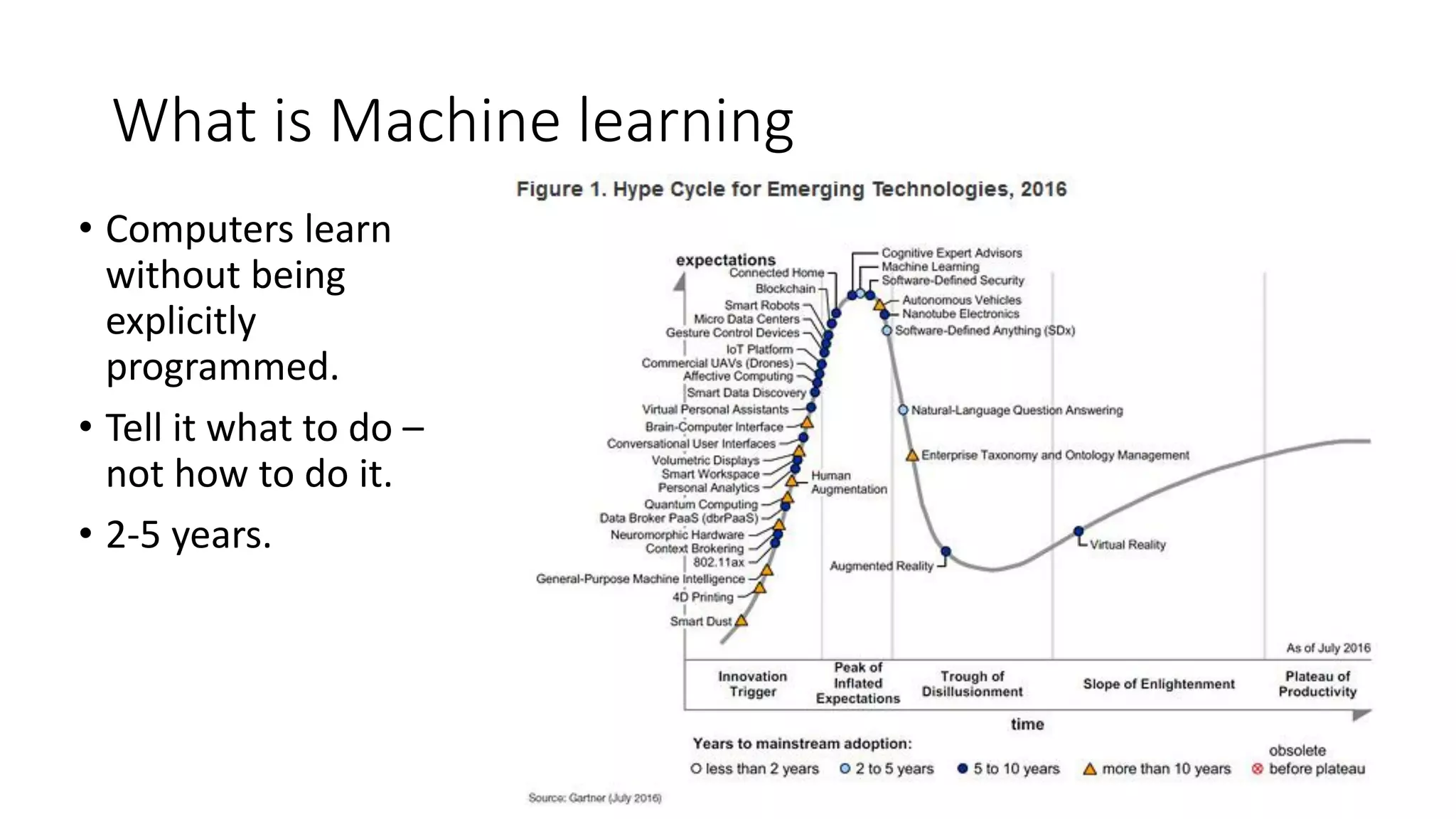
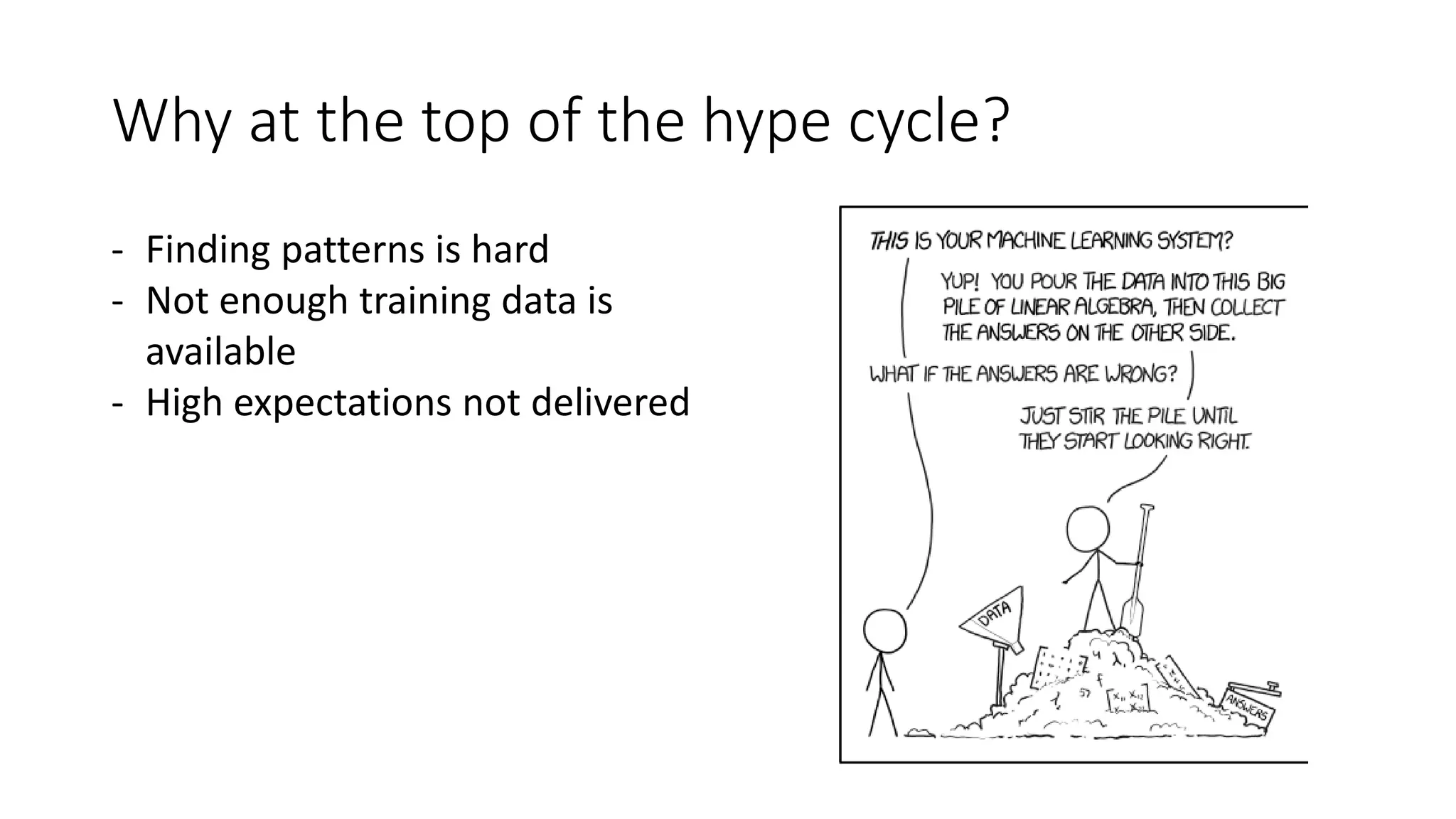
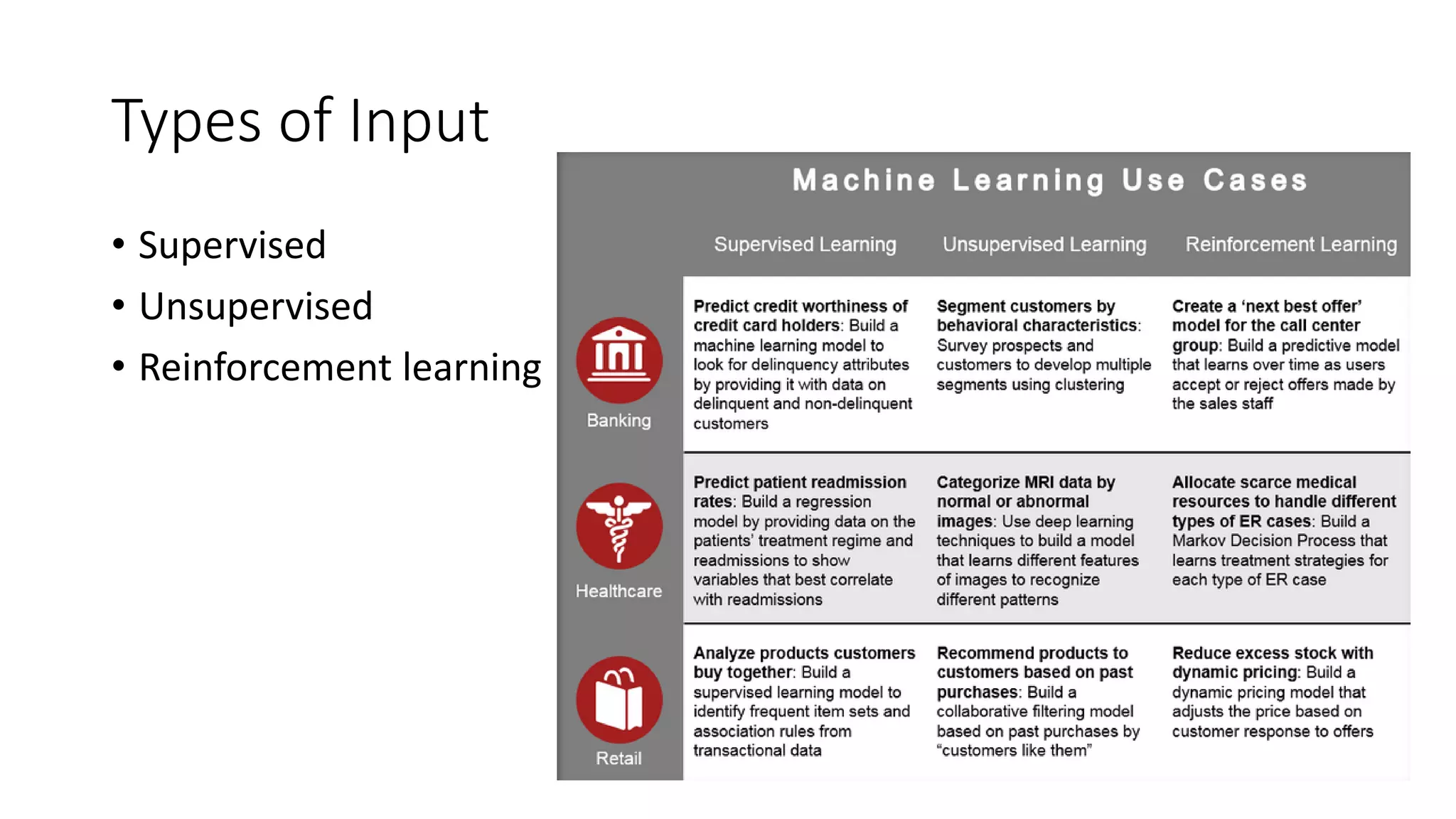
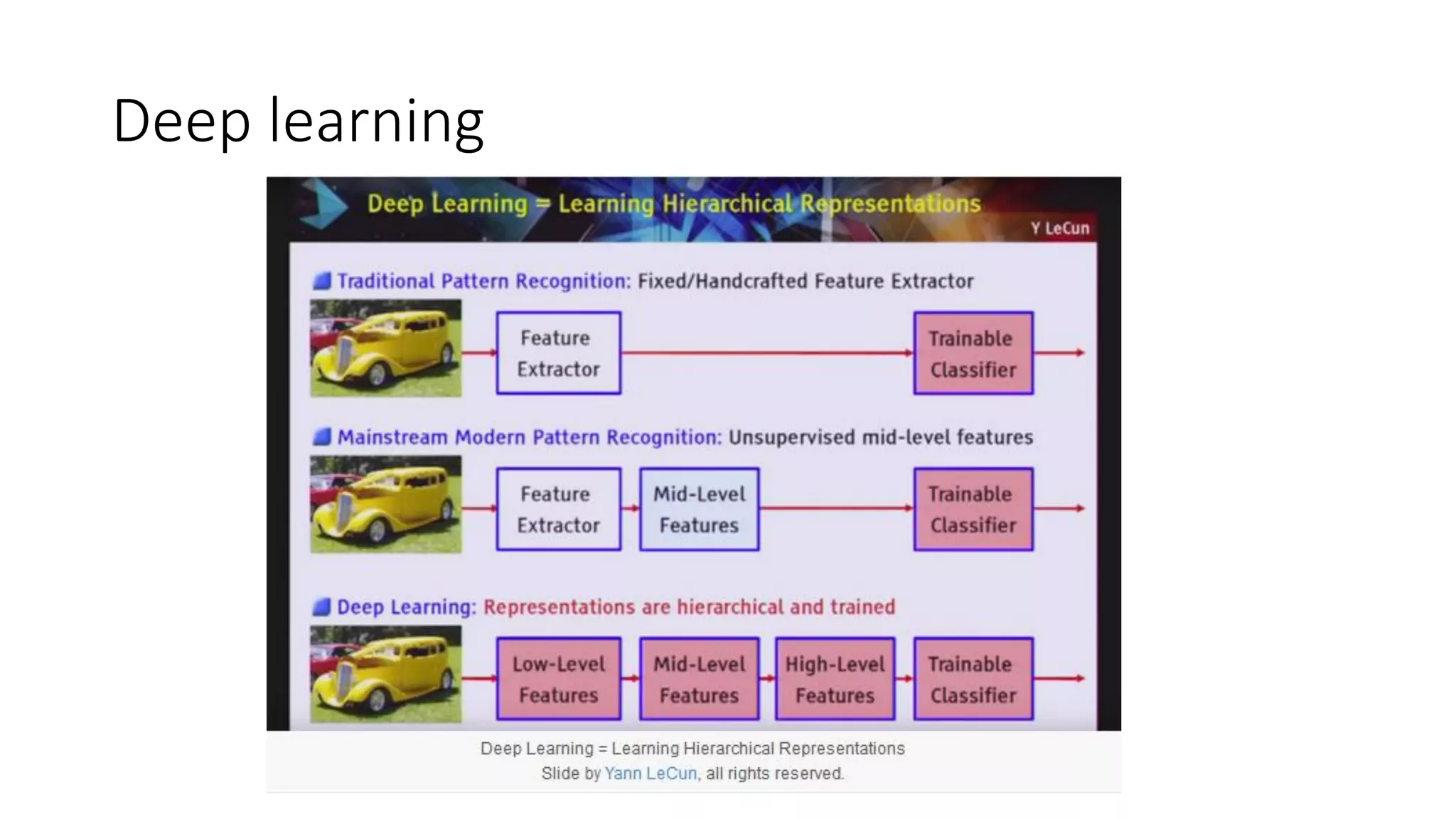
