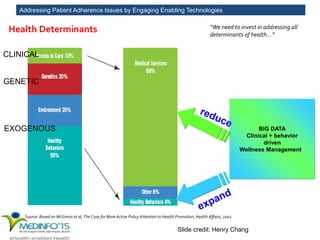
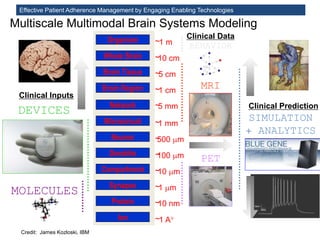
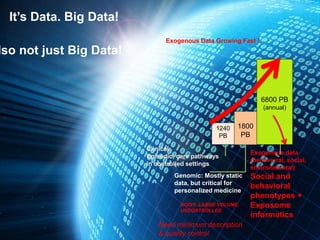
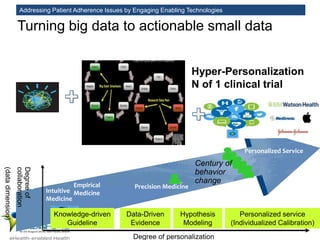
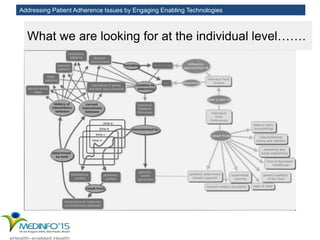
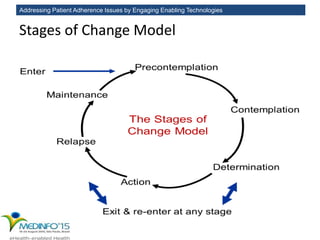
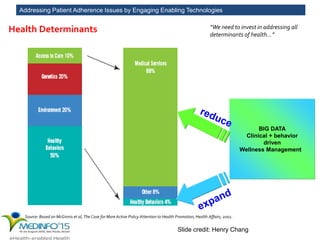
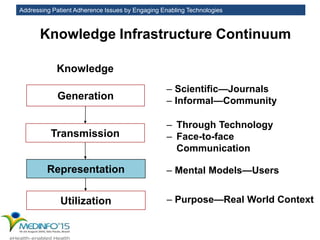
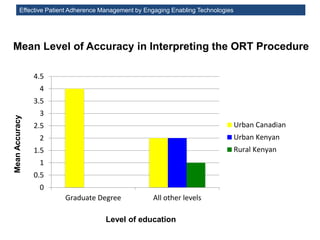
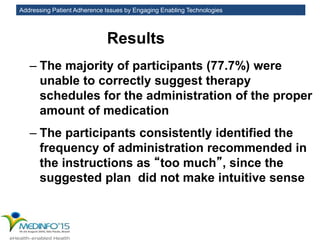
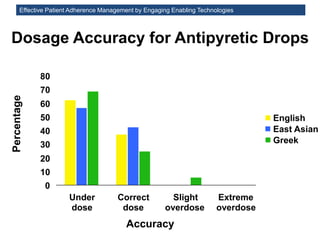
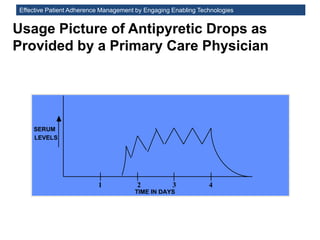
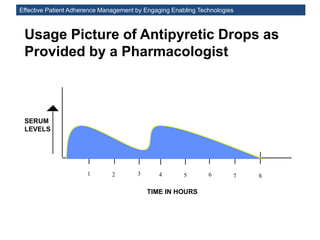
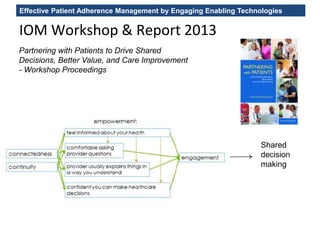
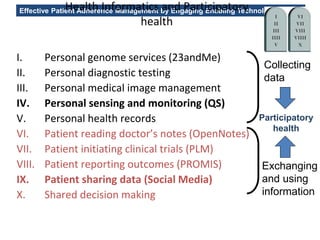
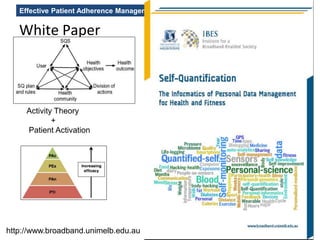
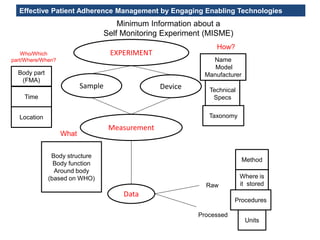
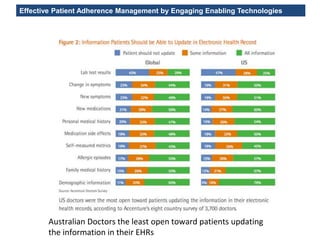
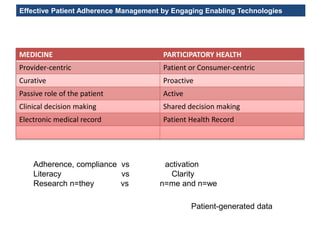
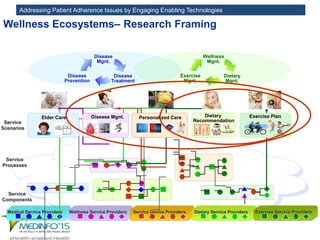
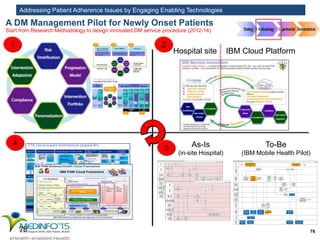
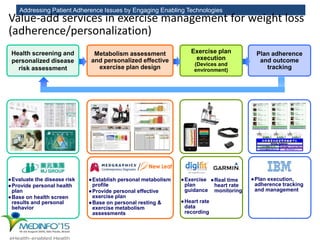
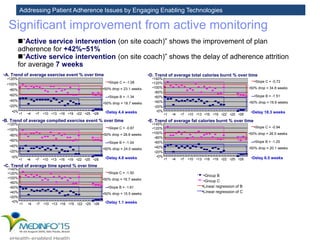
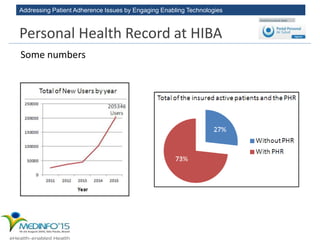
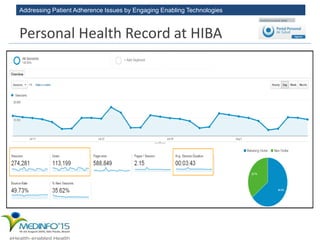
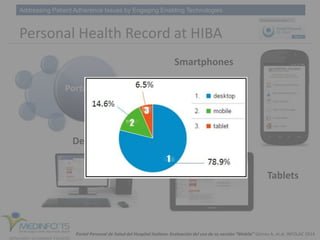
