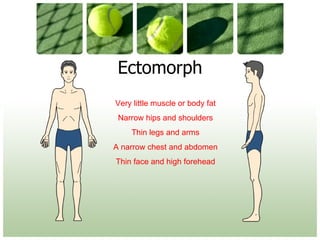
This document discusses different body types (somatotypes) and how they relate to sports performance. It describes the three main somatotypes - endomorph, mesomorph, and ectomorph - based on levels of fatness, muscularity, and thinness. Students learn to assess their own somatotype and understand how different body types are suited to certain sports positions. Key factors that influence an individual's optimum weight for sports are also outlined.