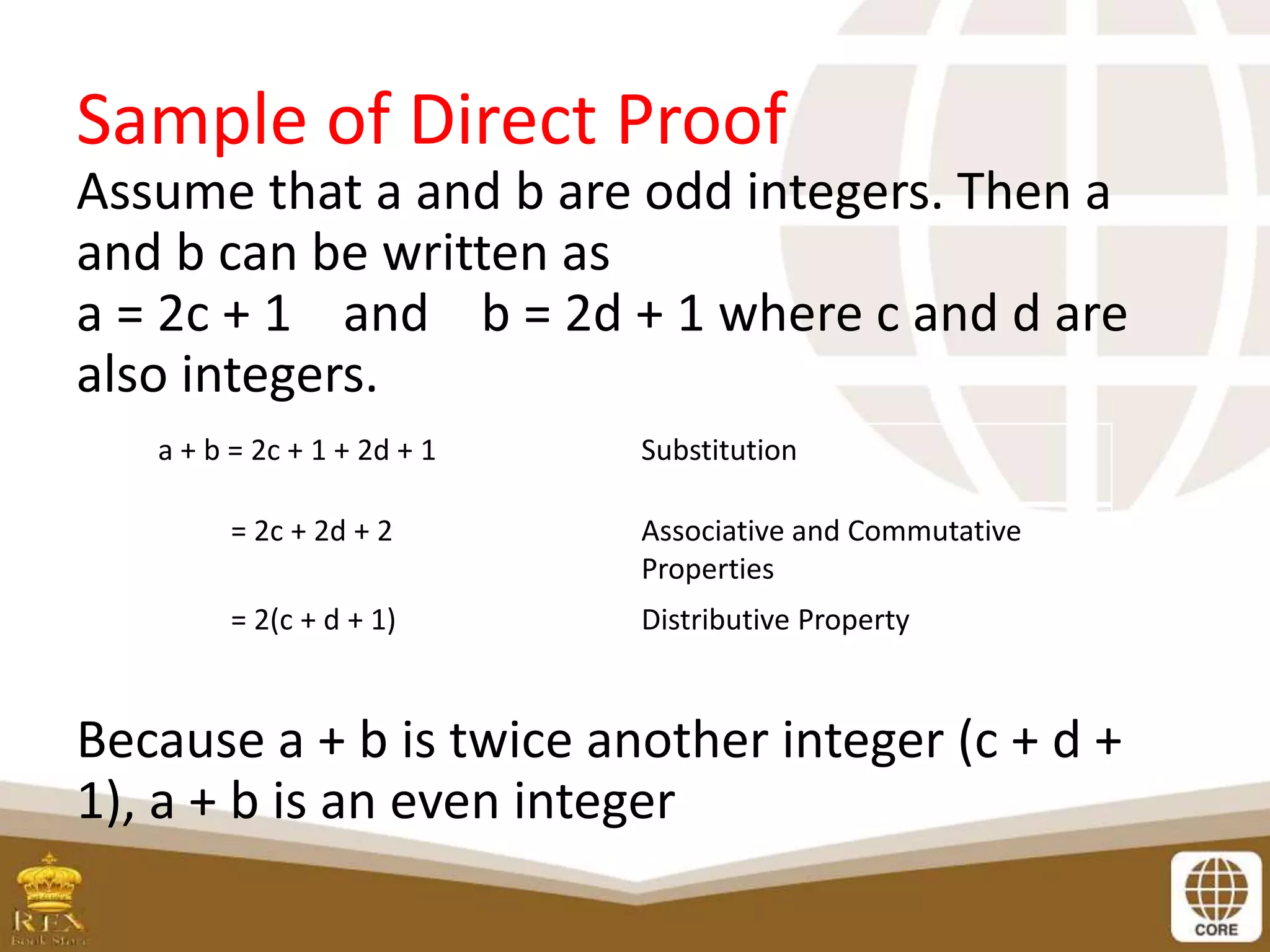
The document discusses different methods of proof in mathematics including direct proof, proof by contradiction, and proof of the contrapositive. It provides examples of each. Direct proof involves assuming a statement P is true and using logical steps to prove another statement Q is true. Indirect proof involves proving the contrapositive or using proof by contradiction. The contrapositive of "if P then Q" is "if not Q then not P". Proof by contradiction assumes the opposite of the statement to be proven and shows it leads to a contradiction. The document also includes exercises asking students to match logical equivalences and complete proofs using logical steps.