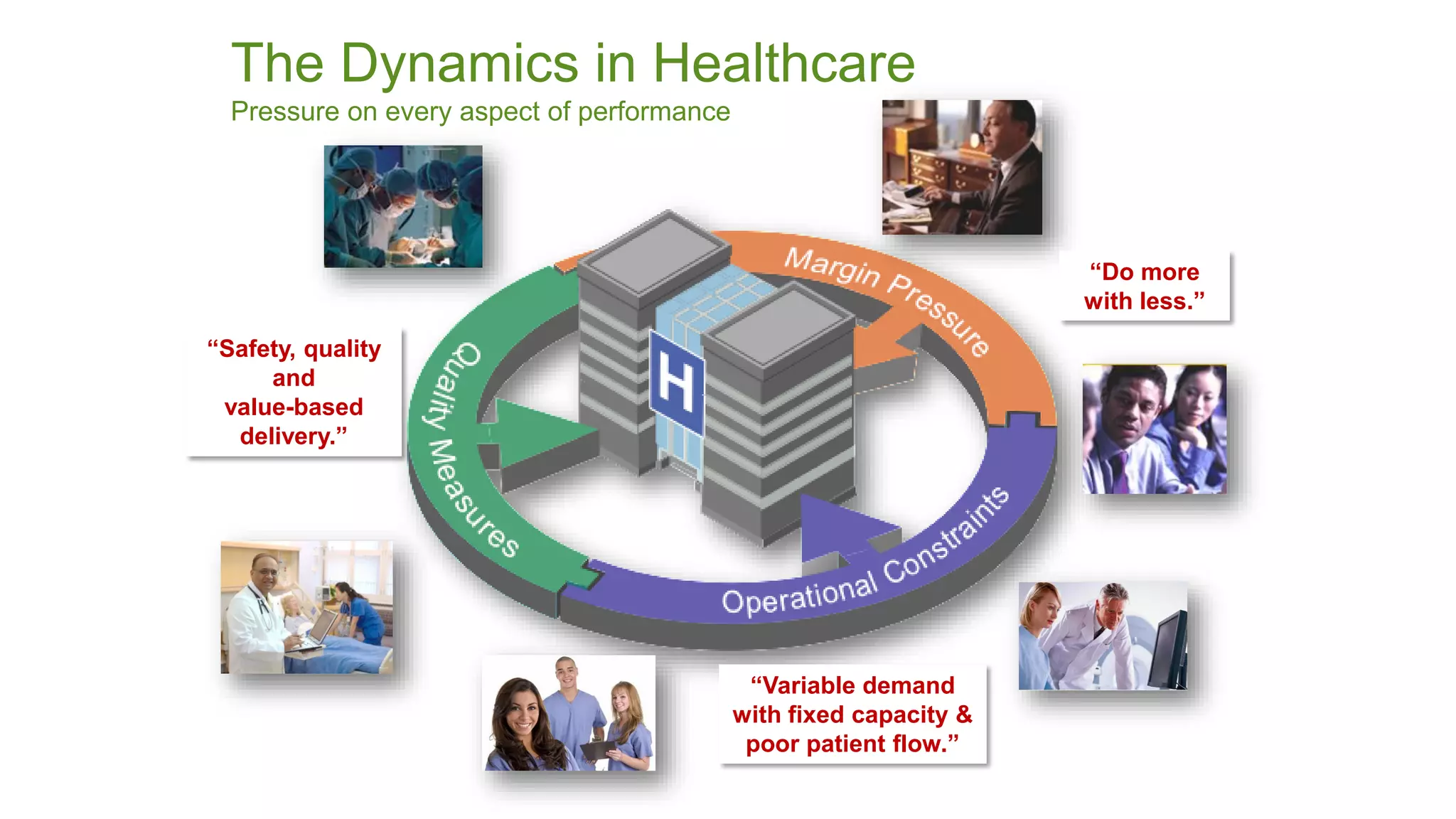
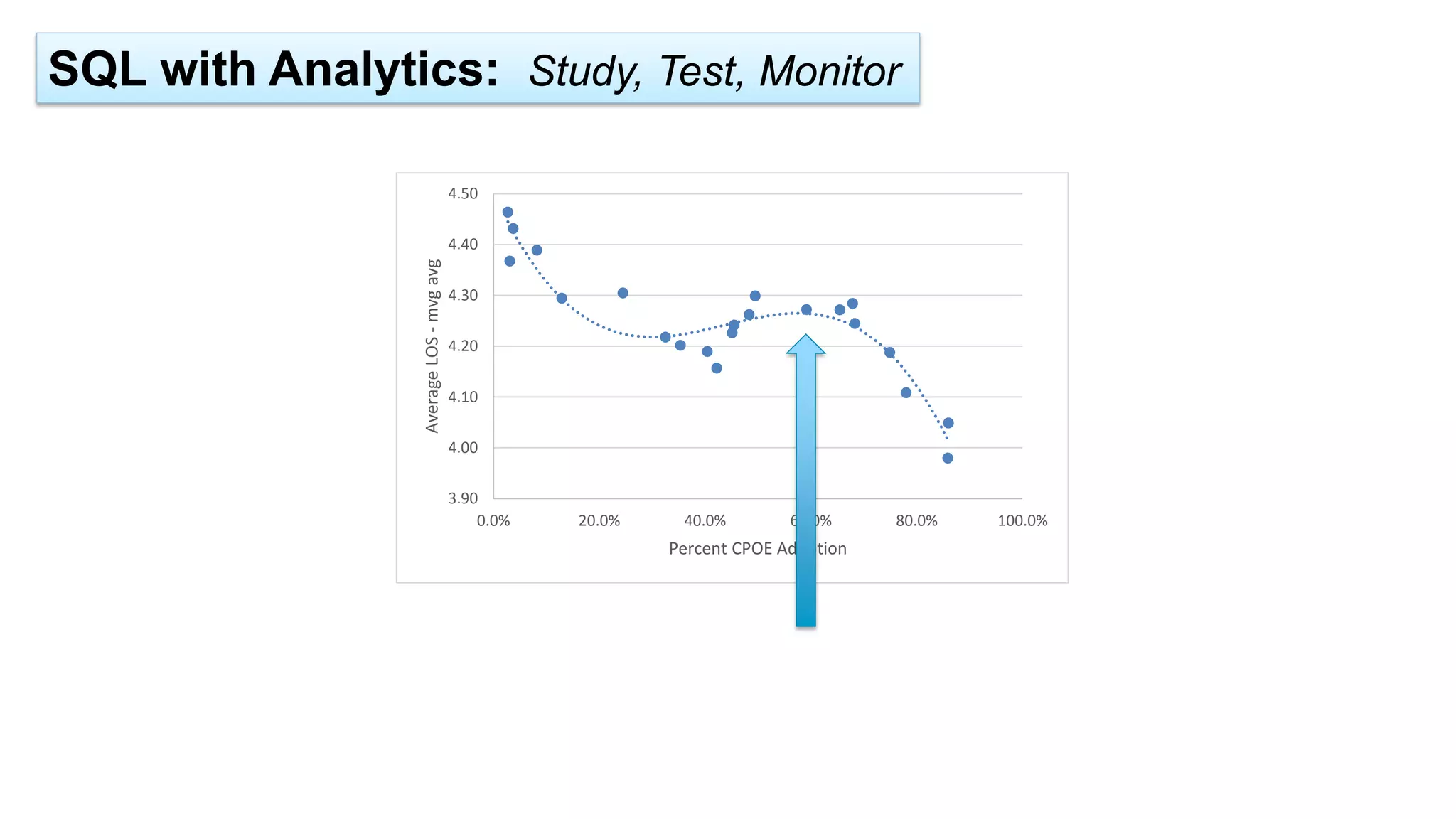
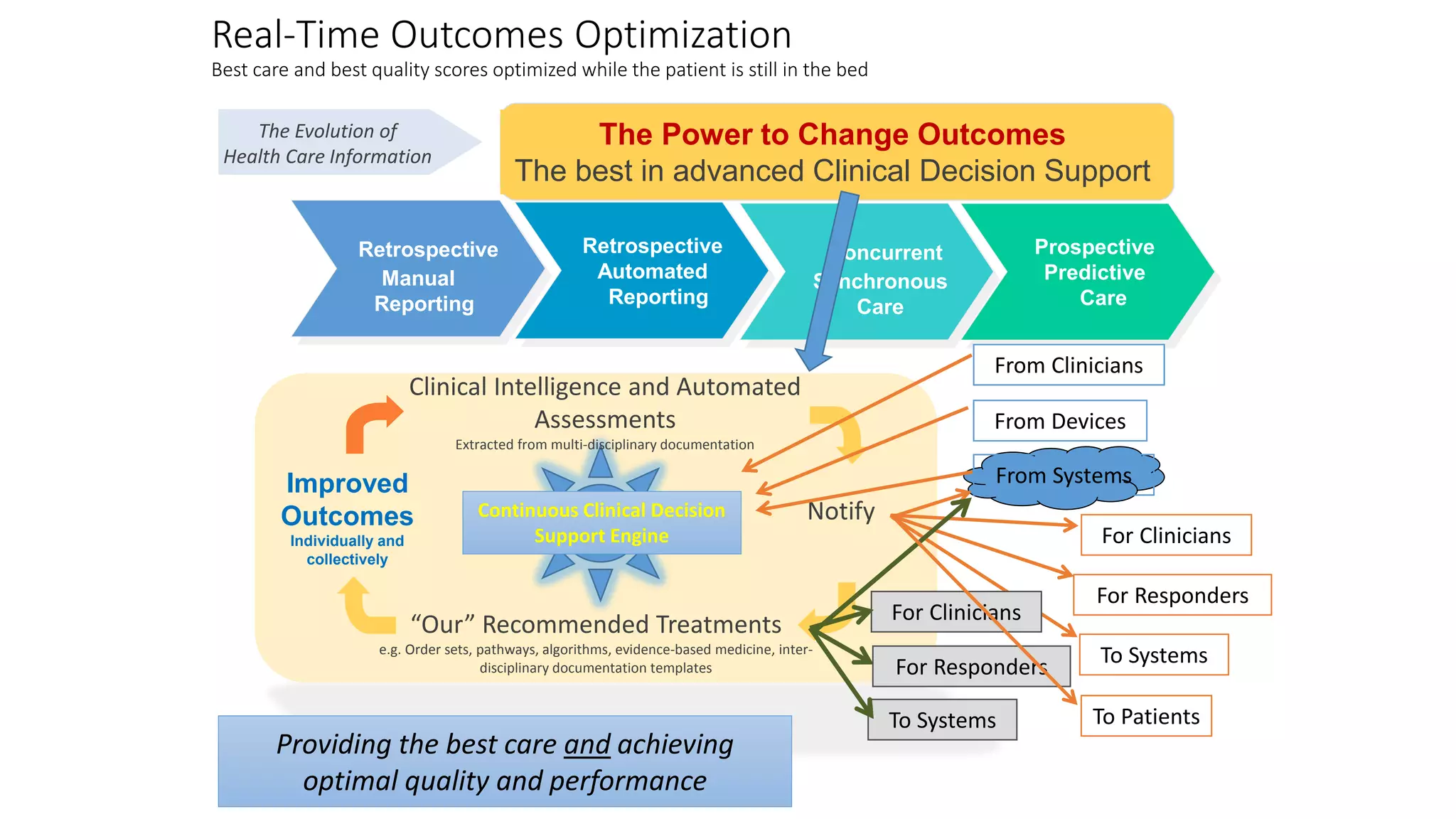
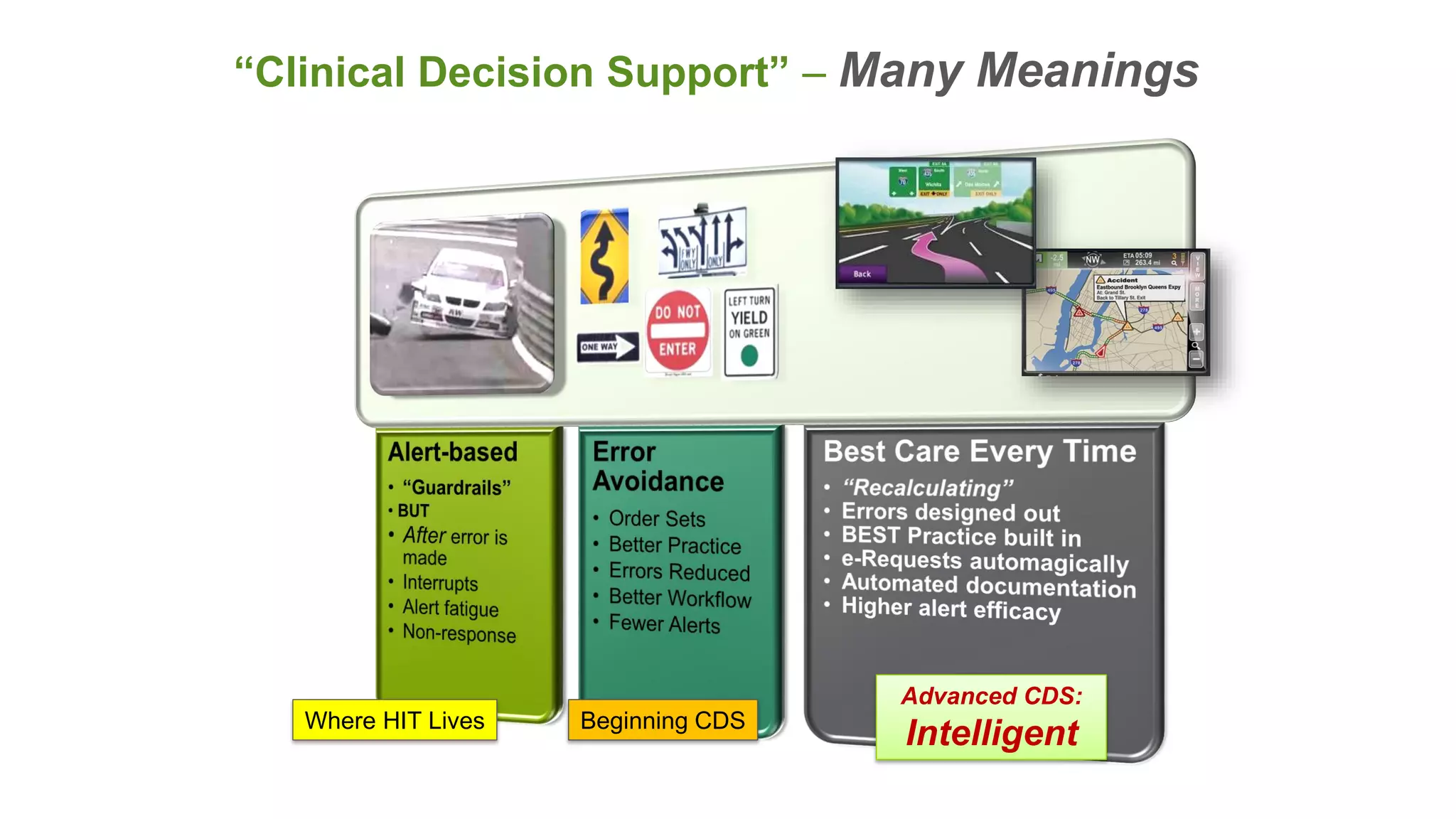
