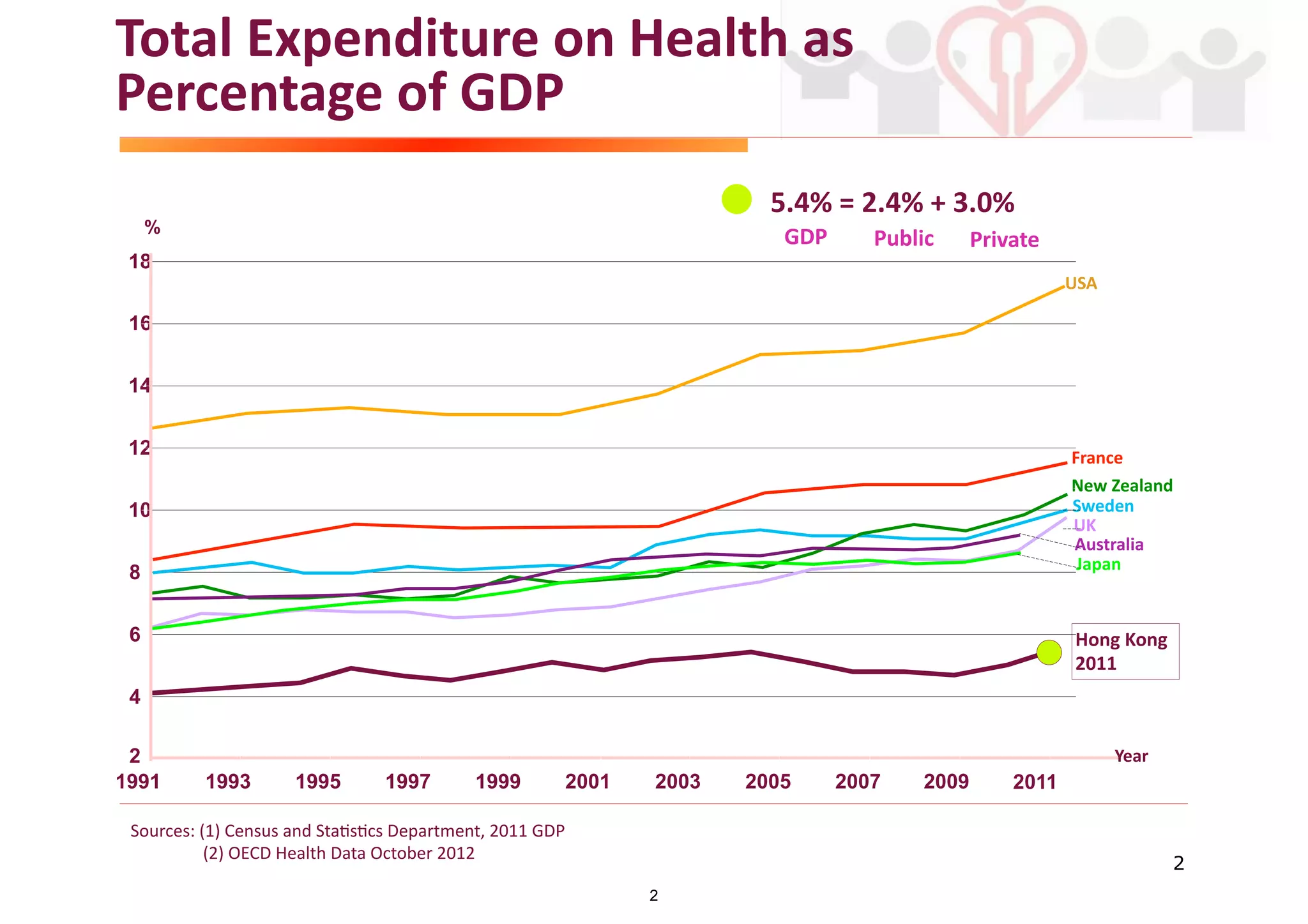
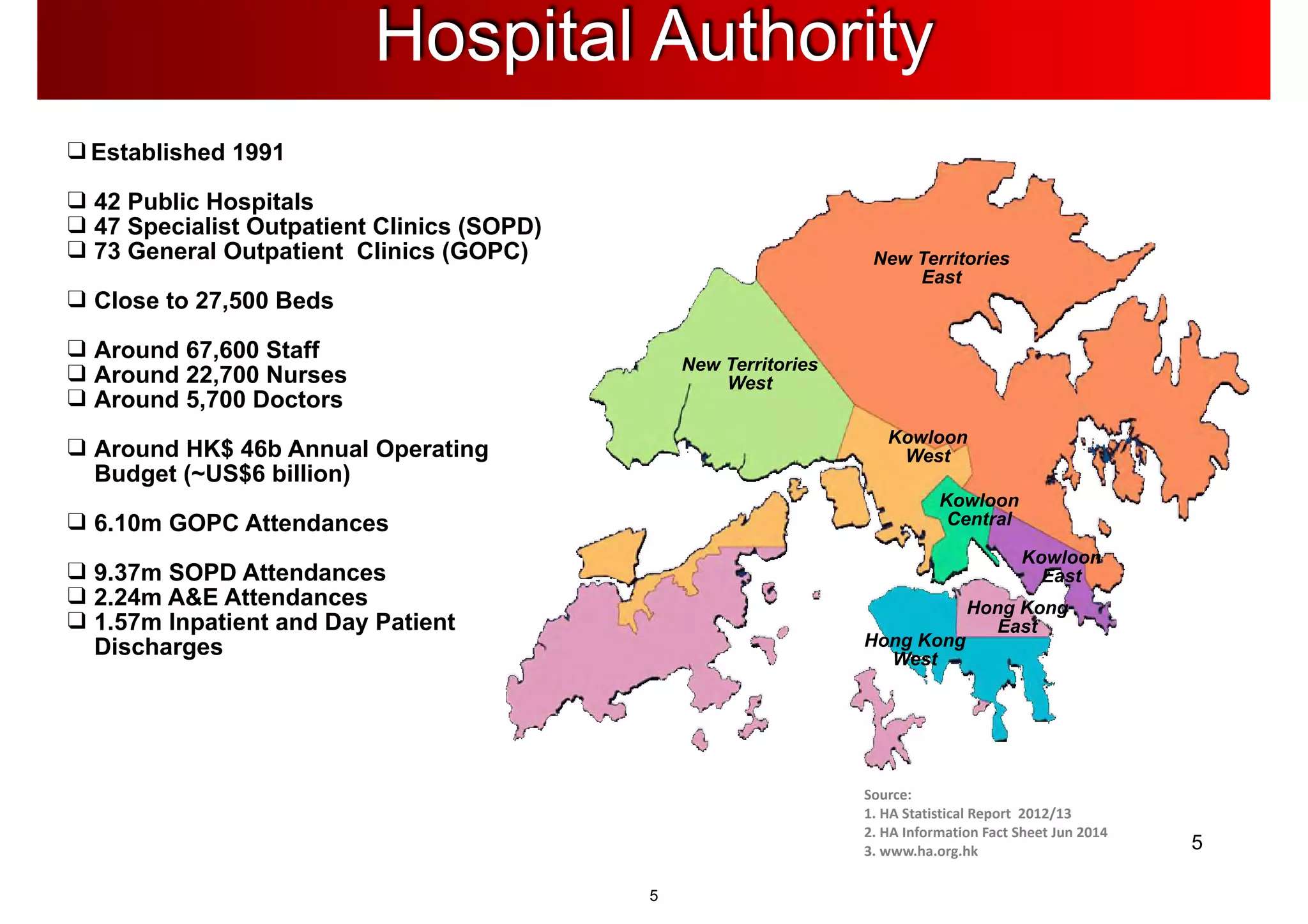
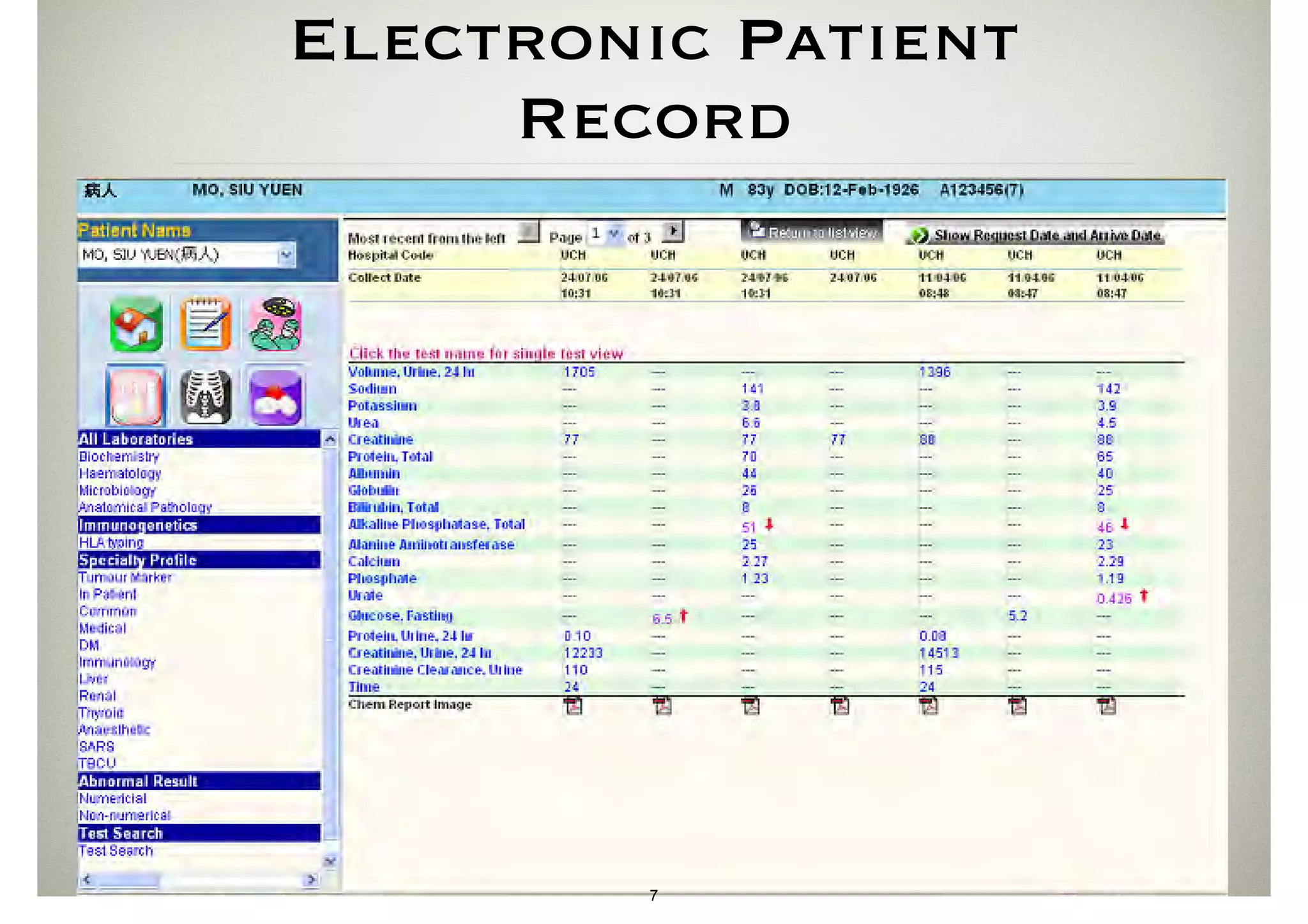
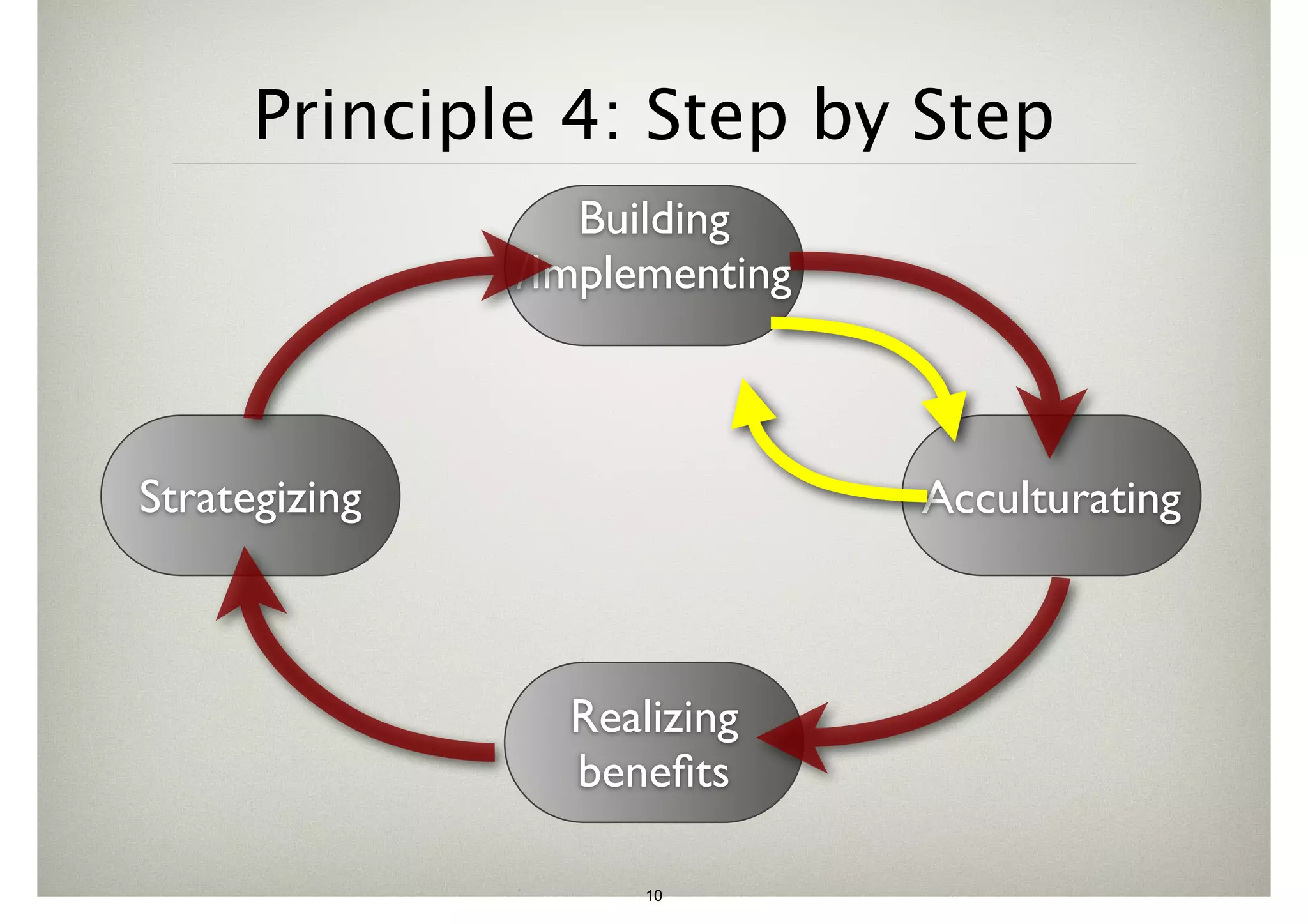
