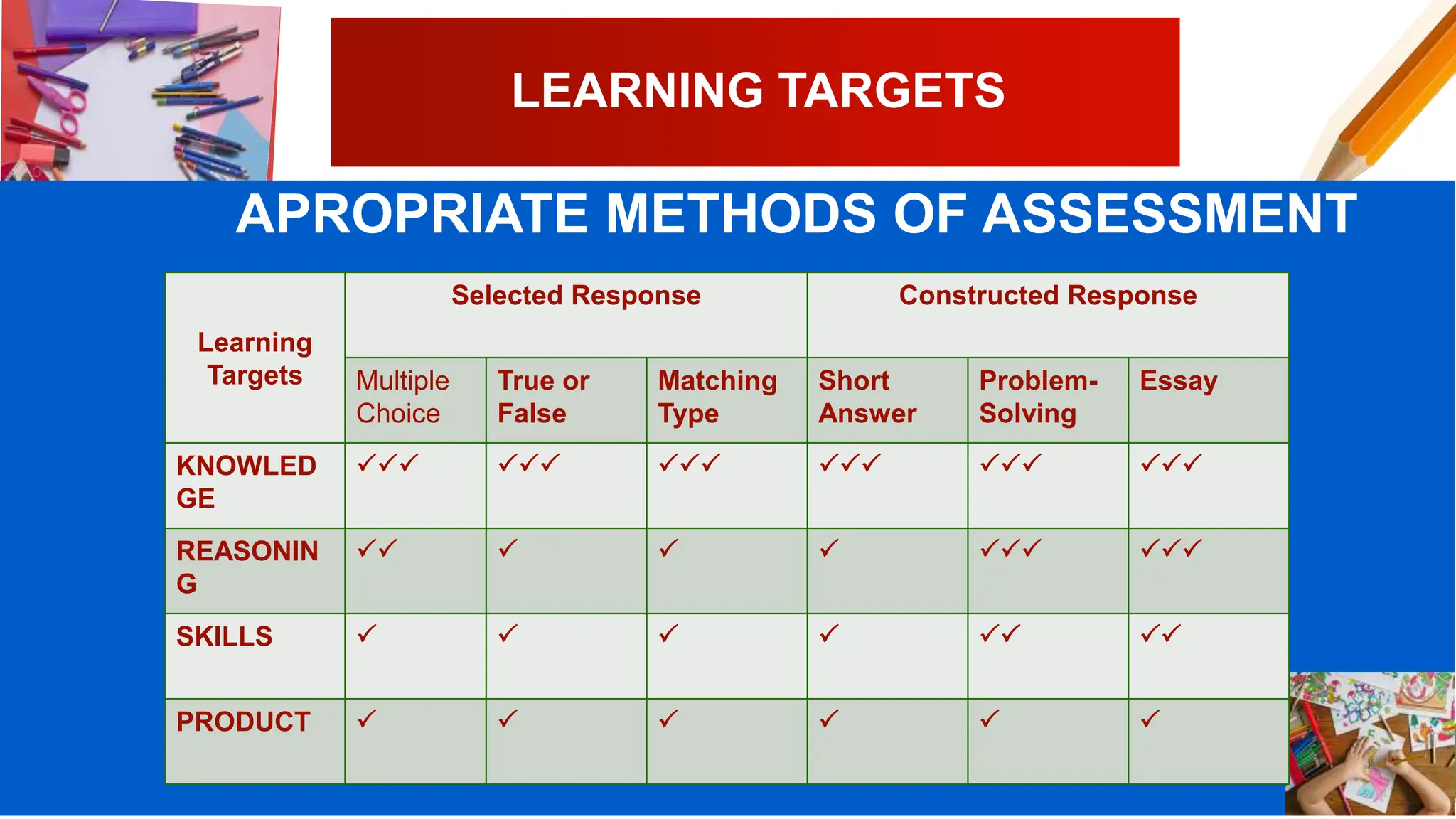
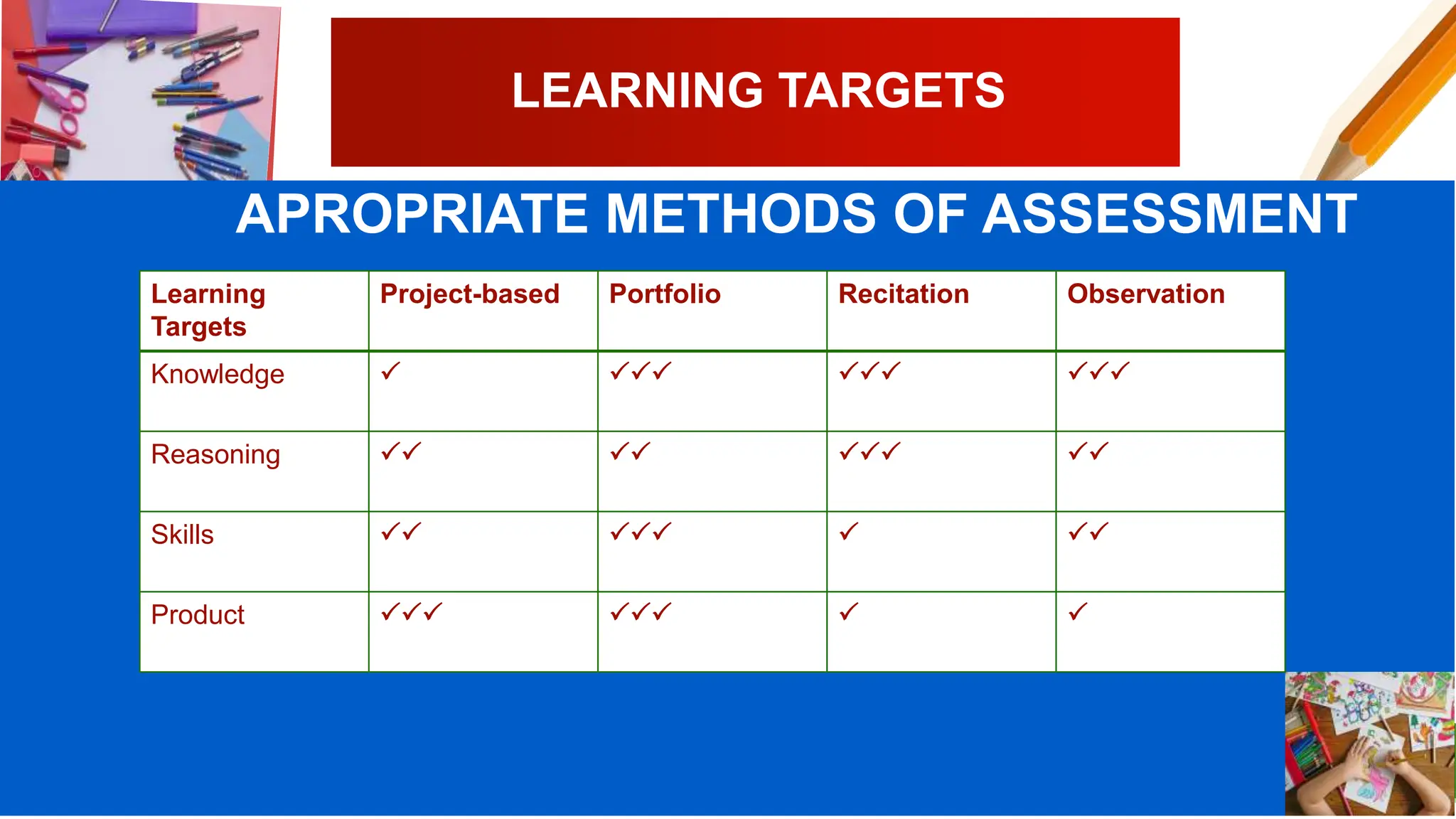
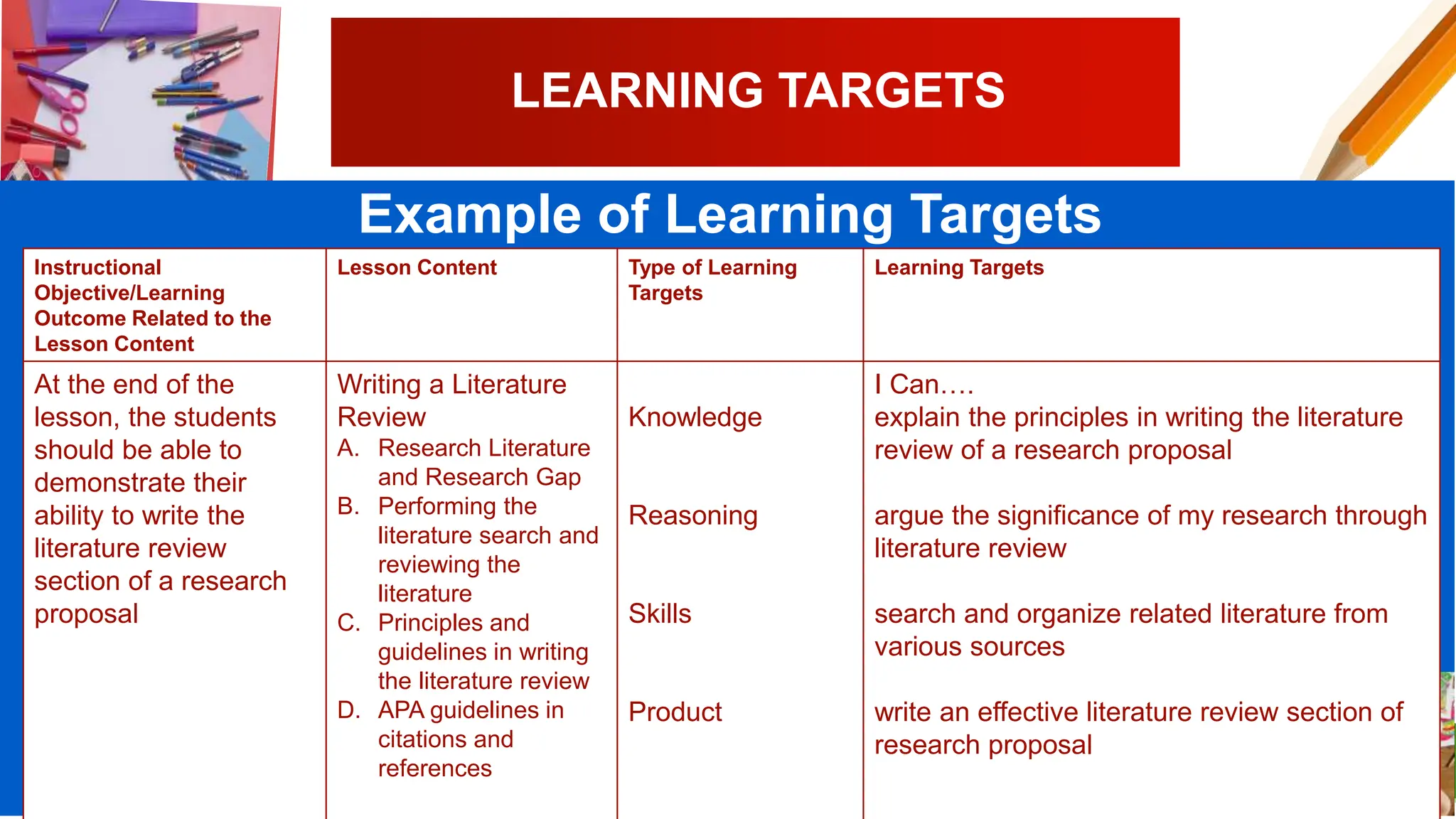
The document discusses different types of classroom assessment including assessment of learning, assessment for learning, and assessment as learning. It also discusses the revised Bloom's taxonomy, which categorizes cognitive processes and knowledge dimensions. Finally, it covers learning targets, including defining learning targets, selecting appropriate targets, and providing an example of targets for writing a literature review.