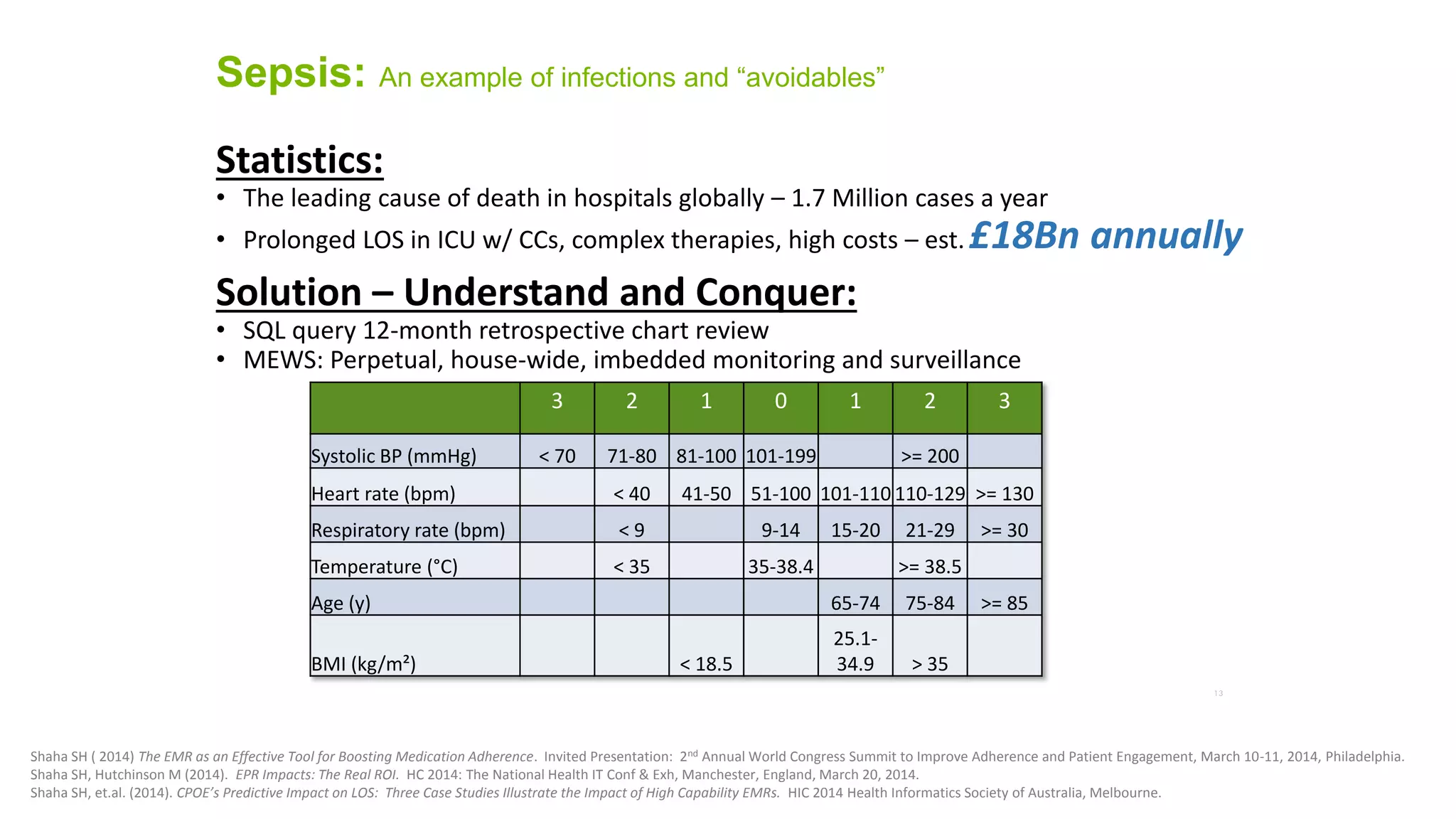
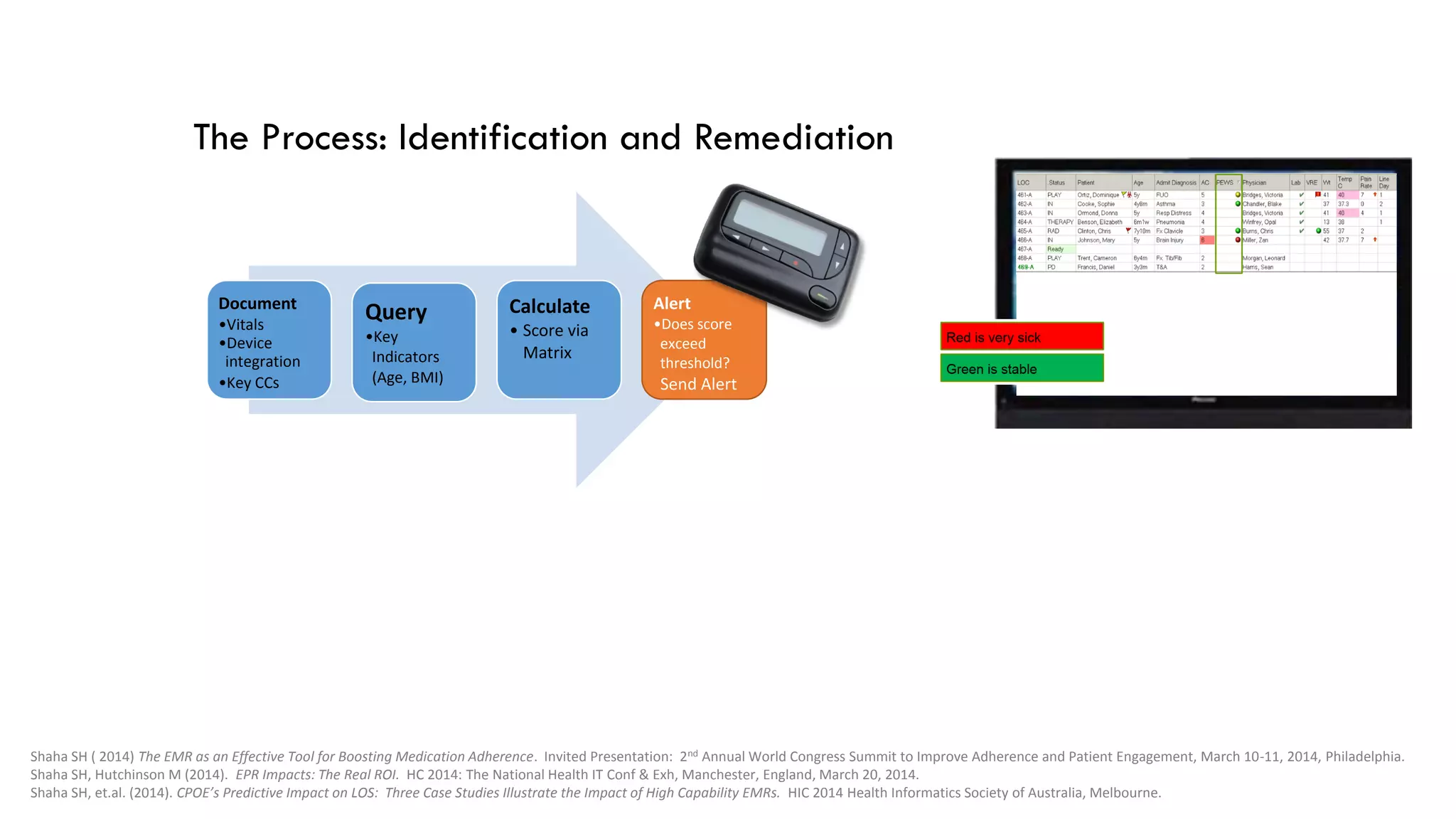
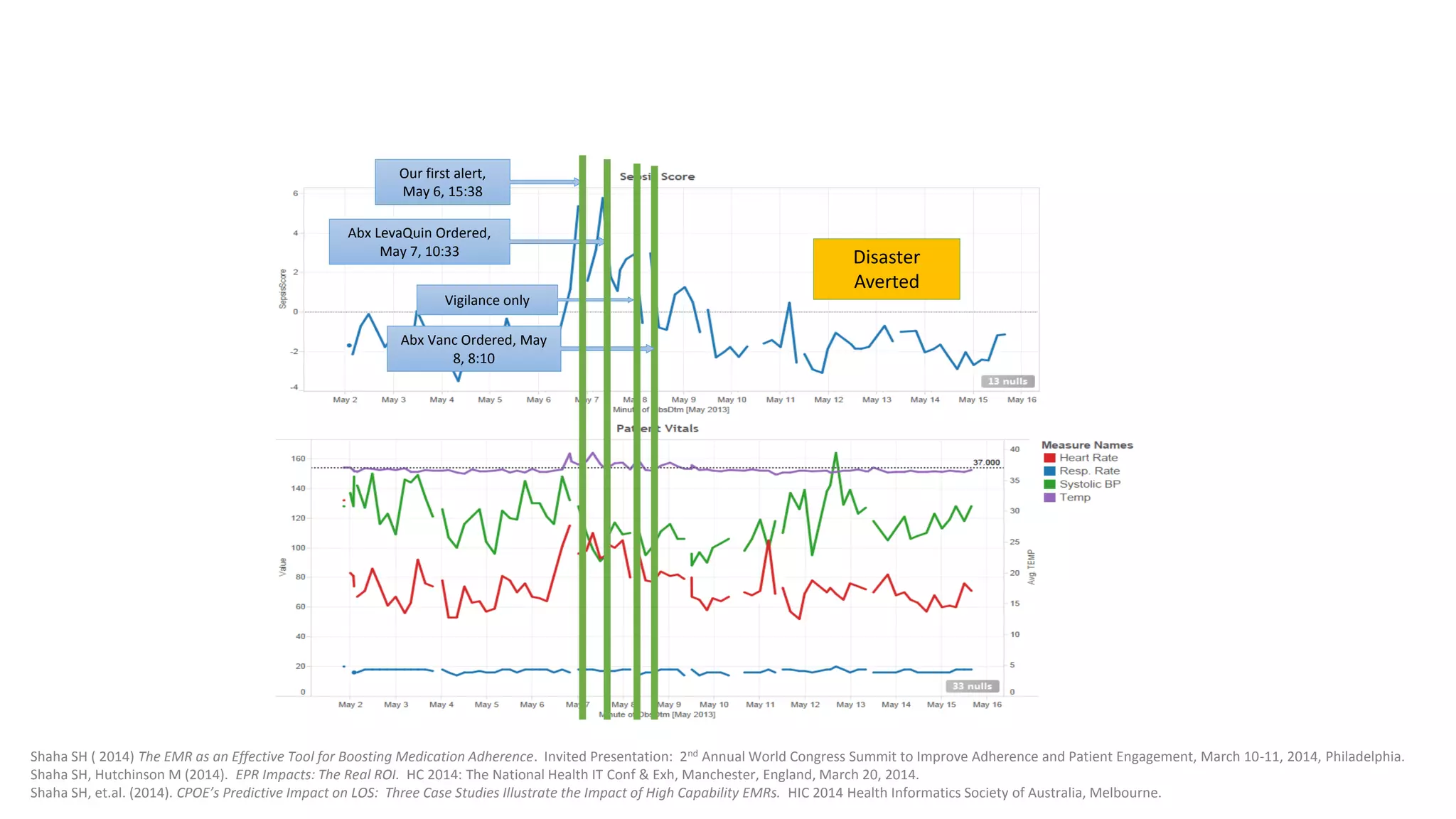
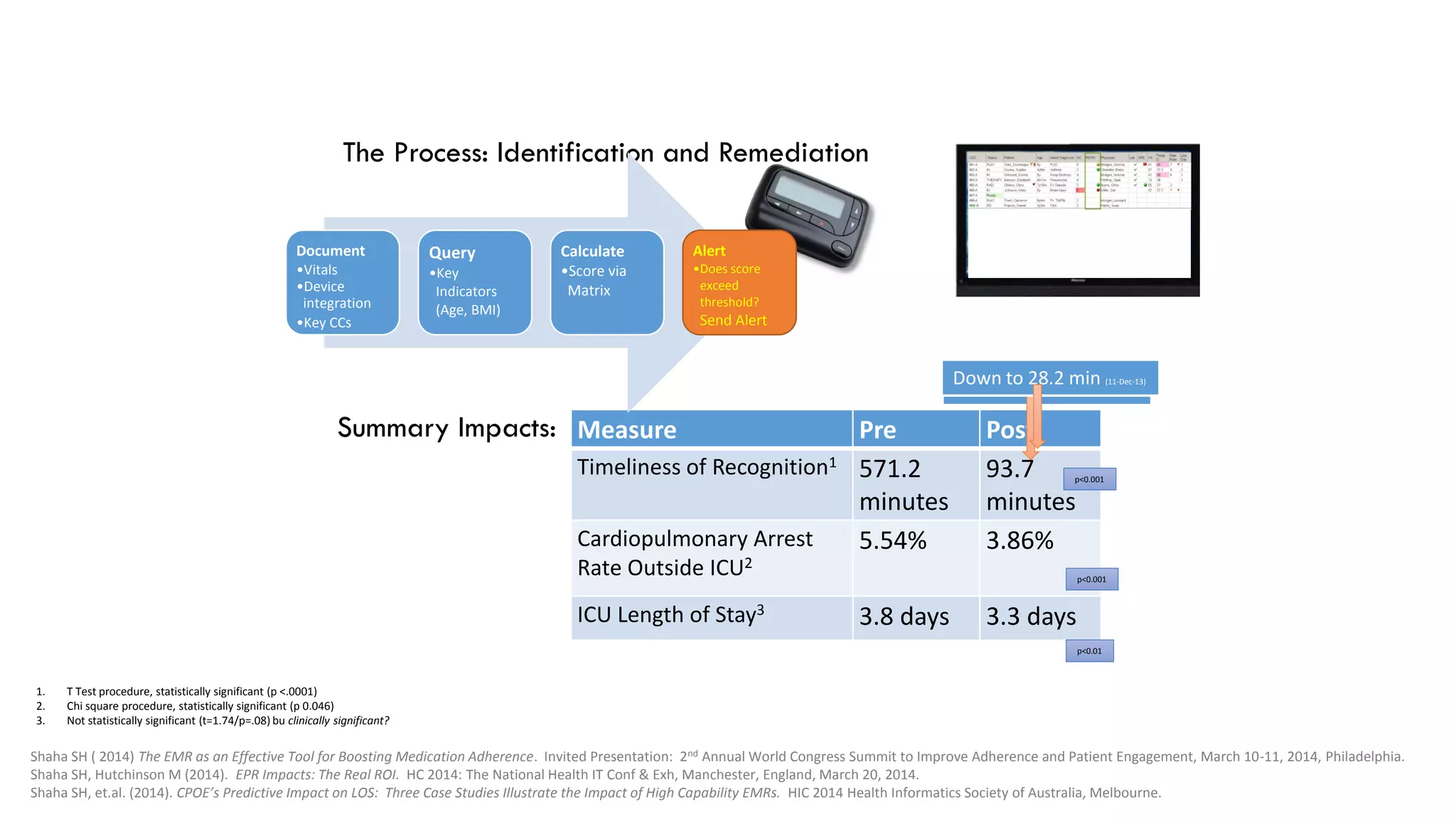