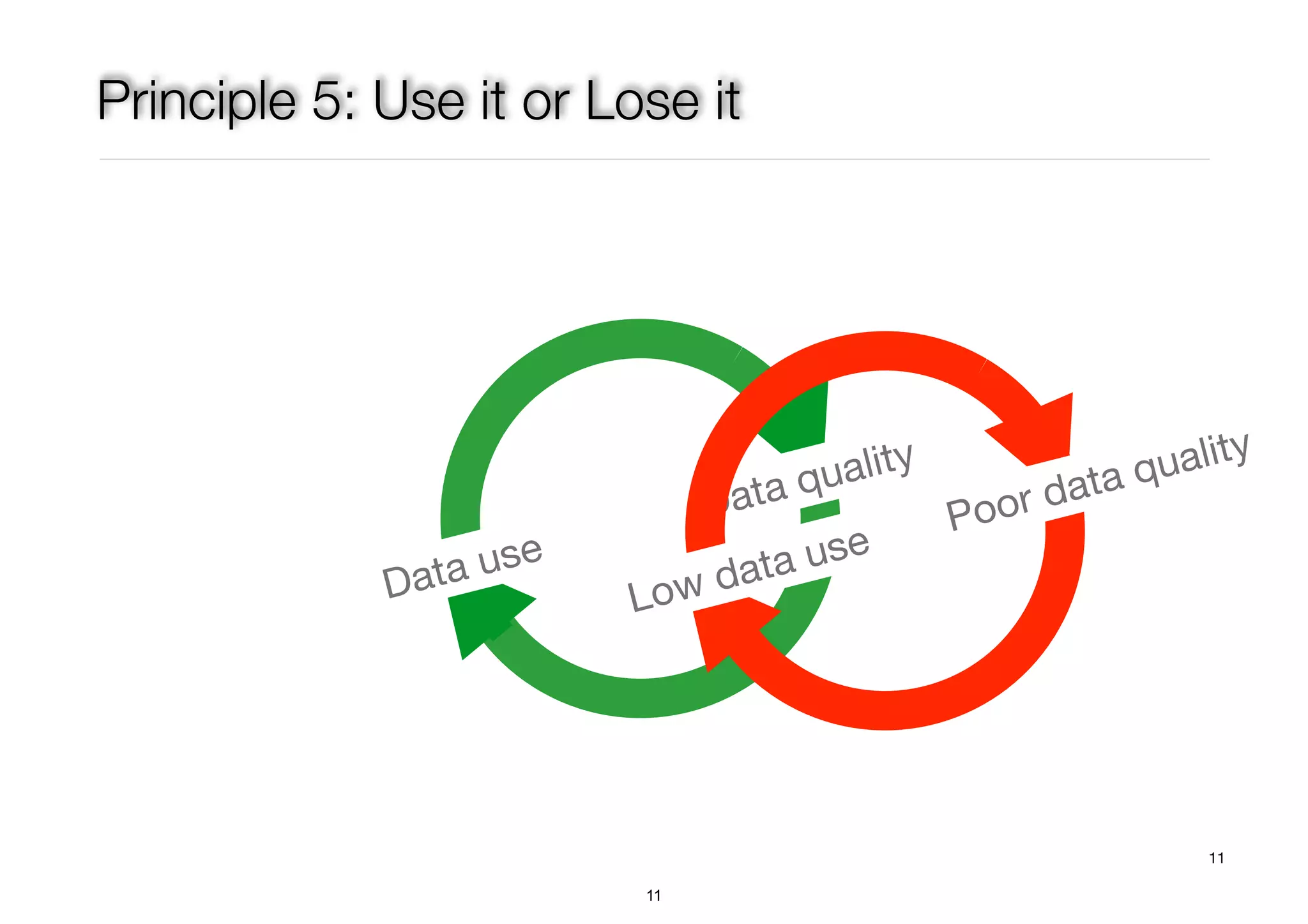
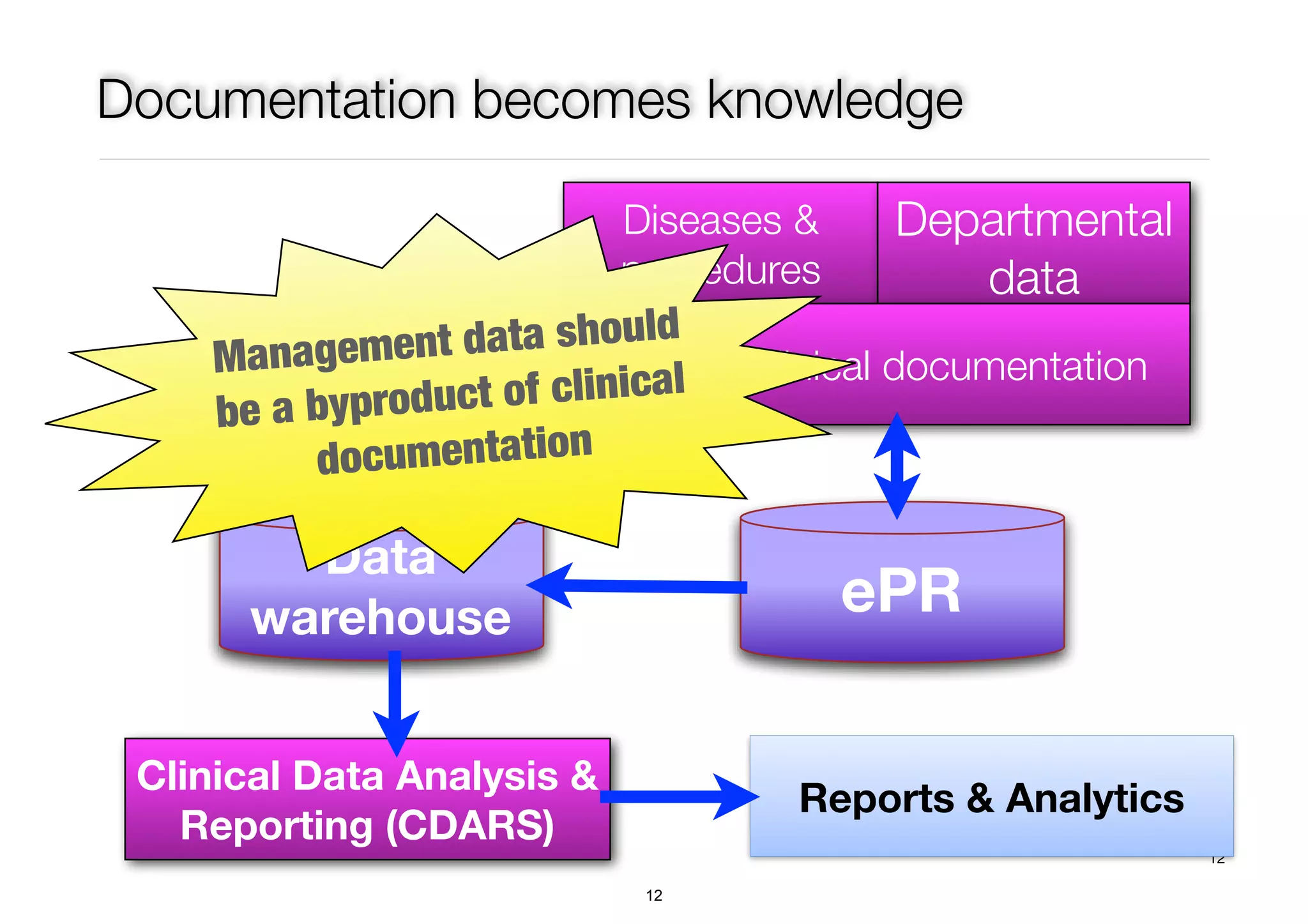
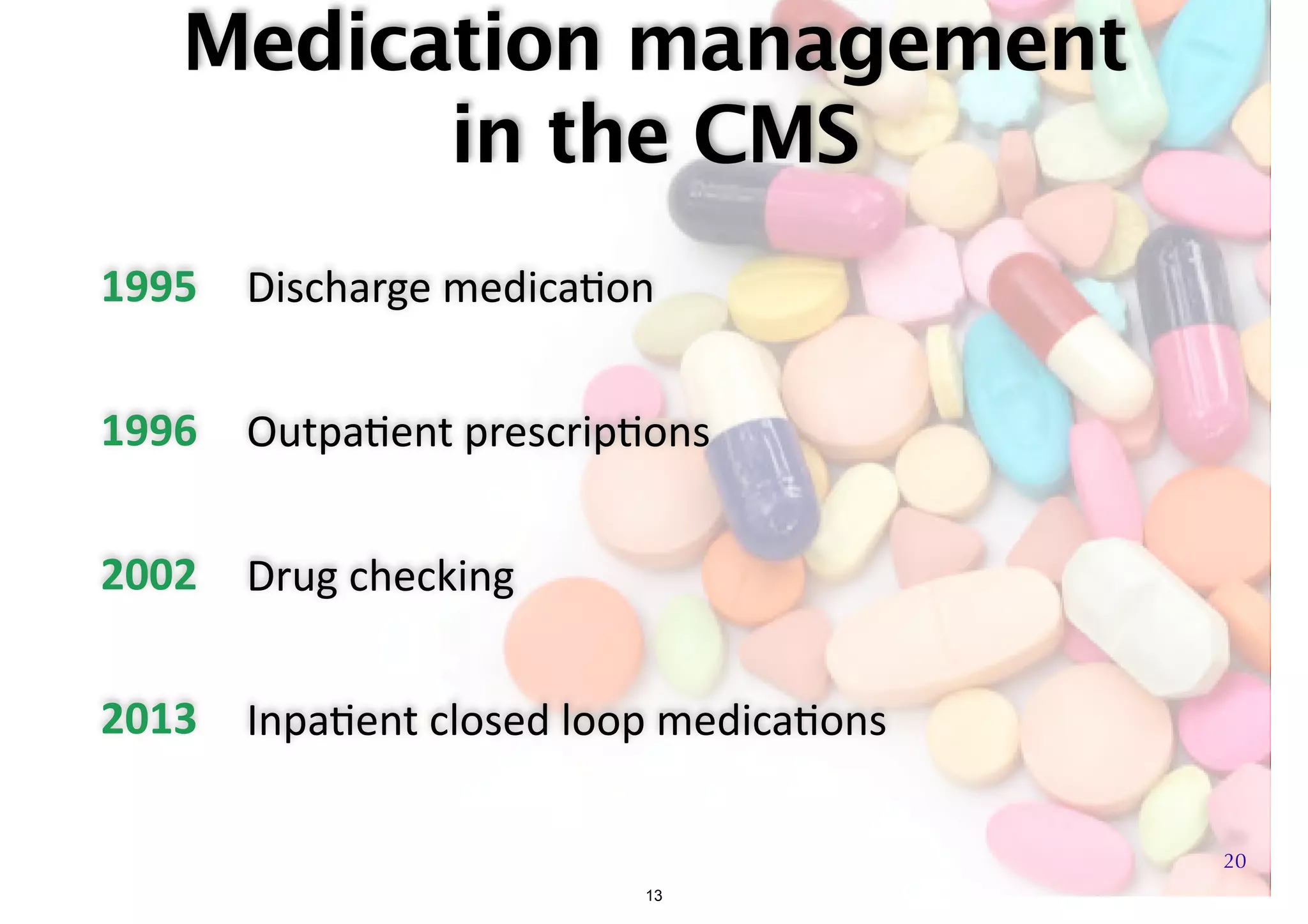
