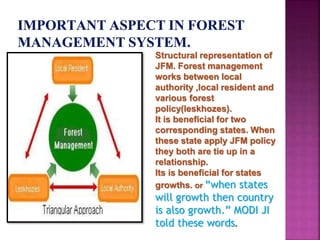
Joint forest management (JFM) involves village communities and state forest departments regenerating and conserving forests through contracts specifying shared authority, responsibilities, and benefits. Two early pilot experiments took place in the 1970s in West Bengal and Haryana. JFM projects now operate in Orissa, Himachal Pradesh, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, and Karnataka, providing employment and environmental benefits by increasing forest cover and biodiversity protection through community involvement.