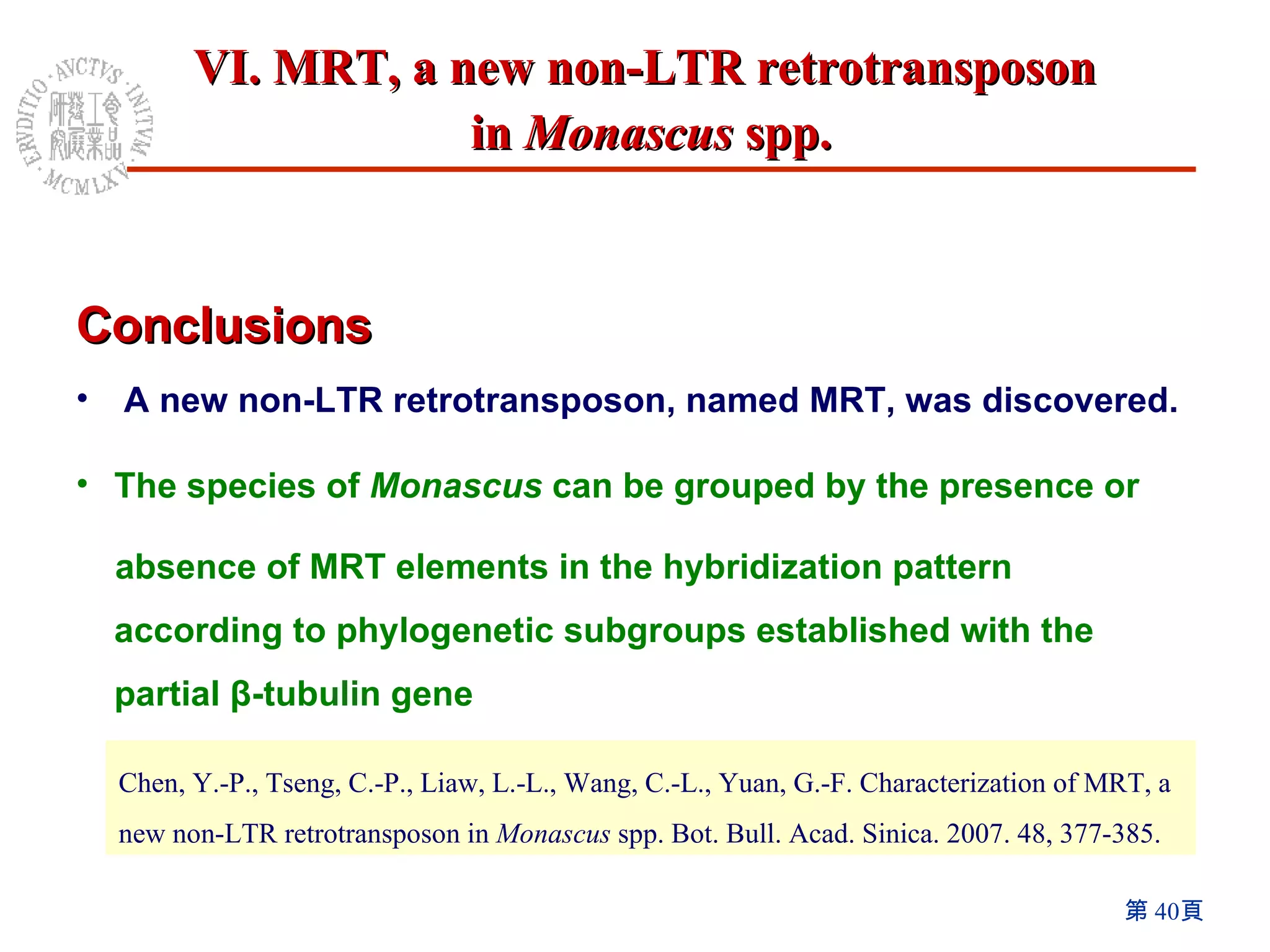
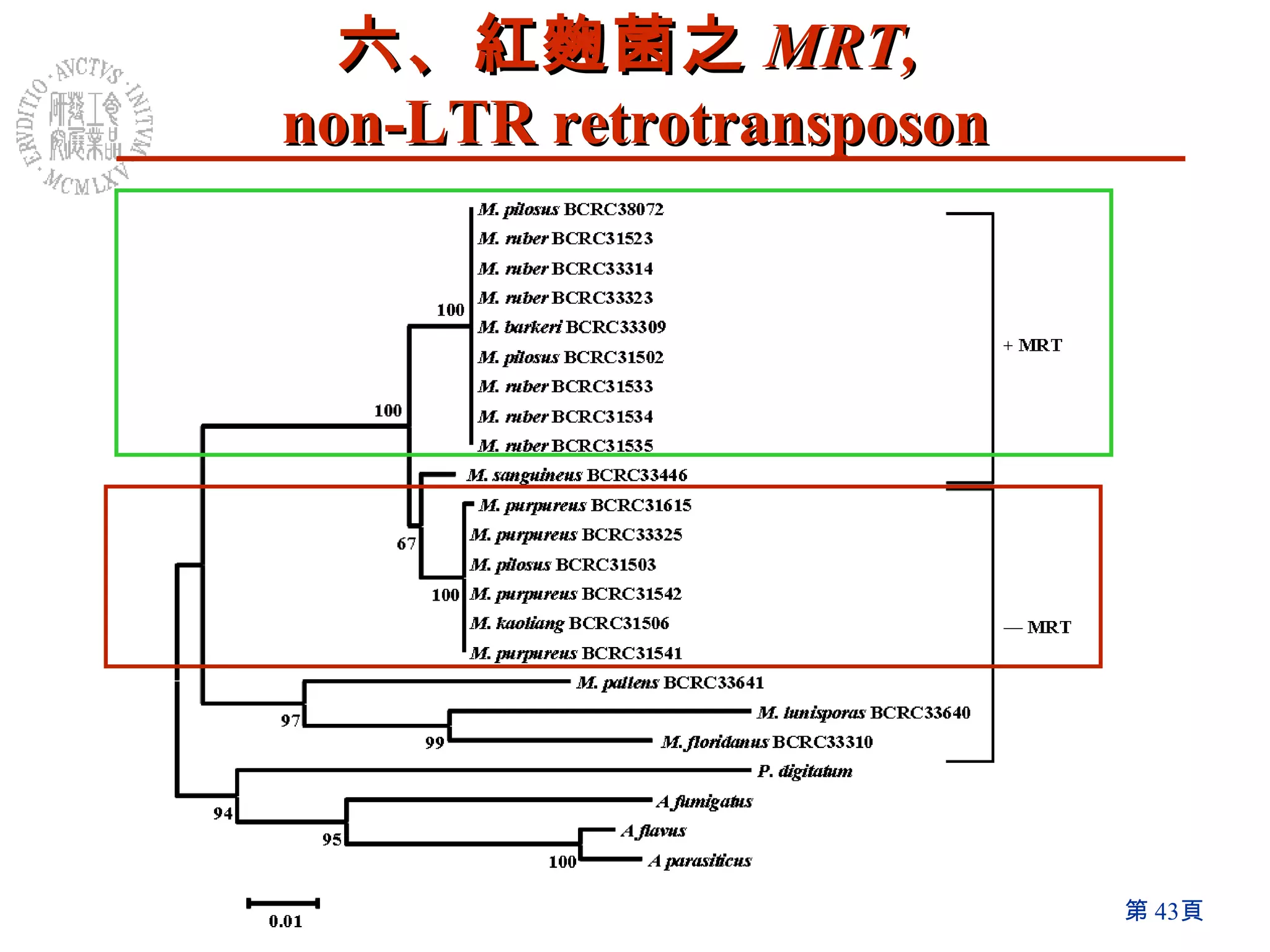
The document summarizes research