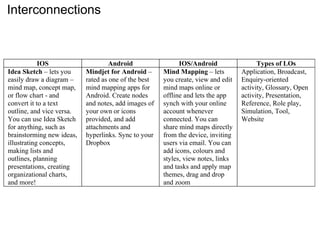
(1) The document presents research on evaluating the quality of mobile learning activities (LAs) using tablets in science education in Europe compared to traditional teaching methods.
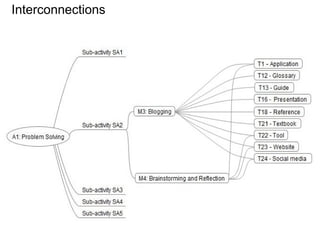
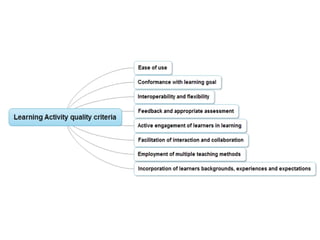
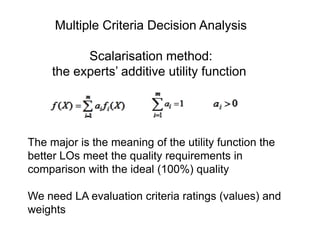
(2) It describes a methodology using multiple criteria decision analysis and fuzzy methods to evaluate LAs based on criteria like flexibility, engagement, interaction, and teaching methods.
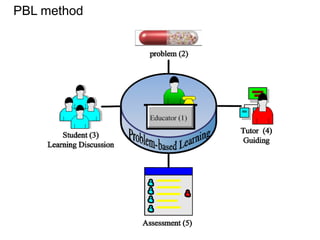
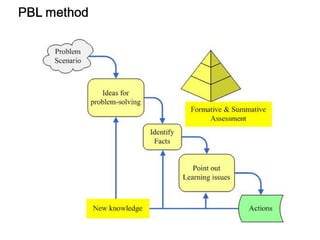
(3) The results found that mobile LAs based on problem-solving, personalization, collaboration and flipped classroom scored higher in quality (82.8%) than traditional LAs(50%), and better suited different learning styles like activists and pragmatists.