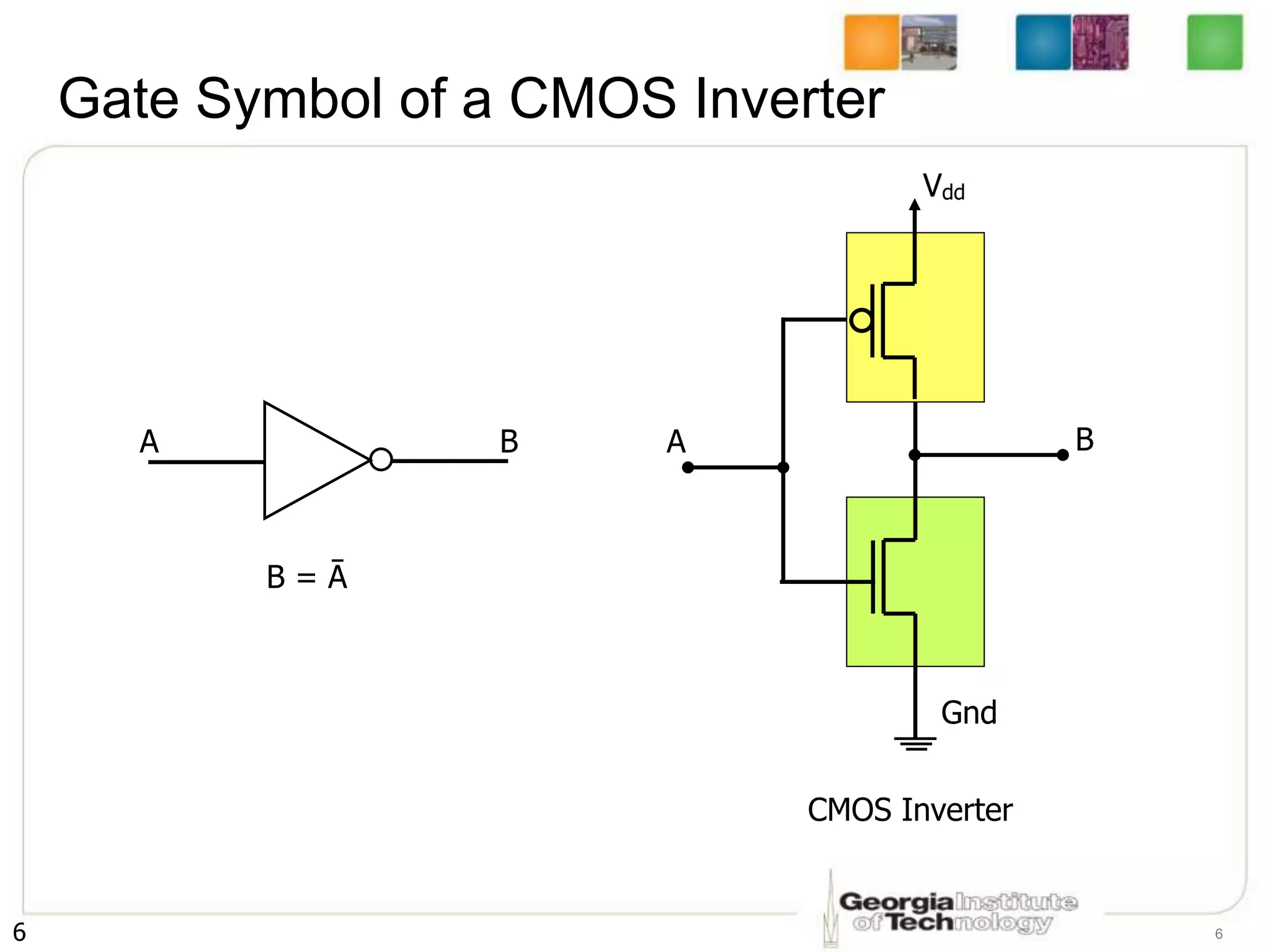
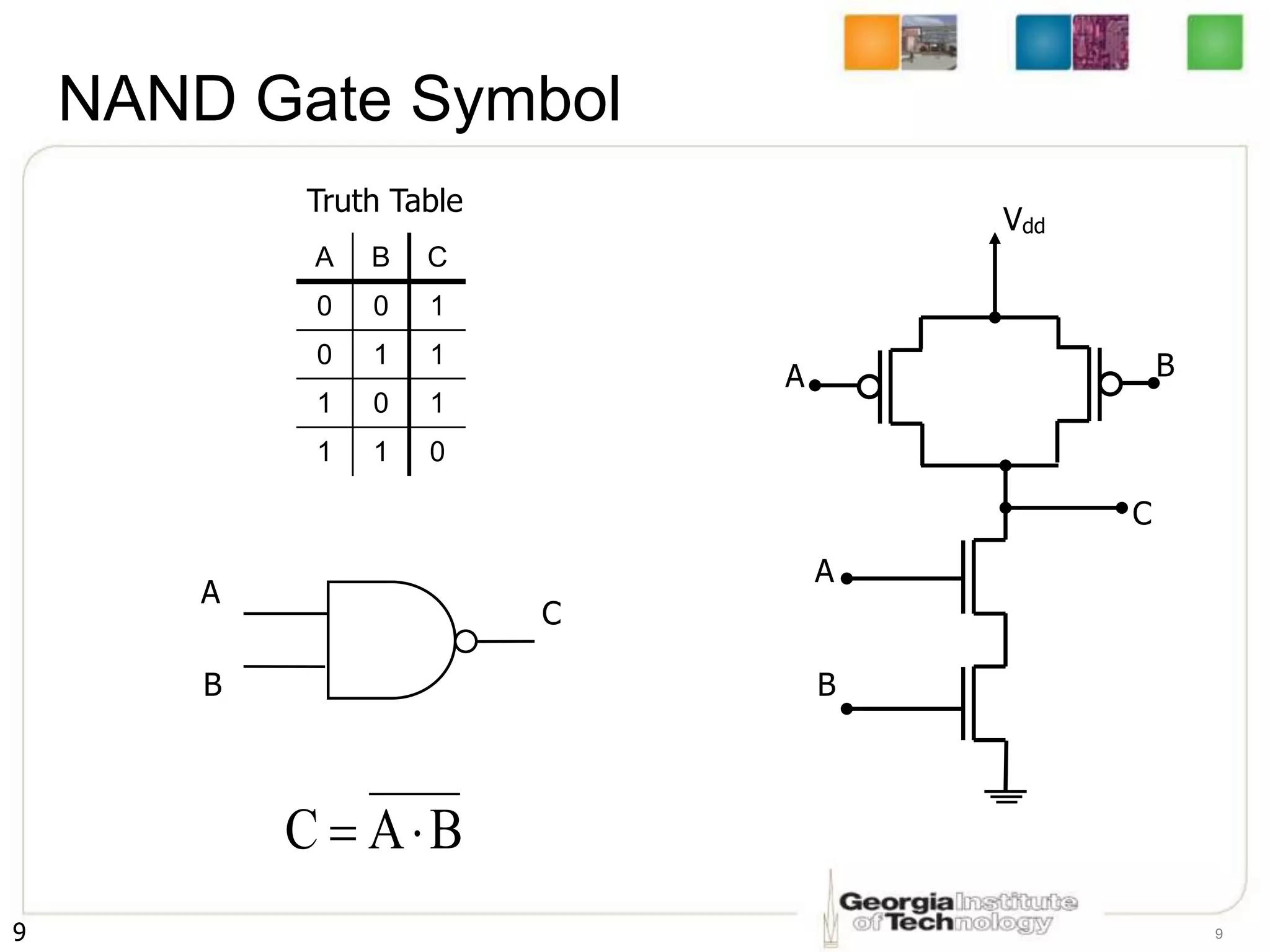
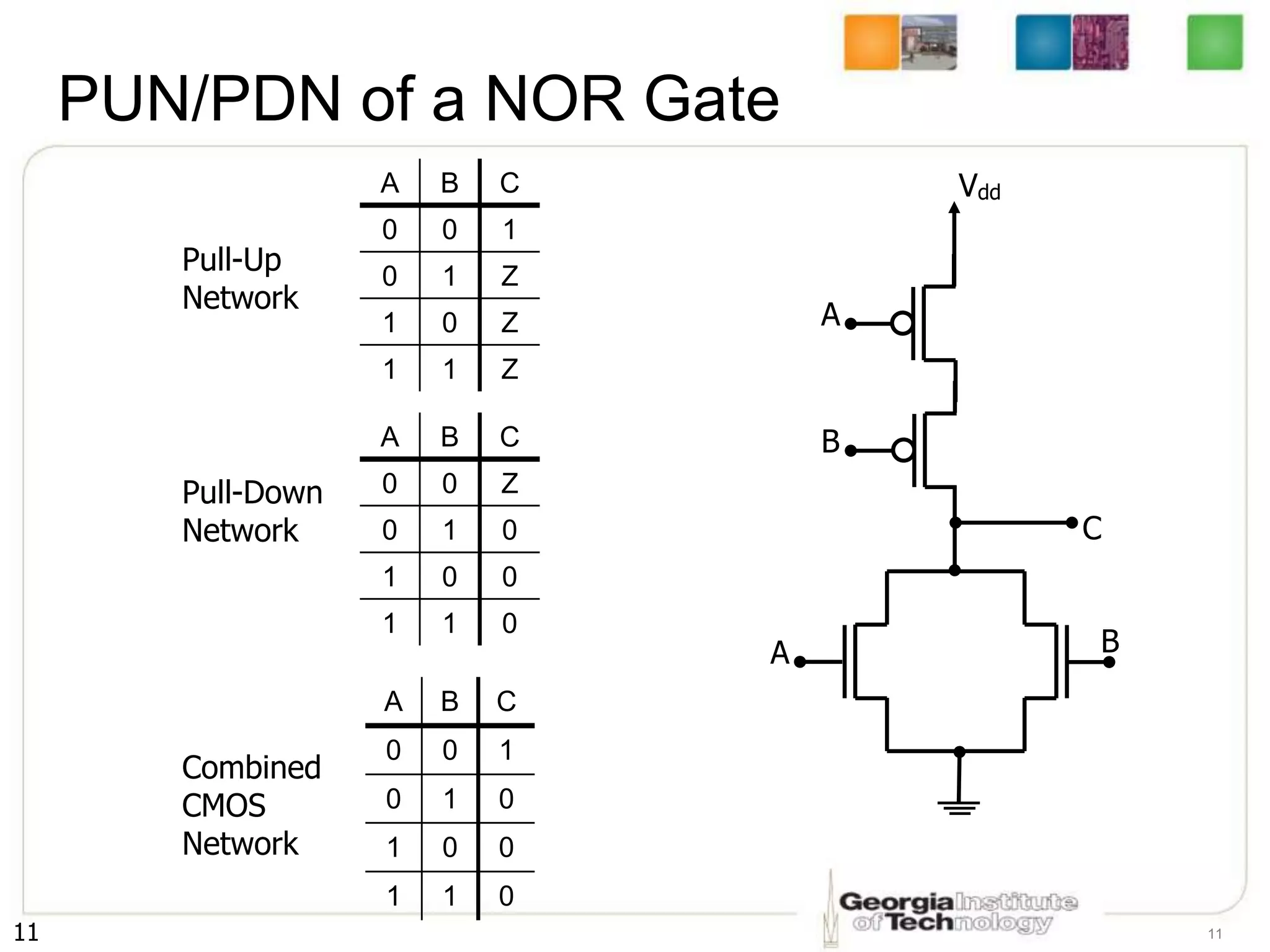
