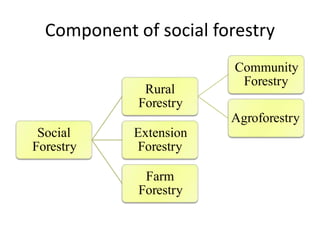
Social forestry aims to achieve environmental benefits and rural development through afforestation on barren lands. It involves managing and developing forests to meet the basic needs of rural populations like fuel, fodder, and manure. The objectives of social forestry in India are to increase forest area, restore ecological balance, meet rural needs, ensure better land use, generate employment, and check pollution. The components of social forestry include farm forestry, extension forestry, rural forestry, community forestry, and agroforestry.