on the Monascus genome project and related genetic studies. Key points include:
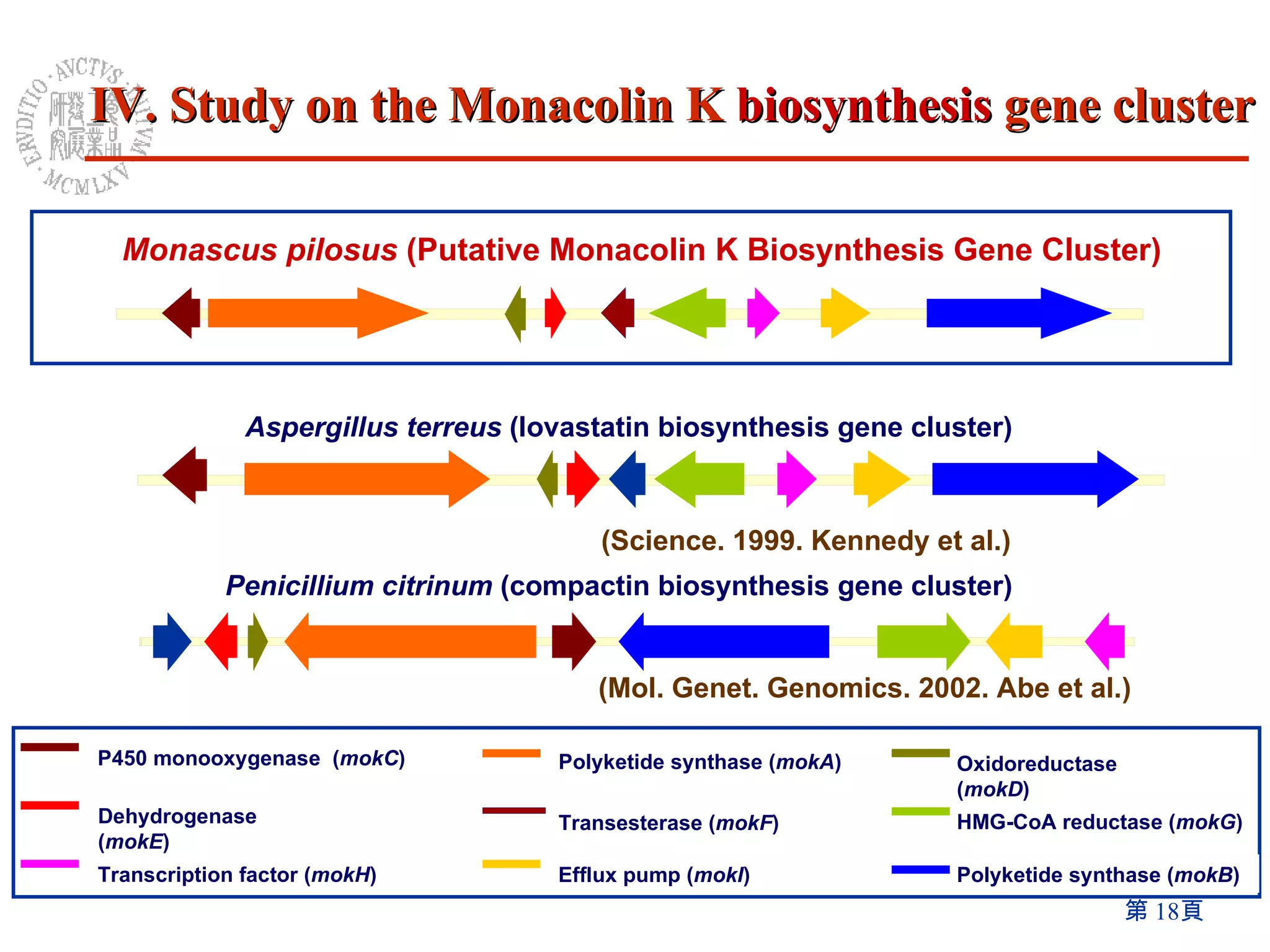