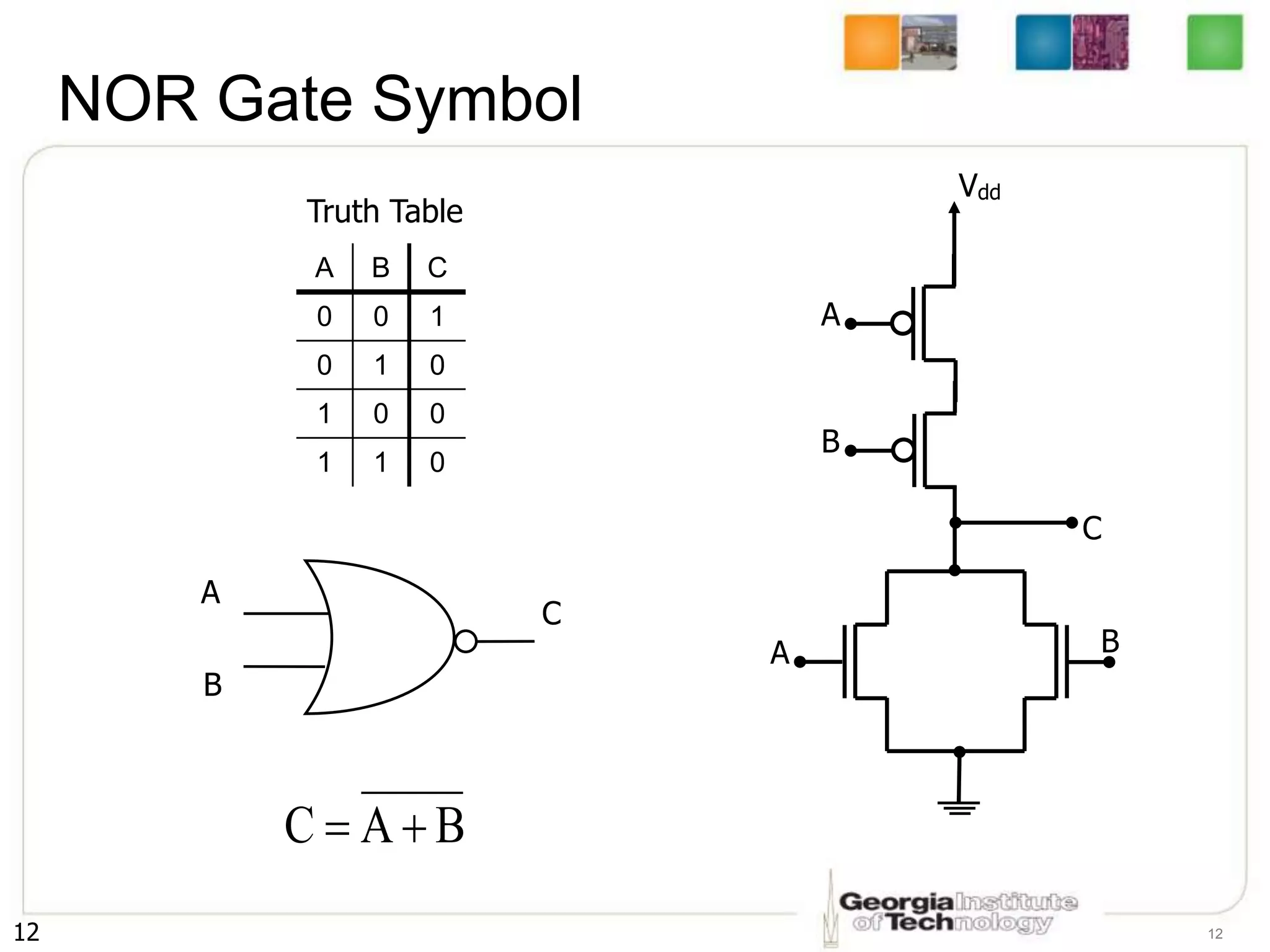
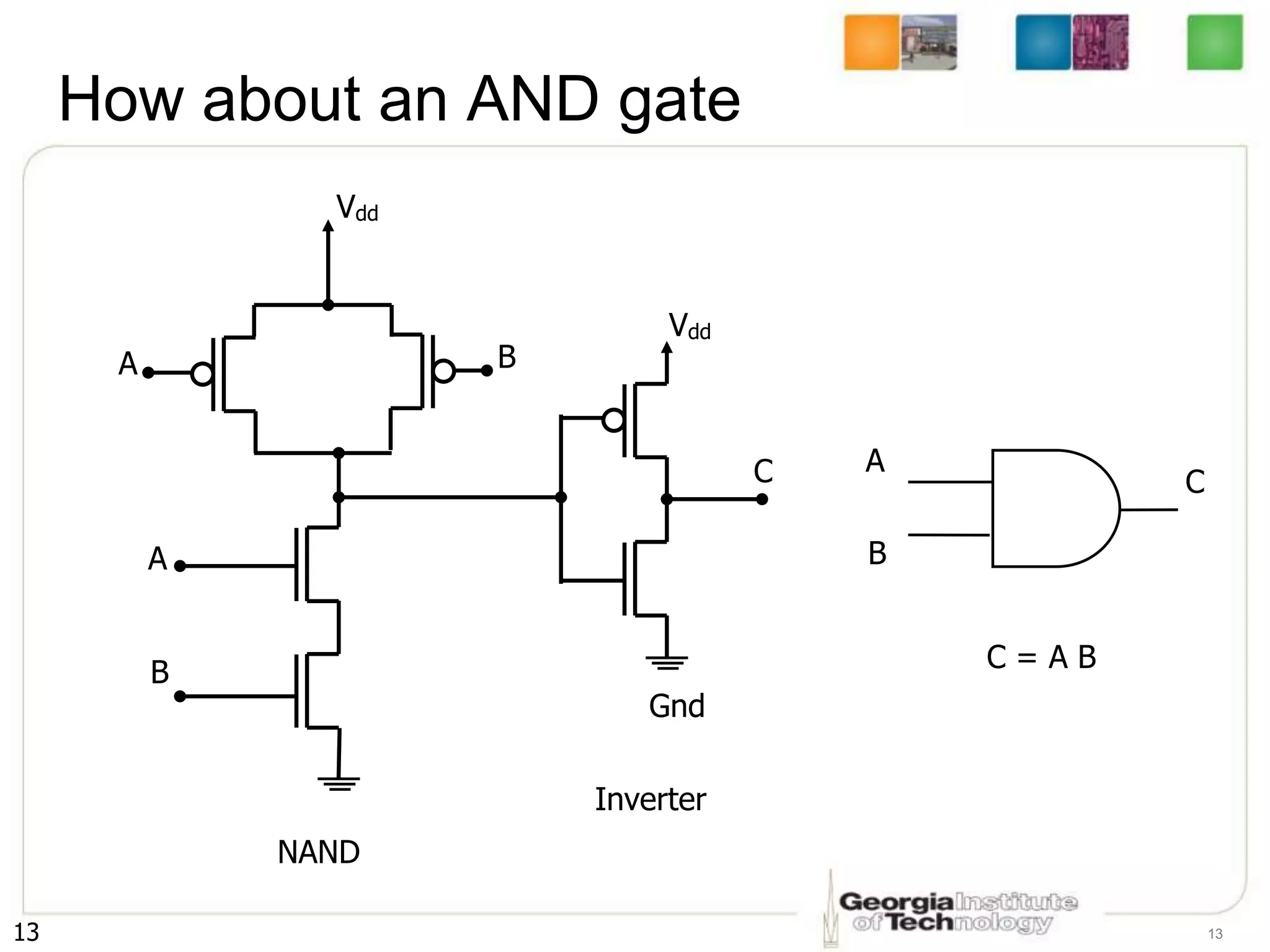
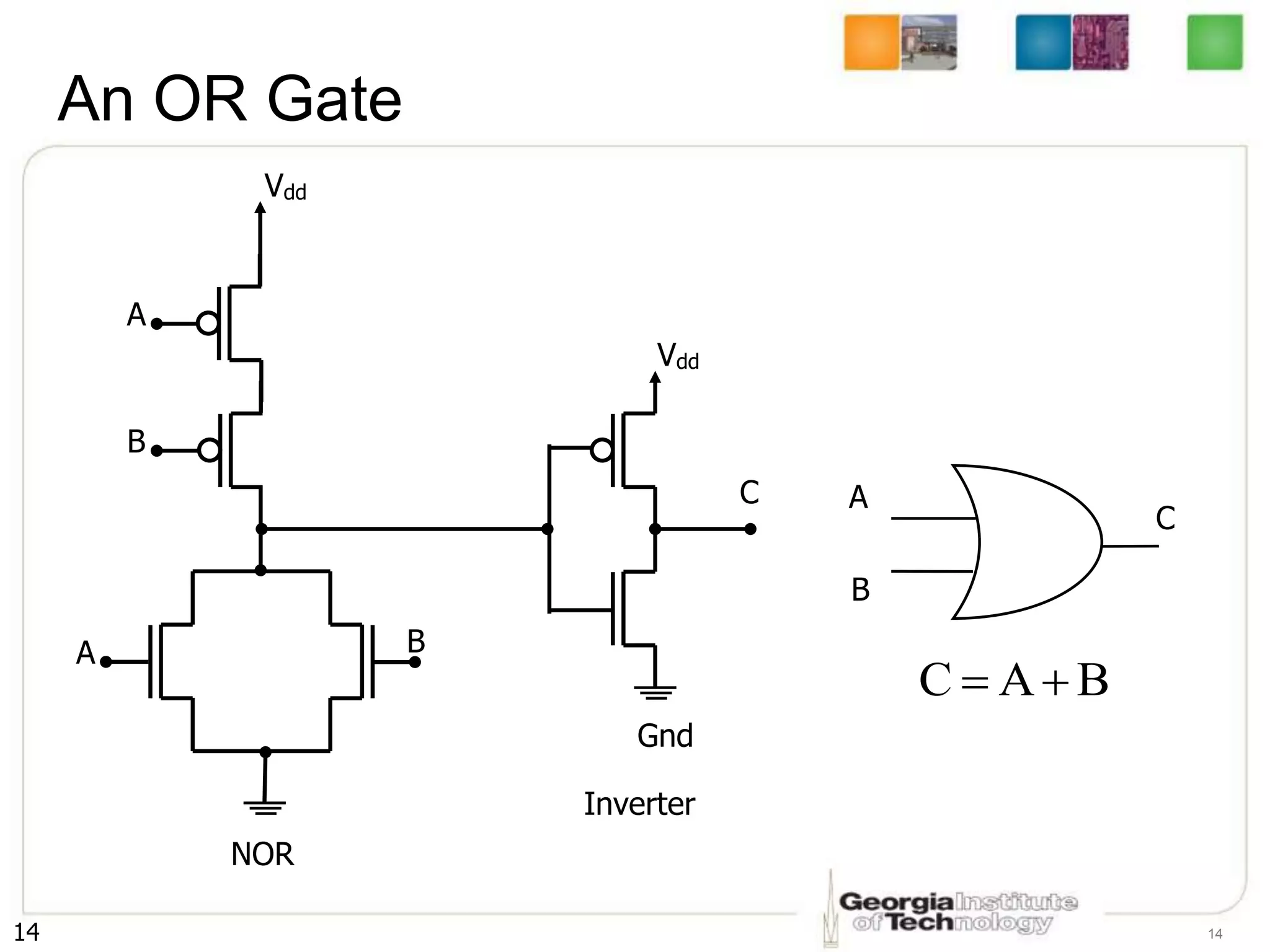