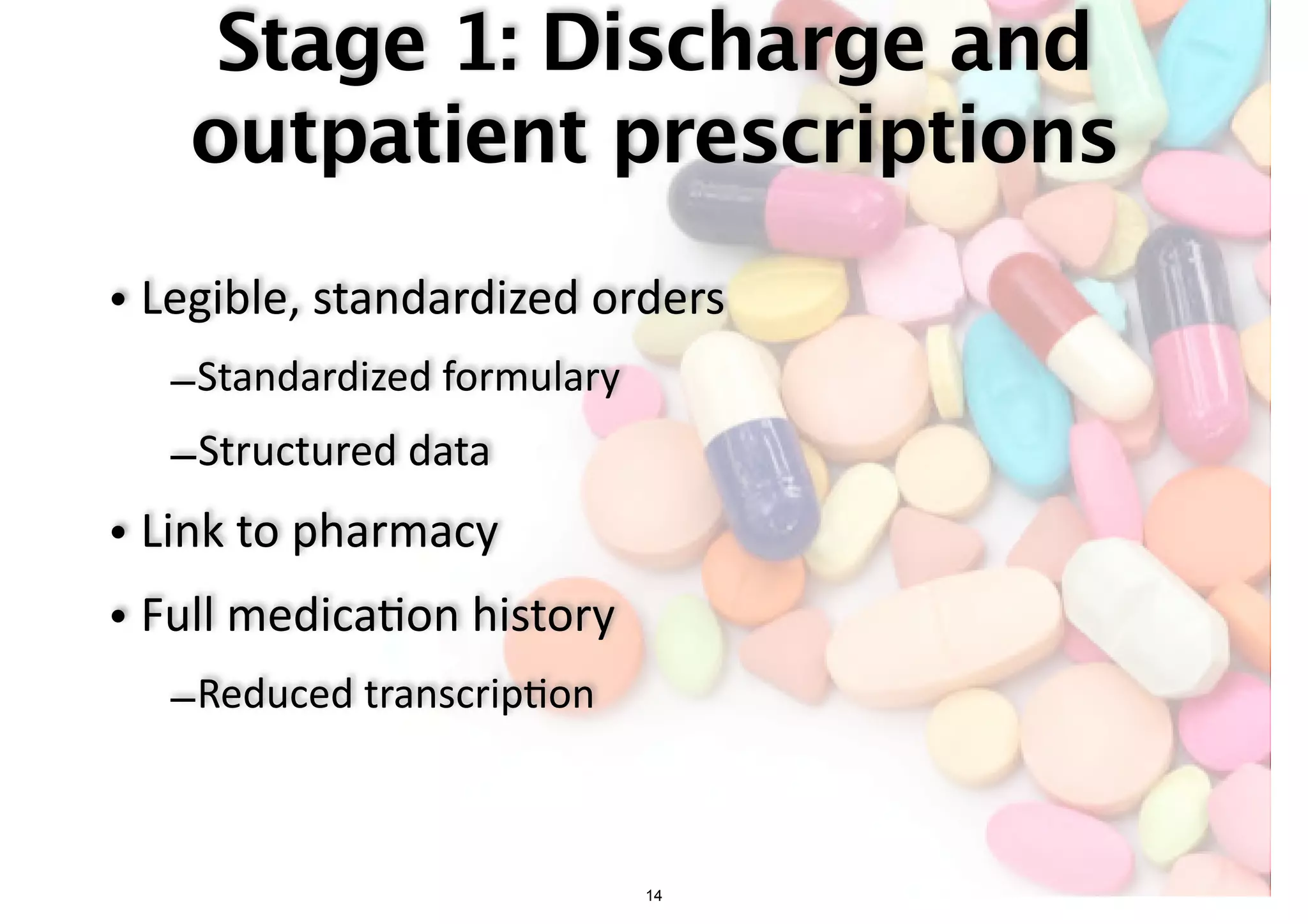
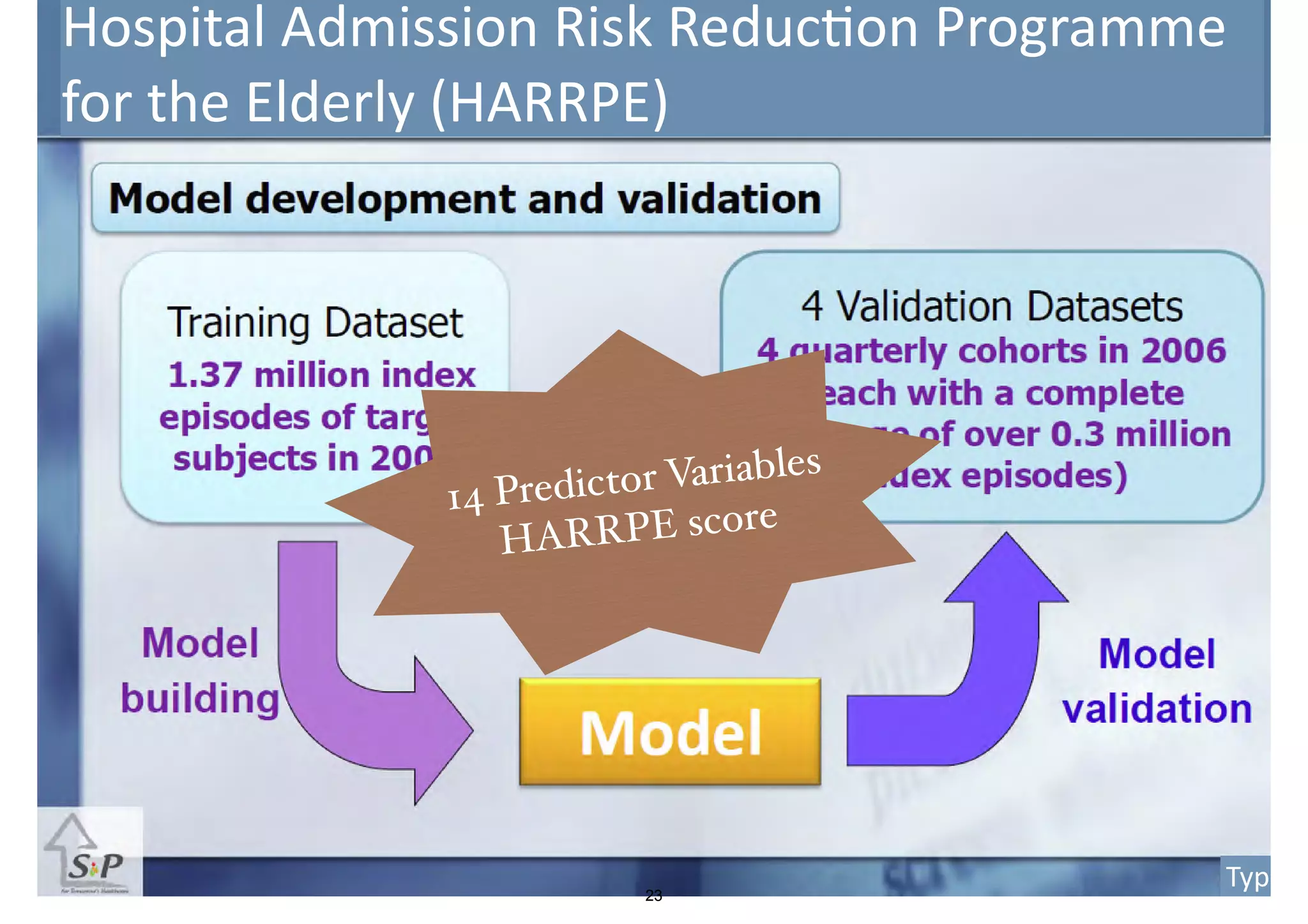
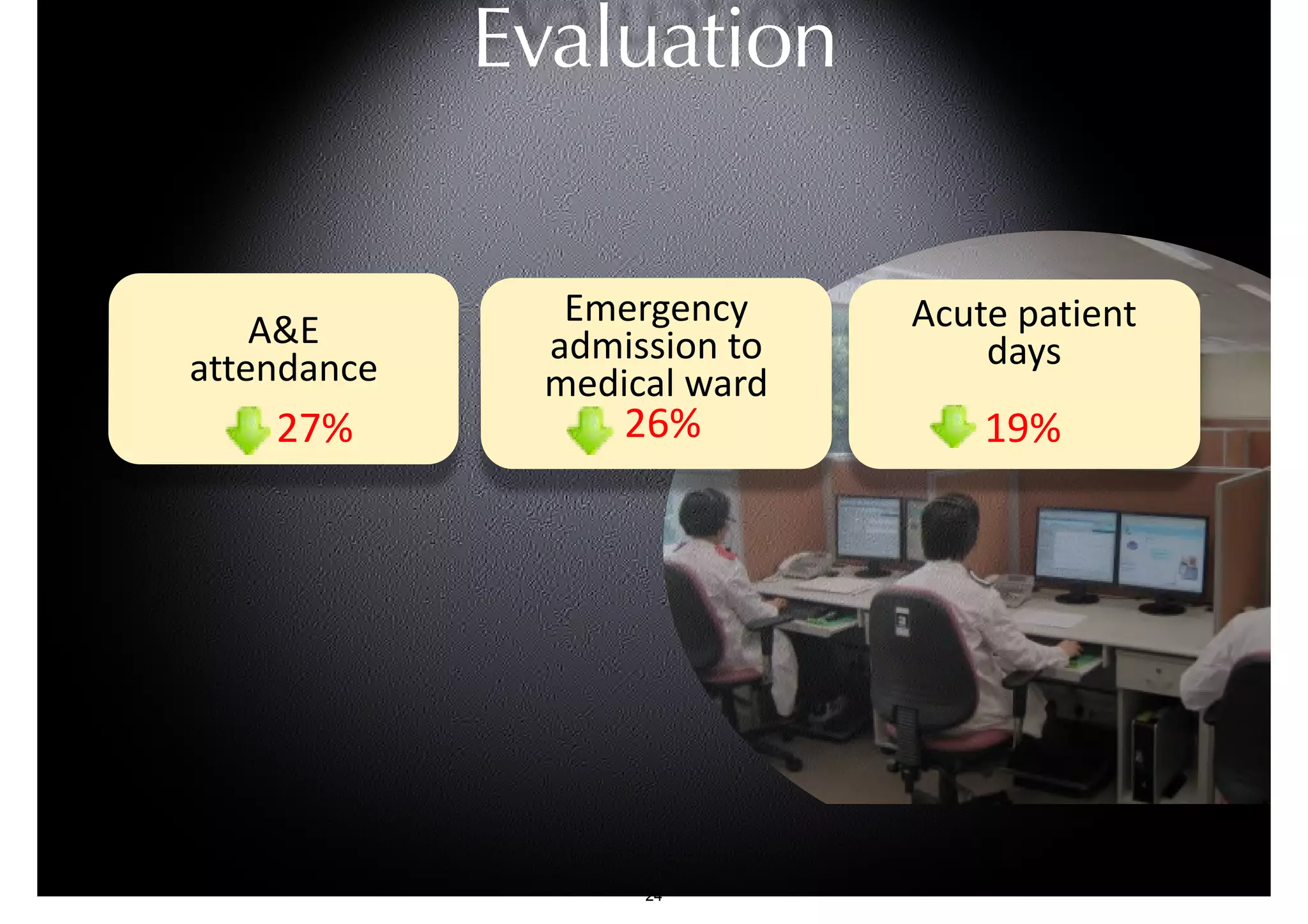
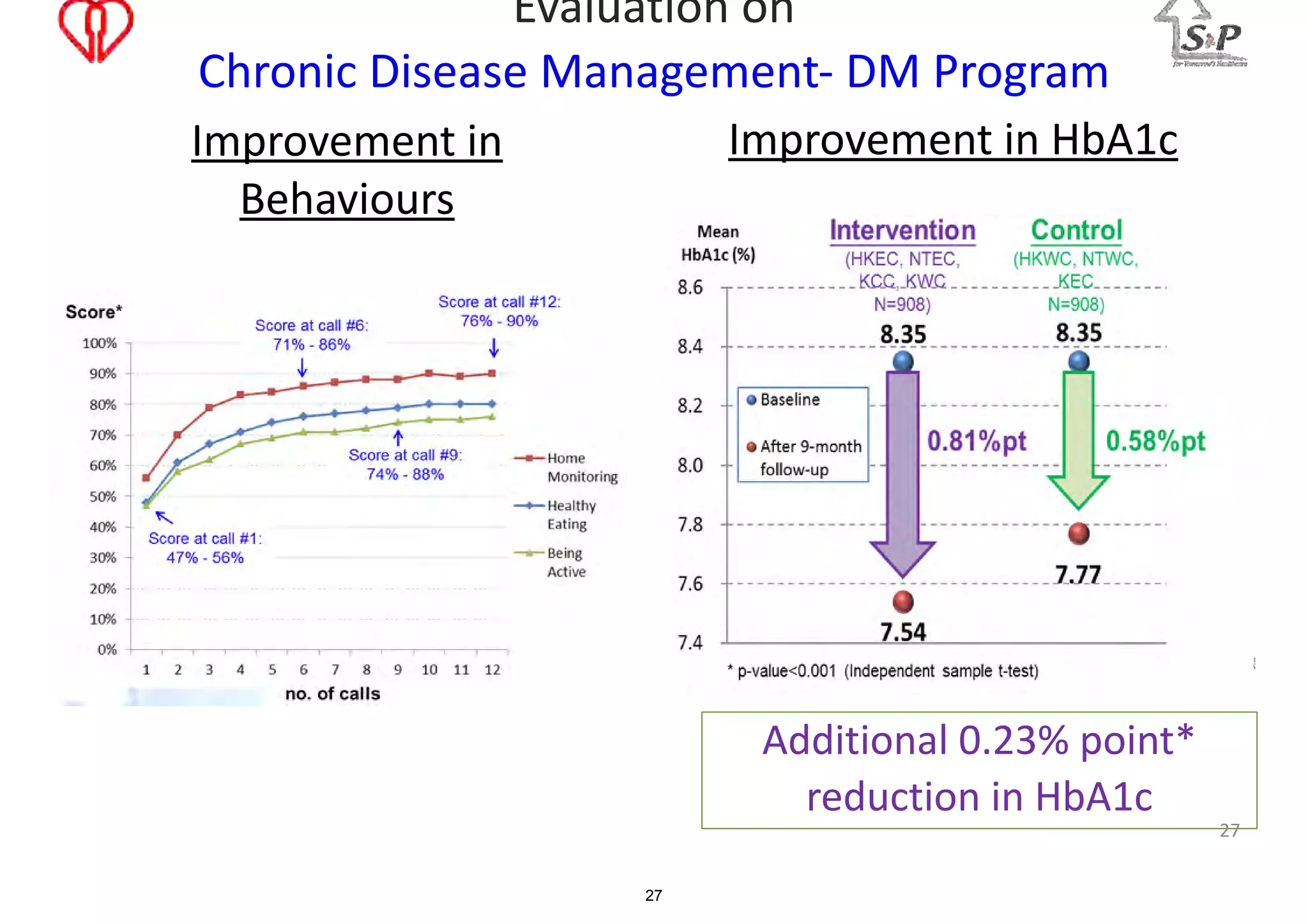
