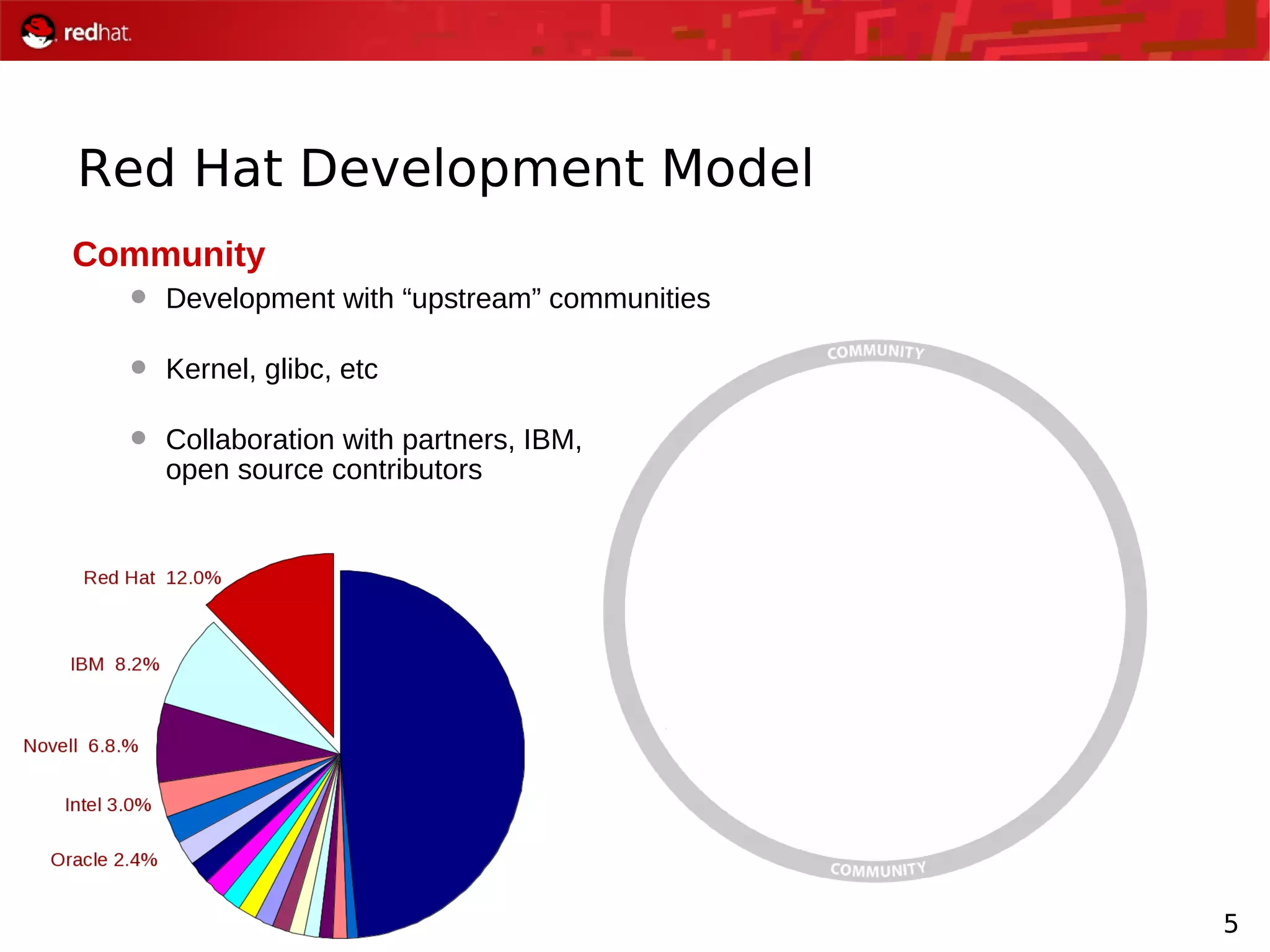
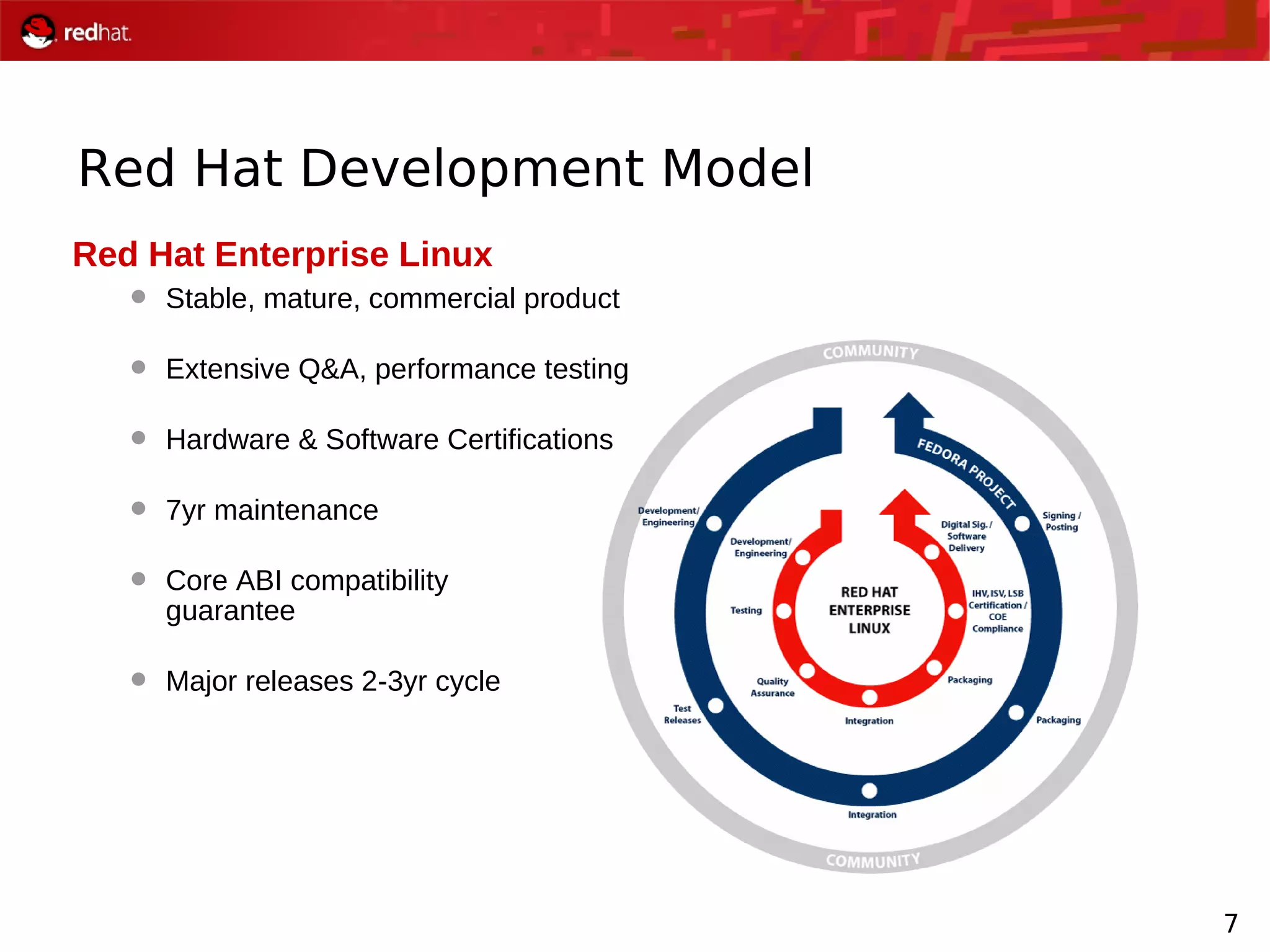
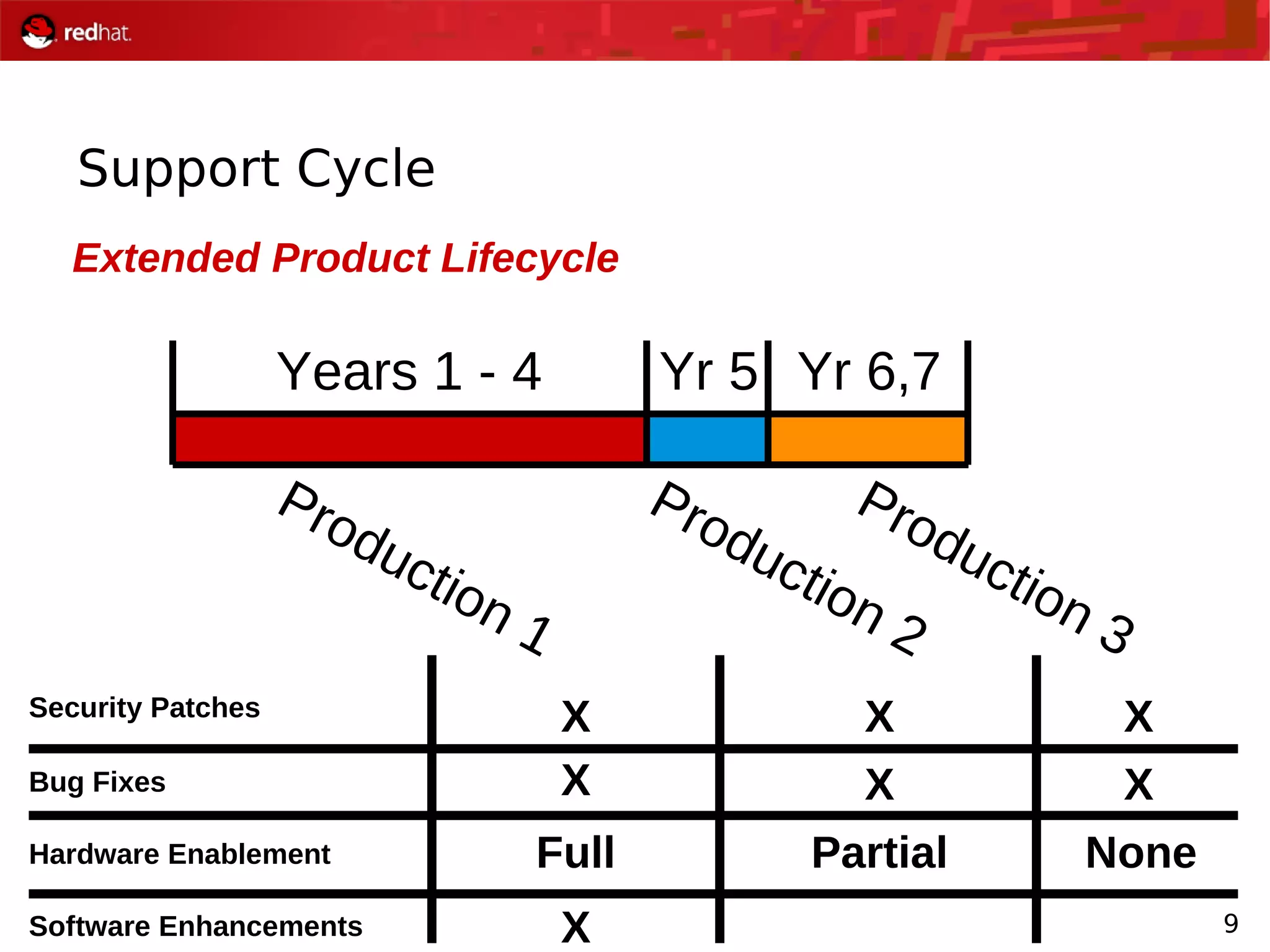