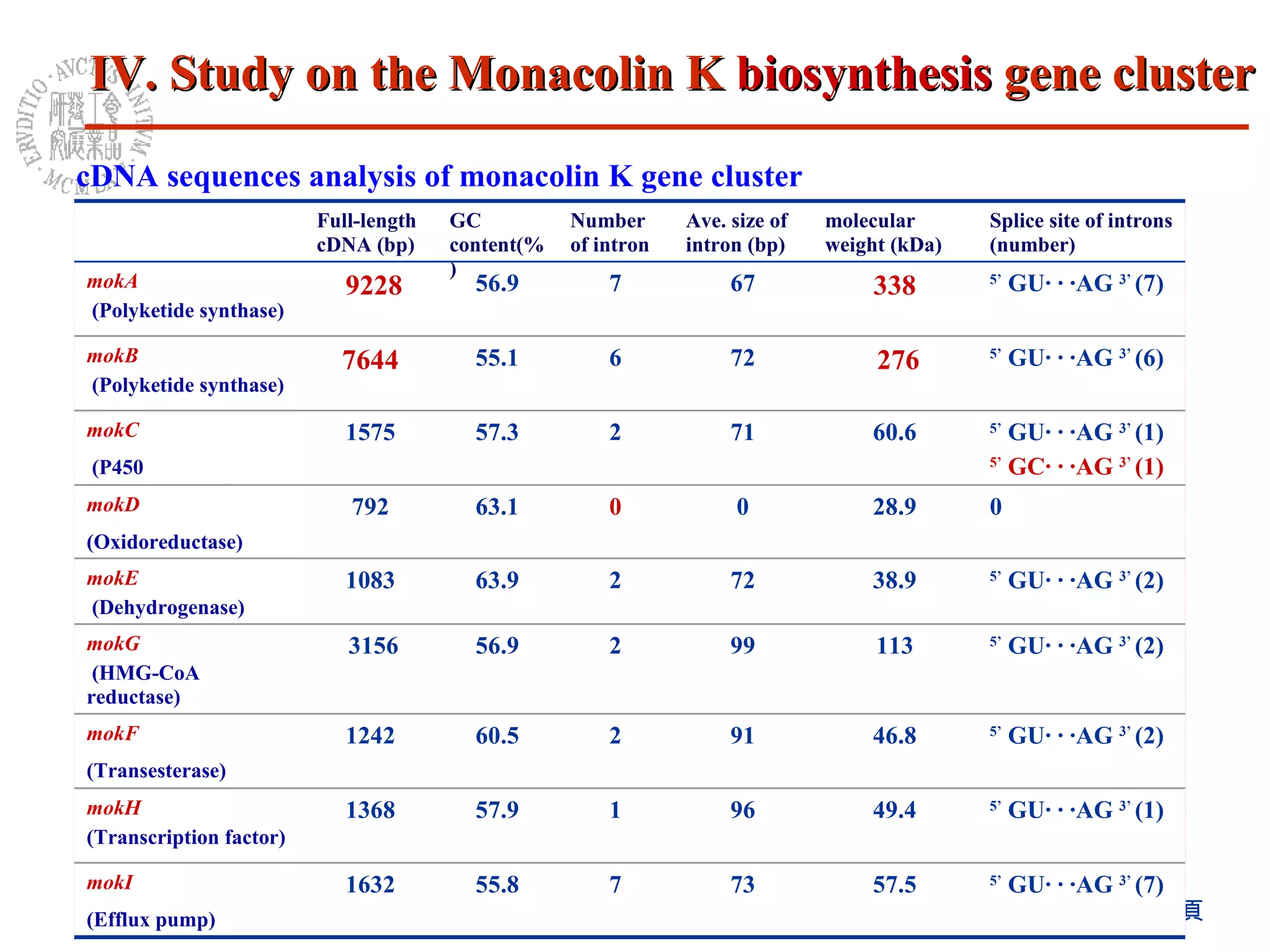
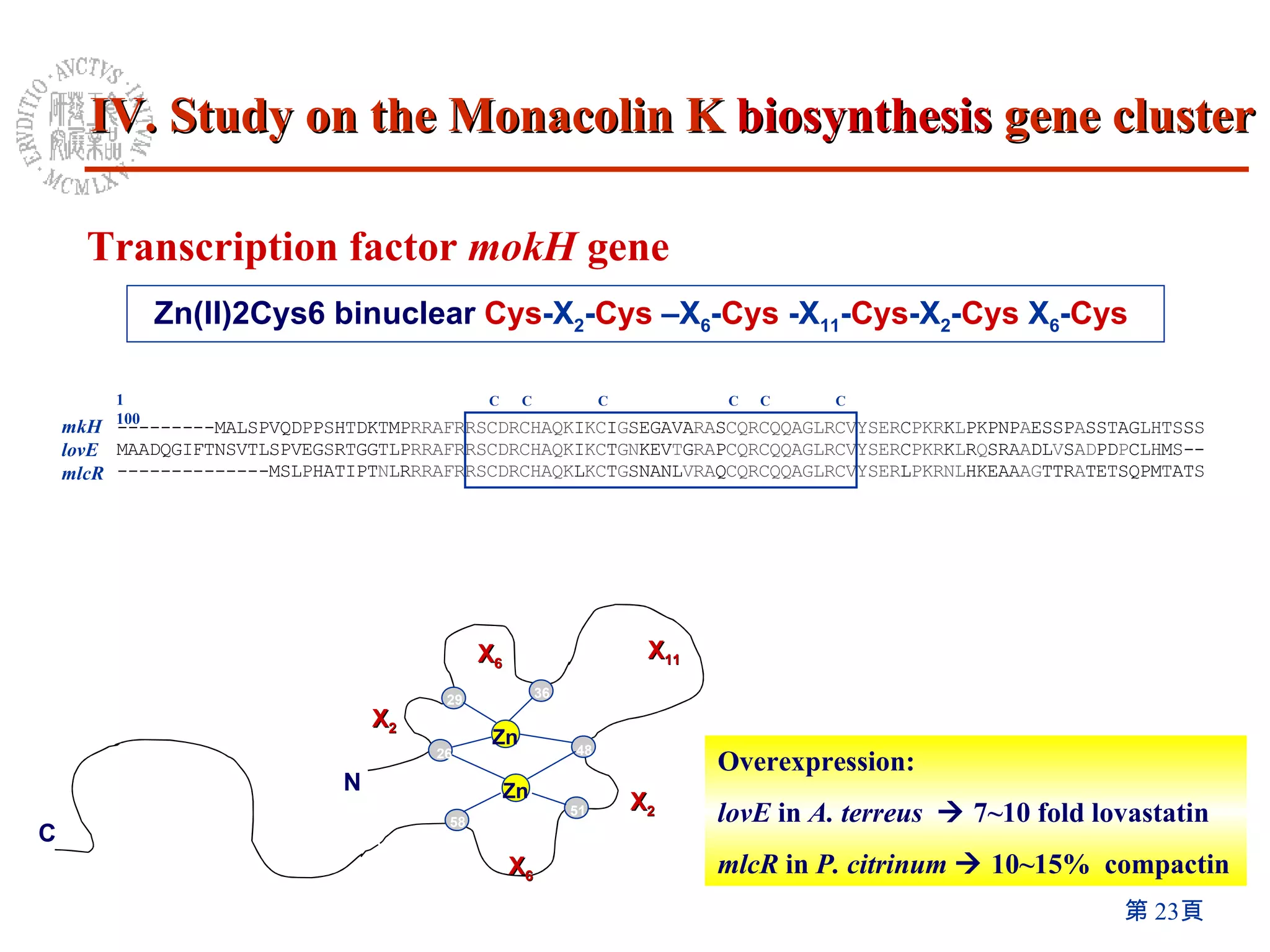