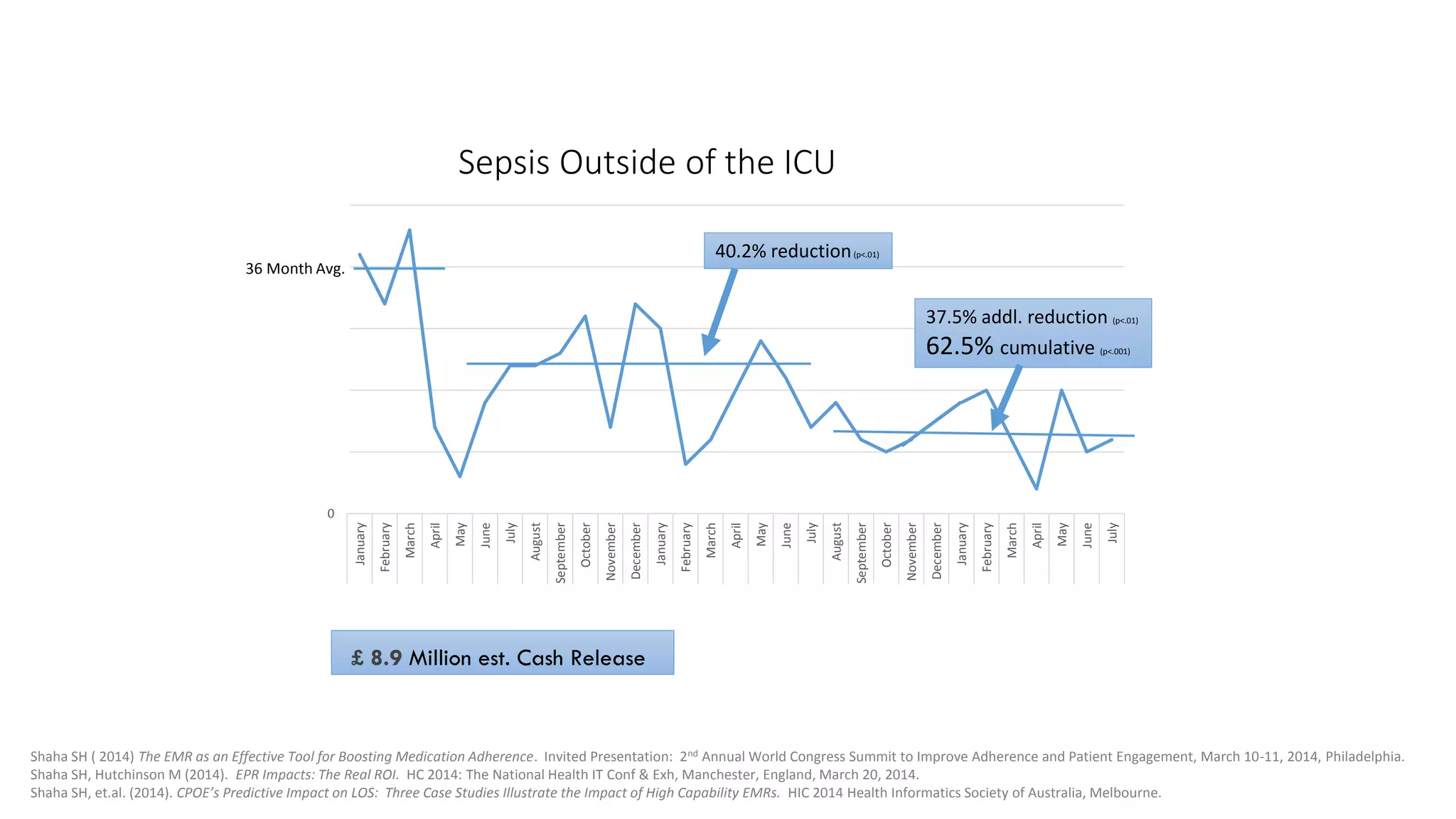
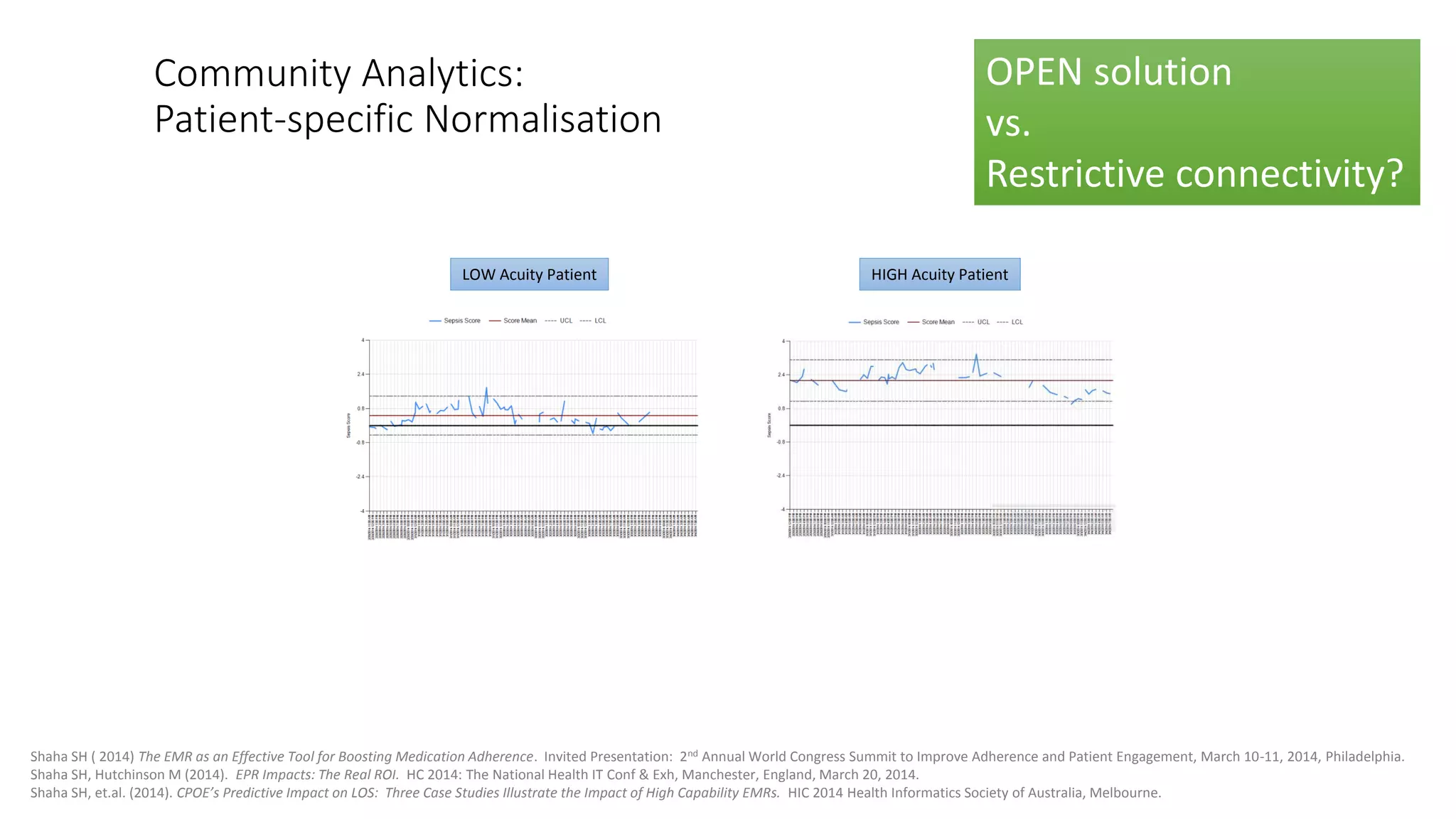
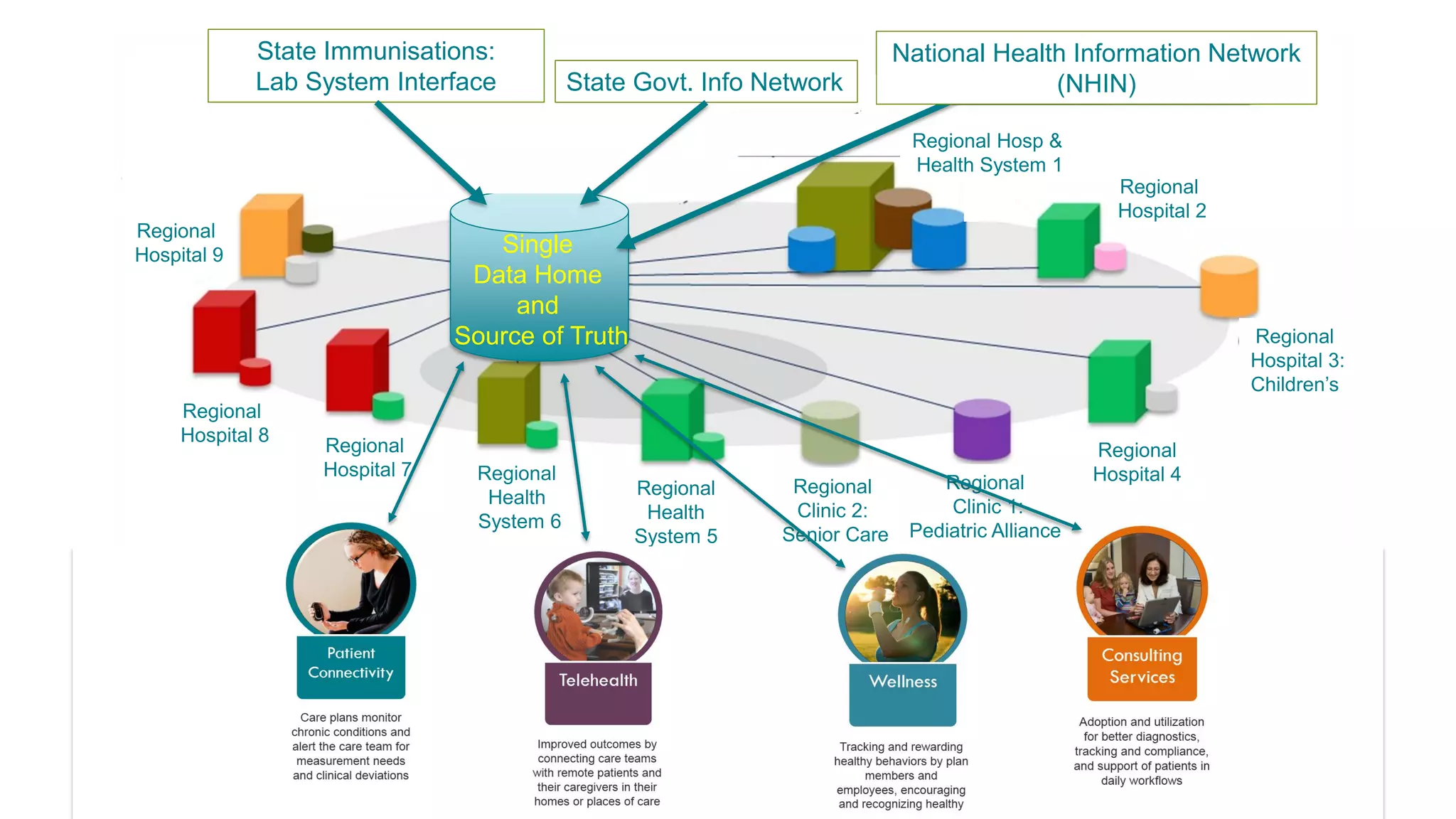
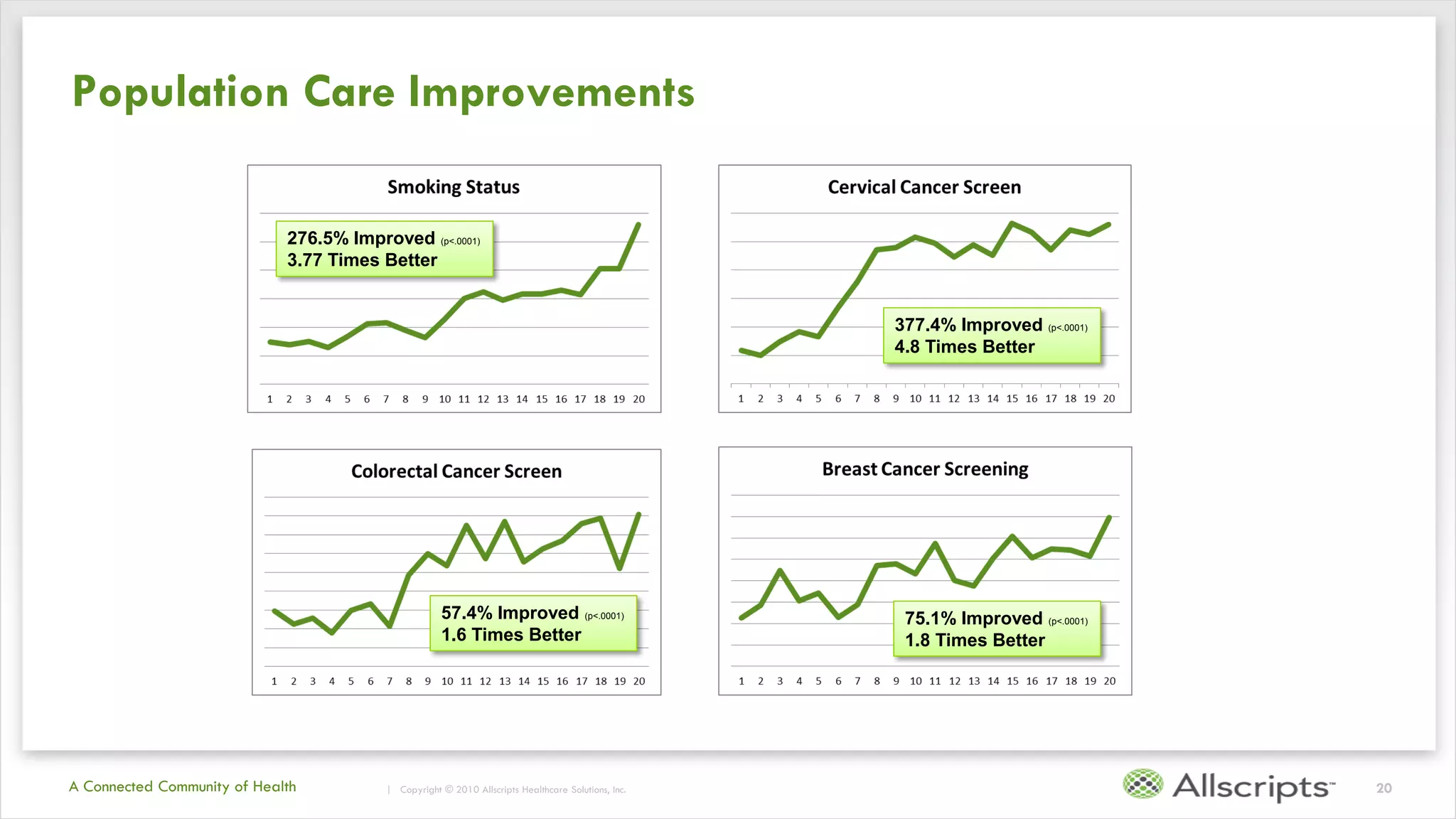
