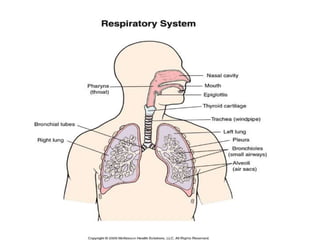
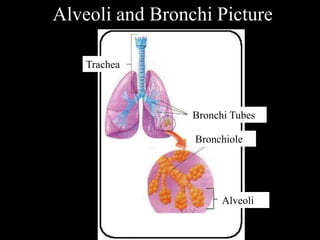
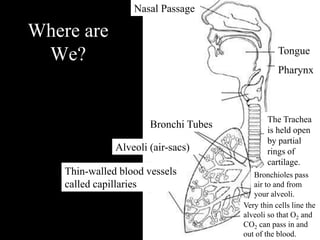
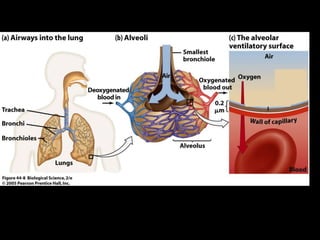
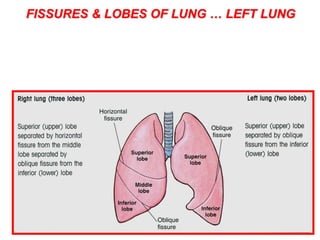
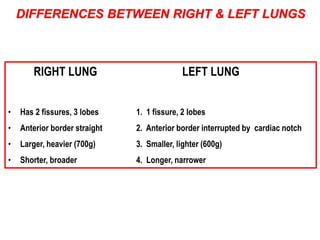
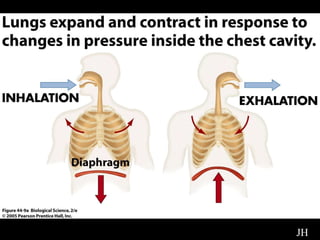
The respiratory system has several functions including gas exchange between air and blood in the lungs, moving air in and out of the lungs, and protecting the lungs from environmental factors. It is made up of the nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli. The larynx contains cartilages like the thyroid cartilage that form the walls of the larynx and connect to other structures. Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli where oxygen moves into the blood and carbon dioxide moves out.