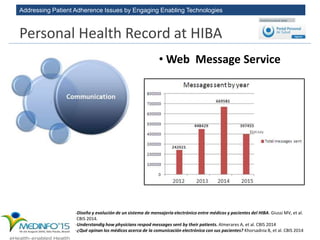
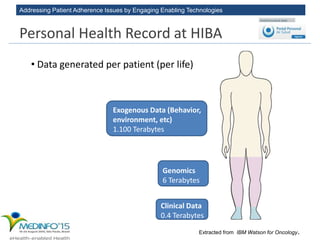
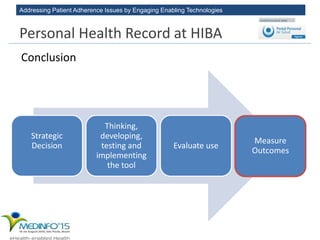
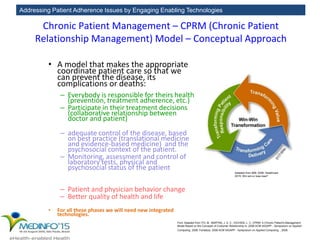
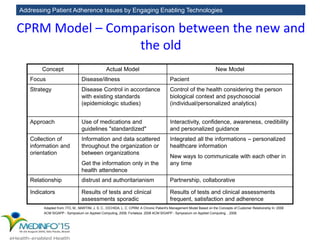
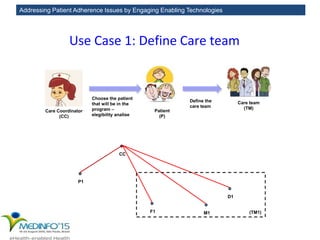
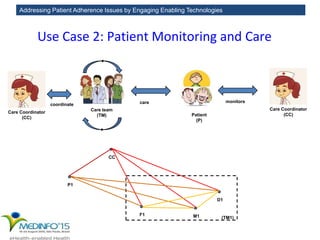
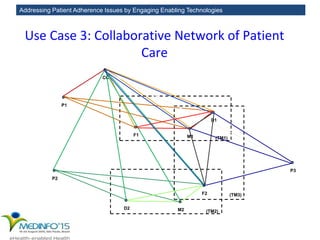
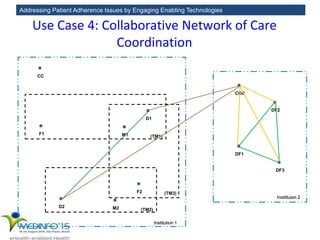
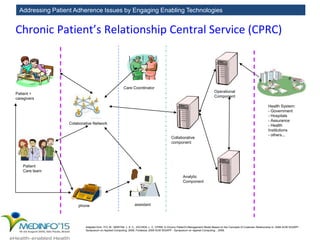
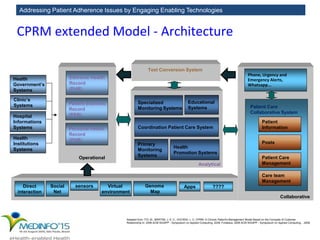
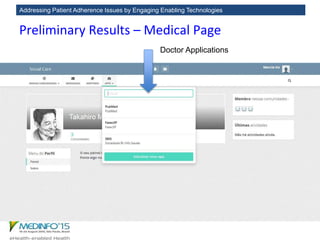
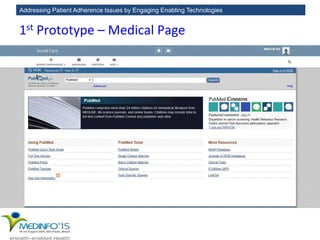
The MedInfo 2015 workshop addressed patient adherence issues through innovative technologies, emphasizing the transition from big data to small, actionable patient-generated data. Presentations covered topics such as technology support for adherence, patient-generated data standards, and chronic adherence management models. Key challenges discussed included the lack of reliable data capture and the need for personalized feedback mechanisms to improve patient engagement and adherence outcomes.