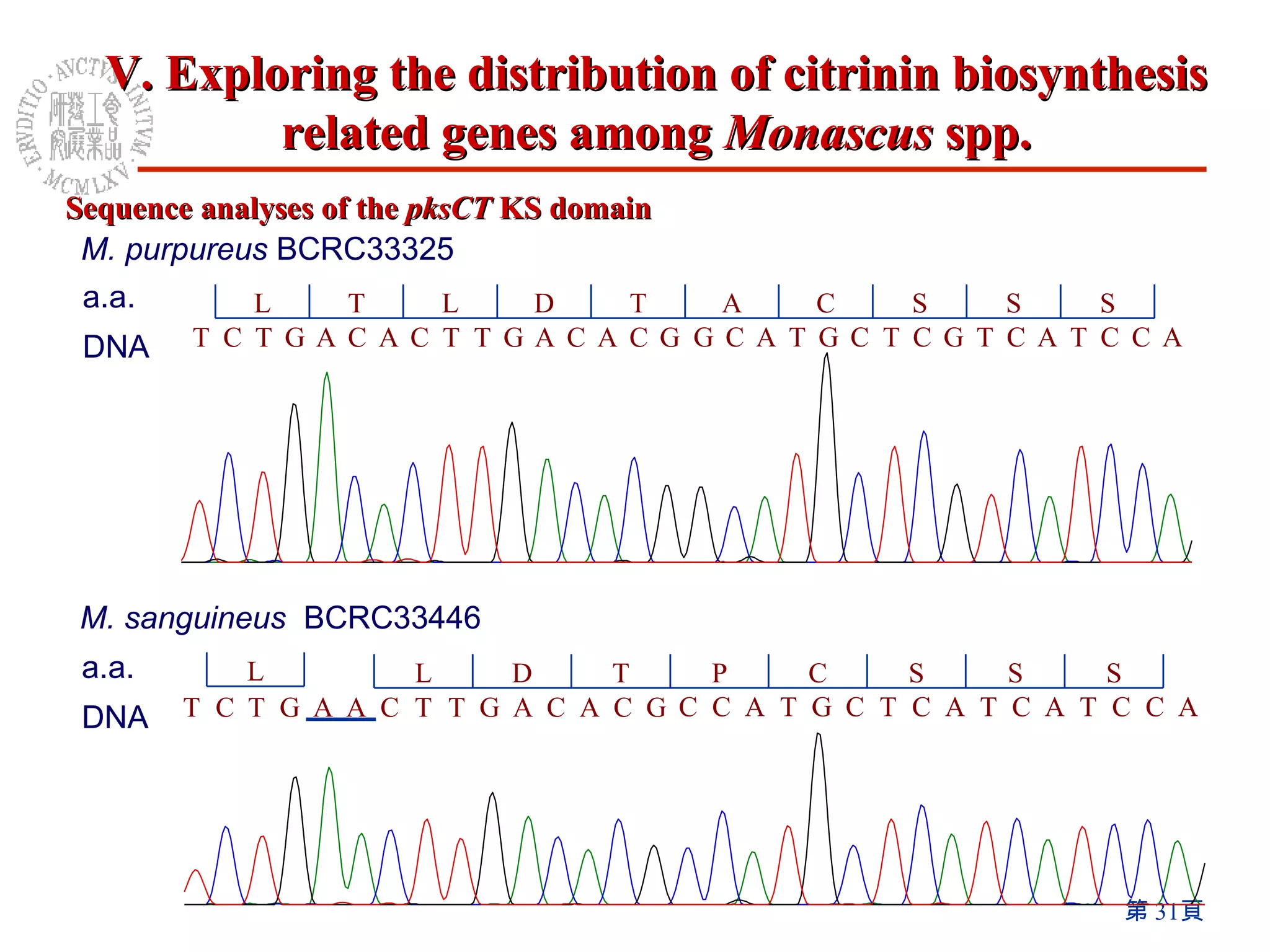
1) The Monascus genome was sequenced to 8x coverage, revealing various genomic features. A Monacolin K biosynthesis gene cluster was identified containing genes for polyketide synthases and other enzymes.
