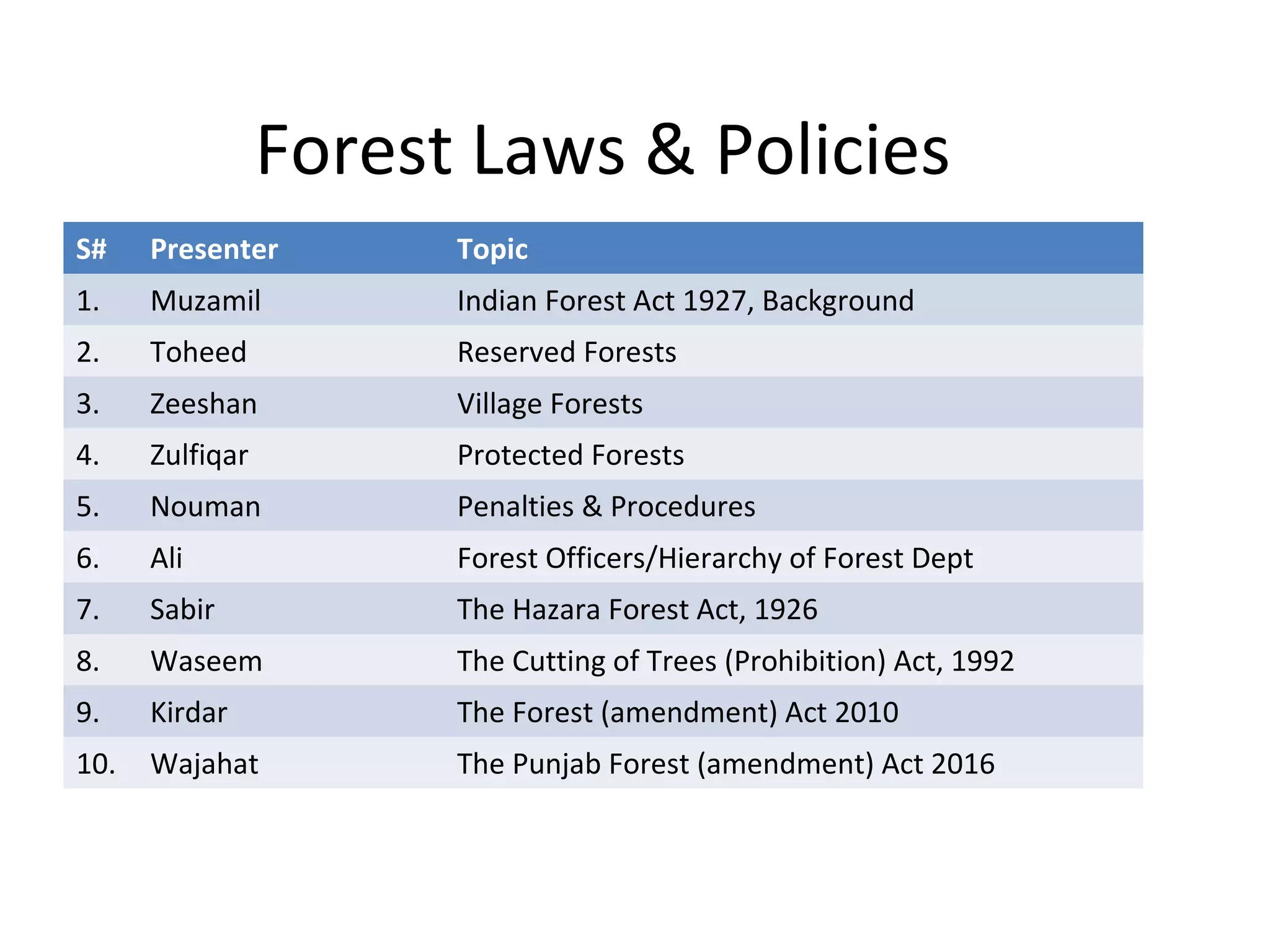
This document summarizes several forest laws and policies in Pakistan, including the Indian Forest Act 1927, the Hazara Forest Act 1926, the Cutting of Trees (Prohibition) Act 1992, the Forest (Amendment) Act 2010, and the Punjab Forest (Amendment) Act 2016. It outlines the key topics, sections, and responsibilities covered in each law/policy. For example, it notes that the Indian Forest Act consolidates rules around reserved forests, village forests, protected forests, penalties and forest officers. The Cutting of Trees Act prohibits tree cutting without approval and establishes penalties. The 2010 and 2016 Acts amended earlier acts to update terminology and allow for unclassed forests and forest companies.