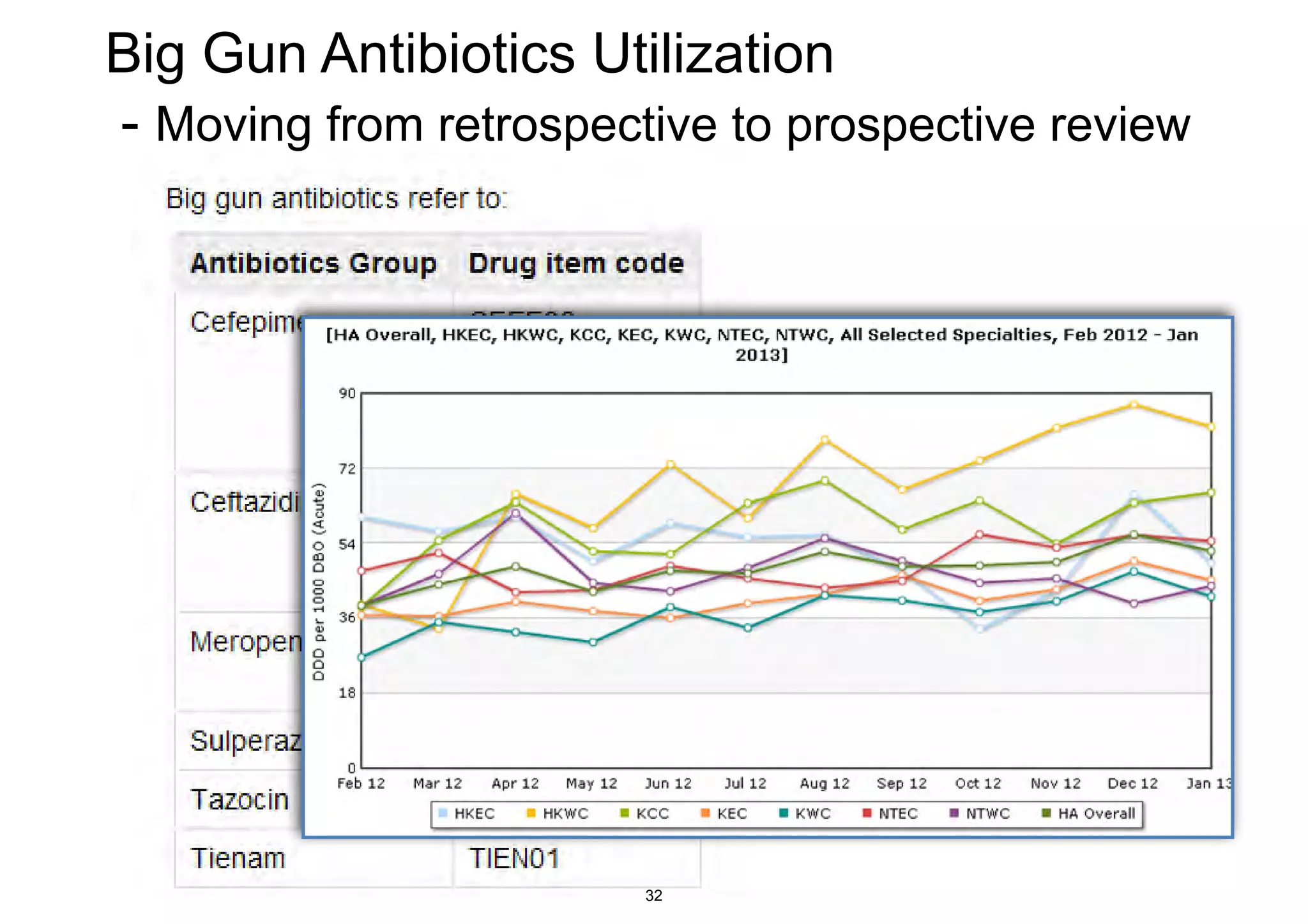
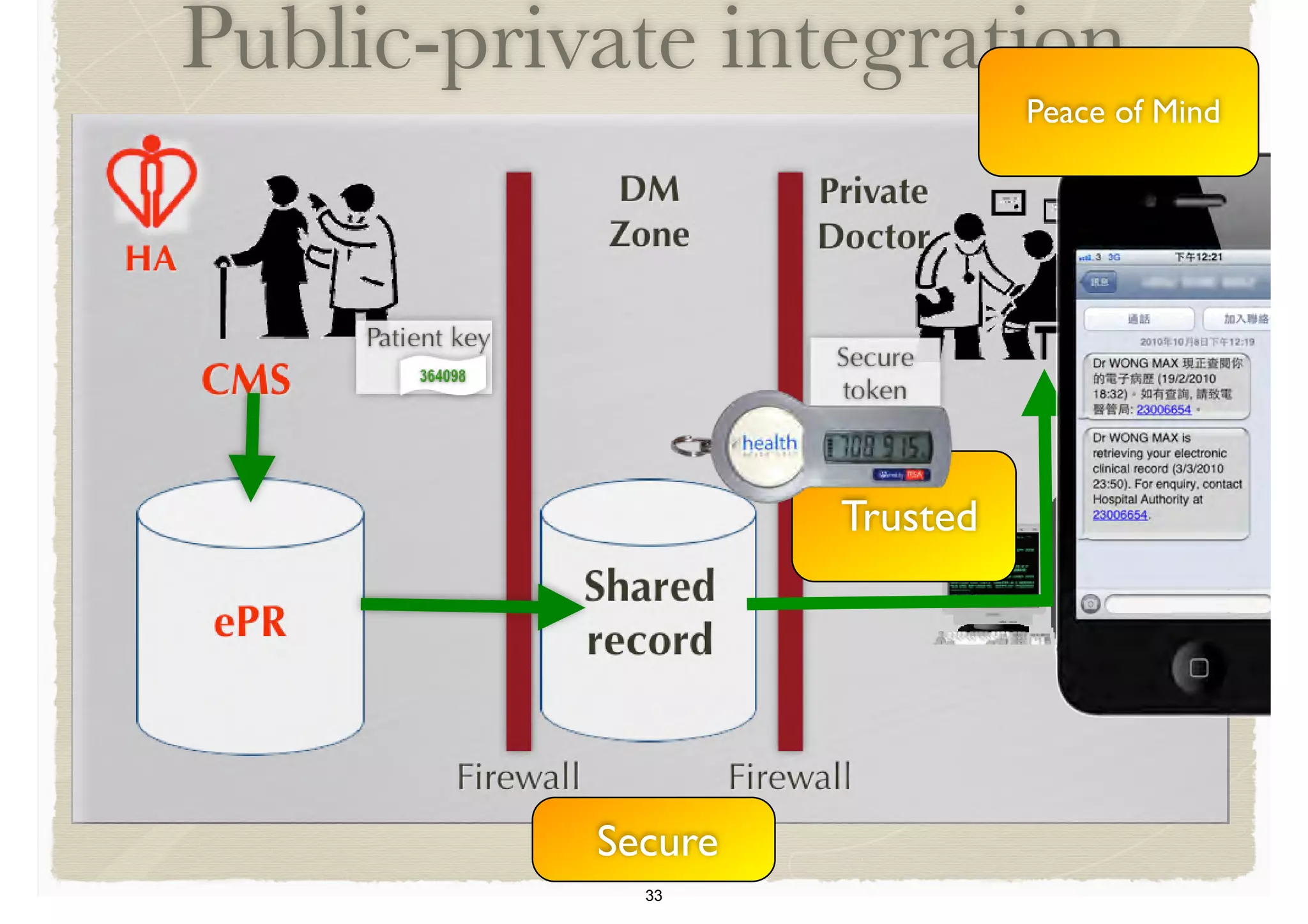
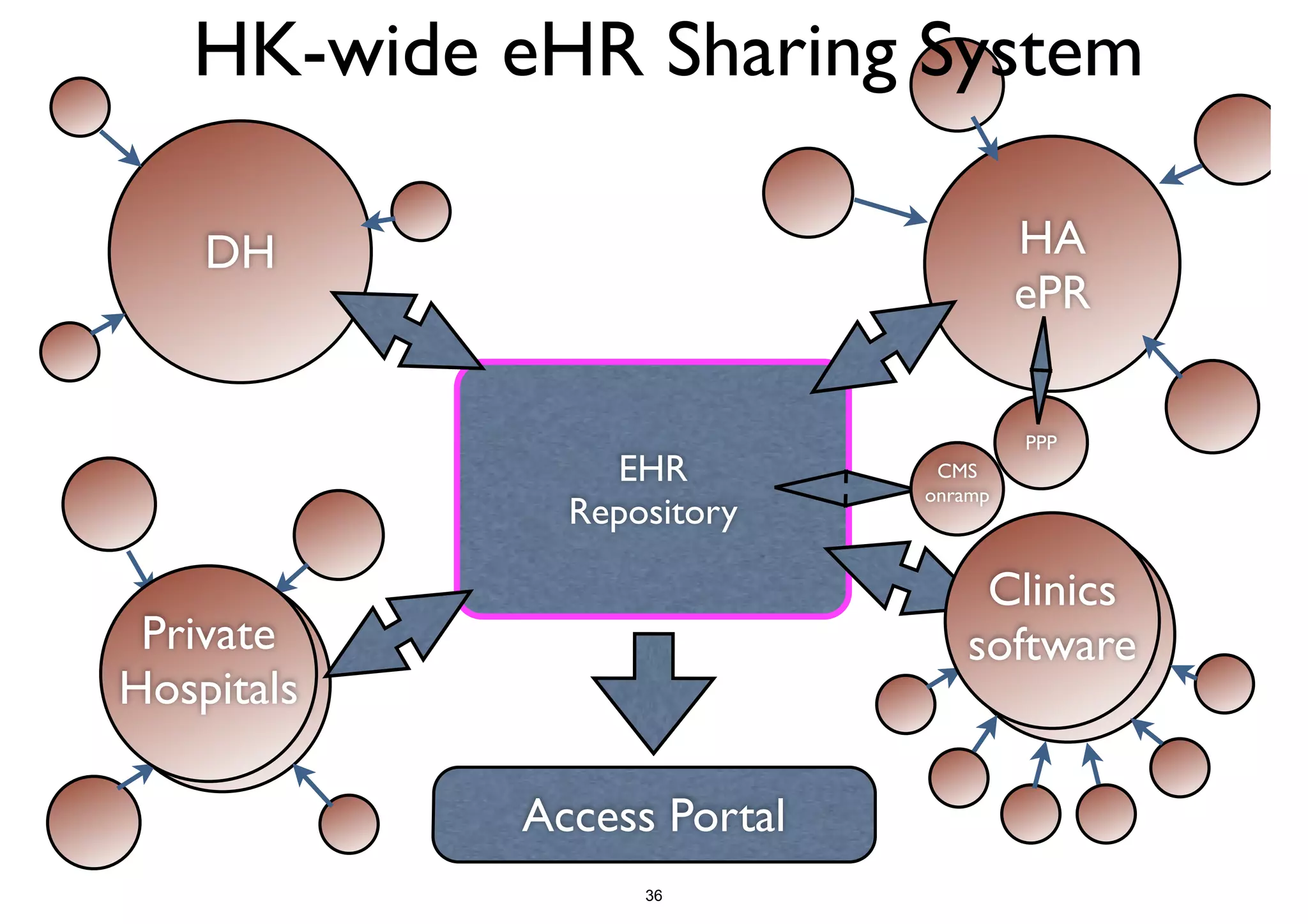