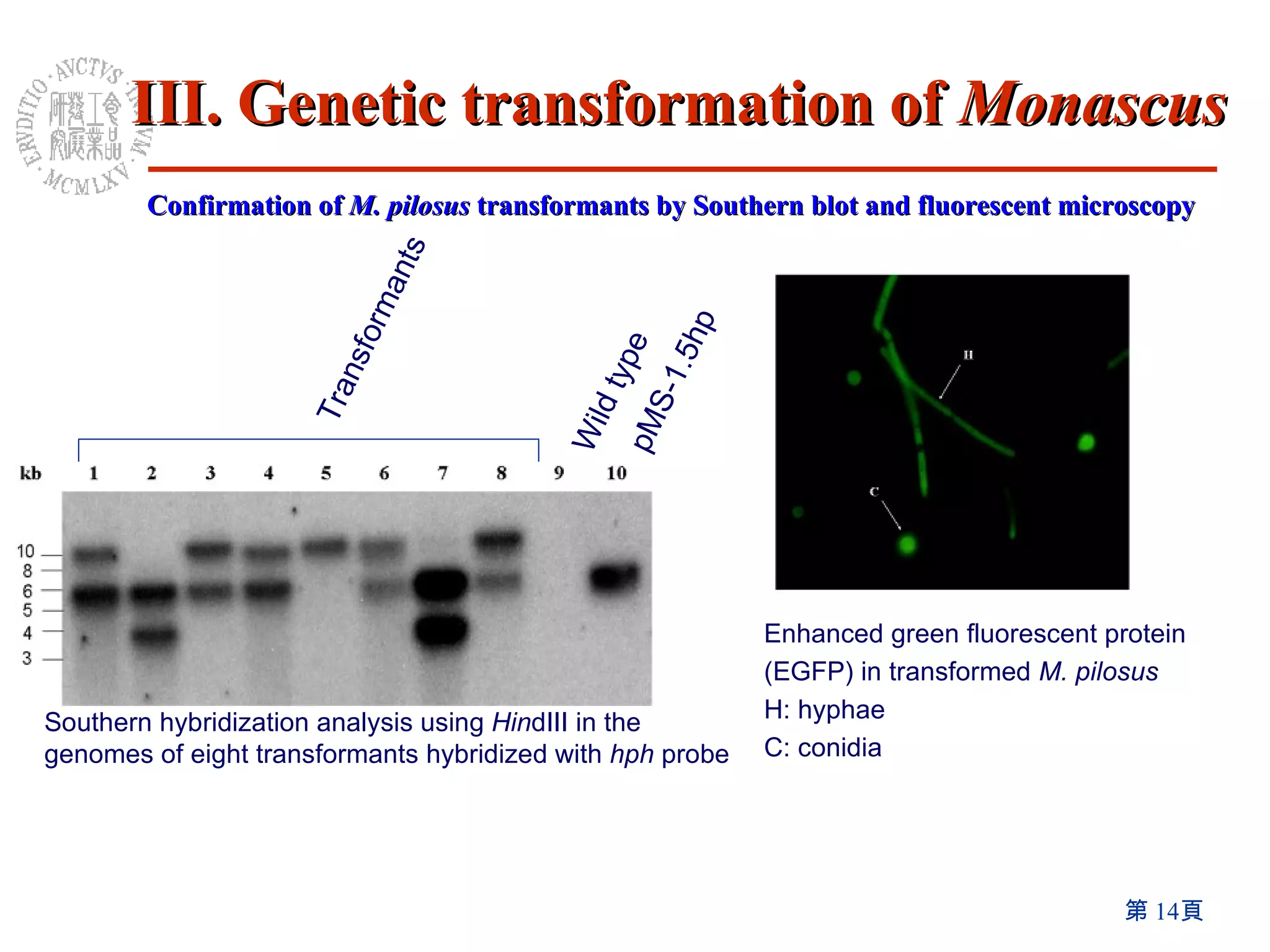
2) An efficient method for genetic transformation of Monascus pilosus was developed using aurintricarboxylic acid.
