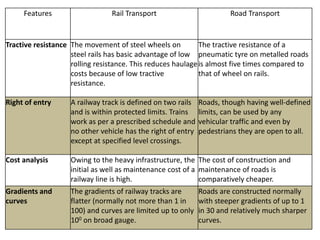
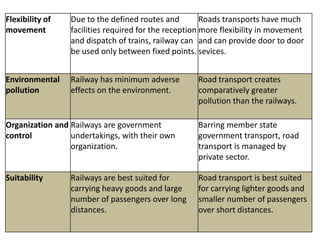
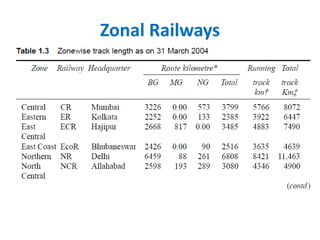
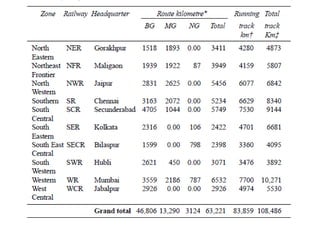
This document provides an overview of railway engineering in India. It discusses the history and development of railways in India, the roles and organization of Indian Railways, key terms related to railway infrastructure, the advantages and disadvantages of railways compared to other modes of transport, and some of the strengths and weaknesses of Indian Railways. The document is divided into multiple sections covering topics like permanent way, types of rails and sleepers, organization of Indian Railways, research and standards organization, and the roles and impacts of railways in India.