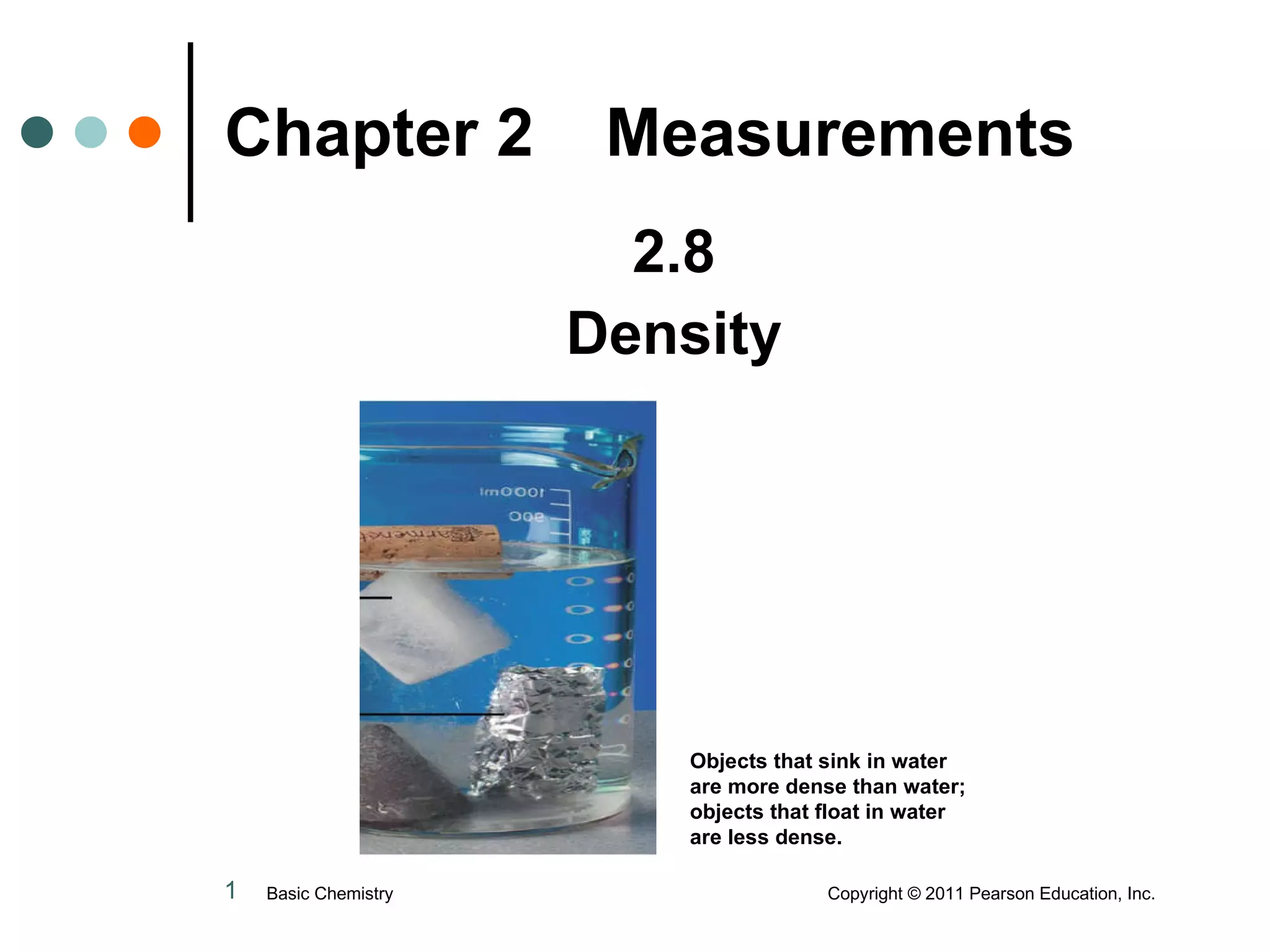
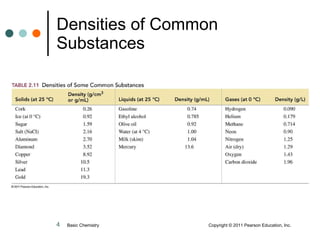
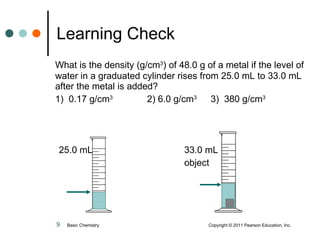
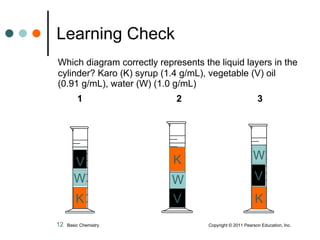
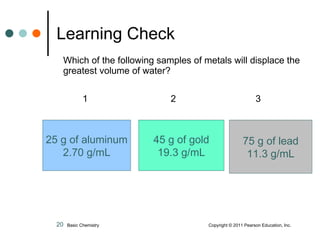
The document discusses density, which is a measurement that compares the mass of an object to its volume. It provides examples of calculating density using measurements of mass and volume or volume displacement in water. Objects that are more dense than water will sink, while less dense objects will float. The document also discusses using density as a conversion factor between units of mass and volume.