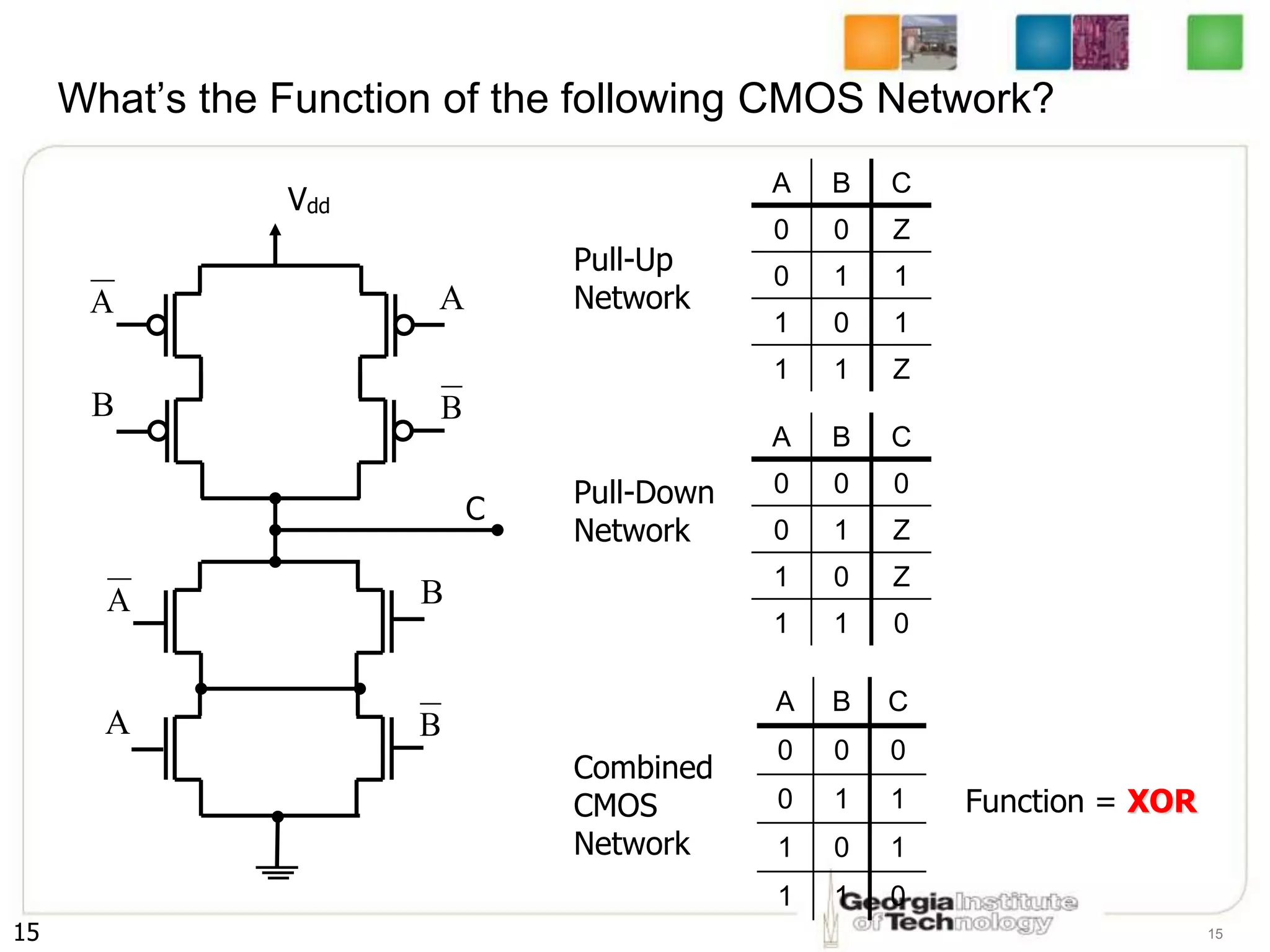
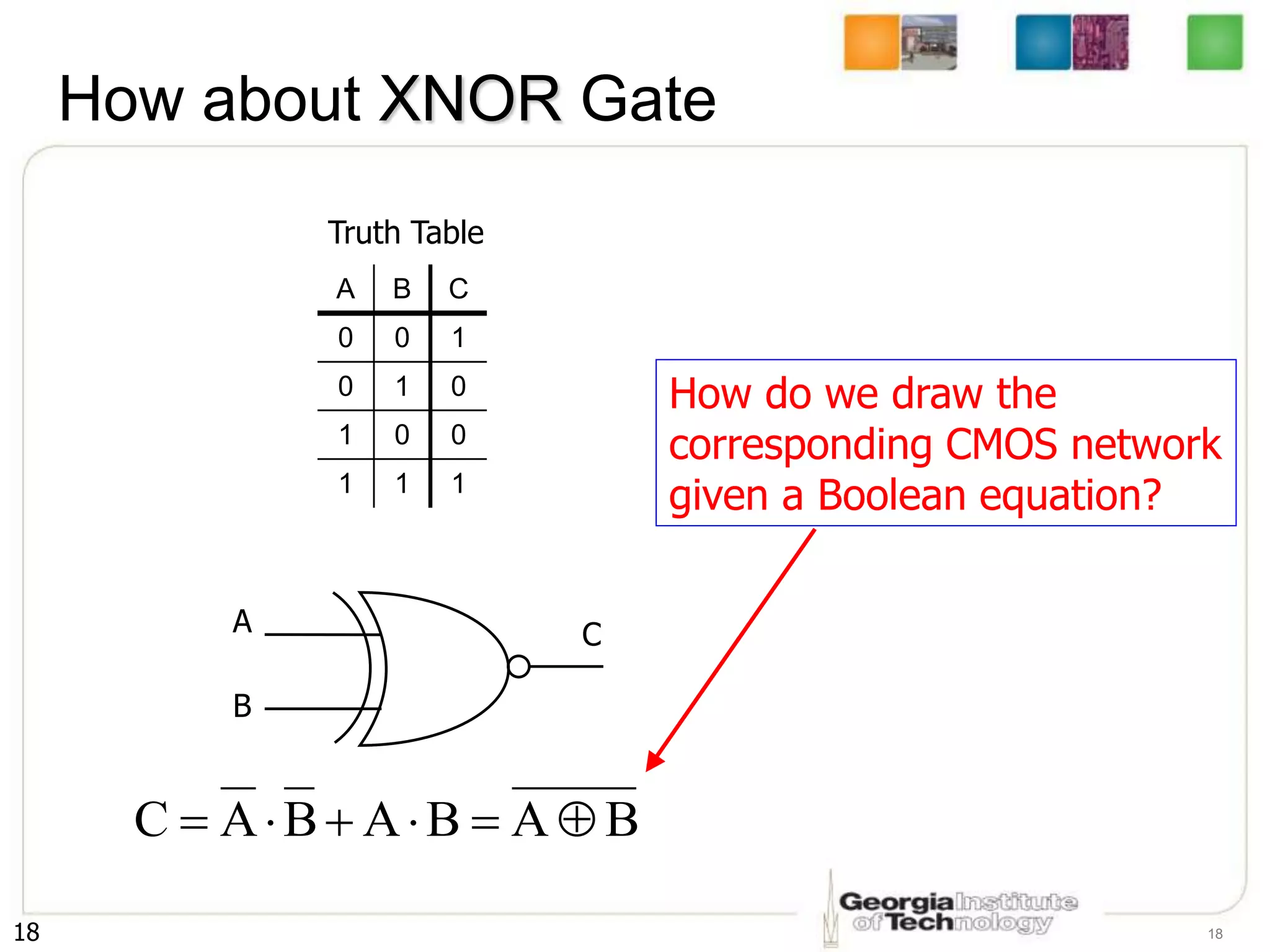
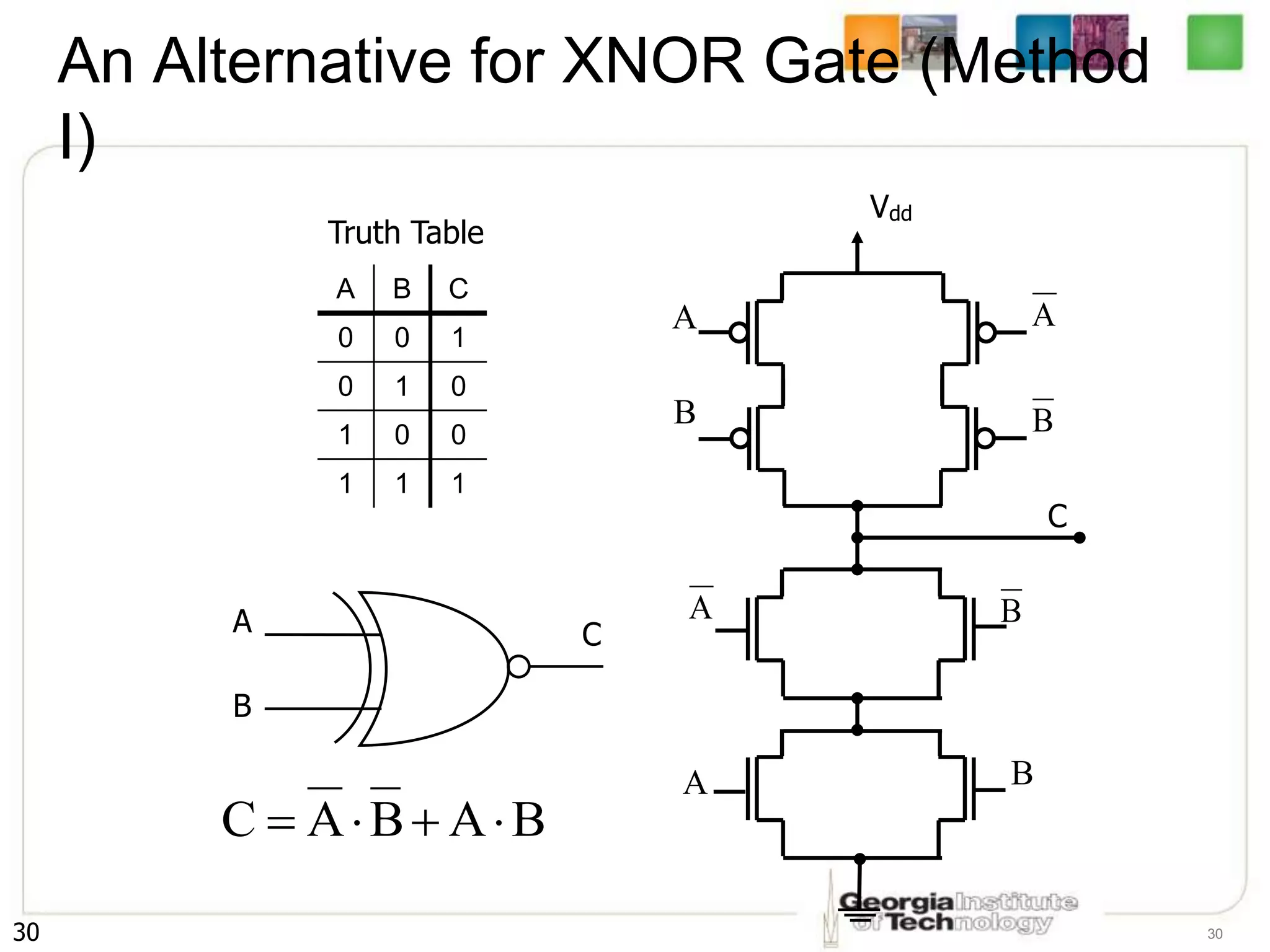
