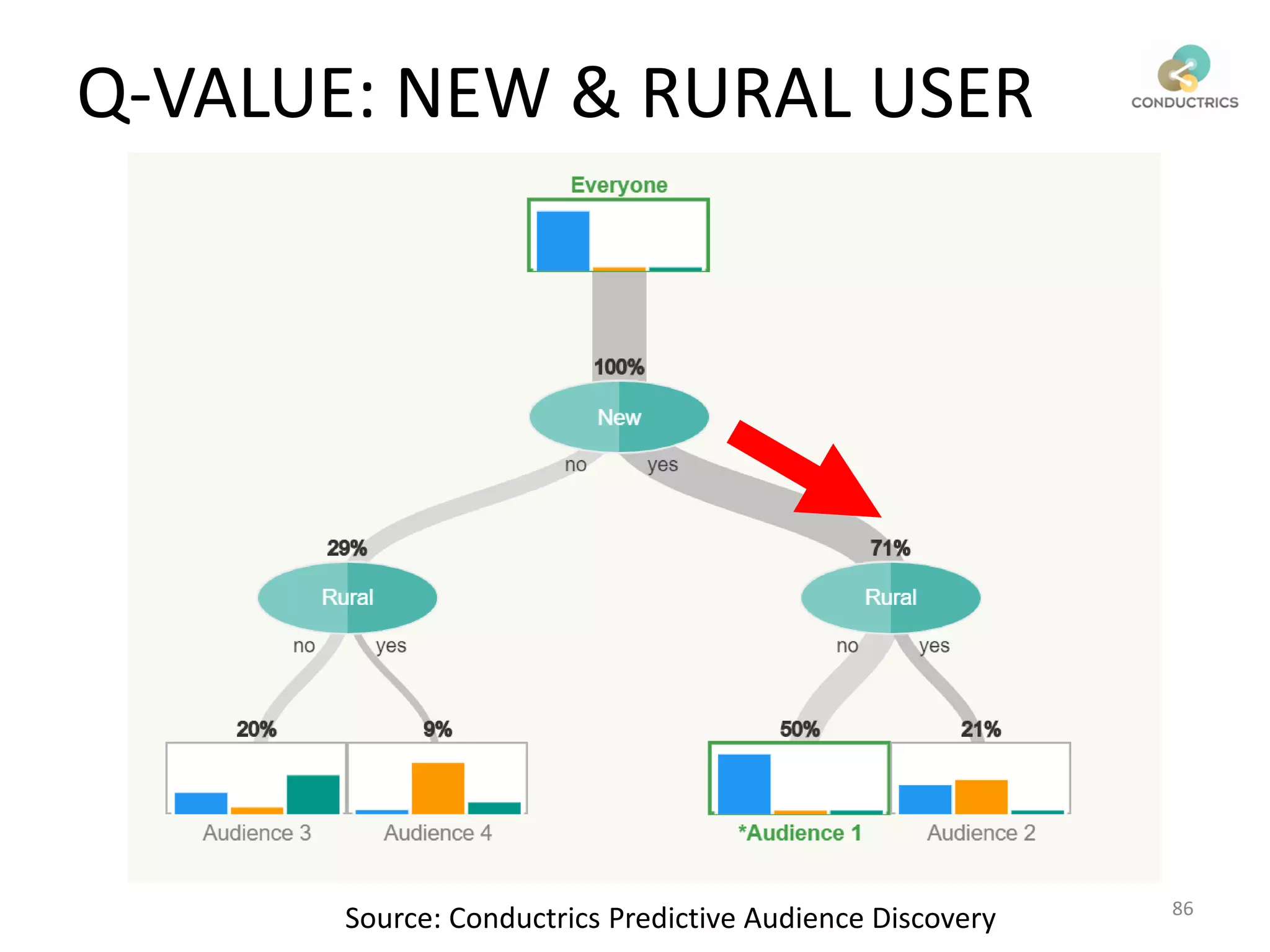
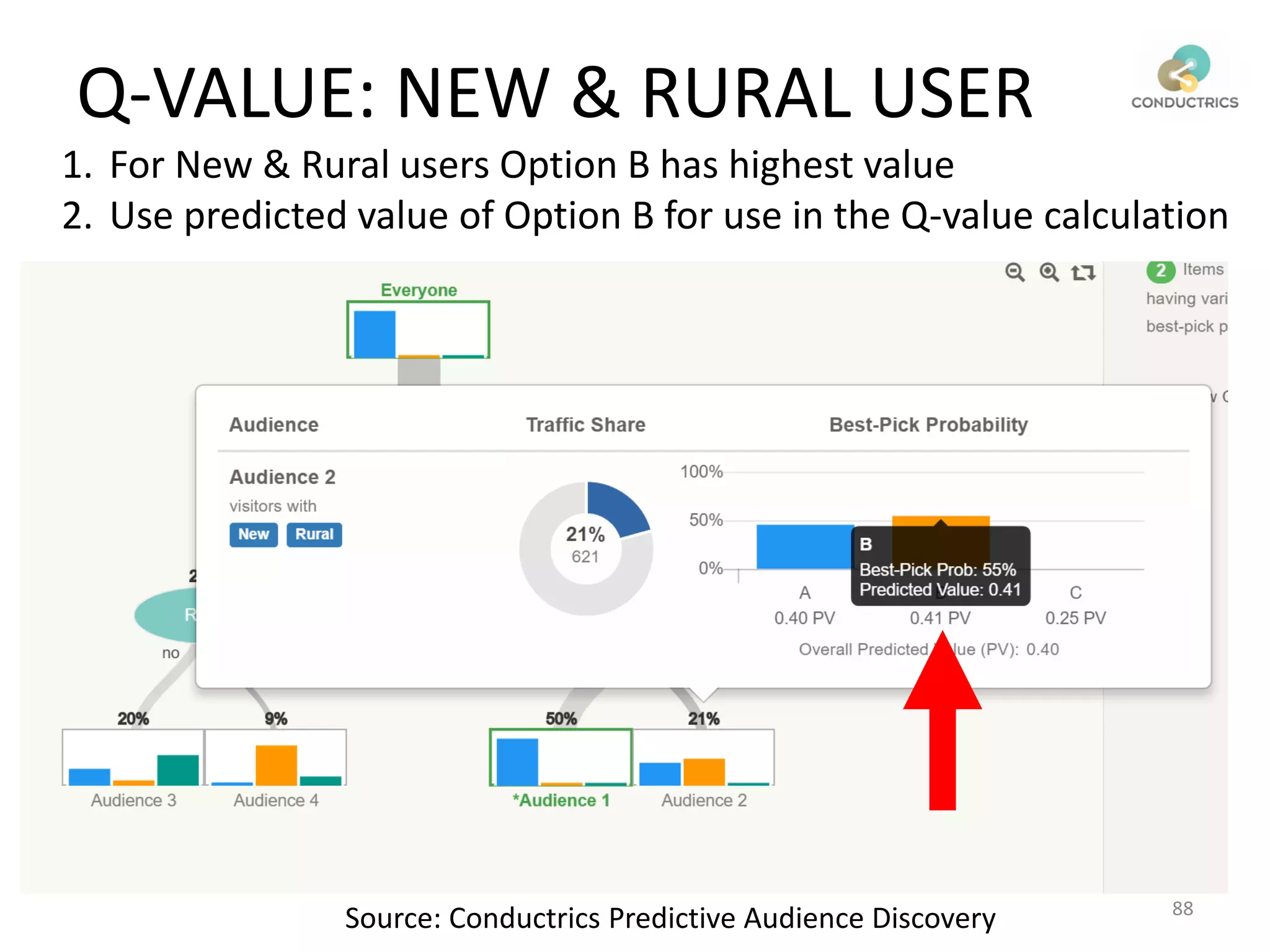
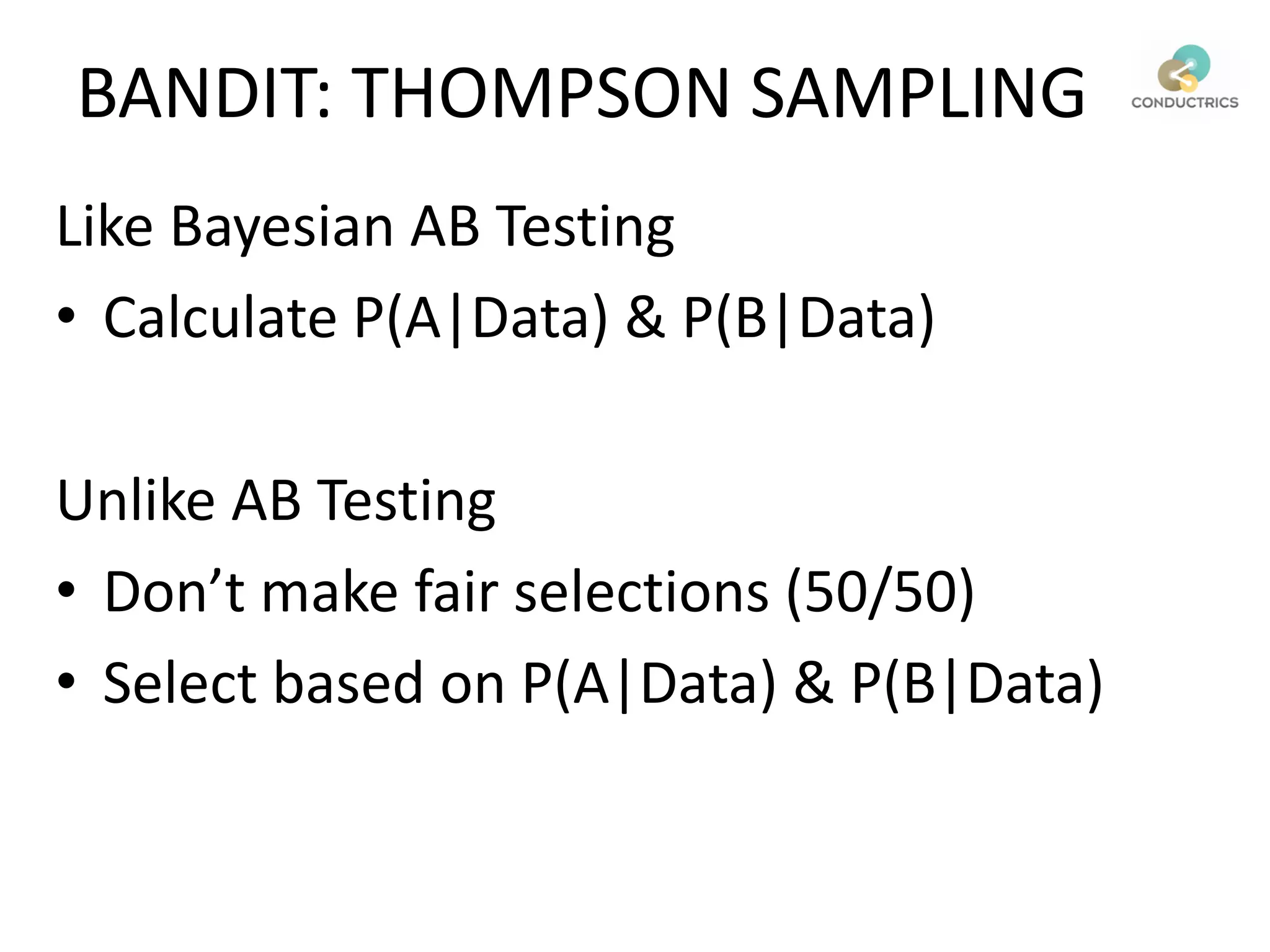
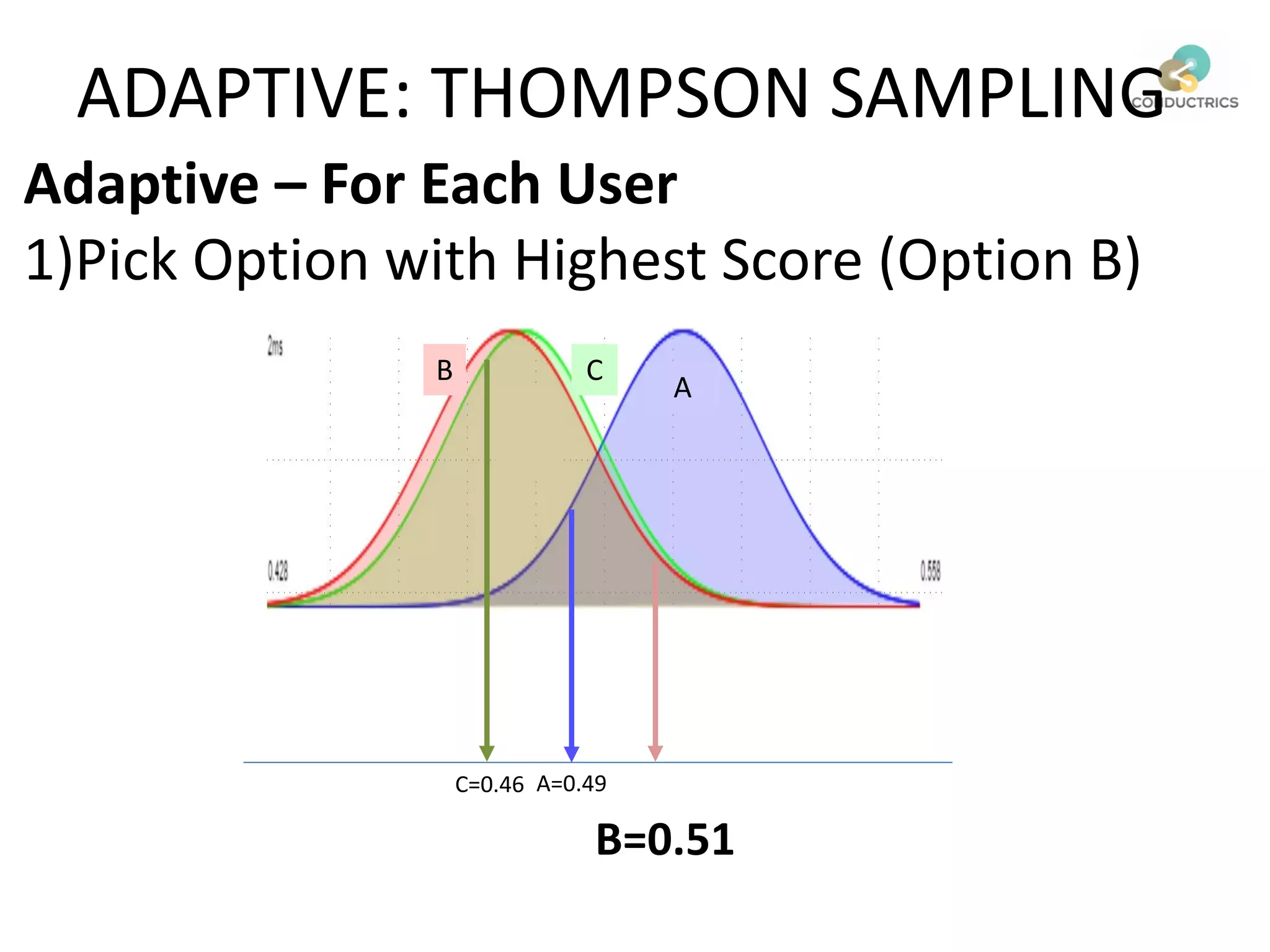
