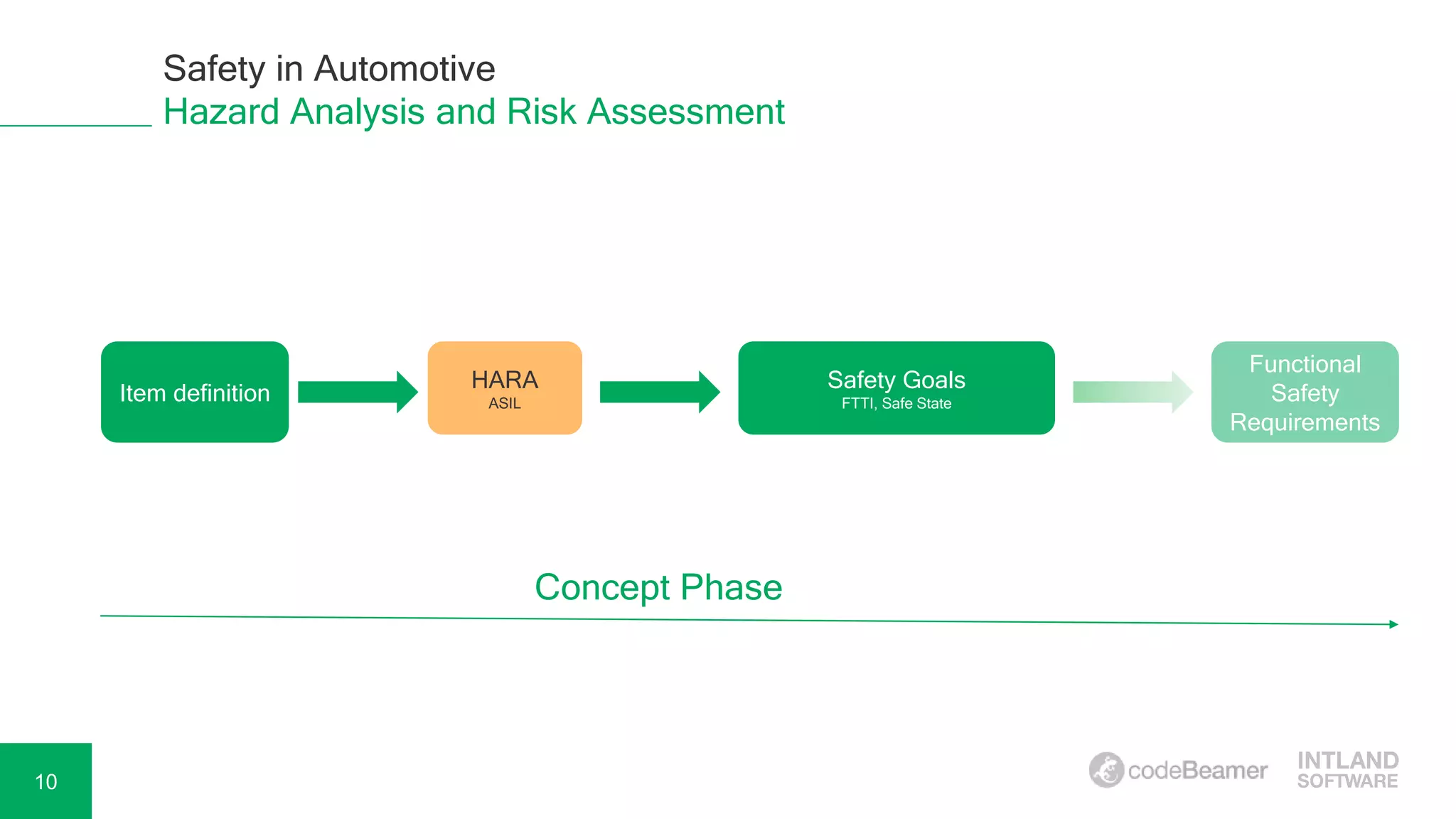
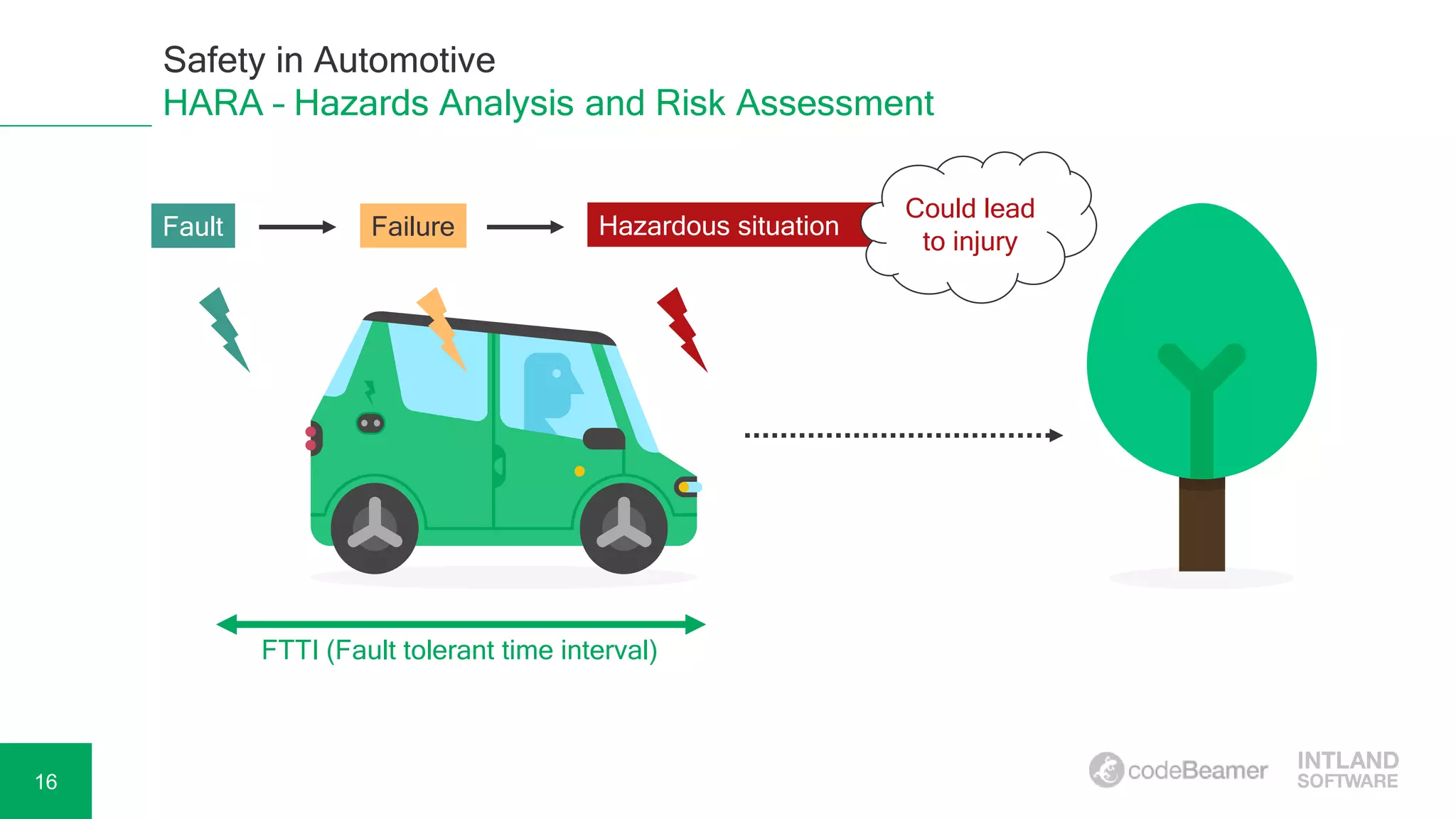
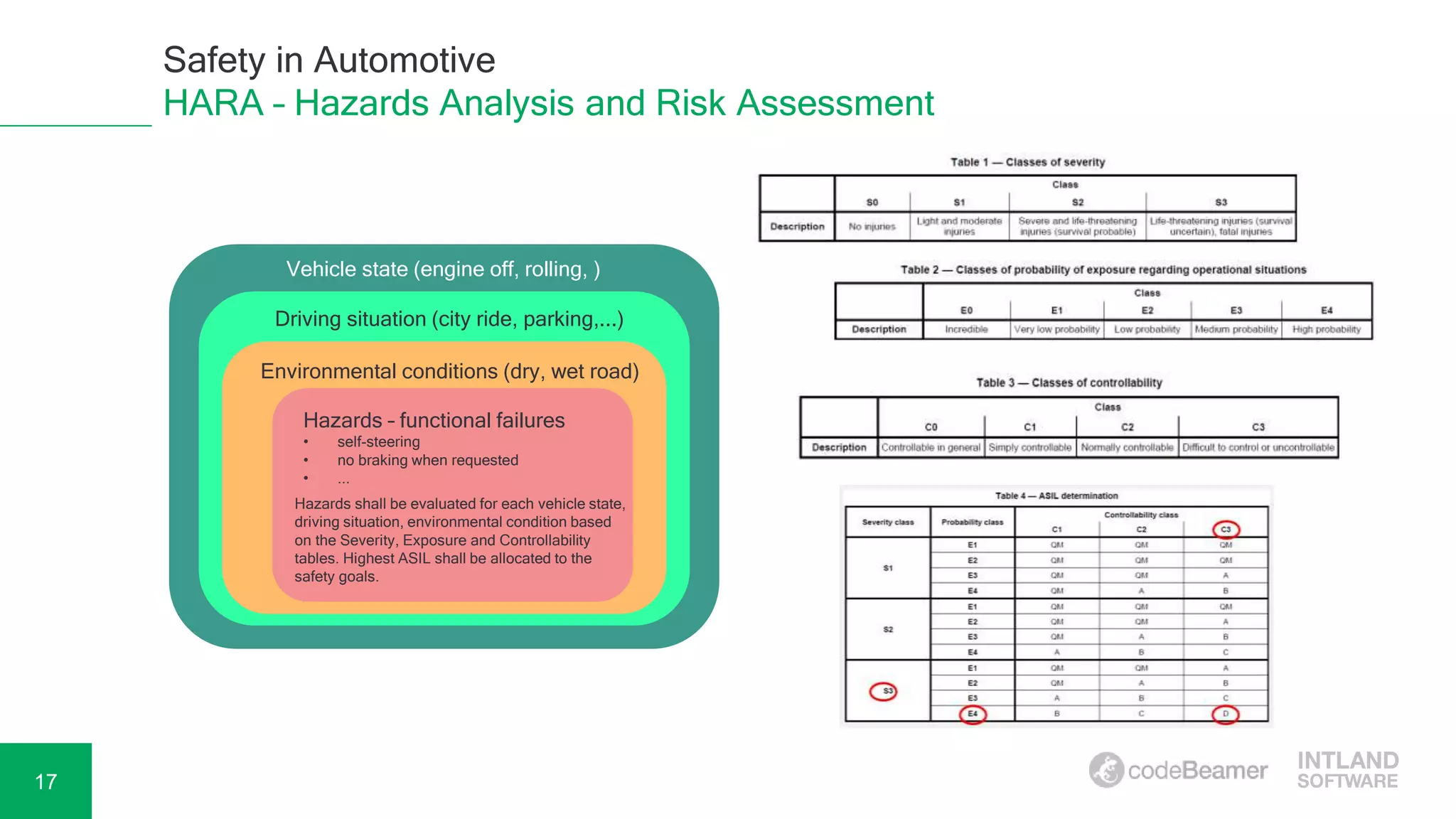
Adela Béres, a functional safety expert with over 10 years of experience, leads a webinar focused on functional safety in automotive development, including hazard analysis, risk assessment, and compliance with ISO 26262. The session will cover key topics such as safety goals, automotive safety integrity levels (ASIL), and verification and validation processes. Attendees will have the opportunity to participate in a Q&A session and access a recording of the webinar afterward.