1. The document discusses CMOS inverters and basic gates like NAND and NOR.
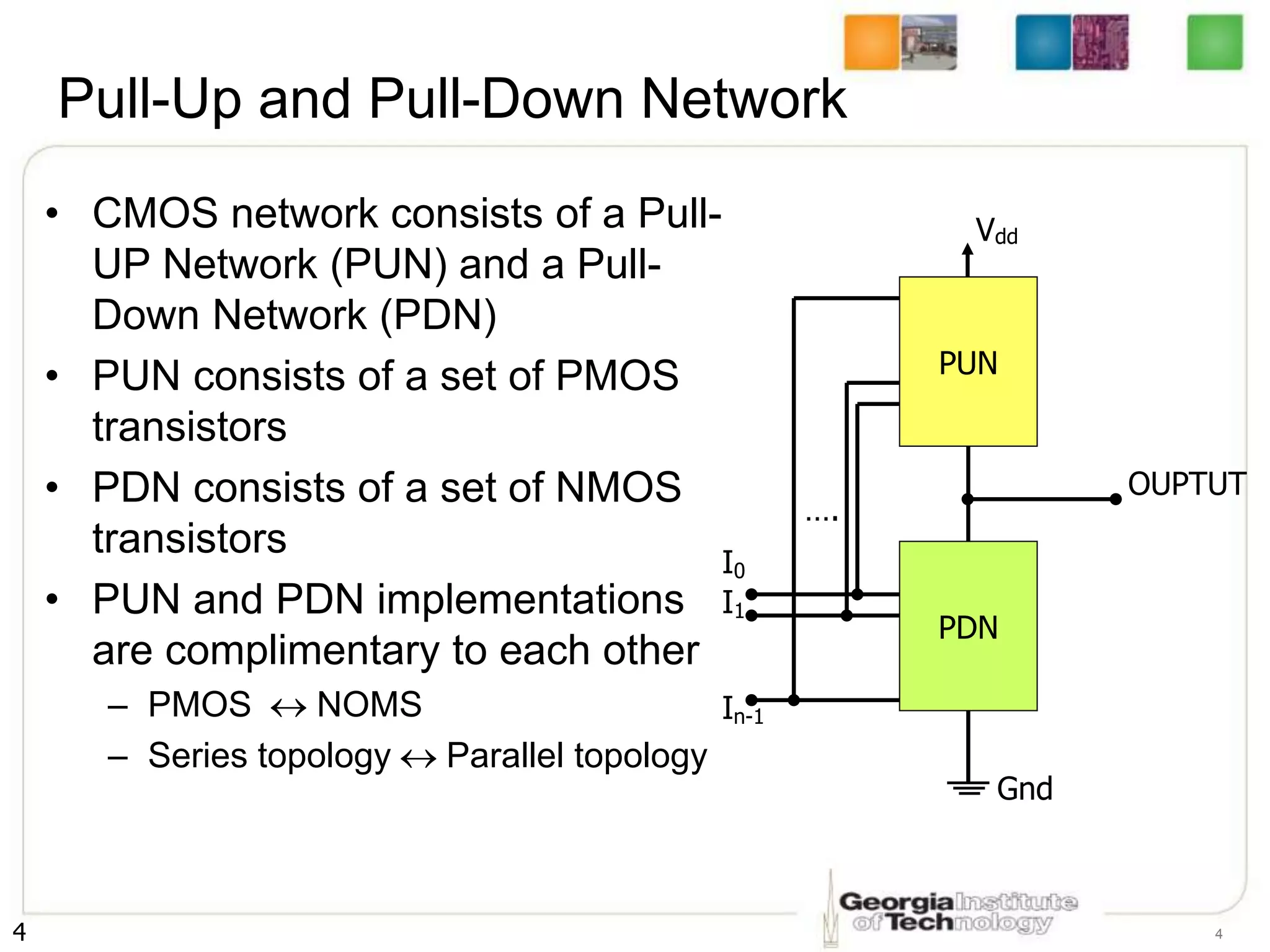