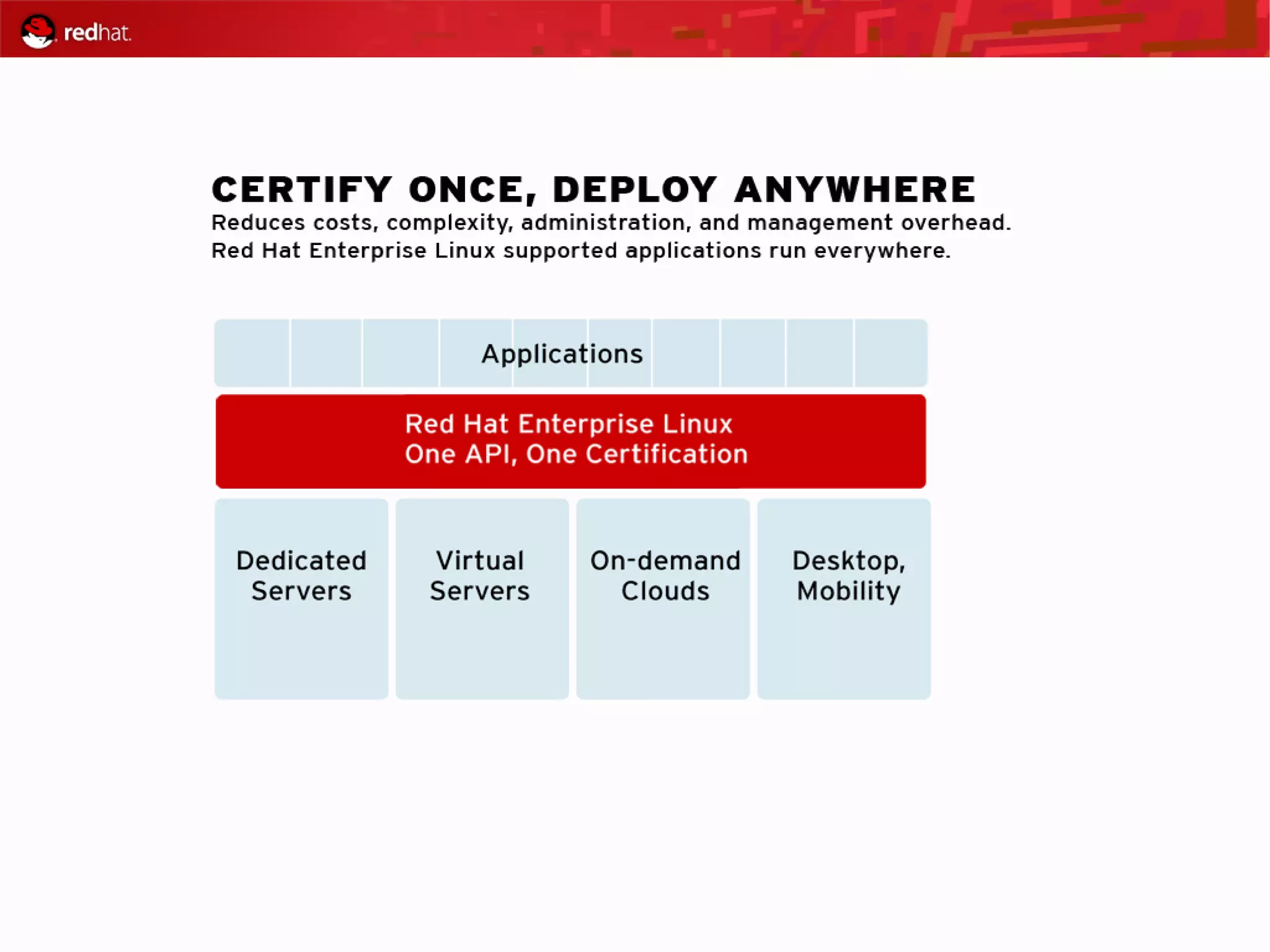
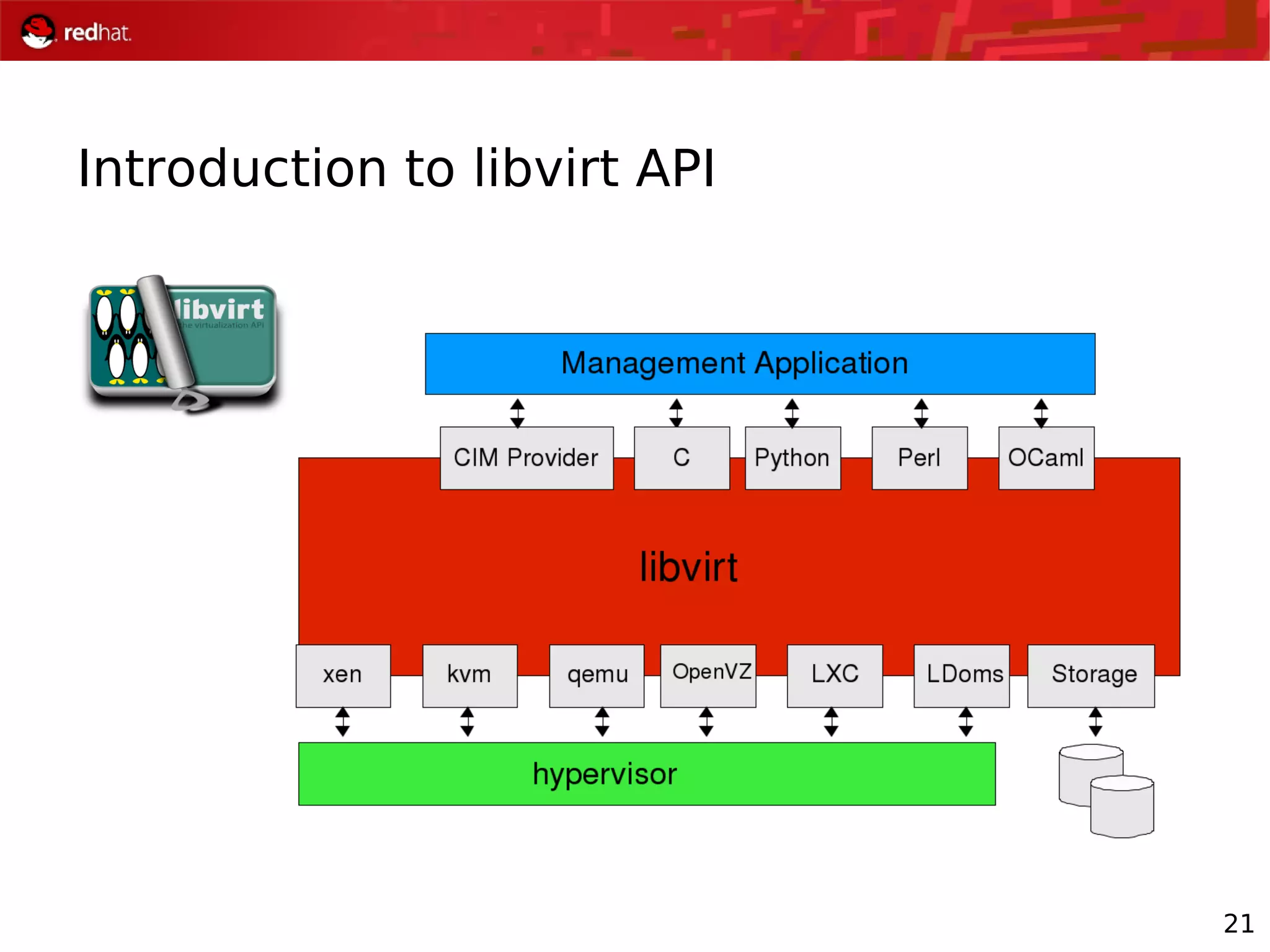
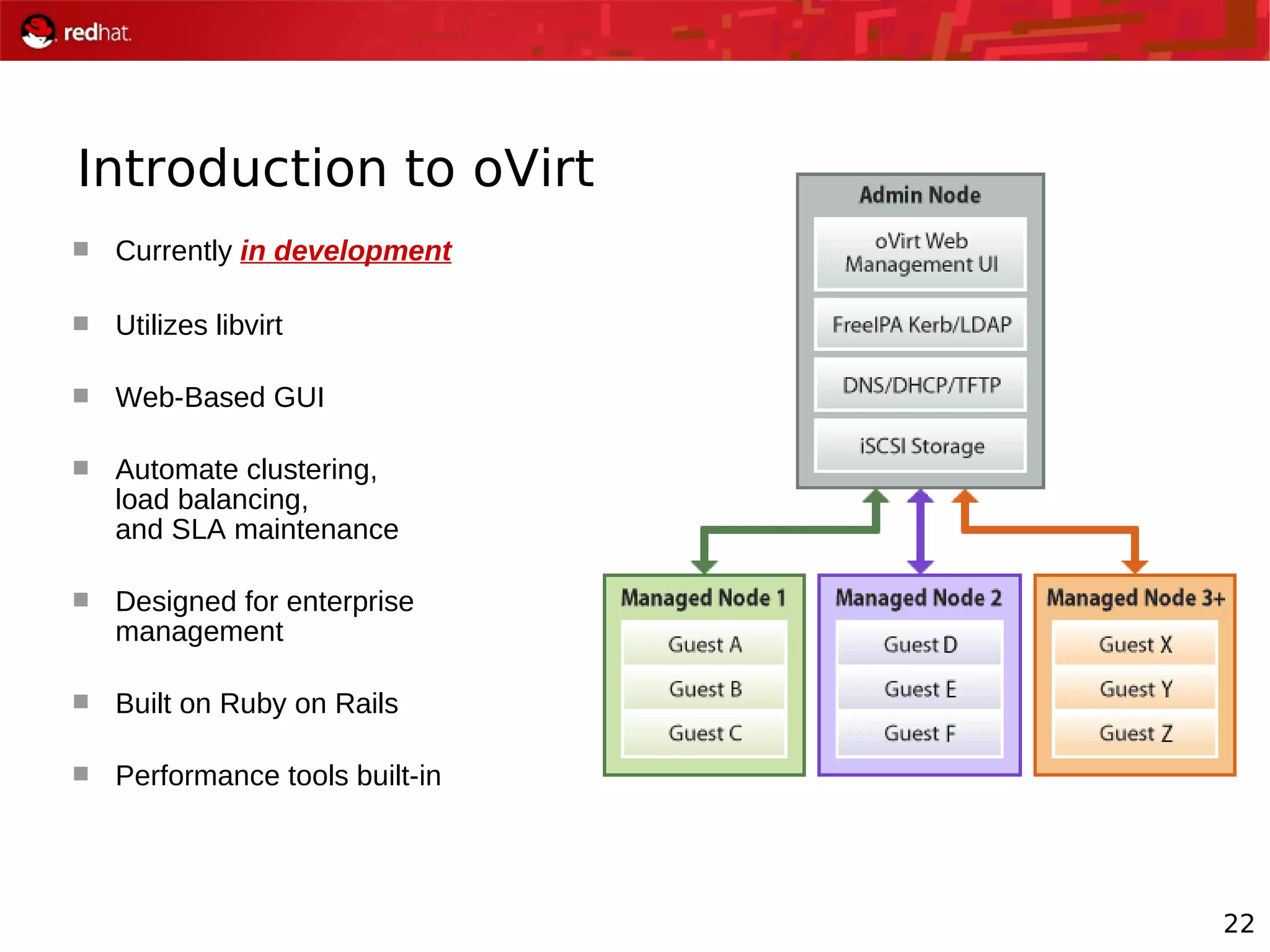
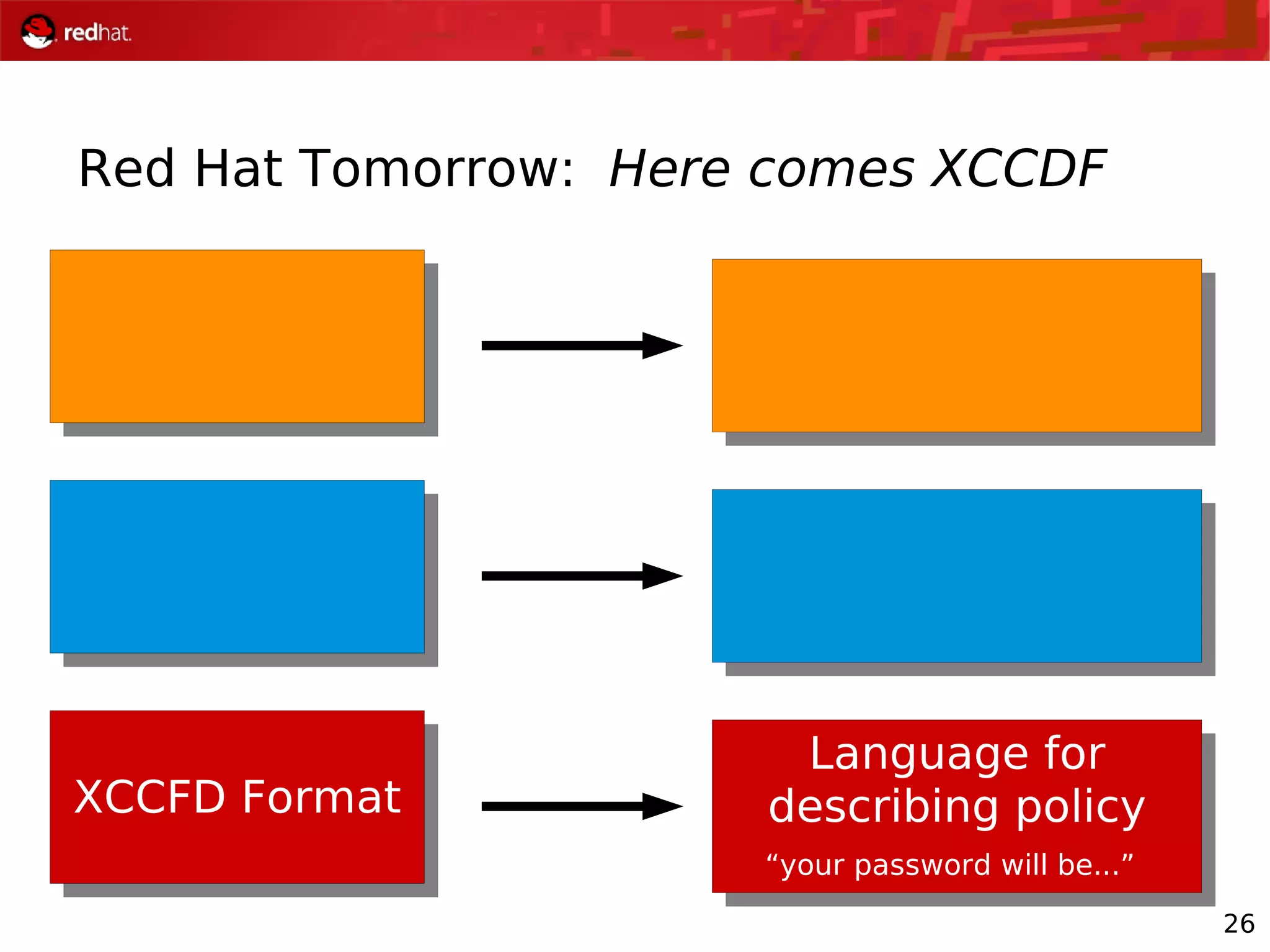