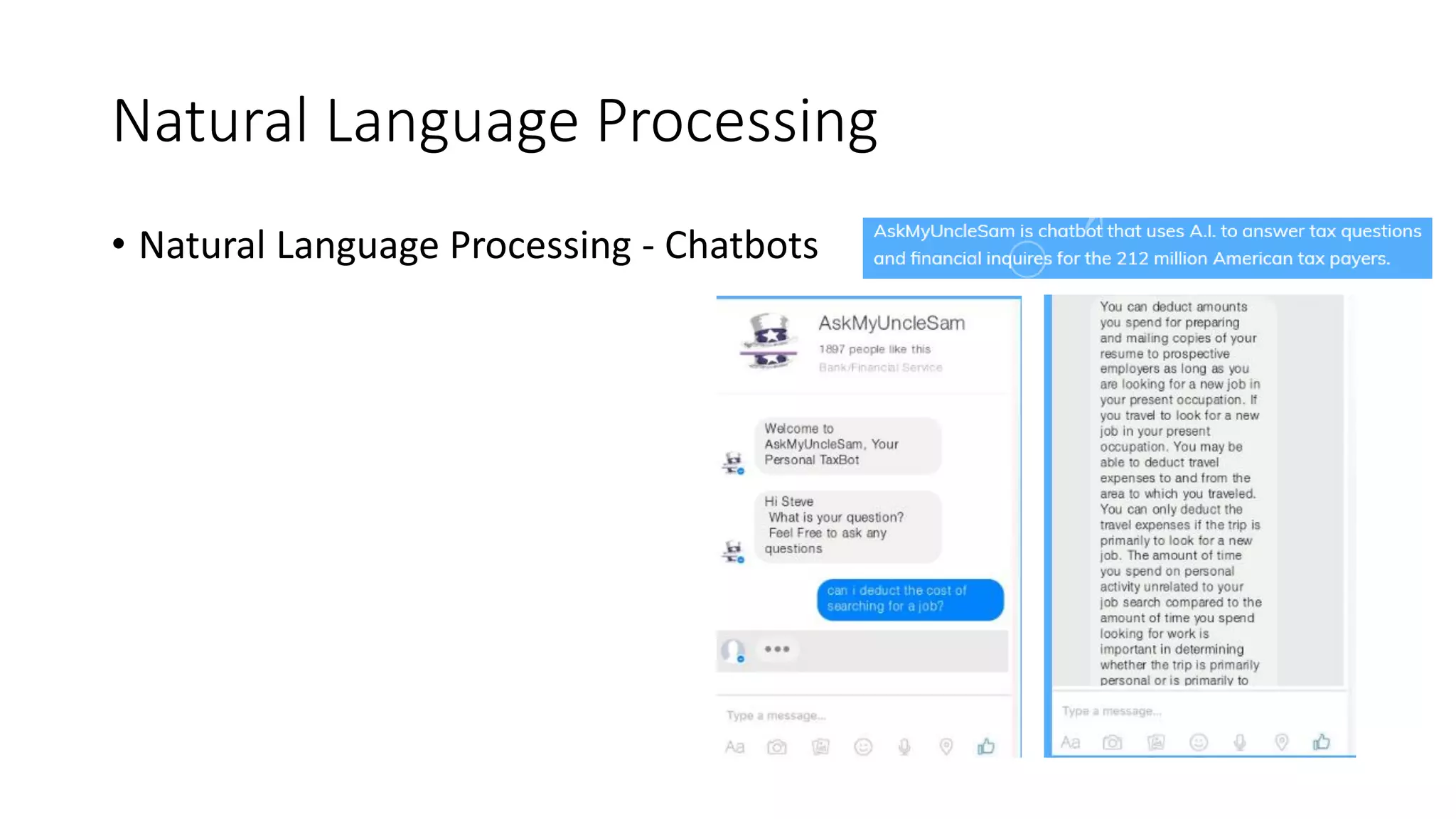
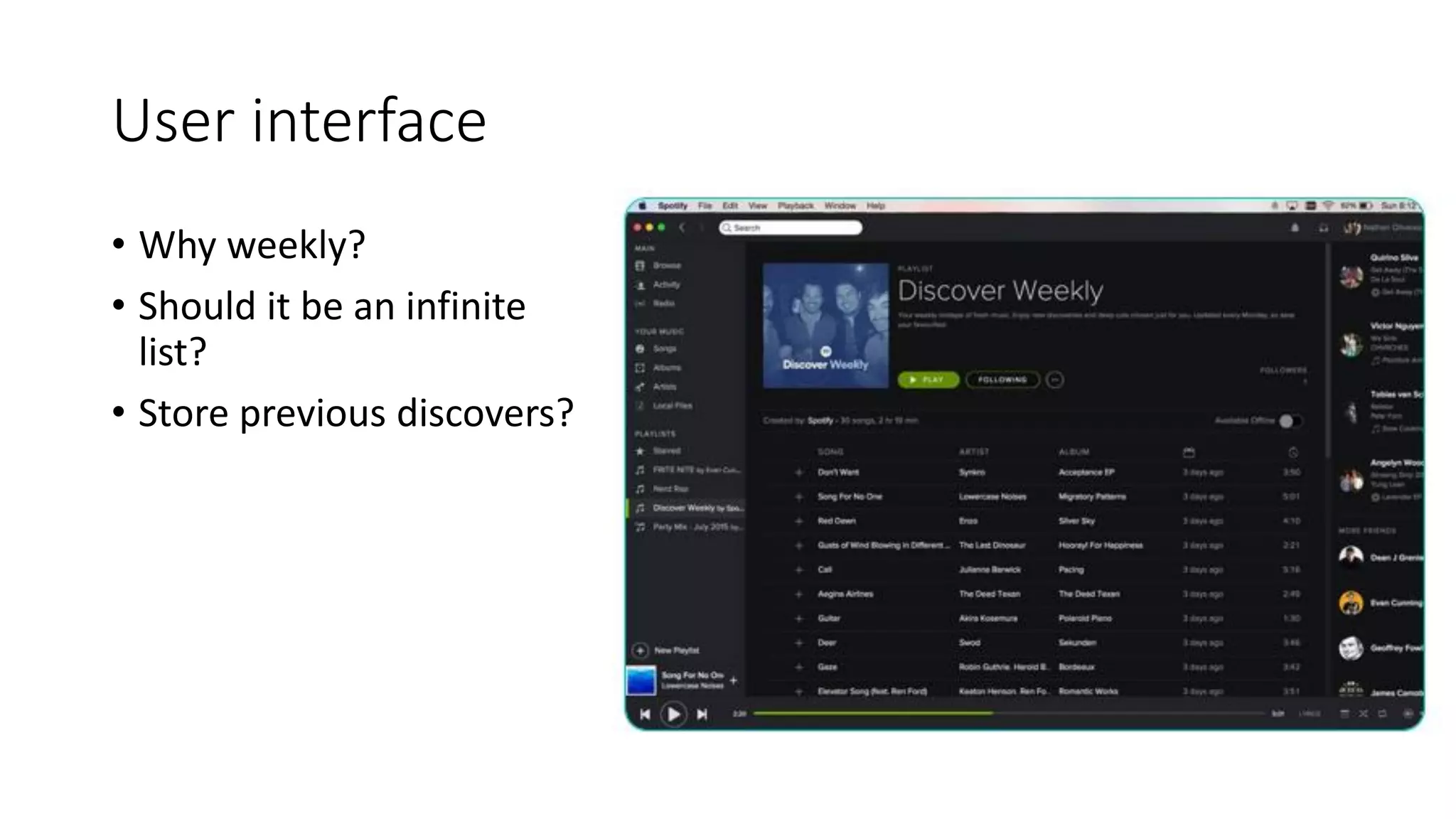
This document discusses machine learning and how product managers can leverage it. It provides an overview of machine learning types like supervised and unsupervised learning. It then gives examples of how machine learning can be applied, such as predicting values, making recommendations, detecting anomalies, and image/audio recognition. The document advises product managers to consider the available data, user experience, and model explainability. It states that the role of product managers is shifting to owning customer data and ensuring its quality and balance. Product managers should start collecting user data and designing interfaces that make sharing data easy.