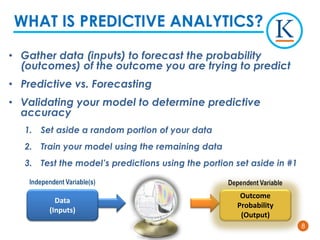
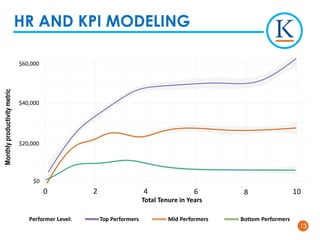
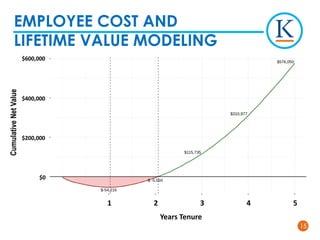
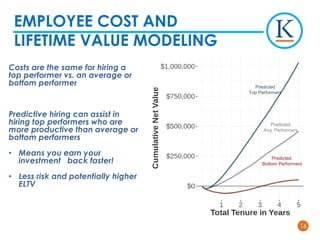
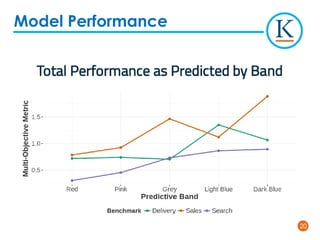
Kforce is evolving its pre-hire talent assessments to use predictive analytics to improve hiring outcomes. It analyzed key performance indicators and found top performers delivered over 100% more productivity than median performers. It developed a predictive model using 11 assessment dimensions to assign candidates a color corresponding to their likelihood of being a top performer. While not perfect, the model identifies patterns in top performers' profiles to predict success. Kforce aims to use predictive analytics to hire more top performers and reduce turnover costs.