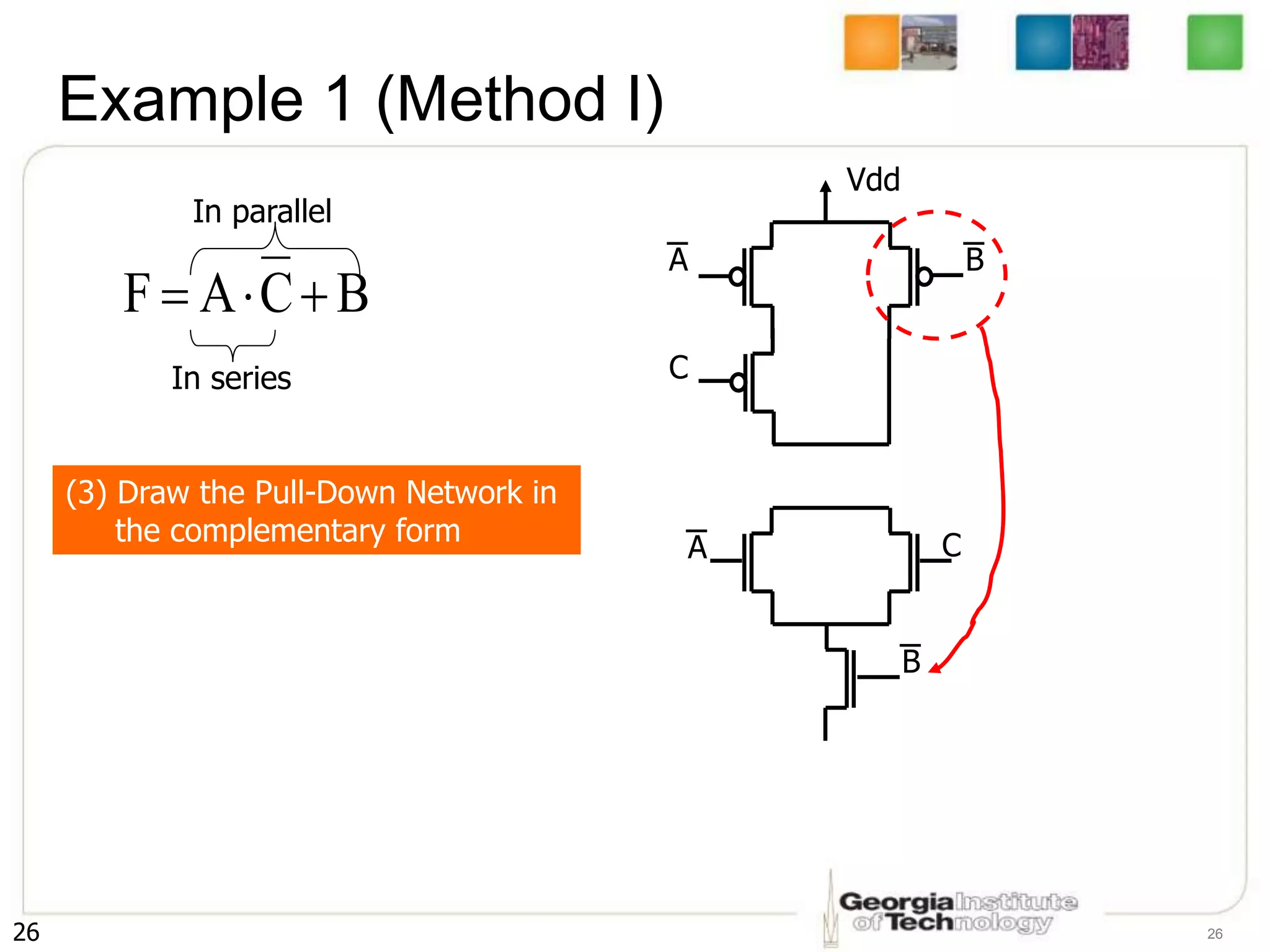
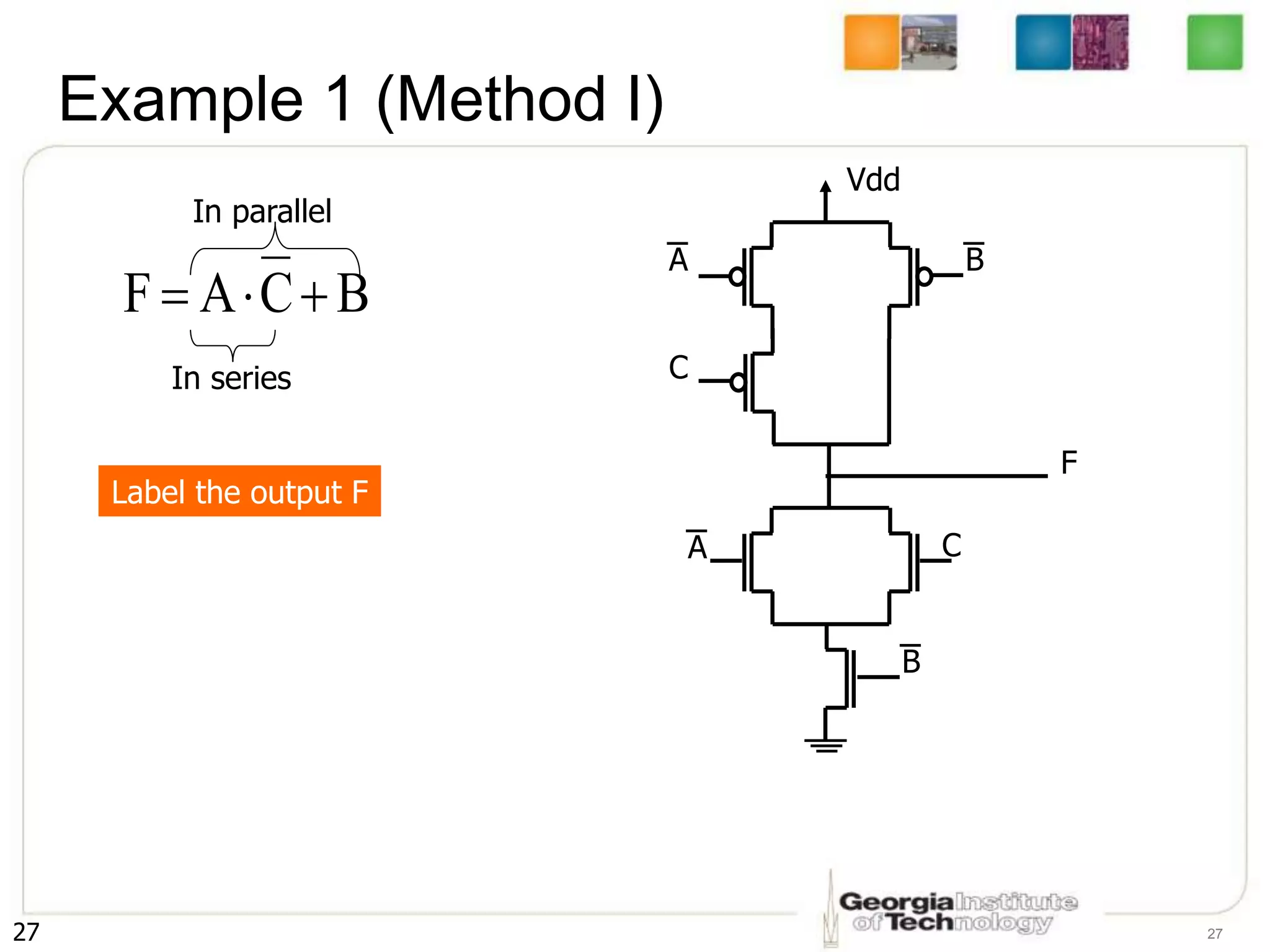
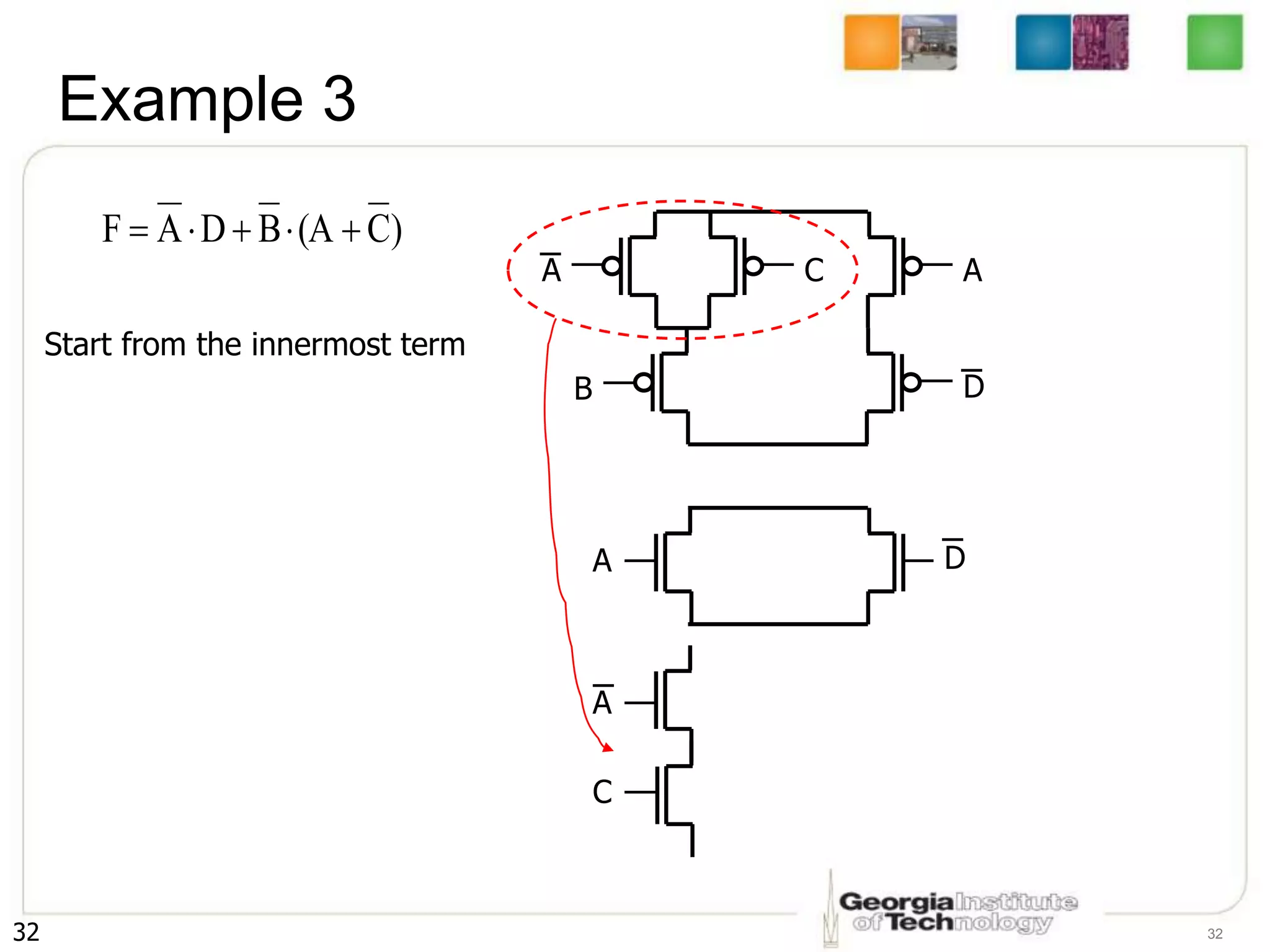
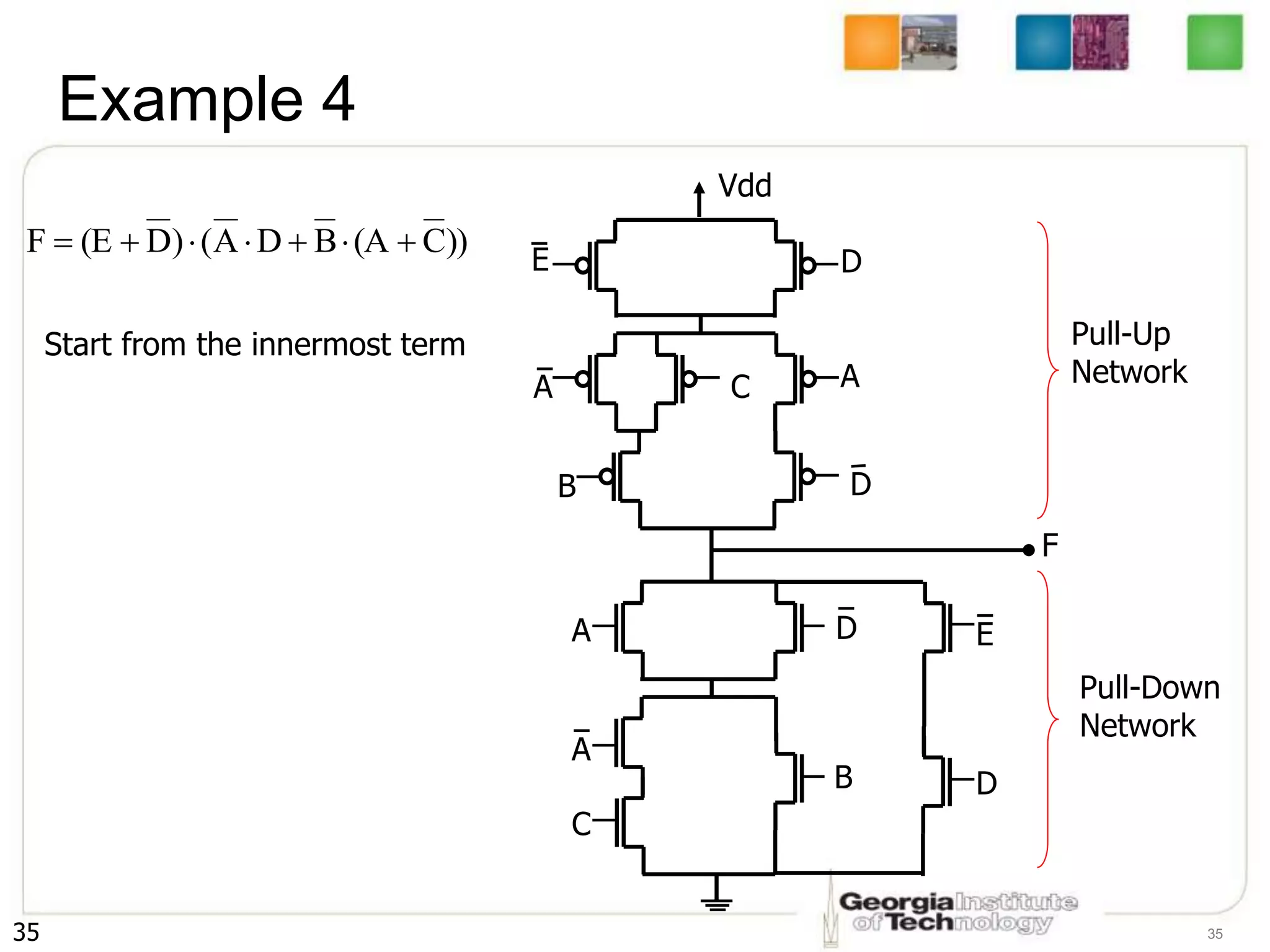
2. It describes how to systematically design the pull-up network and pull-down network that make up a CMOS circuit from a Boolean equation.
3. The key steps are to represent each variable as a transistor, connect transistors in series for AND and parallel for OR, and ensure the pull-up and pull-down networks are complements of each other.