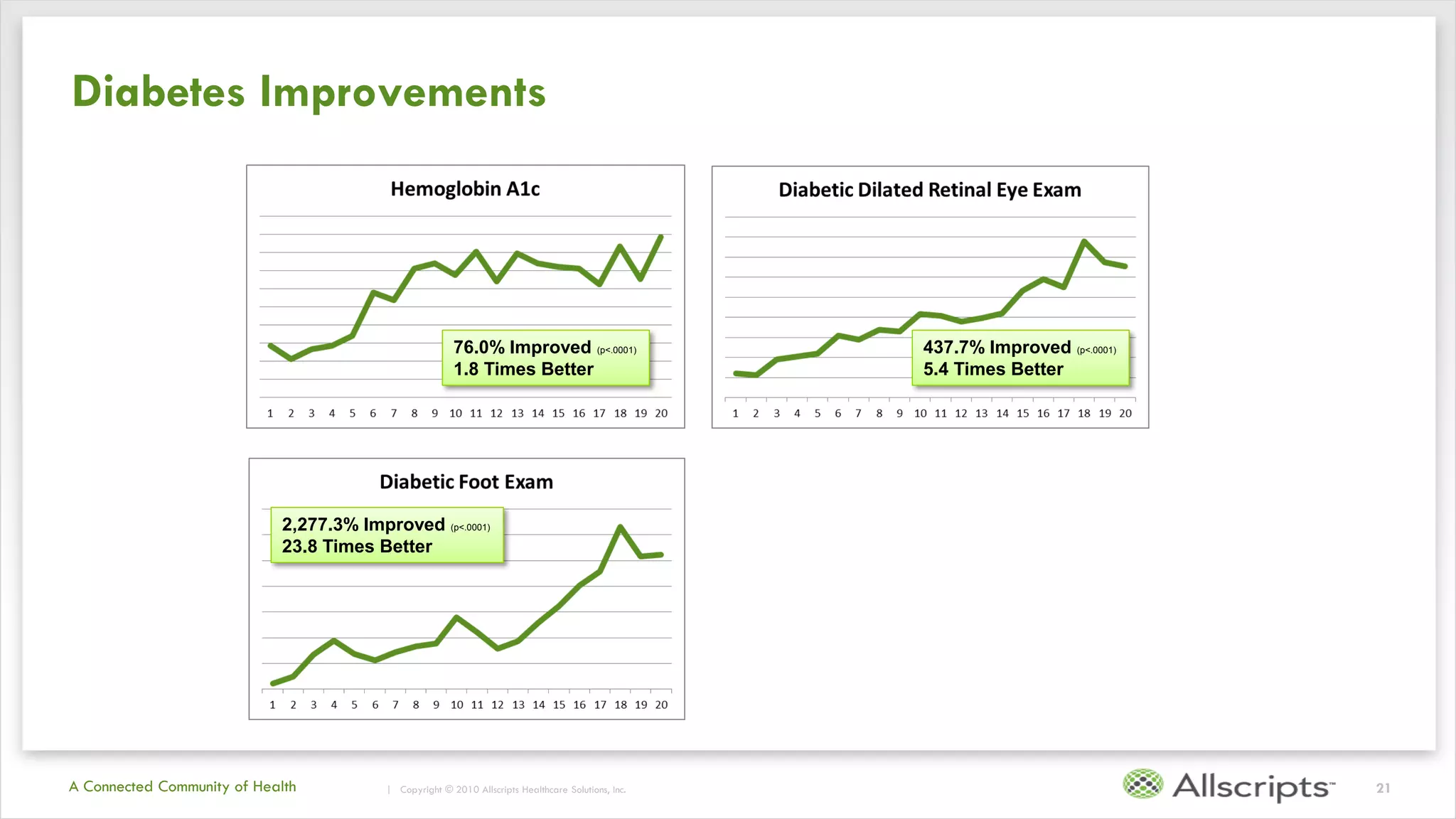
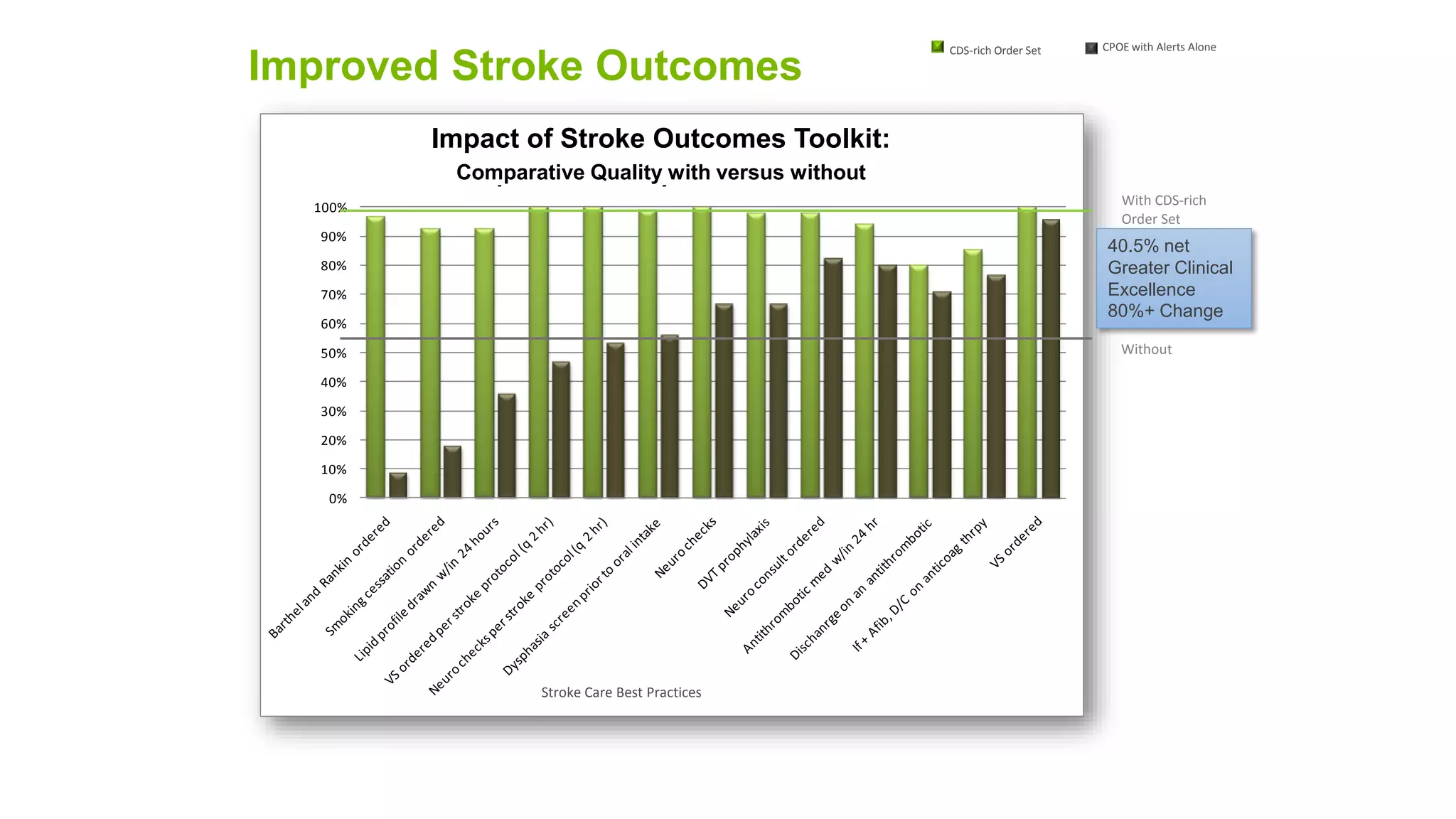
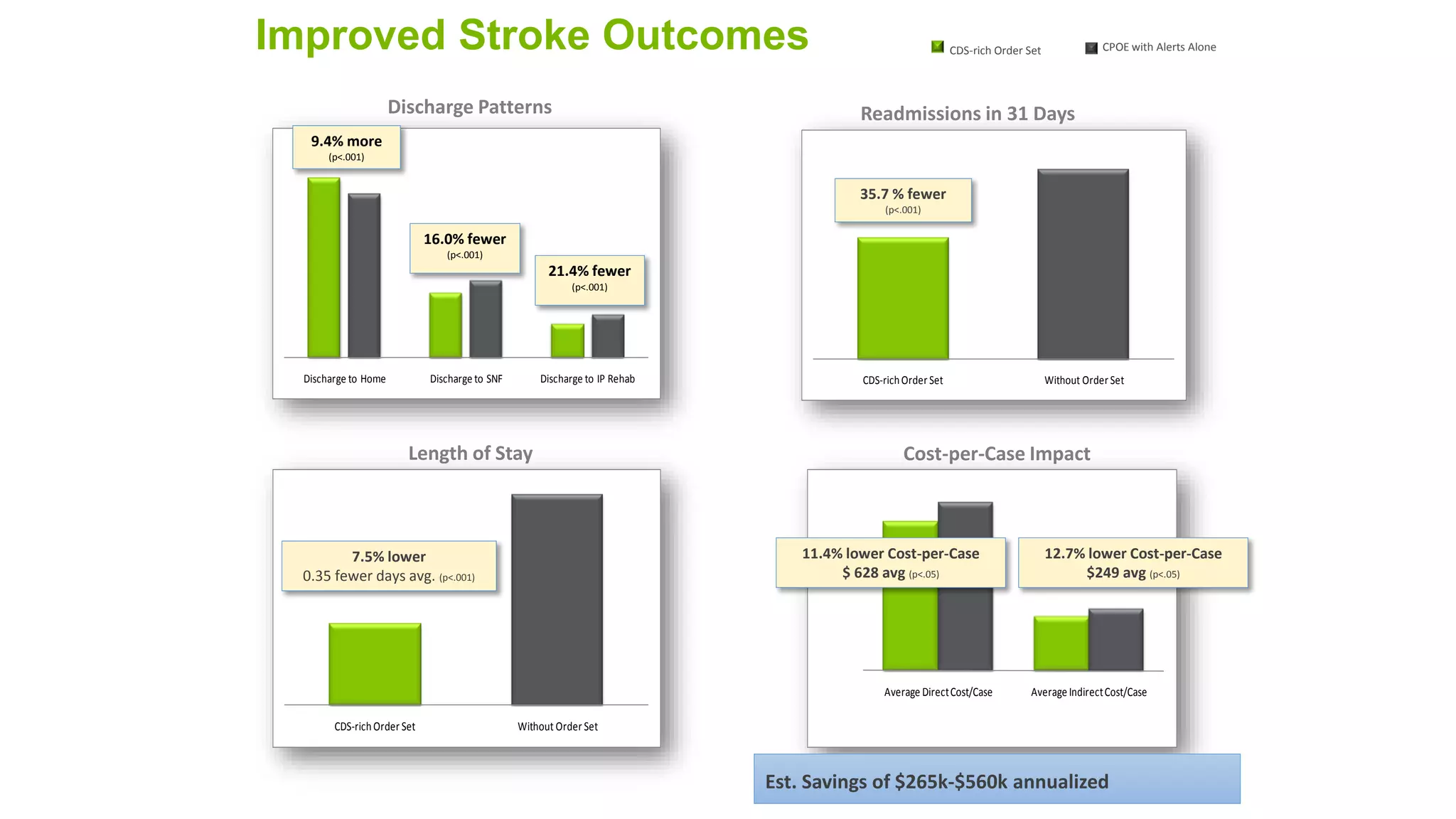
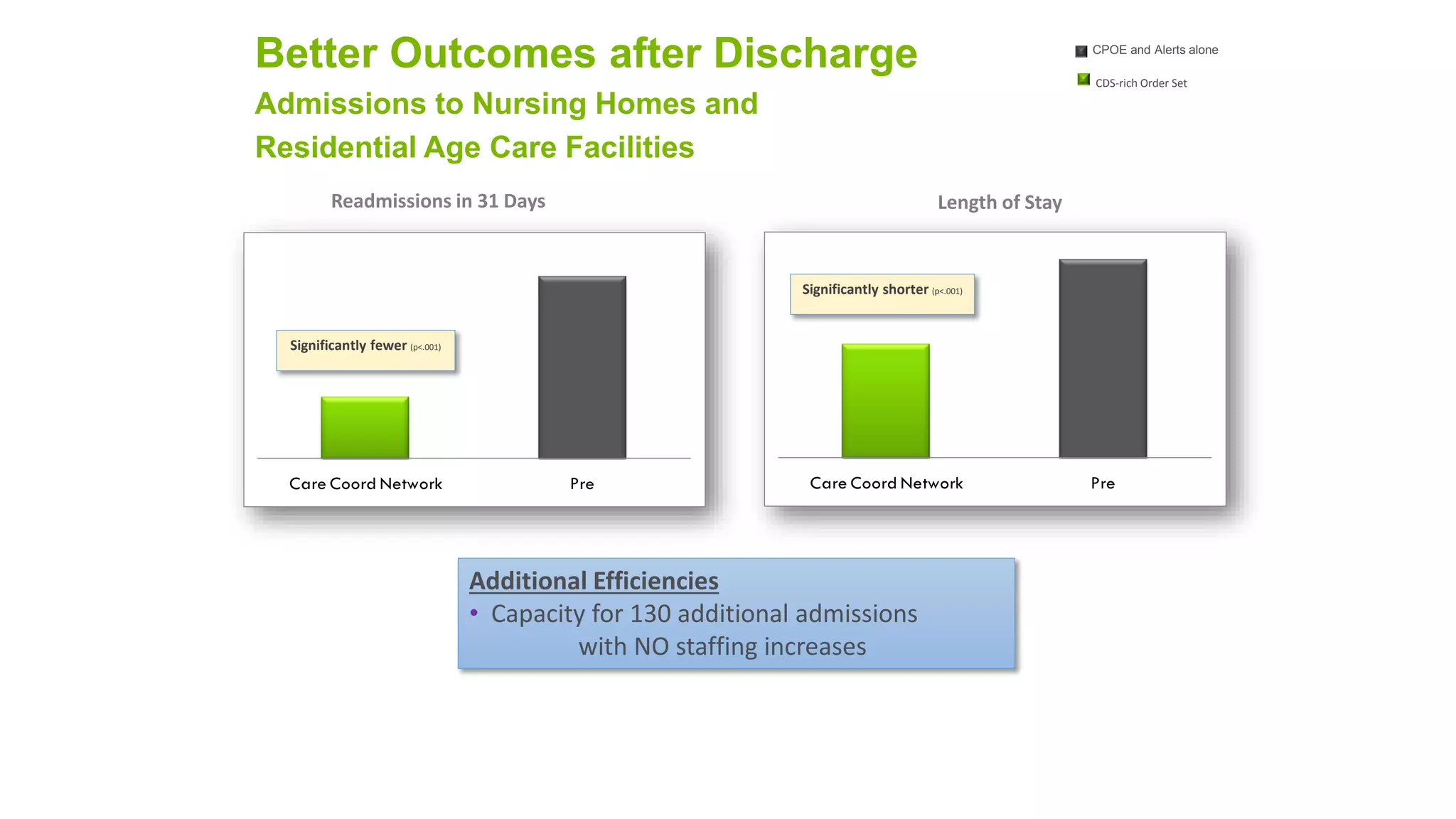