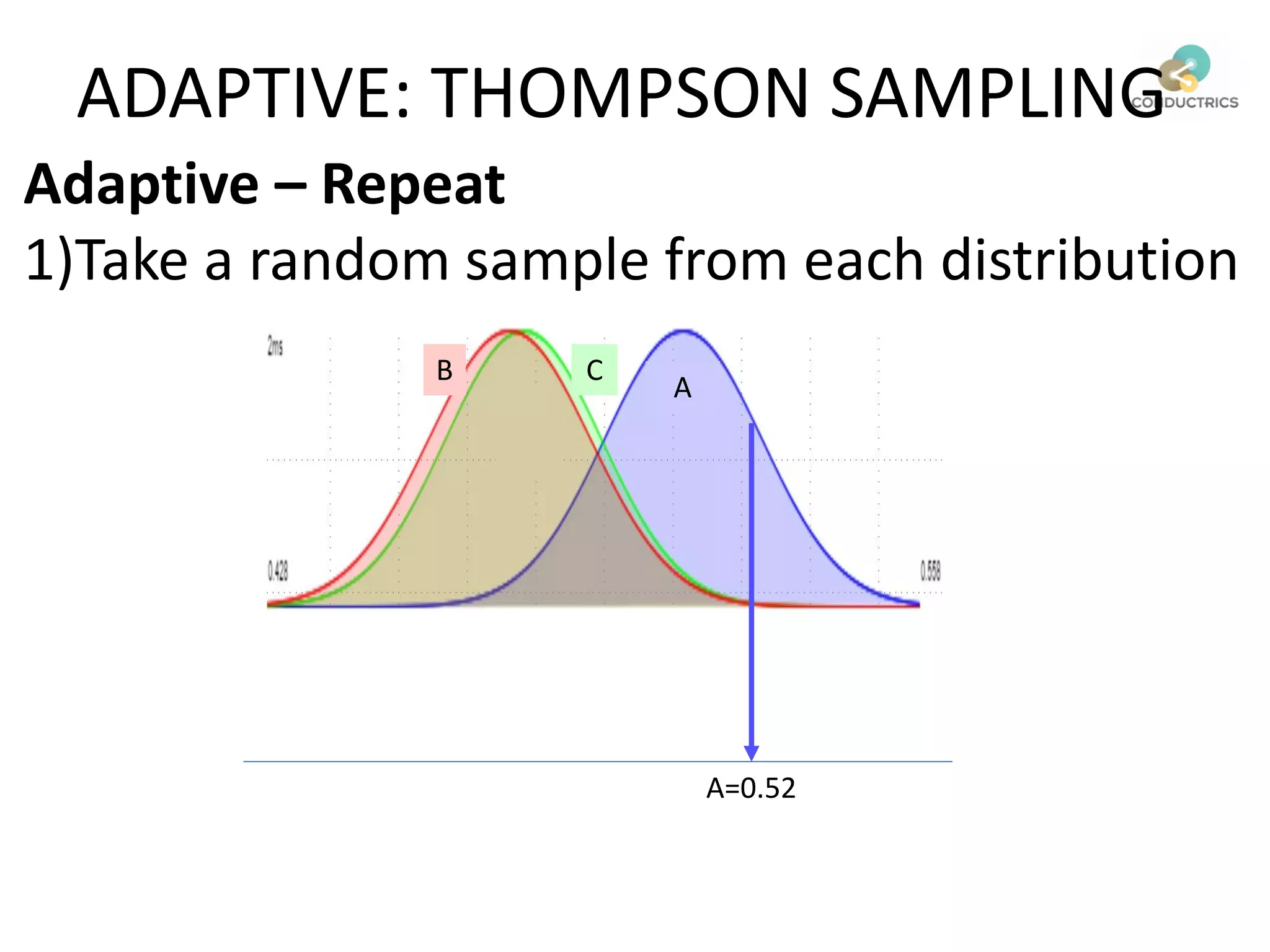
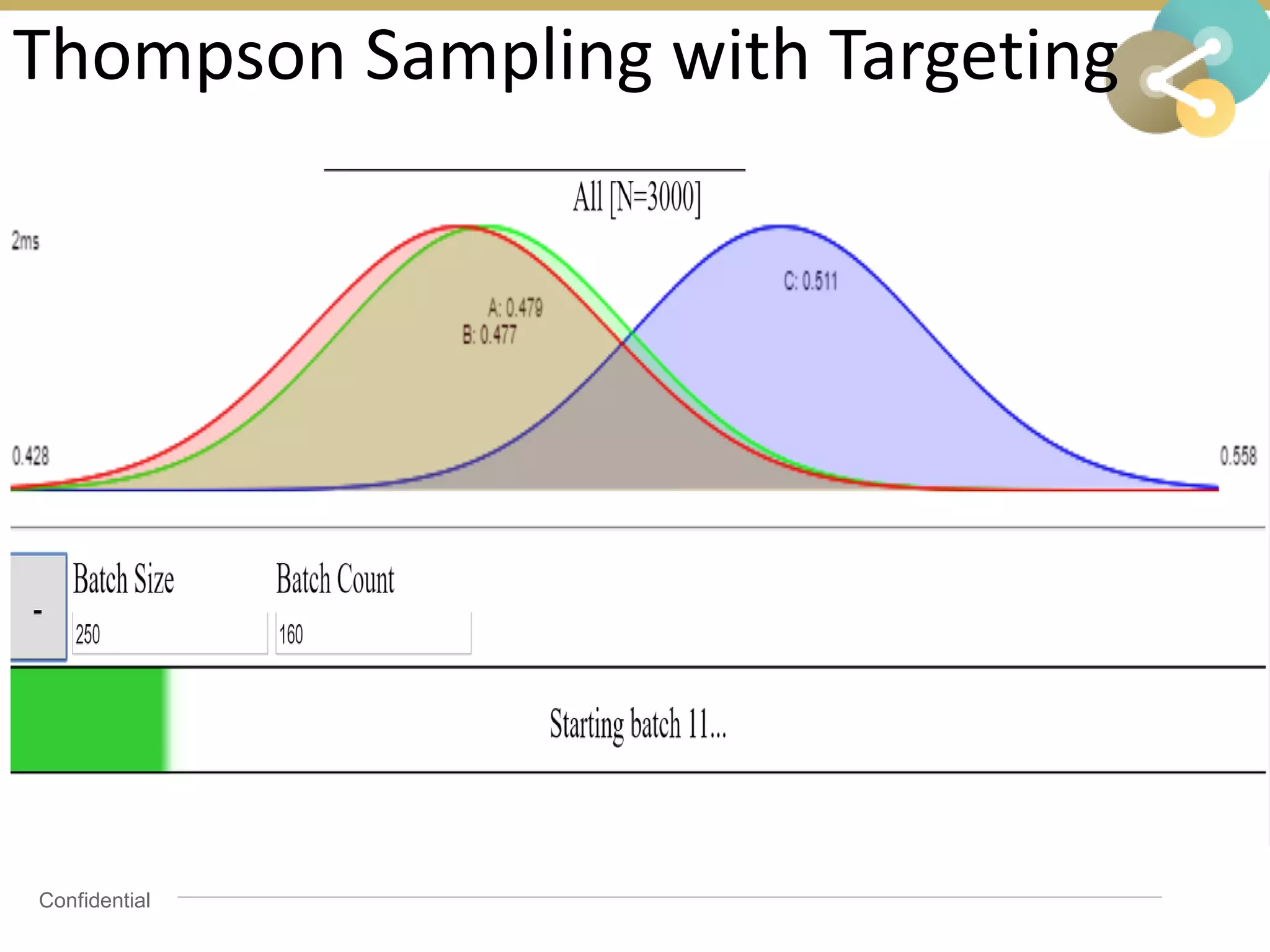
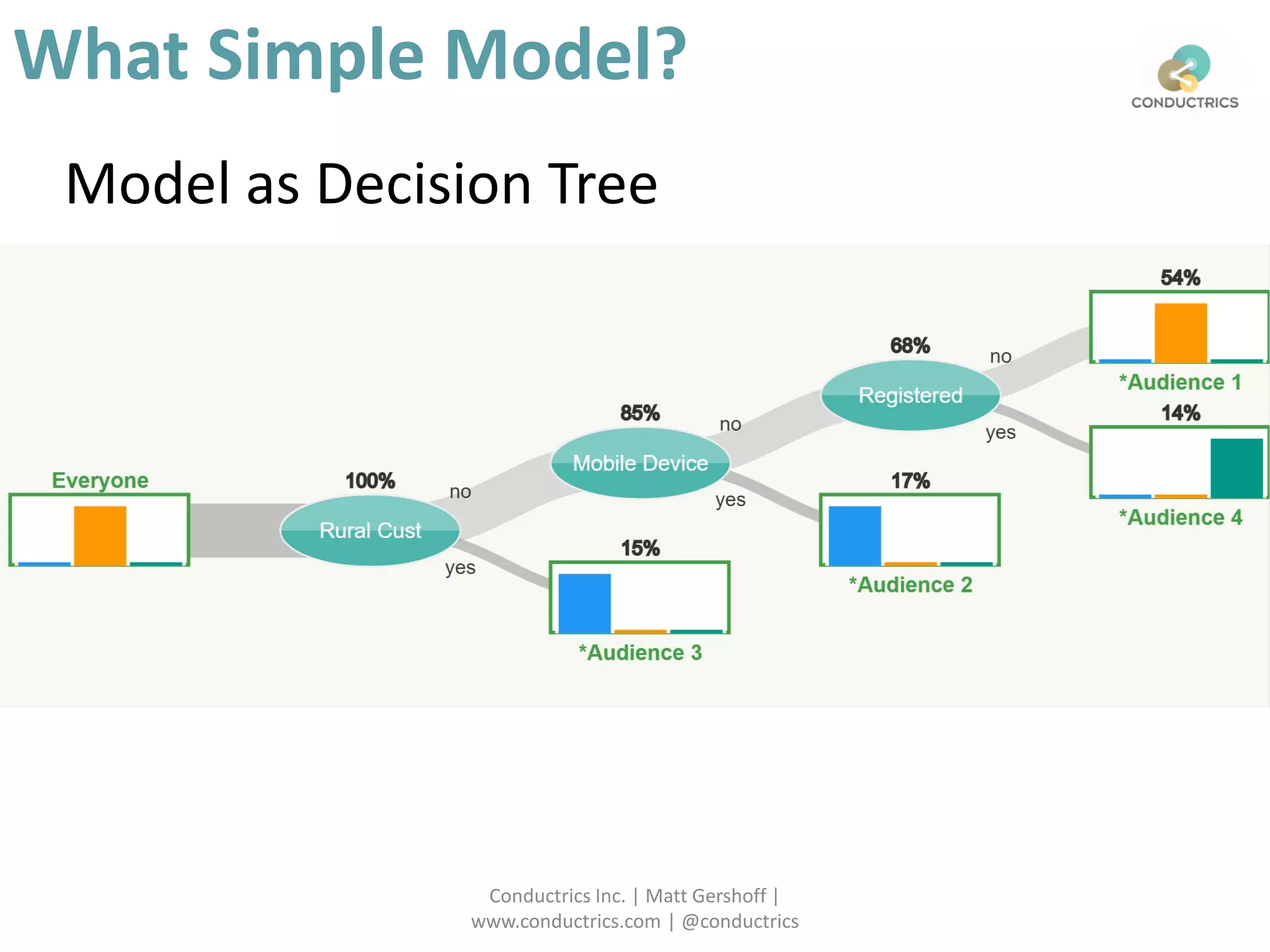
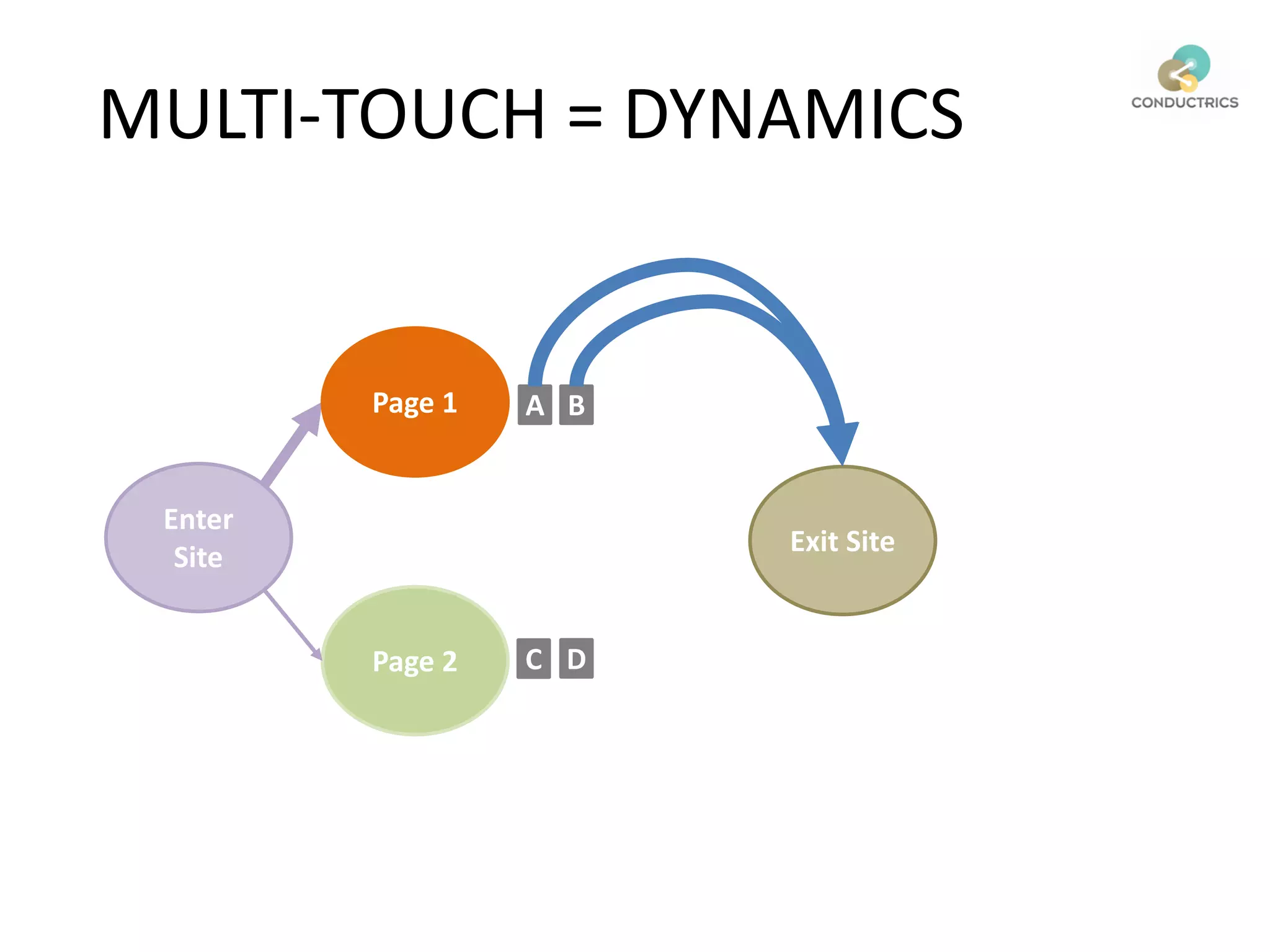
