2) health assessment of gi system
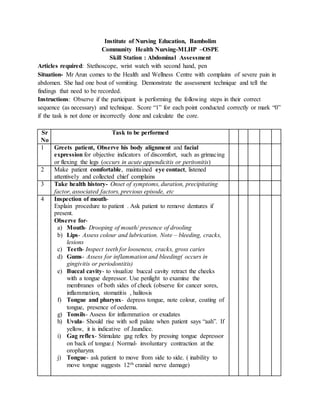
- 1. Institute of Nursing Education, Bambolim Community Health Nursing-MLHP –OSPE Skill Station : Abdominal Assessment Articles required: Stethoscope, wrist watch with second hand, pen Situation- Mr Arun comes to the Health and Wellness Centre with complains of severe pain in abdomen. She had one bout of vomiting. Demonstrate the assessment technique and tell the findings that need to be recorded. Instructions: Observe if the participant is performing the following steps in their correct sequence (as necessary) and technique. Score “1” for each point conducted correctly or mark “0” if the task is not done or incorrectly done and calculate the core. Sr No Task to be performed 1 Greets patient, Observe his body alignment and facial expression for objective indicators of discomfort, such as grimacing or flexing the legs (occurs in acute appendicitis or peritonitis) 2 Make patient comfortable, maintained eye contact, listened attentively and collected chief complains 3 Take health history- Onset of symptoms, duration, precipitating factor, associated factors, previous episode, etc 4 Inspection of mouth- Explain procedure to patient . Ask patient to remove dentures if present. Observe for- a) Mouth- Drooping of mouth/ presence of drooling b) Lips- Assess colour and lubrication. Note – bleeding, cracks, lesions c) Teeth- Inspect teeth for looseness, cracks, gross caries d) Gums- Assess for inflammation and bleeding( occurs in gingivitis or periodontitis) e) Buccal cavity- to visualize buccal cavity retract the cheeks with a tongue depressor. Use penlight to examine the membranes of both sides of cheek (observe for cancer sores, inflammation, stomatitis , halitosis f) Tongue and pharynx- depress tongue, note colour, coating of tongue, presence of oedema. g) Tonsils- Assess for inflammation or exudates h) Uvula- Should rise with soft palate when patient says “aah”. If yellow, it is indicative of Jaundice. i) Gag reflex- Stimulate gag reflex by pressing tongue depressor on back of tongue.( Normal- involuntary contraction at the oropharynx j) Tongue- ask patient to move from side to side. ( inability to move tongue suggests 12th cranial nerve damage)
- 2. Assessment of Abdomen- To locate the organs and make documentation more specific, the abdomen is divided into four quadrants- right upper, right lower, left upper and left lower. Clock wise examination of quadrants is done. The epigastric, Umblical and hypogastric areas are further delineated. Sequence of assessment is inspection, auscultation, percussion and palpation. ( percussion and palpation stimulate bowel sounds and thus are done after auscultation of the abdomen) -Ask patient to breath slowly and deeply through the mouth during the examination to promote relaxation -Ask patient to identify painful areas of the abdomen and explain that you will assess these at the time of examination Ask patient to empty bladder before the abdominal assessment Maintain privacy and expose the Abdomen. Provide patient warm towel. 5 Inspection of abdomen- Inspect abdomen from sternum to pubis. a) Note contour of abdomen – round/ flat/ concave b) Observe for distention and asymmetry, which could indicate presence of Mass c) Look for peristaltic waves – indicative of intestinal obstruction in adult or pyloric stenosis in infant d) Observe for scars / pigmentation eg in pregnancy striae or loose folds in weight loss e) Observe for venous network on the abdomen in hepatic obstruction, portal hypertension or ascitis f) Assess umbilicus for inversion (normal) or eversion in clients with umbilical hernia or extreme ascitis presence of redness/discharges, masses, flat, weeping g) Observe for –Mild pulsationsin very thin patients, vigorous pulsations in patients with right ventricular hypertrophy. Or with Mass anterior to aorta. h) If presence of an Ostomy - observe colour, character , appearance of peri stomal skin , amount and character of the effluent in the pouch. 6 Ausculatation of abdomen- Listen to bowel sounds and vascualar sounds for 4 to 5 min. a) Warm diaphragm and place it lightly in the centre of all four quadrants. Follow a pattern of assessment ie- clockwise examination of quadrants. b) Count frequency and character of bowel sounds for one full minute. ( move the stethoscope to various areas within the in quadrant if you are unable to elicit sounds in the centre Normal bowel sounds- 5 to 34 bowel sounds per minute
- 3. Abnormal bowel sounds - Hyper peristalsis ( more frequent, high pitched gurgling sounds eg in diarrhea, gastroenteritis or intestinal haemorrhage. - Paralytic ileus- Absence of bowel sounds seen In peritonitis / in intestinal obstruction, the bowel sounds may be absent in the quadrant in which the obstruction occurs. c) Auscultation using firmer pressure with diaphragm over the aortic, renal, iliac and femoral arteries for presence of bruits (swishing sounds) d) Listen for friction rub – heard over diseased liver, spleen or gall bladder. 7 Percussion of abdomen - Place your middle finger or index finger on patients skin and then strike that finger with the same finger on your opposite hand to elicit sounds to elicit sounds. -All four quadrants are percussed in a systematic, clockwise manner to identify fluid, masses or air. Normal- (a) Tympany over abdomen b) dullness or flat sound over liver and full bladder Abnormal- Decreased tympany and increased dullness caused due to presence of fluid or Mass. 8 Palpation of abdomen - Stand to right side of patient. I) Light palpation- Roll hand over abdominal area starting with heel of the hand, progressing to the palm, and finishing at finger tips, palpate with flattened finger tips each quadrant in systematic manner, noting muscular resistance, tenderness, pulsations, enlargement of organs, presence of mass. If patient complains of abdominal pain, palpate the area of pain last. Normal- Abdomen will feel soft and supple, relaxed and free of tenderness Abnormal- If you feel resistance with a distended abdomen, - Board like tenderness, pain on light palpation. II) Deeppalpation- Is used to assess enlarged organs and presence of Masses. a) Palpation of Liver- Bimanual palpation- Liver is not normally palpable. i) Ask patient to inhale. ii) Stand at side of patient , place your left hand under the rib cage and use the palmar surface of the fingers of right hand to palpate liver just below the right costal margin . Normal- Liver edge feels firm, smooth Abnormal- Liver edge will feel hard, firm (in cancer liver), pain in case of vascular engorgement as congestive heart failure, hepatitis or abscess.
- 4. -If liver border is more than 1 to 3 cm, then liver is considered to be enlarged. b) Rebound tenderness is seen in patients with peritonitis. ( patient feels pain when you release hand quickly after slow palpation) To Assess for appendicitis/ peritoneal inflammation, Gently press your flattened finger tips approximately 6-8cm into the quadrant opposite that in which you elicited pain, and then quickly release the pressure. The patient will feel a sudden, sharp pain over the original area of discomfort if rebound tenderness is present. Contraindication- Never deeply palpate the right lower quadrant if appendicitis is suspected Deeppalpation to be avoided in clients with rigid abdomens or those who have pancrestitis or ectopic pregnancy because the procedure can be very painful and can cause serious injury to the patient. 9 Assess forAscitis- a) With patient in supine position place palm of hand against the lateral abdominal wall. With the other hand , tap the opposite wall of the abdomen and check for fluid wave. b) Identify areas of greatest abdominal girth and using ‘measuring tape’ measure the abdominal girth 10 Make the patient comfortable, replace the articles and document findings, Refer patient to FRU if required. Name and signature of evaluator: