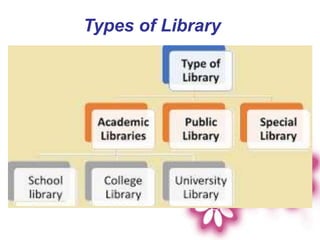
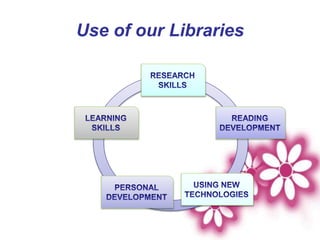
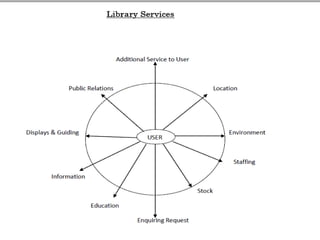
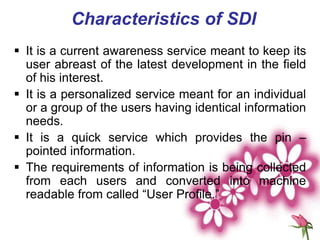
The document presents an introduction to library services by Dr. M.C. Subangi, emphasizing the importance of libraries in education and research. It covers various topics including the history and types of libraries, library science principles, functions, and services such as reference, current awareness, and document delivery. Additionally, it highlights the evolving role of libraries in the information age and outlines guidelines for library usage.