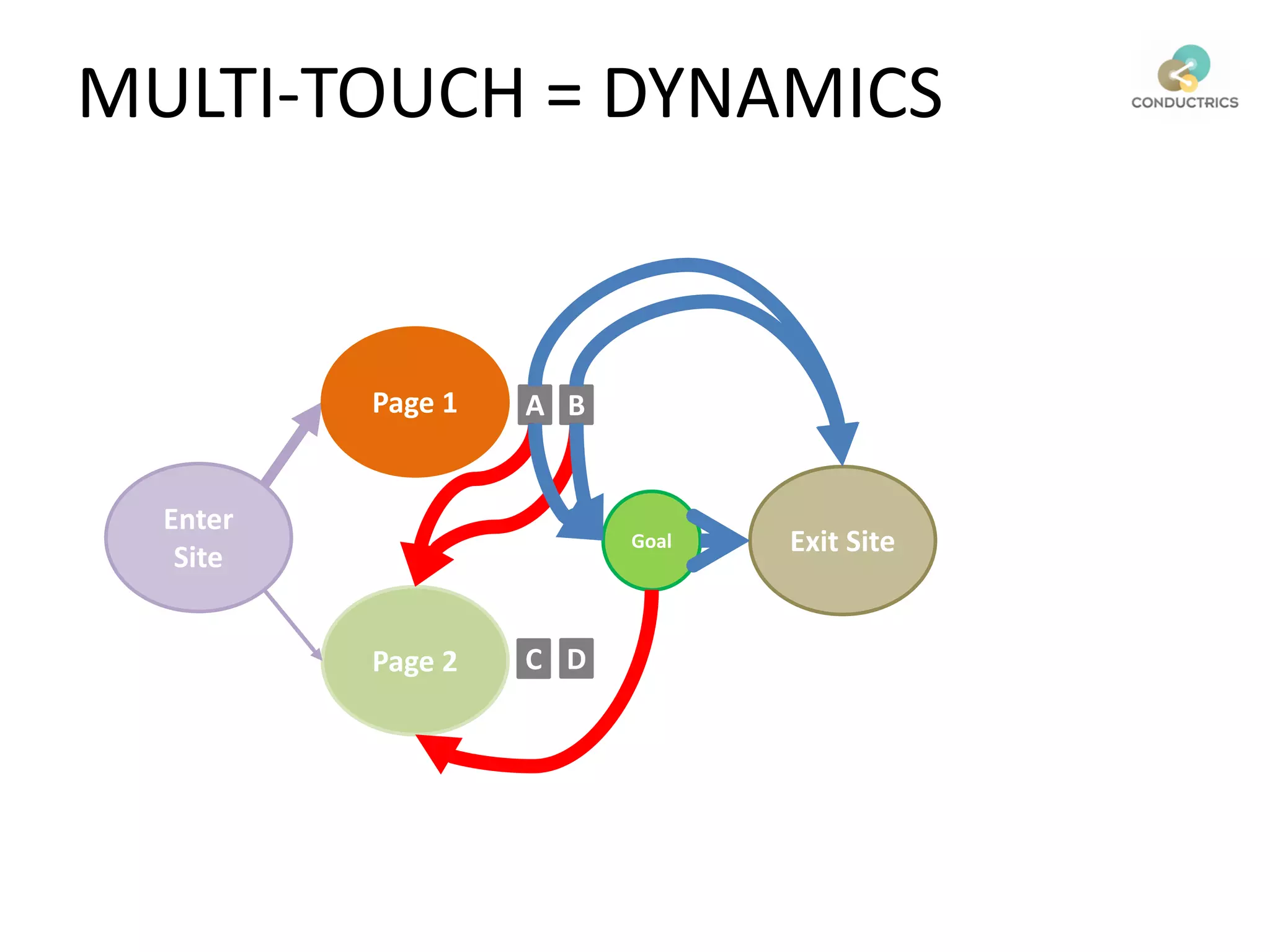
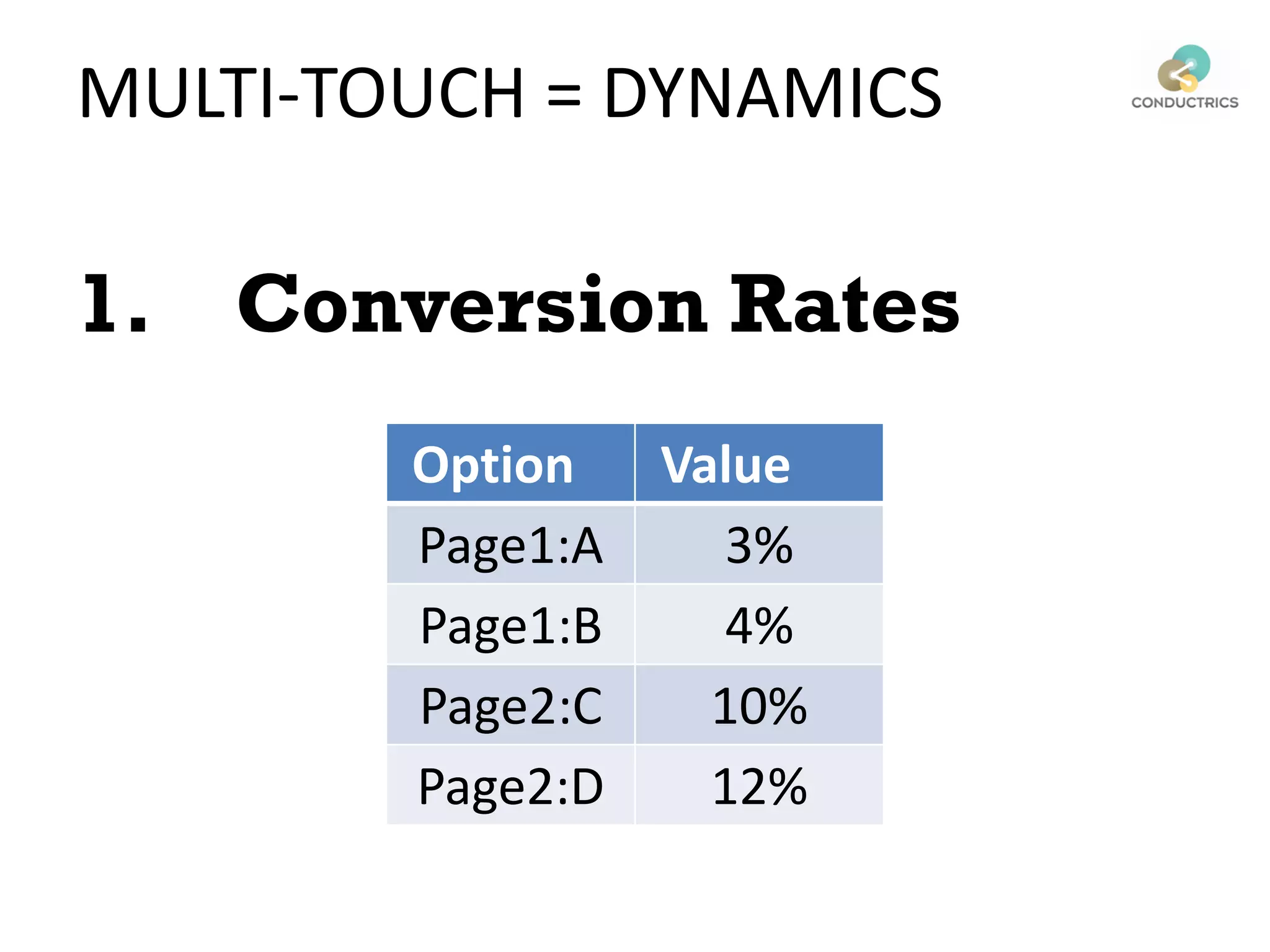
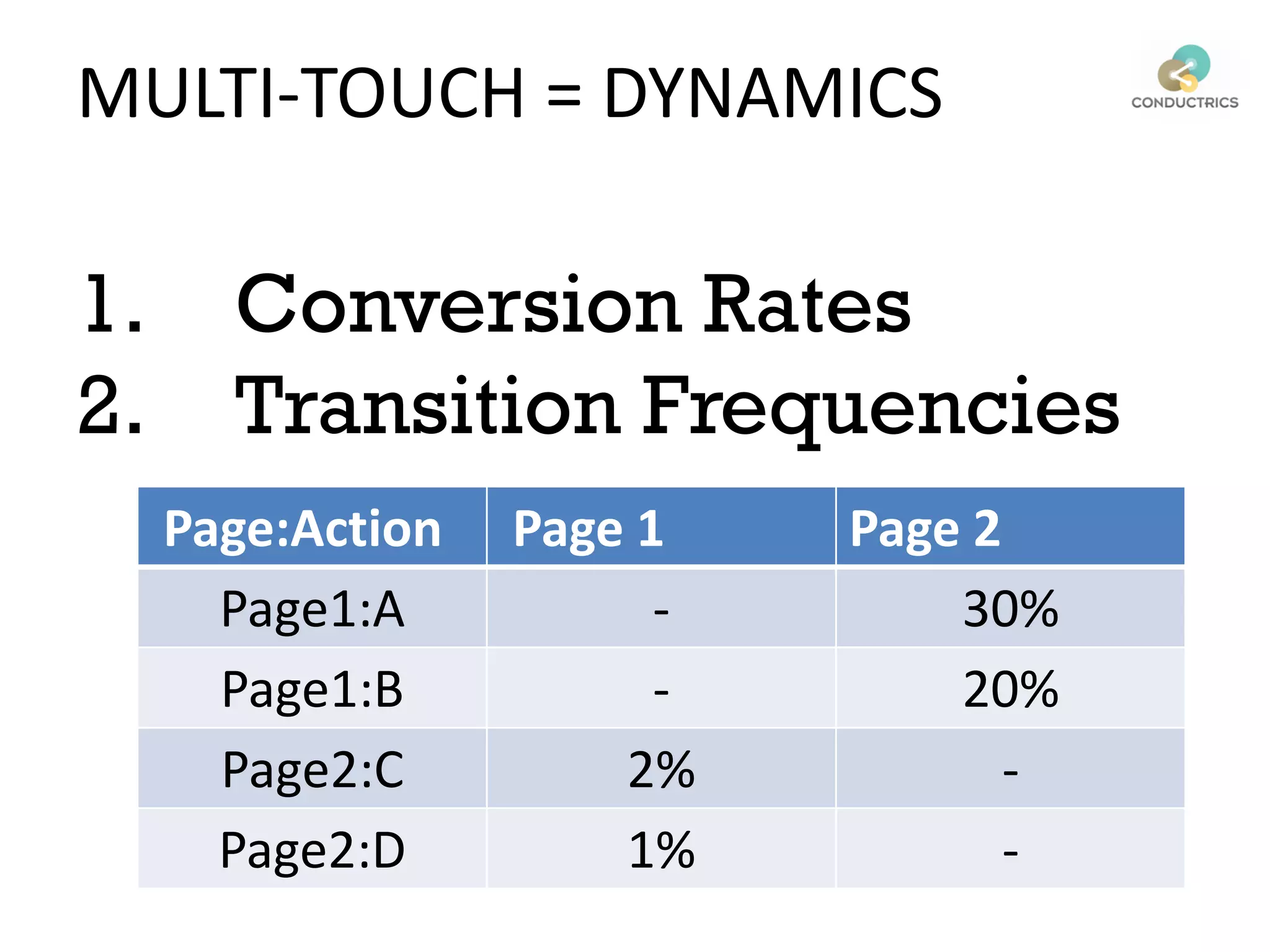
This document discusses reinforcement learning and