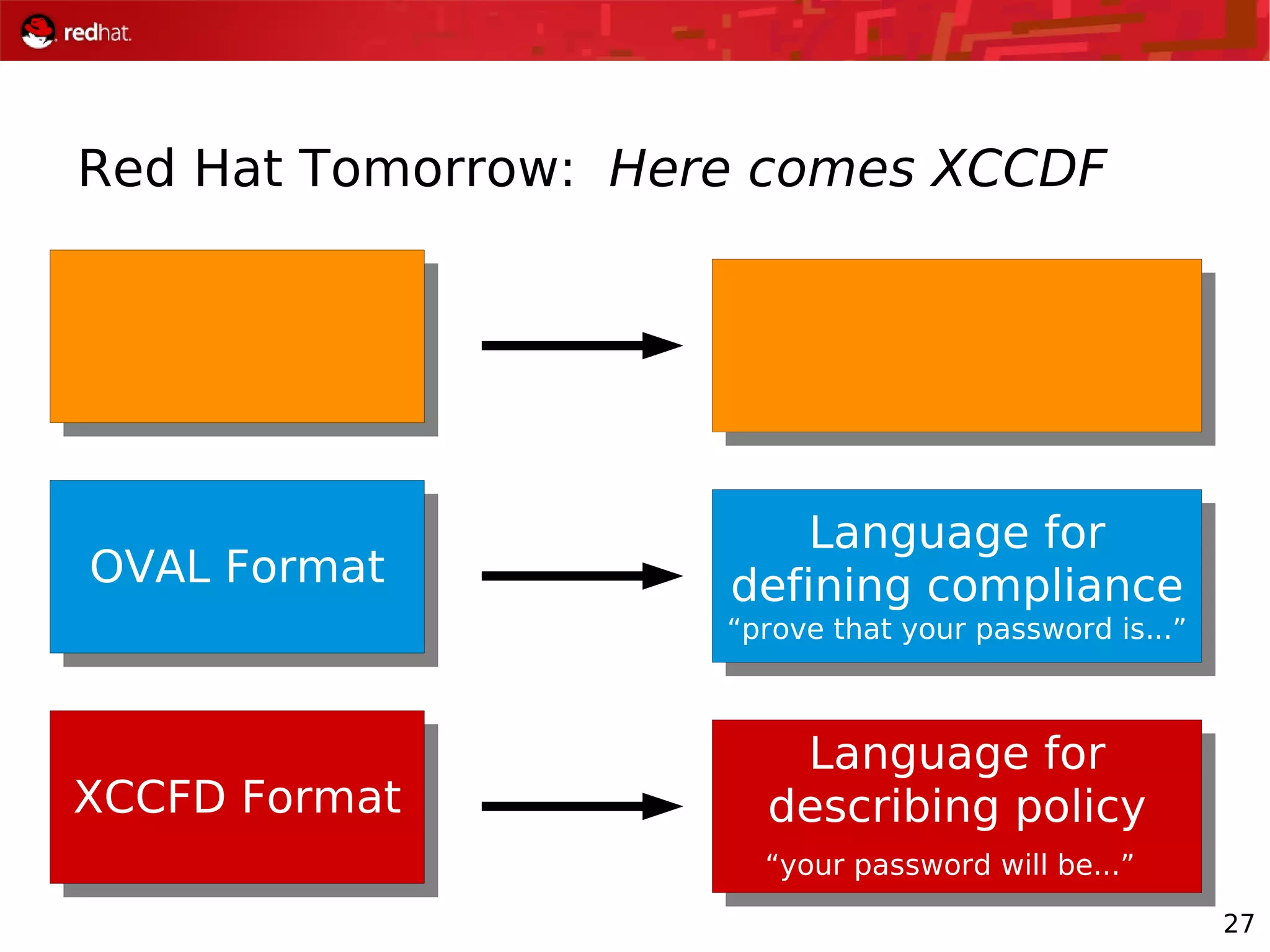
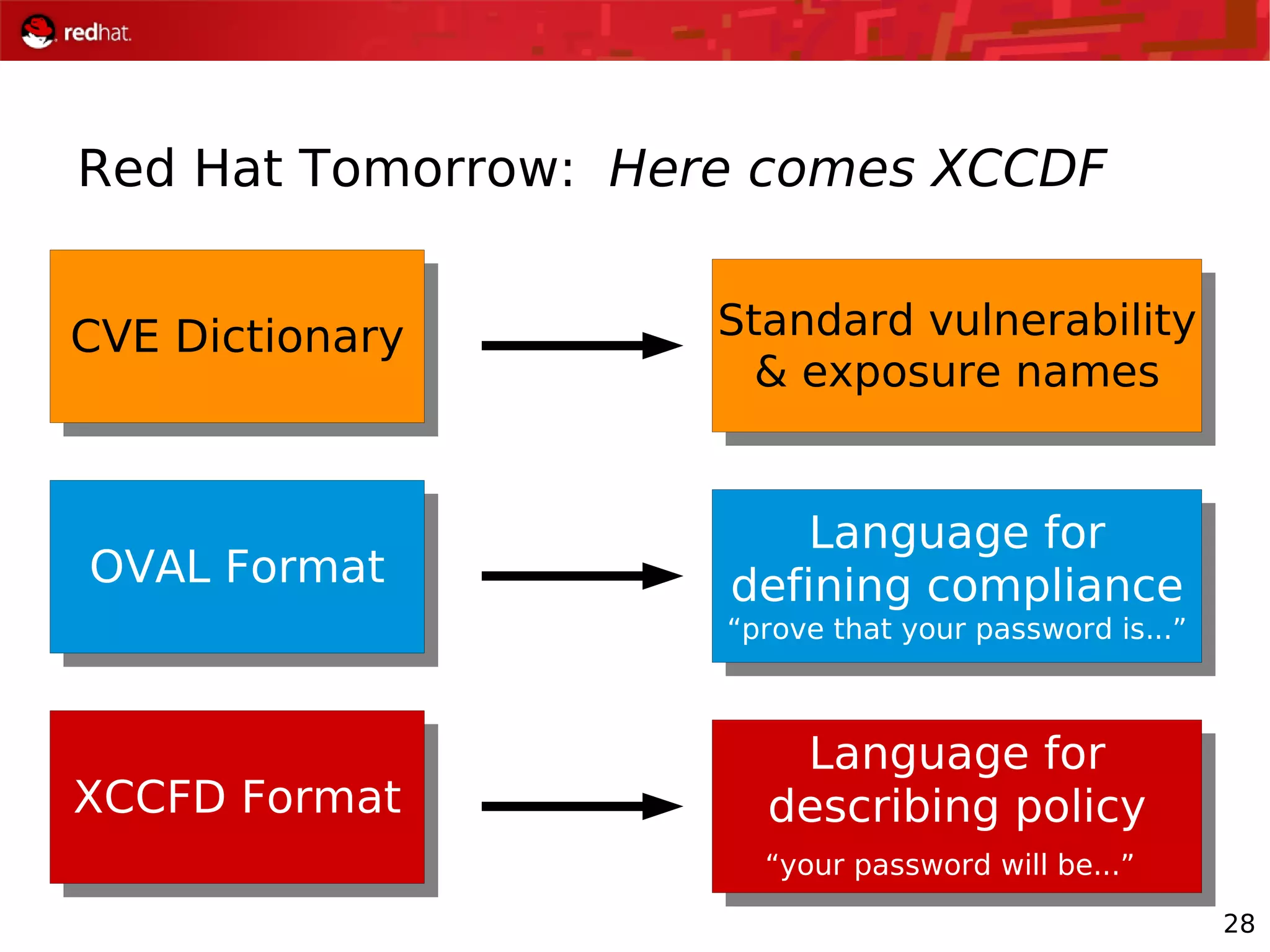
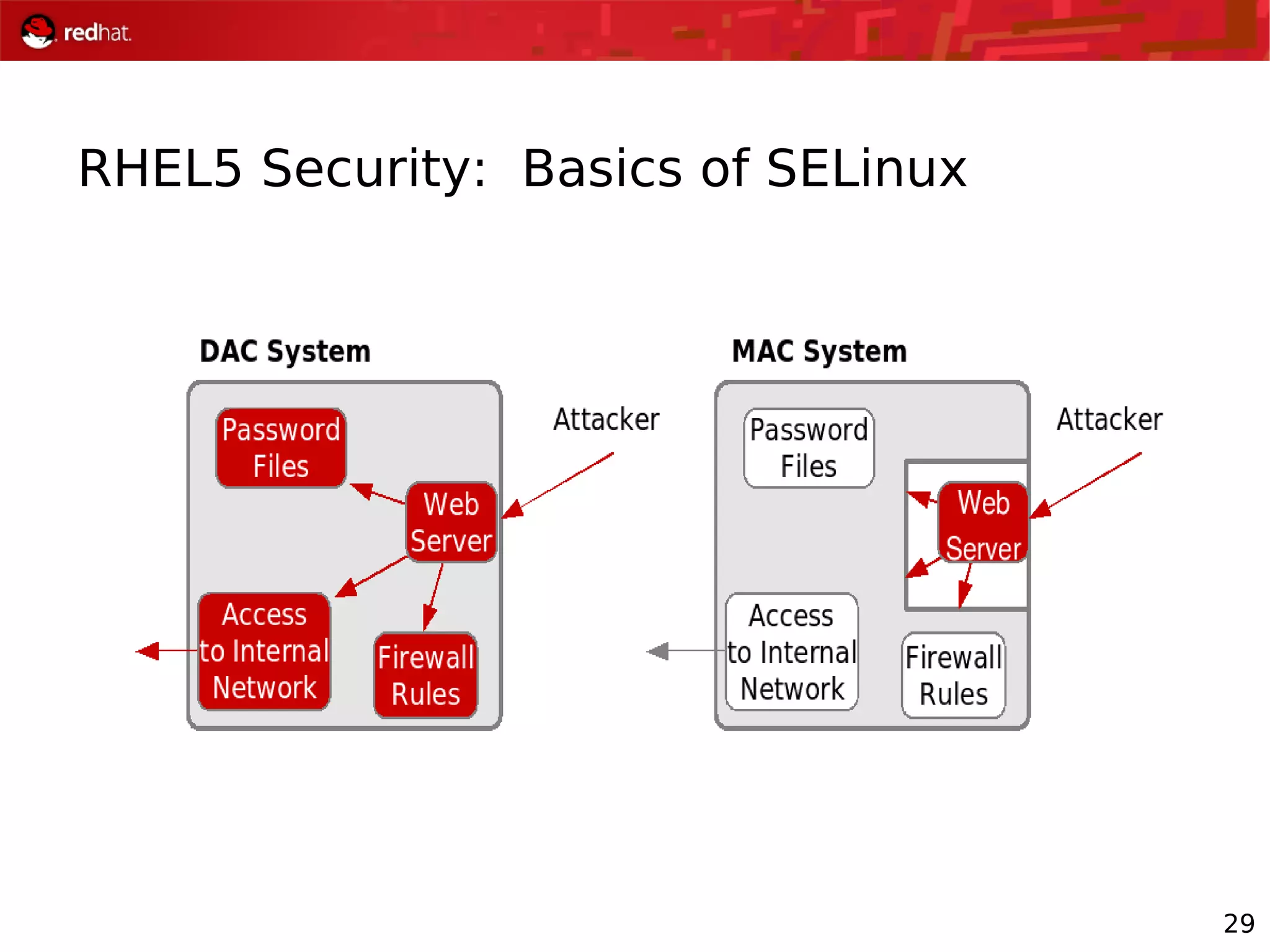
