The document primarily discusses Java programming concepts, including class design, inheritance, access modifiers, method definitions, and array handling. It provides examples illustrating the creation and usage of classes, methods, arrays, and vectors, as well as concepts like recursion and exception handling. Additionally, it highlights the importance of modifiers such as public, private, and protected in the context of class and method accessibility.


![ [modifier] class Nameofnewclass [extends
Nameofsuperclass implements interface] { }
public
friendly
final
abstract](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193725/85/2-3-320.jpg)






















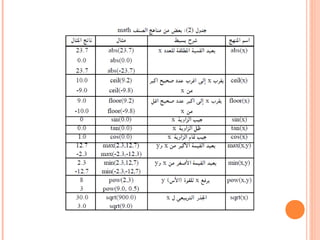




![MAIN
public static void main(String args][( } ...... {
publicmain
staticmainclass method.
voidmain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193725/85/2-31-320.jpg)

![class MyClass
}
int x;
public MyClass (int value)
{
x = value ;
}
{
...
public class ConsDemo
{
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyClass t1 = new MyClass( 10 );
MyClass t2 = new MyClass( 20 );
System.out.println(t1.x + " " + t2.x);
}
}
The output:
10 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193725/85/2-33-320.jpg)








![array size
int [ ] ai; // one dimensional array of type int
short [ ][ ] as ; // two dimensional array of type short
object [ ] ao; // array of type object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193725/85/2-42-320.jpg)
![...
// creates three objects stored in one dimensional array
Exception ae[ ] = new Exception[3];
//create 6 objects stored in two dimensional array
Exception aao[ ][ ] = new Exception[2][3];
int [ ] Factorial = {1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040}
char ac[ ] = {'n','o','t',' ','a',' ','s','t','r','i','n','g'};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193725/85/2-43-320.jpg)
![array_name[ ]=new array_type [array-size[
int int_table[ ] = new int[5[;
Integer int_obj_table[ ] = new Integer[5[;
Short graph[ ][ ]=new short [3[] [;
Graph[0][ ]= new short[4[;
Graph[1][ ]= new short[2[;
Graph[2][ ]= new short[7[;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193725/85/2-44-320.jpg)
![
Array-type array-name [ ] = {e1,e2,e3….};
char mchat[ ] = {‘t’,’e’,’x’,’t’};
char mychar[ ] = “text”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193725/85/2-45-320.jpg)
![
Array-name[index[;
Arr1[3;]
Arr1
length](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193725/85/2-46-320.jpg)




![
short array_1 [] = {1,2,3,4,5};
short array_2 [] = new array[3];
System.arraycopy(array_1,1,array_2,0,3);
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193725/85/2-51-320.jpg)
![
int x = new int[3[;
void SumUp(int b] [(;
,
SumUp(x(;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160426193725/85/2-52-320.jpg)