its applications to optimization problems in marketing. It begins with definitions of reinforcement learning and multi-armed bandit problems. It then discusses how Bayesian AB testing, multi-armed bandits, and Thompson sampling can be used to solve single decision problems. The document also covers how reinforcement learning handles more complex multi-touchpoint optimization and attribution problems using techniques like Q-learning. It concludes by discussing how reinforcement learning approaches can be used for automation and predictive targeting based on user attributes.












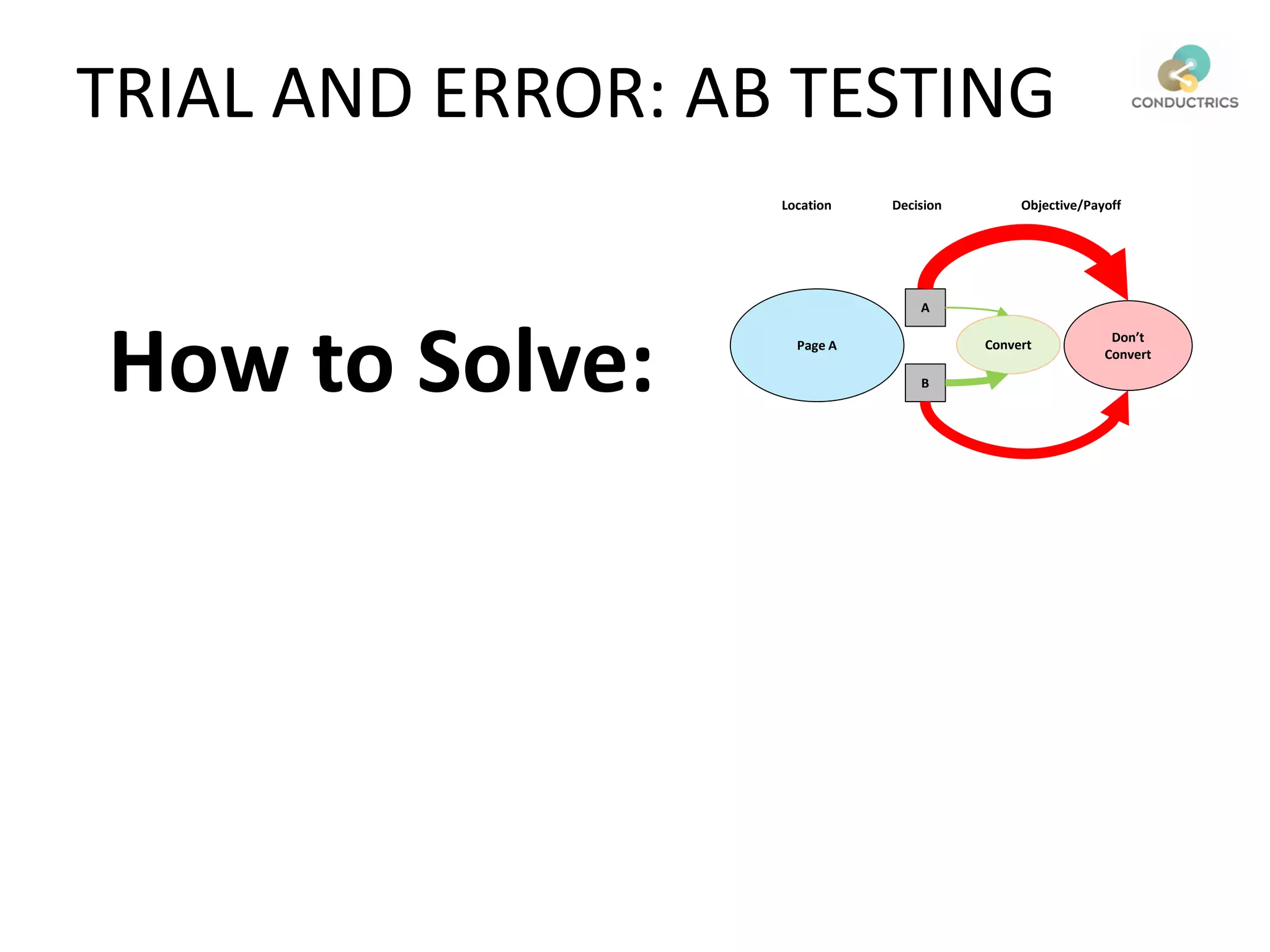



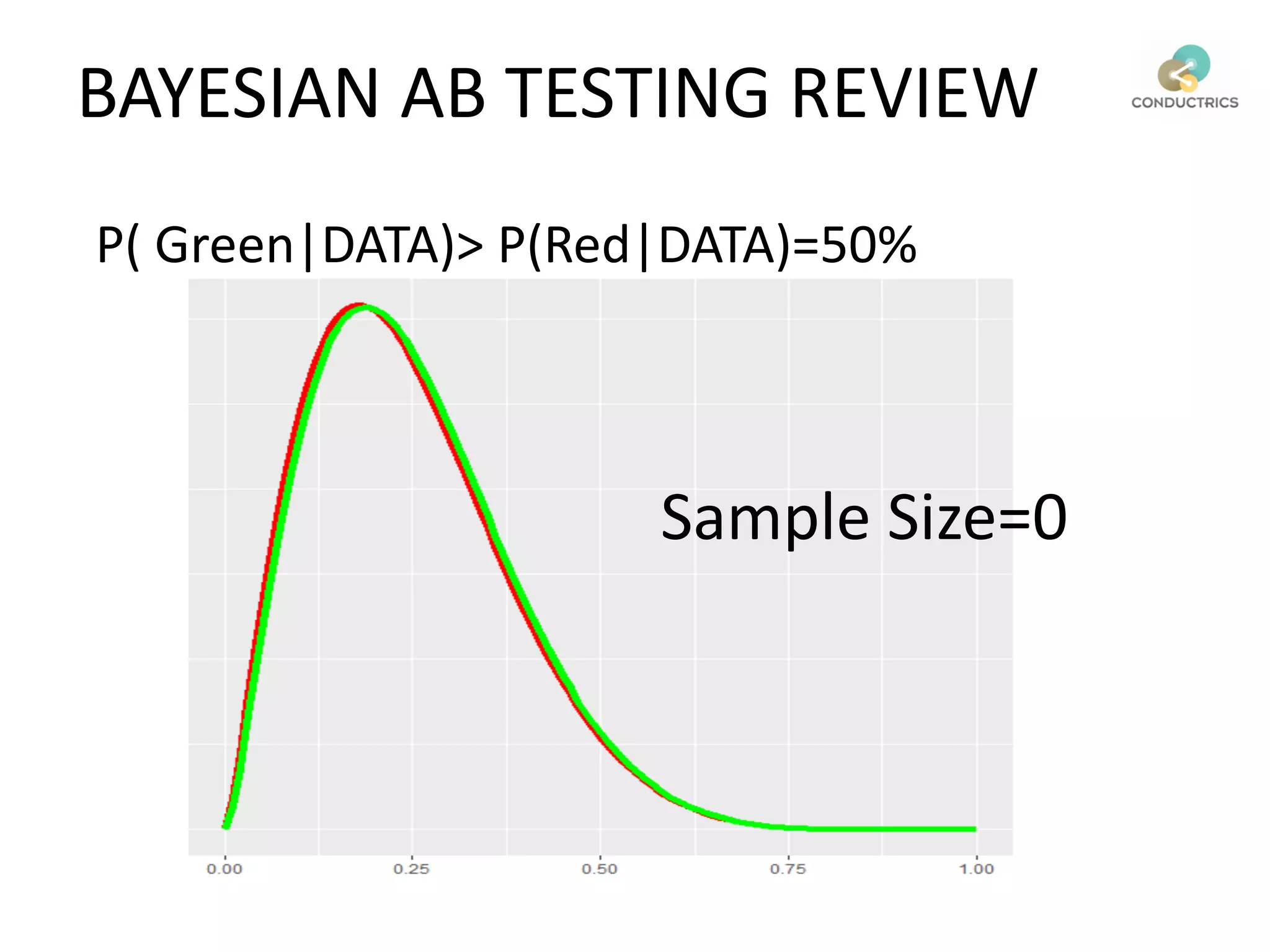