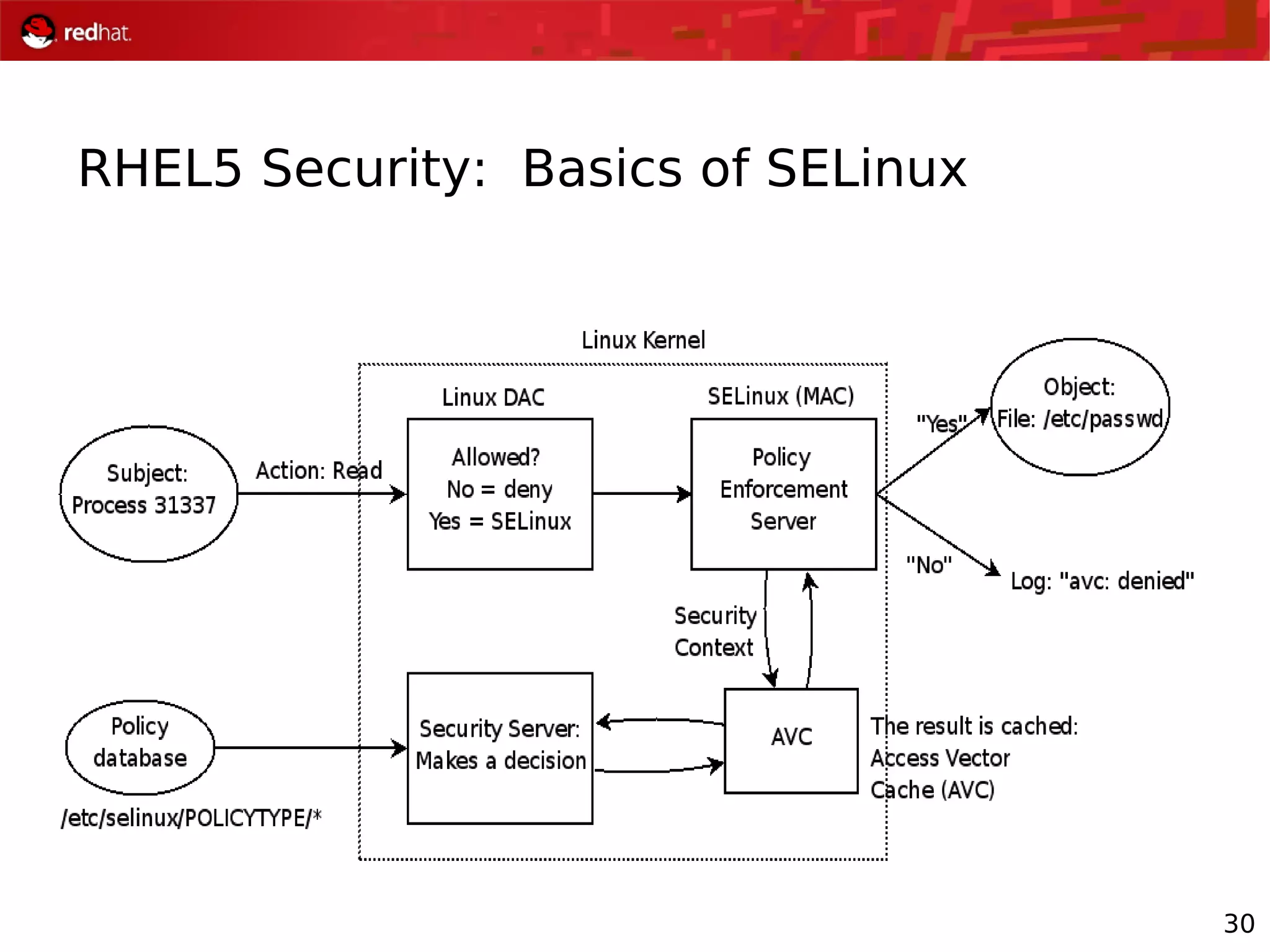
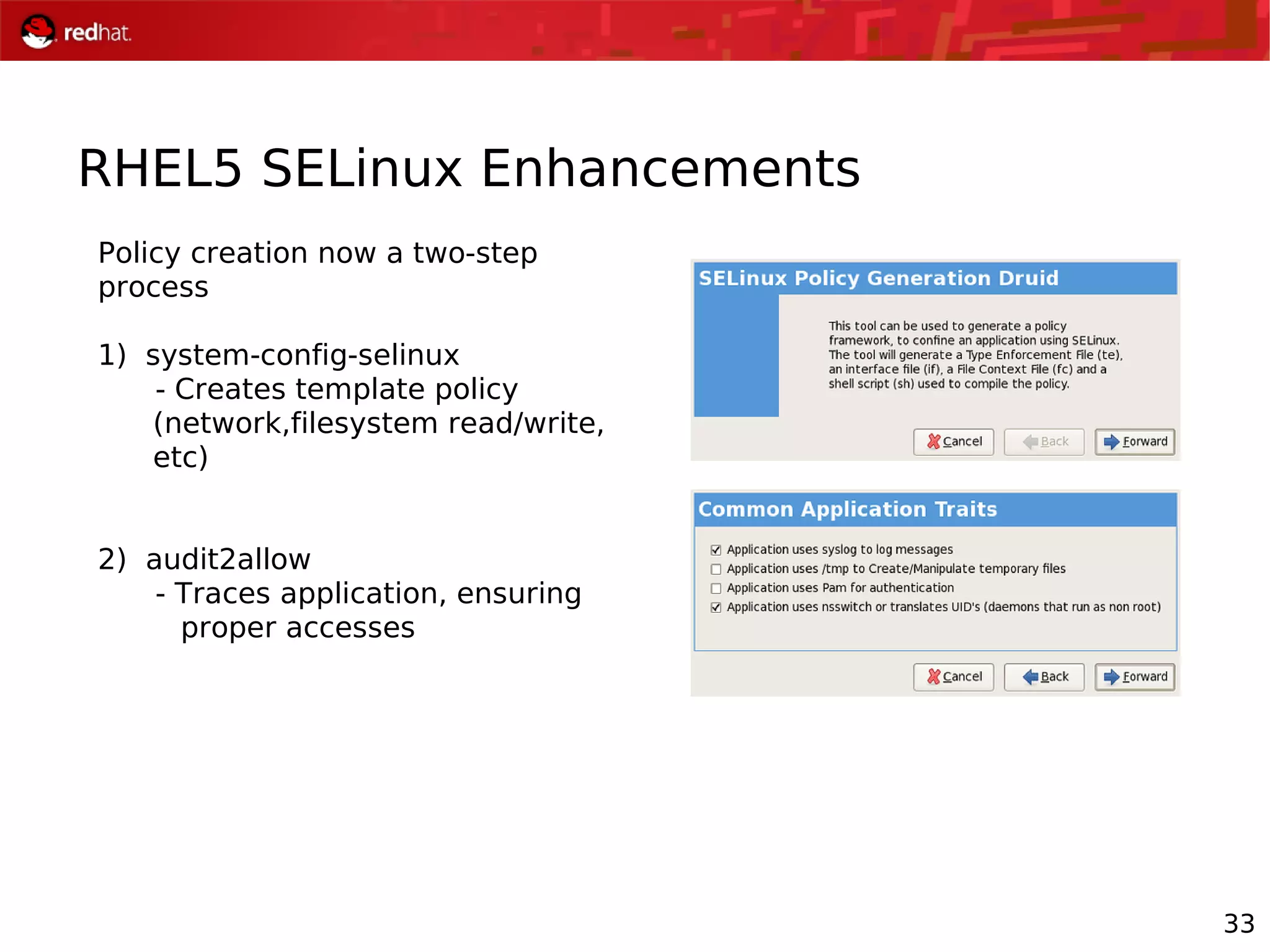
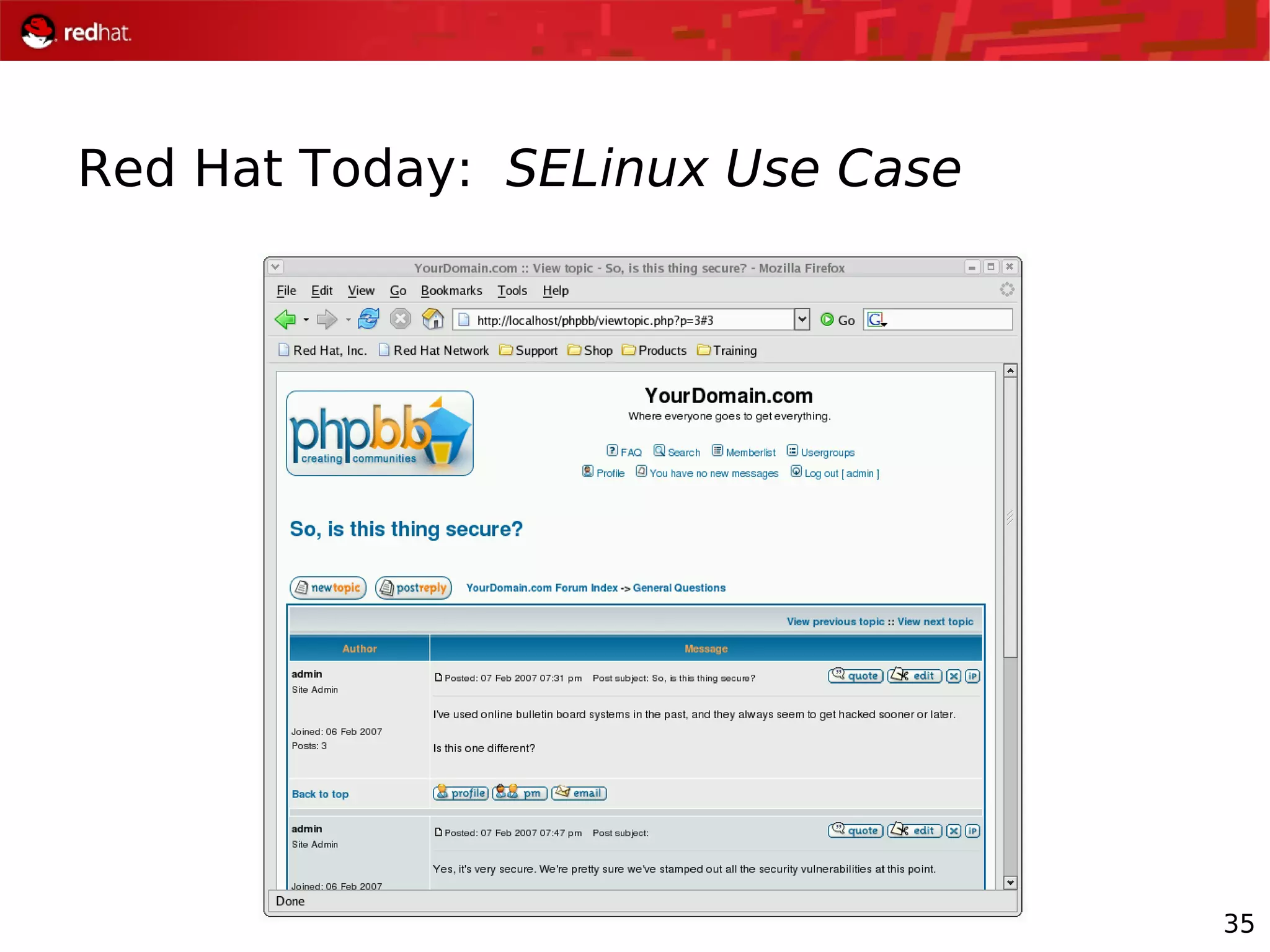
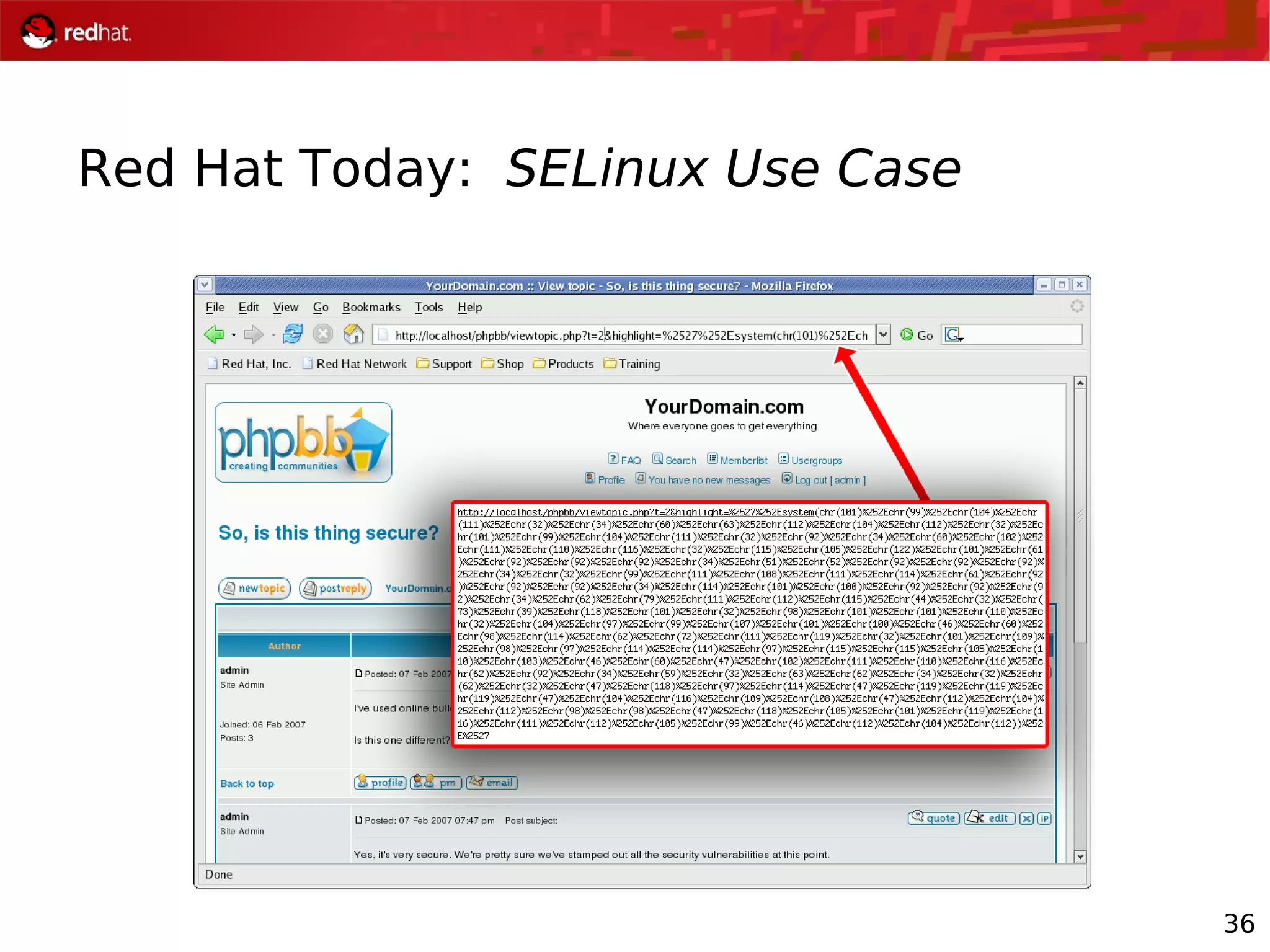