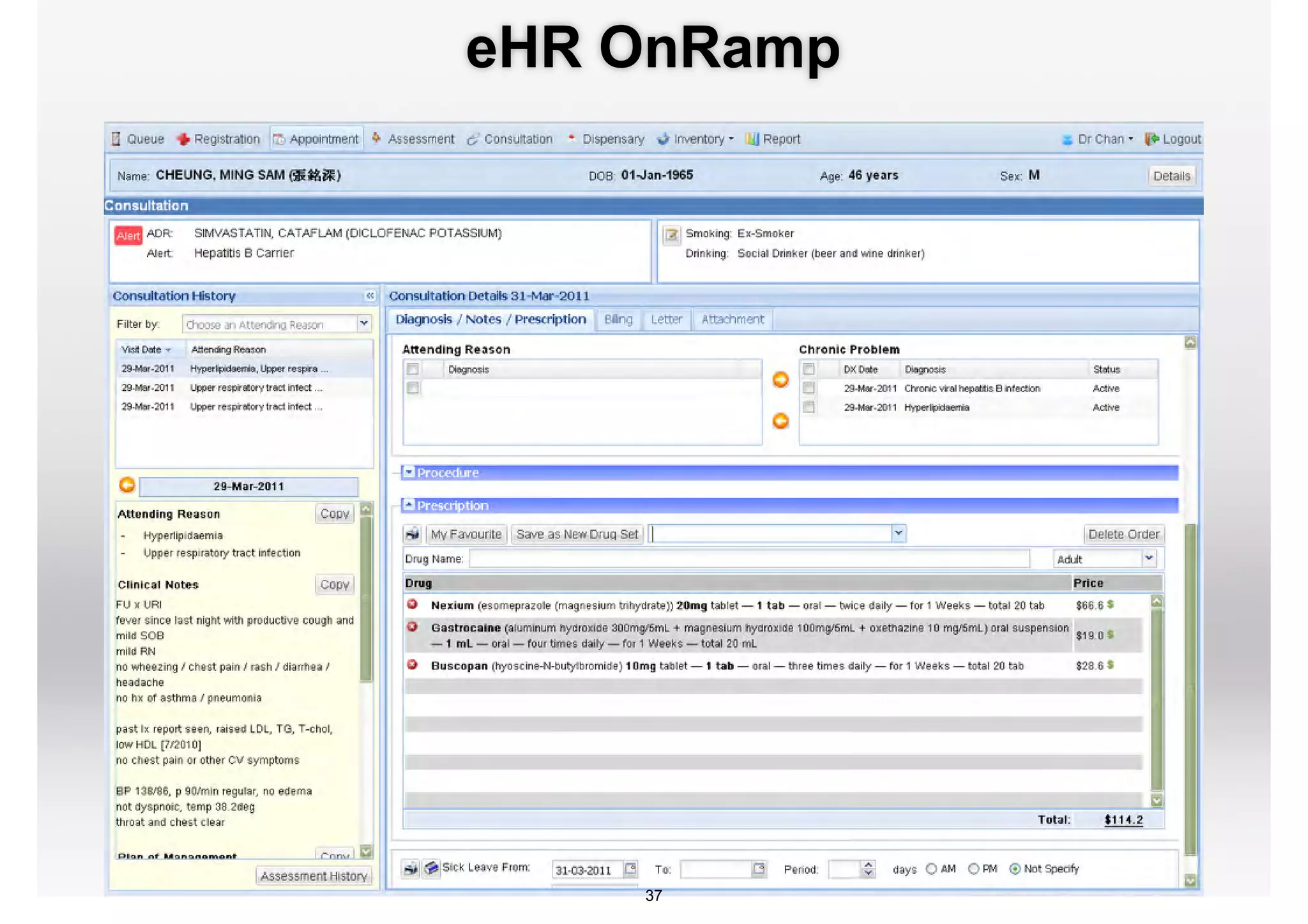
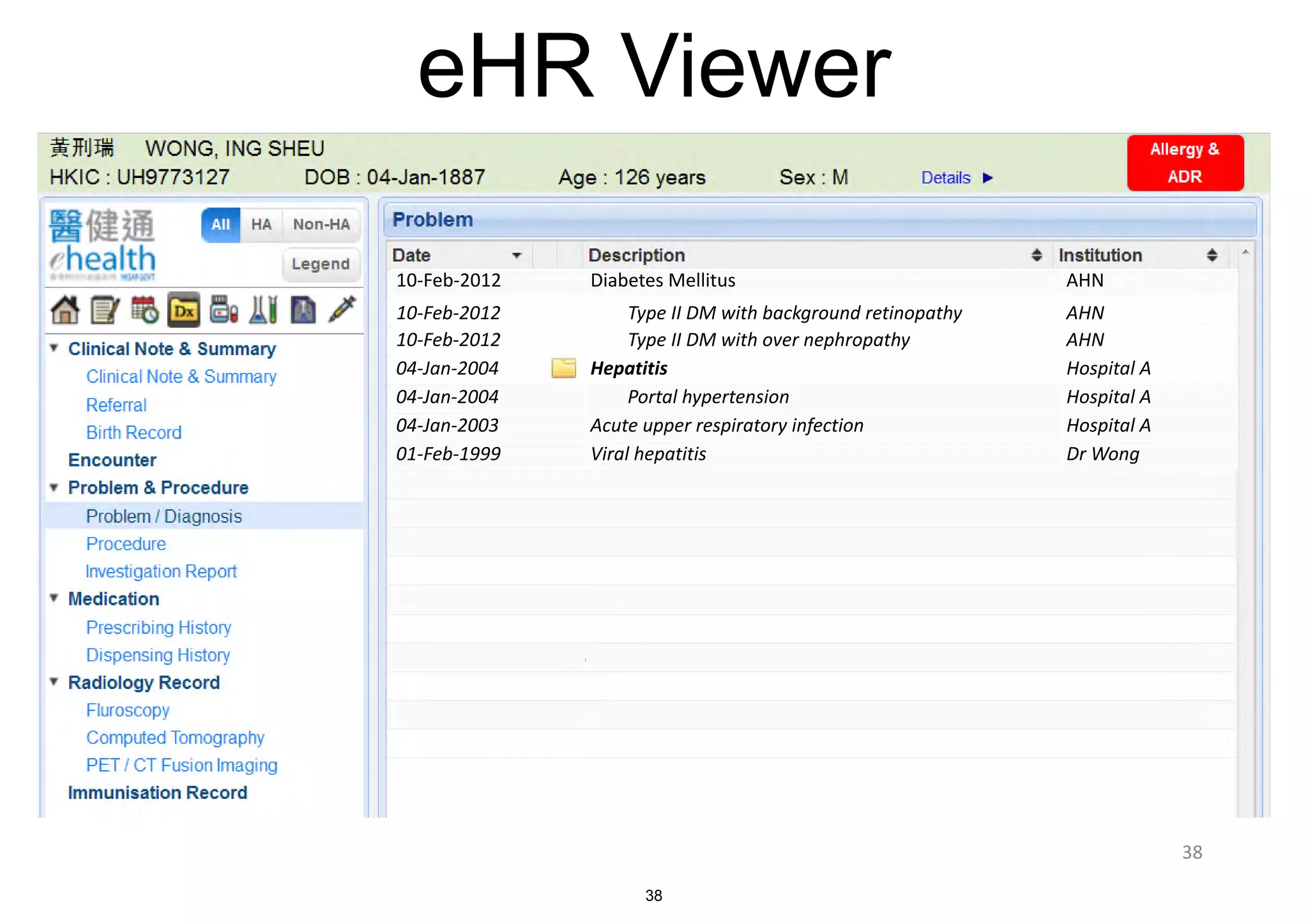
The document discusses the advancements in health informatics in Hong Kong, emphasizing the establishment of a standardized eHealth system aimed at improving healthcare delivery efficiency and safety. With a focus on data management and patient safety, the system has led to significant operational improvements and cost savings in healthcare services. It also highlights the ongoing development of integrated electronic health records and the impact of health informatics on chronic disease management and patient intake processes.