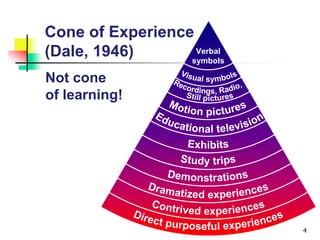
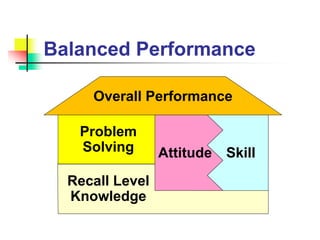
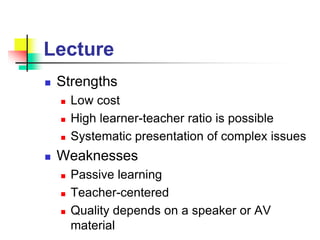
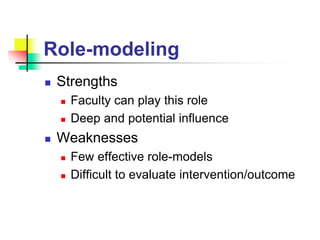
This document discusses various strategies for education and learning. It begins by explaining how much memory is typically retained from different teaching methods based on research. It then discusses key terminology used in education strategies. The bulk of the document provides summaries of the strengths and weaknesses of different specific strategies, including lecture, reading, problem-based learning, learning projects, role-modeling, group discussion, demonstration, role-play, simulated patients, simulators, reflection with playback, and clinical experiences. It concludes by matching different taxonomies of learning objectives with recommended strategies and briefly discussing different types of meetings for education.