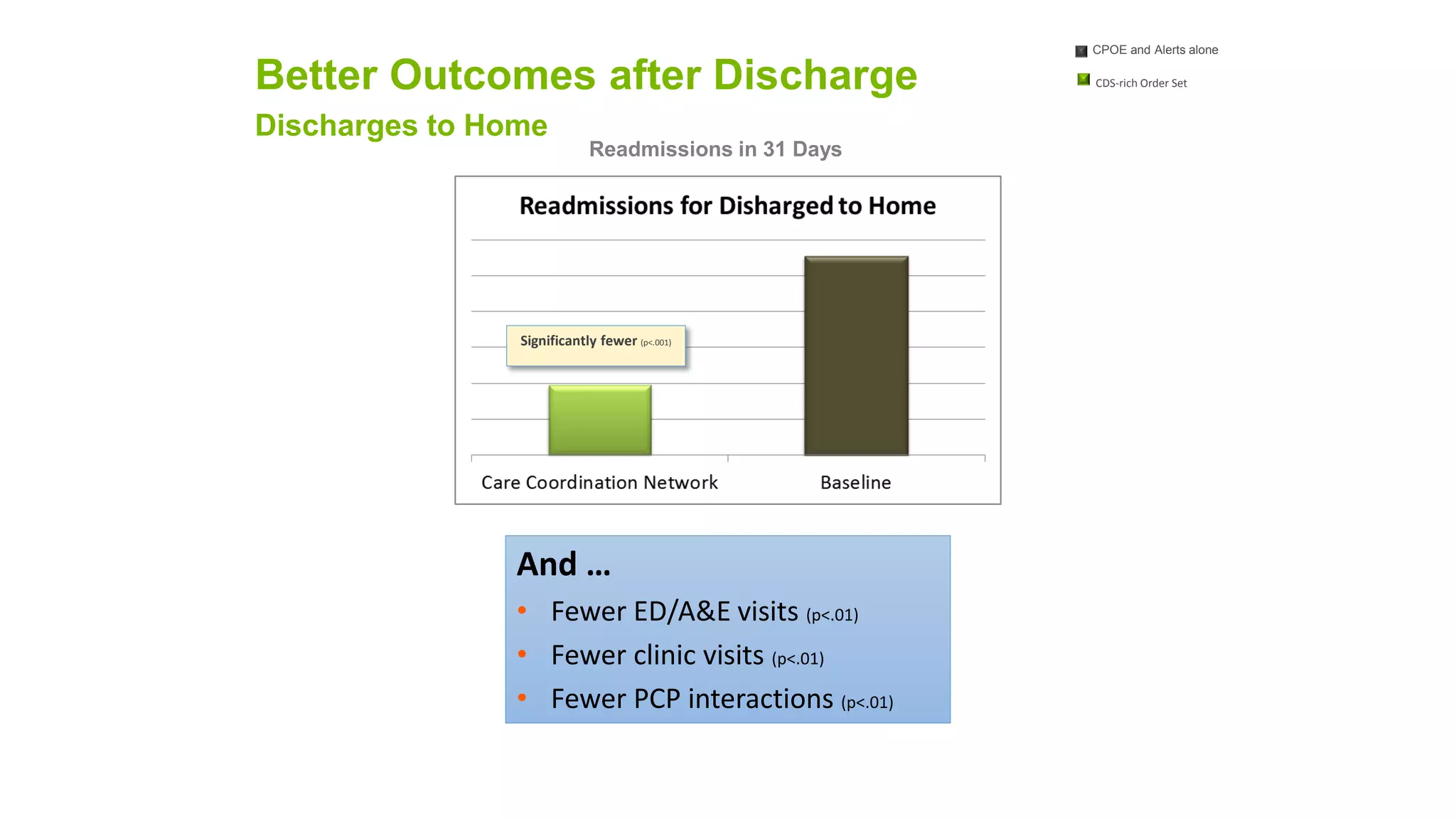
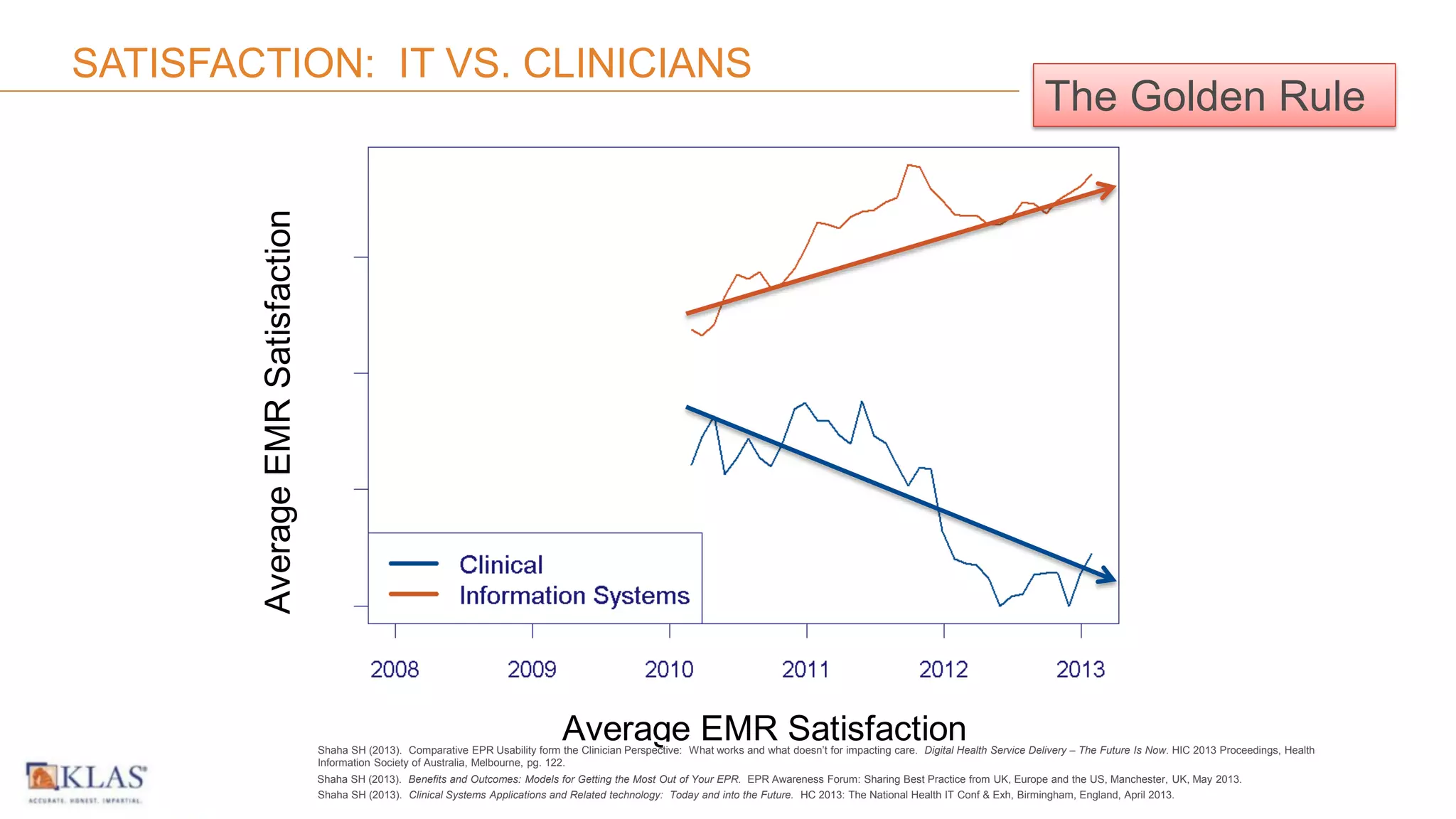
This document summarizes the background and work of Prof. Steven H. Shaha, who has published over 100 peer-reviewed publications and presentations on using analytics and clinical decision support systems to improve healthcare quality and outcomes. Some key points discussed include using analytics of electronic medical record data to reduce sepsis rates and length of ICU stays, developing alert systems to more quickly recognize and treat at-risk patients, and creating connected networks between healthcare providers to better monitor population health and improve outcomes for conditions like diabetes.