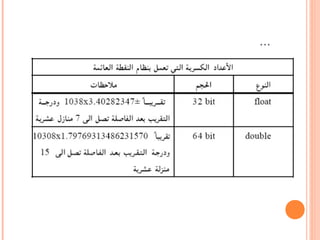
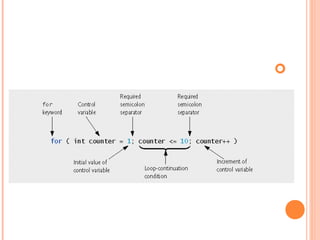
The document provides a detailed overview of programming concepts including variable types, control structures, expressions, and exception handling. It covers basic data types such as int, char, and boolean, as well as various control flow mechanisms like if-else statements, switch-case statements, and loops (for, while, do-while). Additionally, the document discusses the handling of exceptions and string manipulation in Java.
































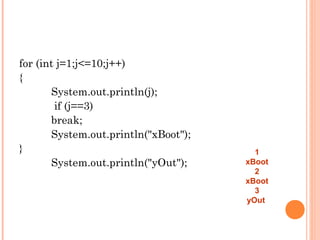
![1
2 // do...while repetition statement.
3
4 public class DoWhileTest
5 {
6 public static void main( String args[] )
7 {
8 int counter = 1; // initialize counter
9
10 do
11 {
12 System.out.printf( "%d ", counter );
13 ++counter;
14 } while ( counter < = 10 ); // end do...while
15
16 System.out.println(); // outputs a newline
17 } // end main
18 } // end class DoWhileTest
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Declares and initializes
control variable counter
Variable counter’s value is displayed
before testing counter’s final value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193715/85/2-36-320.jpg)









![public class StringsDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String pal = "Dot saw I was Tod";
StringBuffer dest = new StringBuffer(pal);
System.out.println(dest);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193715/85/2-48-320.jpg)
![String pal = "Dot saw I was Tod";
String pal = new String("Dot saw I was
Tod");
char[] alQuds = { 'A', 'l', 'Q', 'u', 'd','s' };
String s2 = new String(alQuds);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193715/85/2-49-320.jpg)



