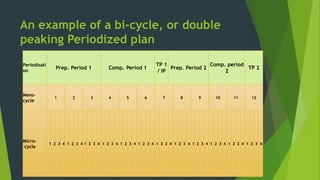
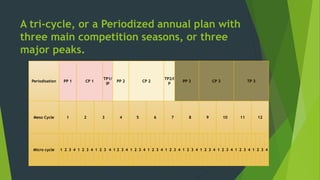
The document discusses periodization in sports training, which is the strategic distribution of training cycles to optimize athlete performance for competitions. It outlines three types of periodization: single, double, and triple, each designed for different levels of athletes and specific sports. Additionally, it details the aims and training contents of preparatory, competition, and transitional periods, emphasizing systematic development and regulation of training loads.