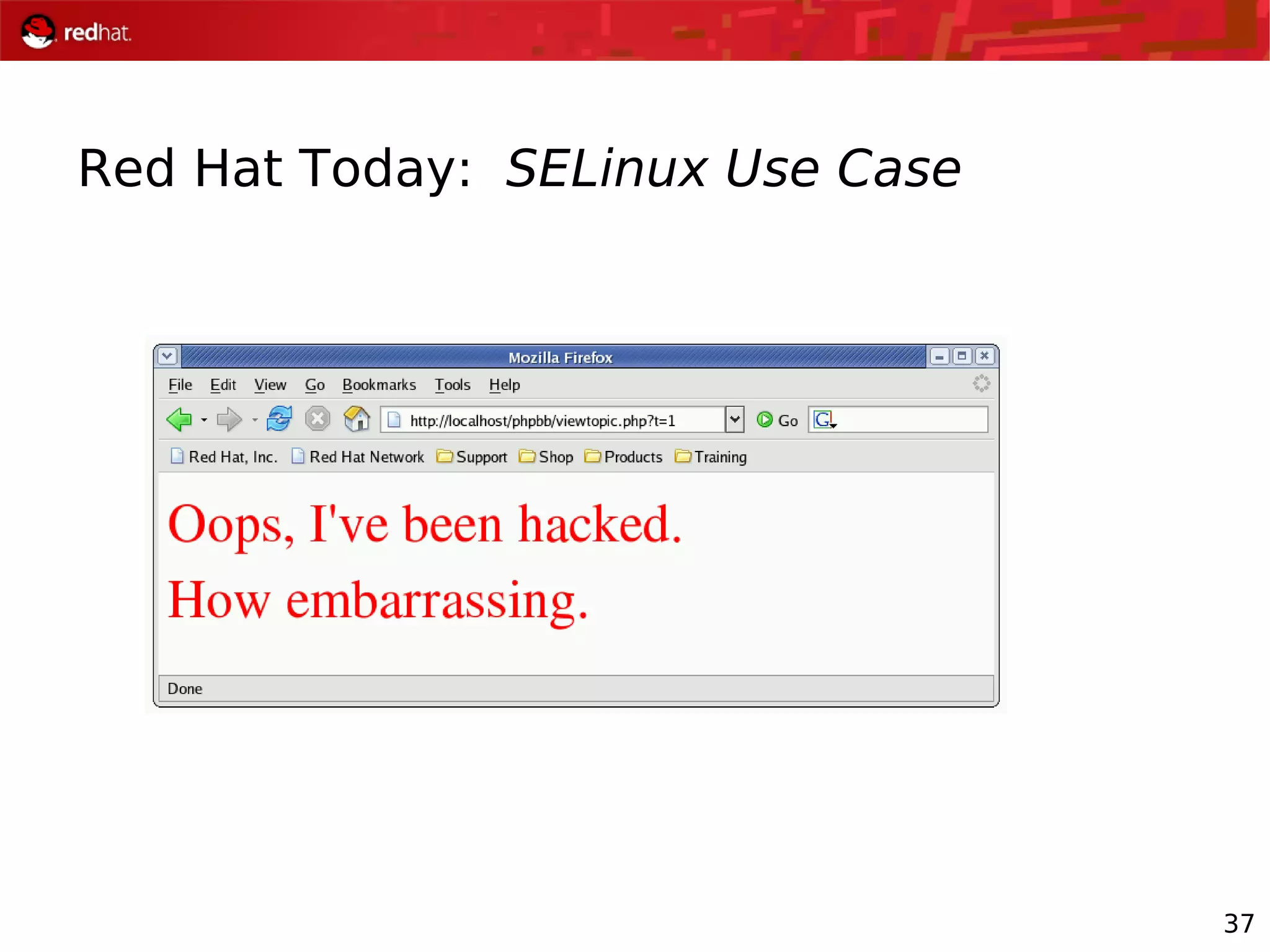
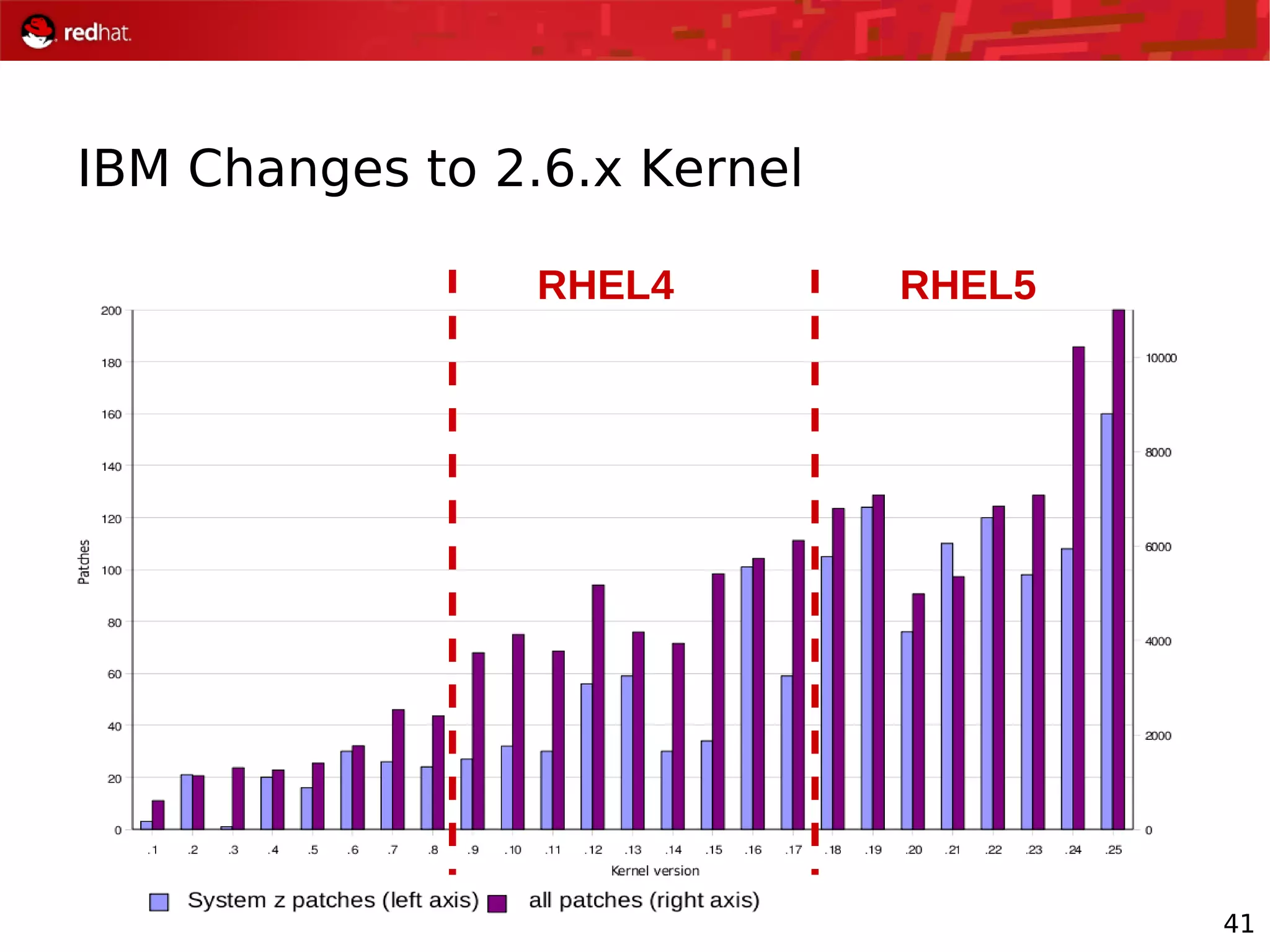
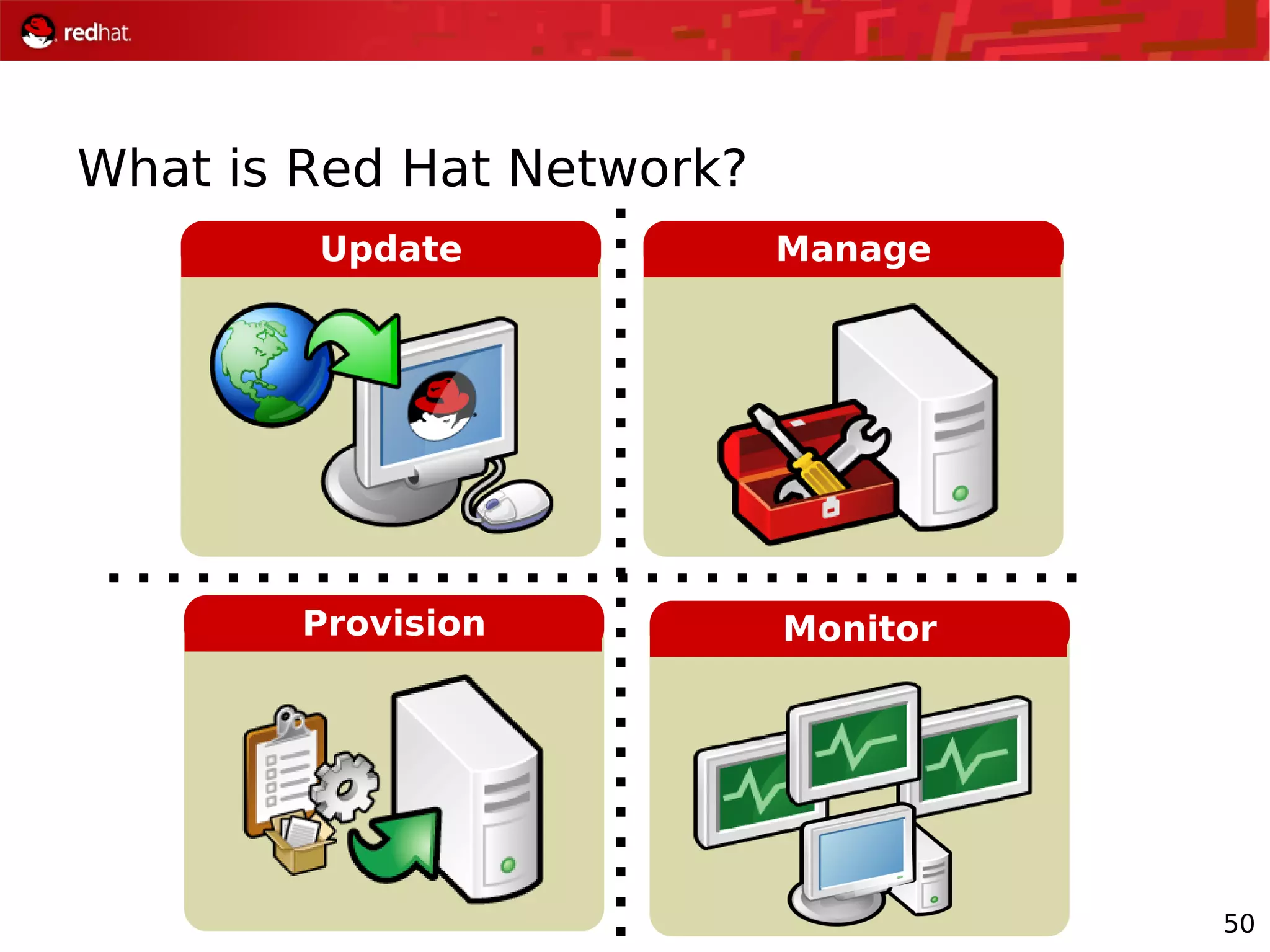
The document presents an update from Red Hat on their systems and technologies, particularly focusing on Red Hat Enterprise Linux for System Z. It covers the company's overview, technical updates on virtualization, security enhancements, and the introduction of new features over various kernel versions. Additionally, it highlights collaborations with IBM and future developments in their enterprise solutions.