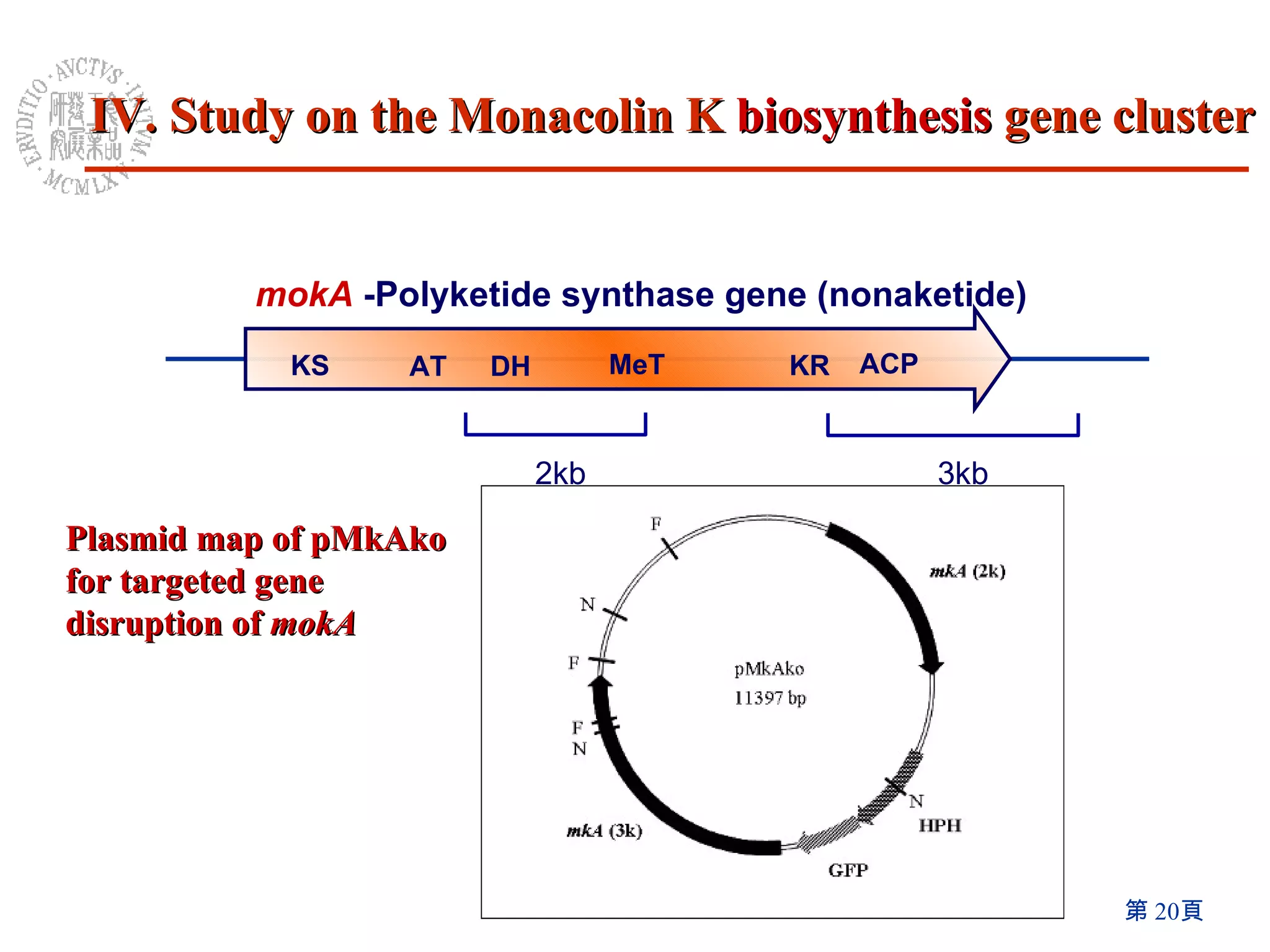
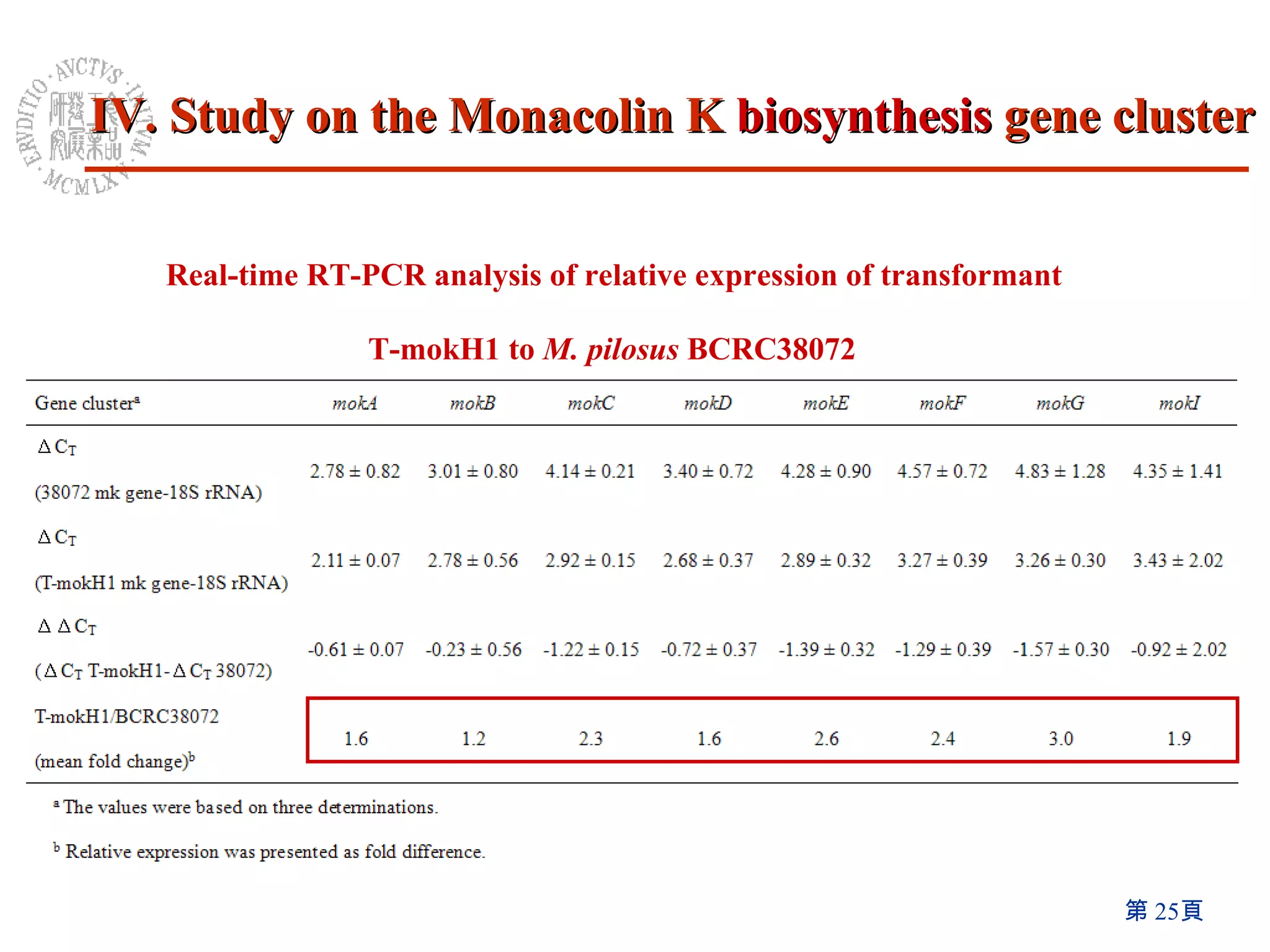
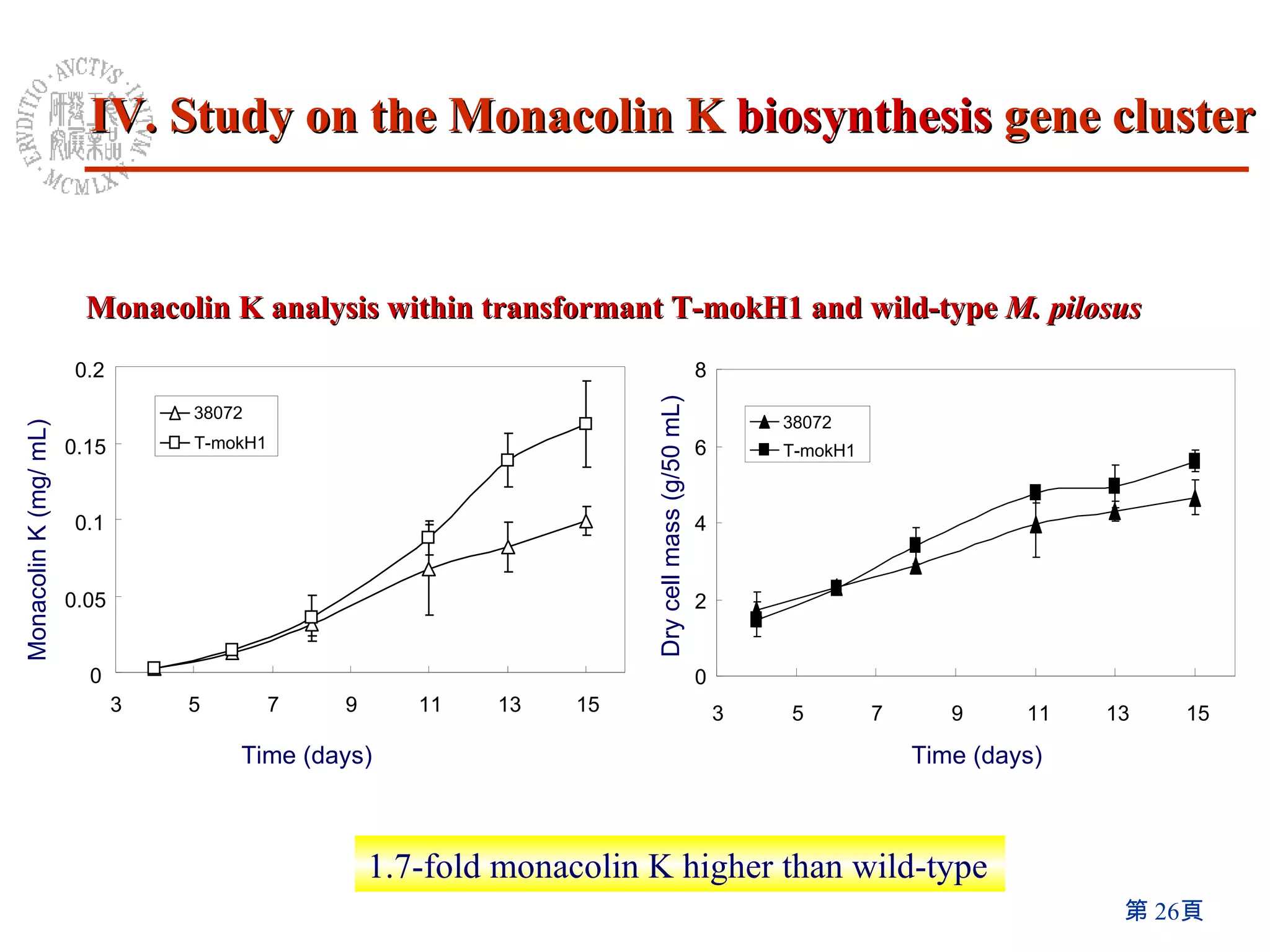
3) Disruption of the mokA gene and overexpression of the mokH transcription factor gene resulted in loss of and increased Monacolin K production, respectively.