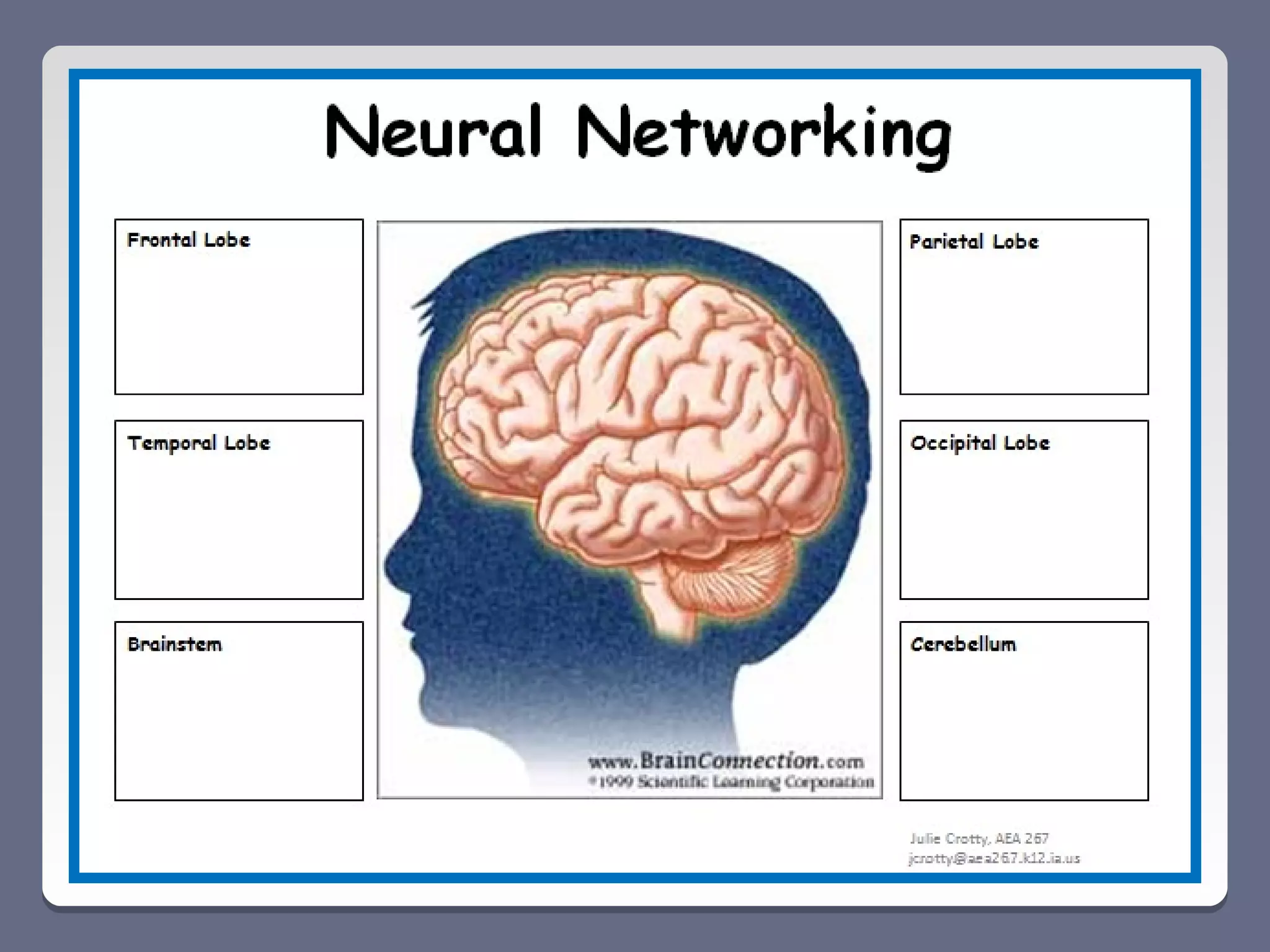
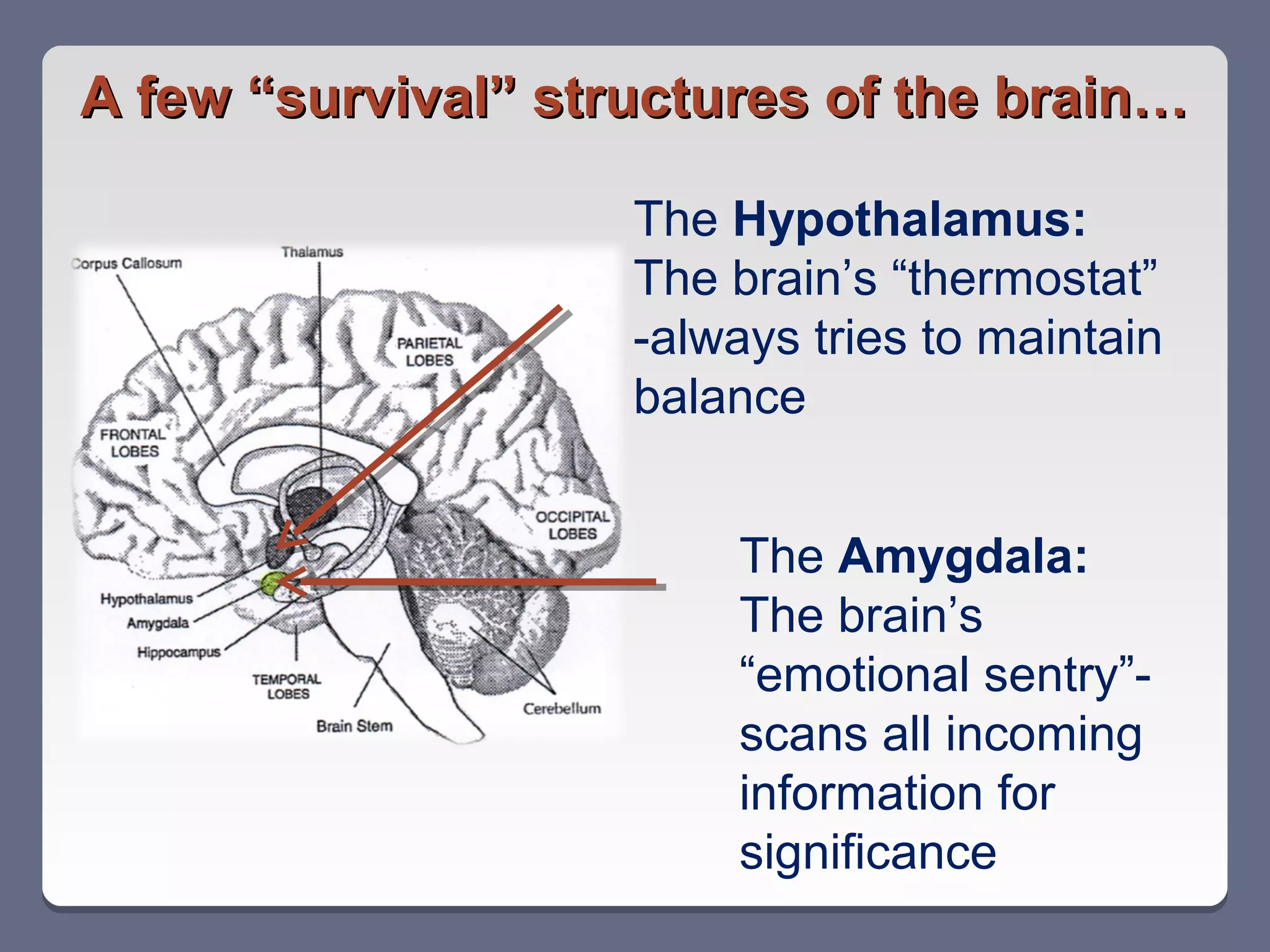
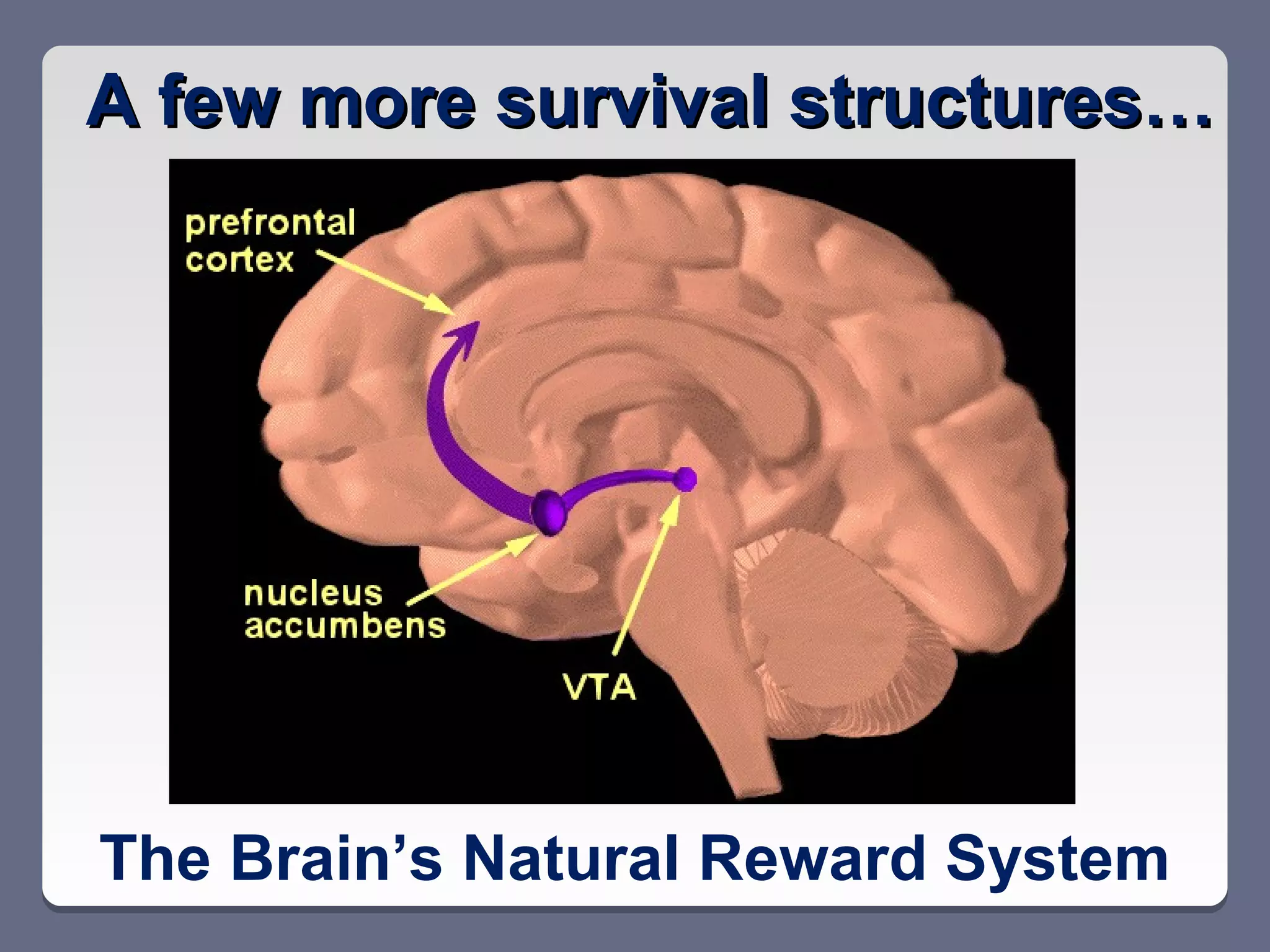
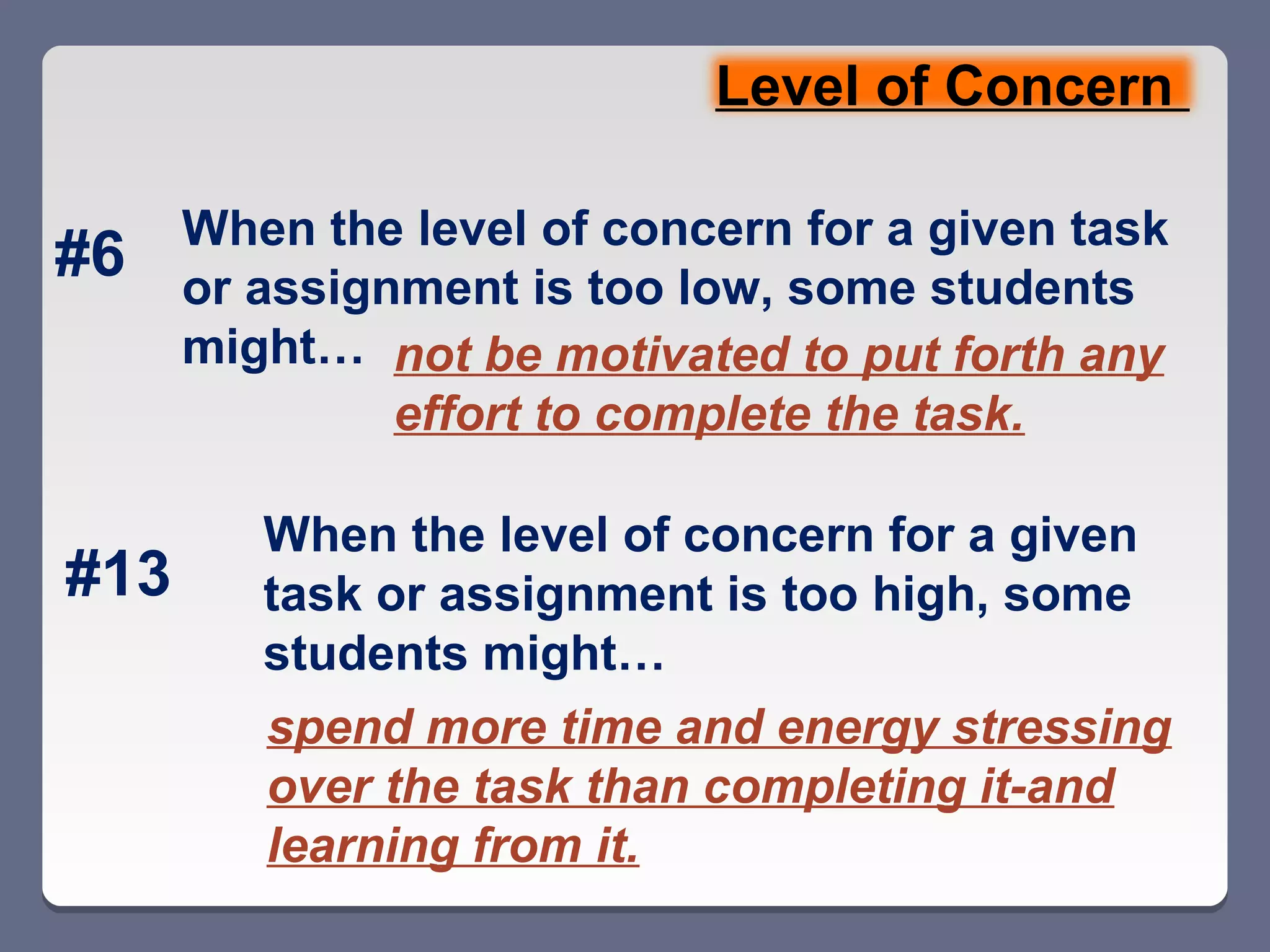
This document summarizes key points from a professional development session on brain-based learning and motivation for educators. It discusses how the brain's main functions are ensuring survival and how it has structures like the hypothalamus and amygdala that help maintain homeostasis and scan for threats. It also notes the brain's natural reward system and four basic psychological needs. The document then covers seven elements that impact student motivation, including chance for success, level of concern, intrinsic motivation, content relevance, collaboration, choice, and feedback. It provides examples of how each element can positively or negatively influence learning.