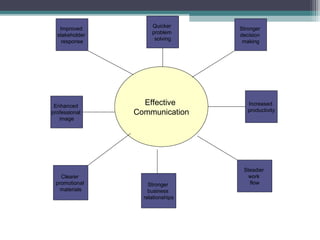
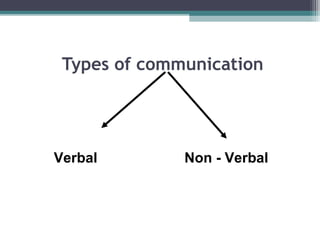
This document provides information on effective communication. It begins by establishing ground rules for an interactive session and brainstorming. It then lists various aspects of communication such as verbal and non-verbal communication, facial expressions, body language, listening skills, and dressing sense. It discusses managing conflicts and positive interactivity. It defines communication and provides the steps in the communication process. It outlines the basics of effective communication and describes passive, aggressive, and assertive styles of communication.