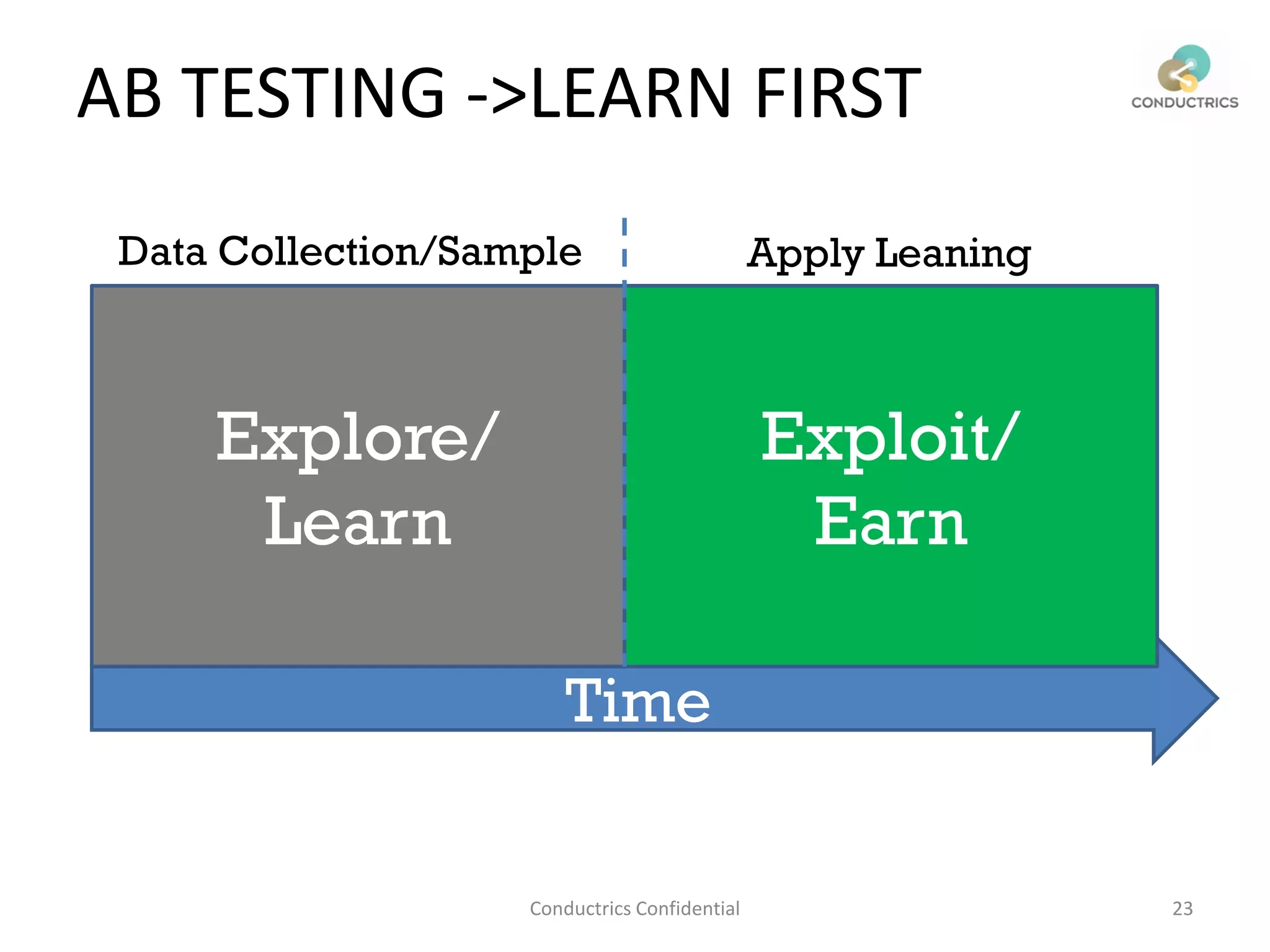
















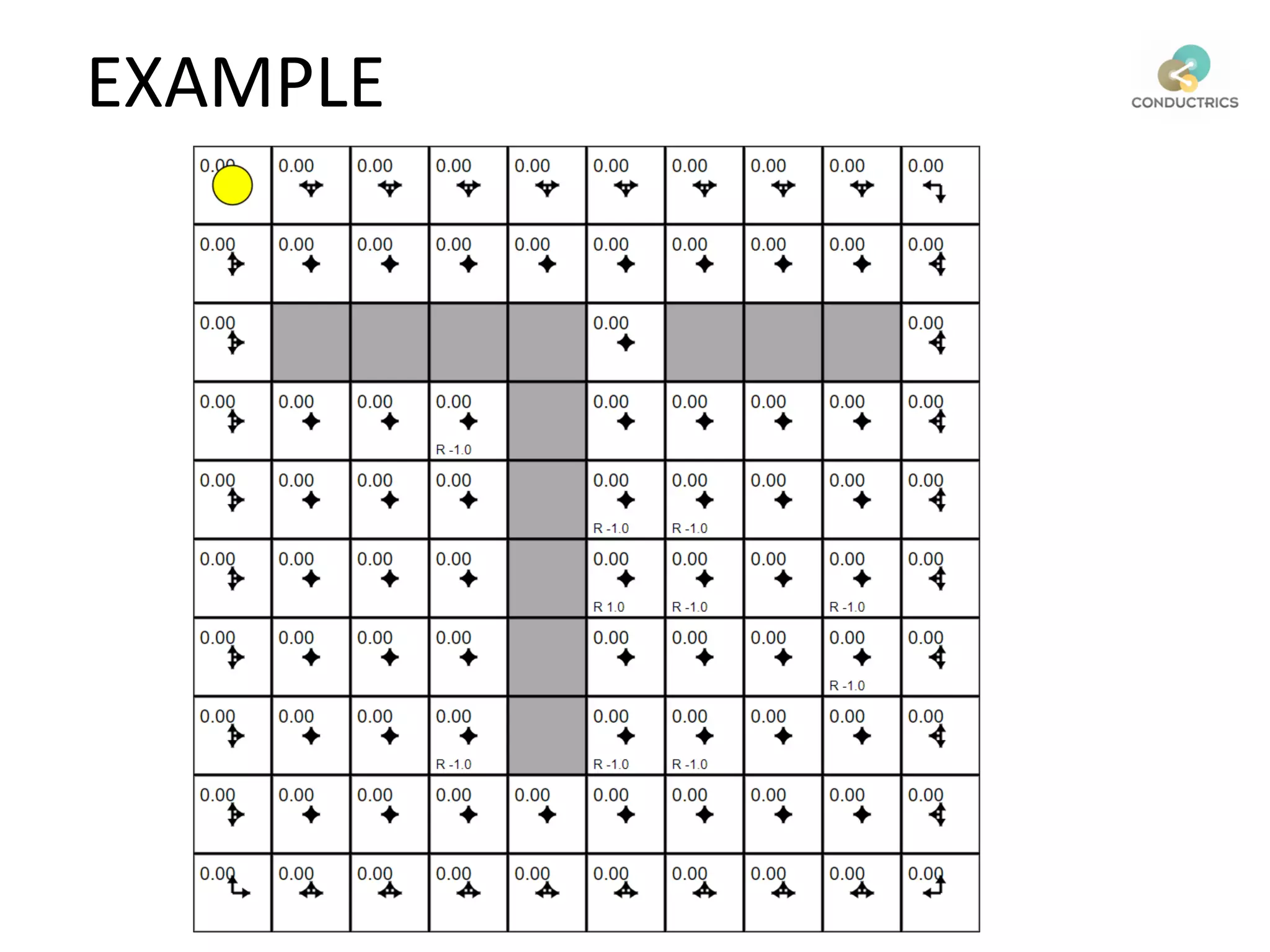













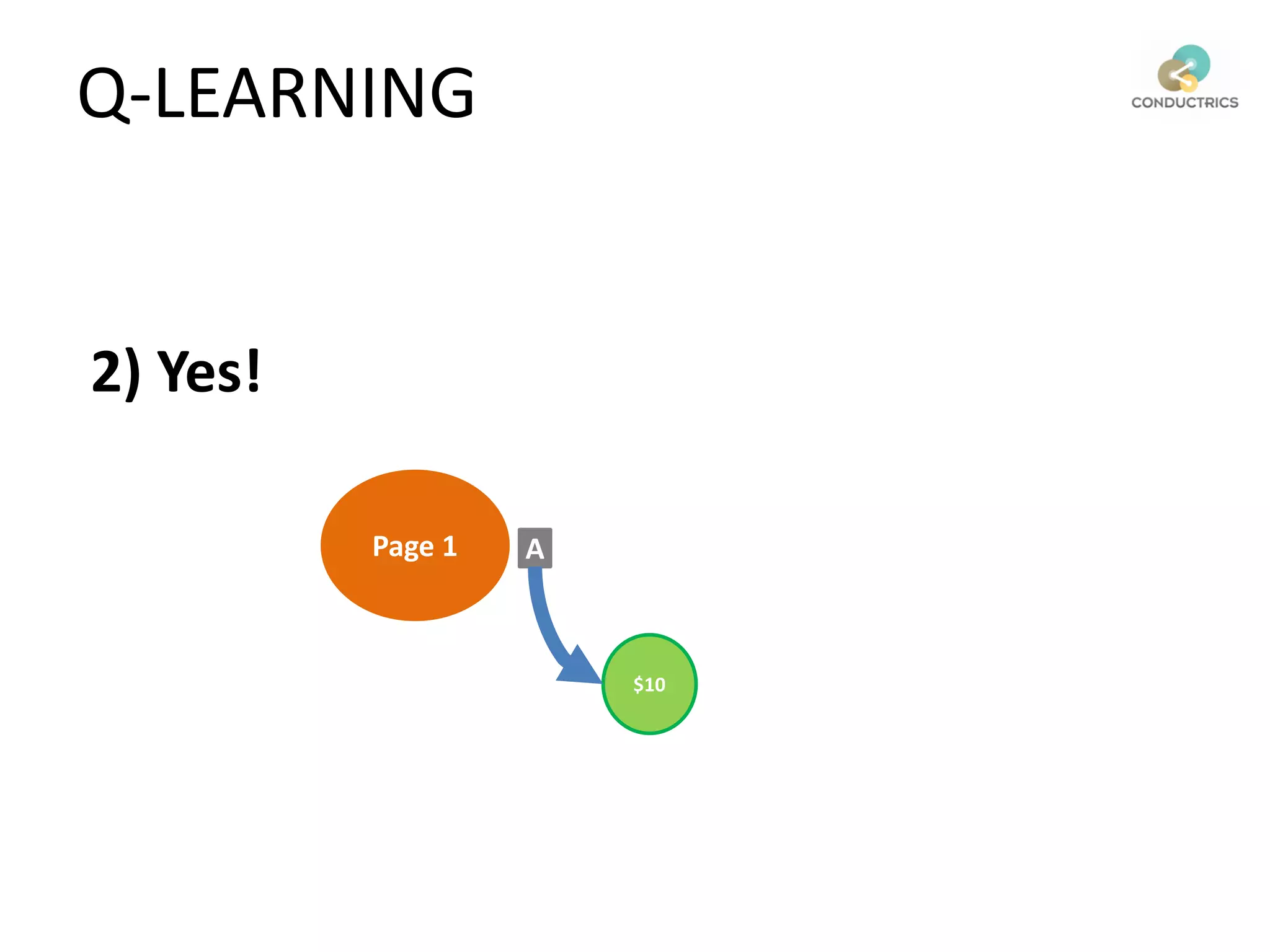
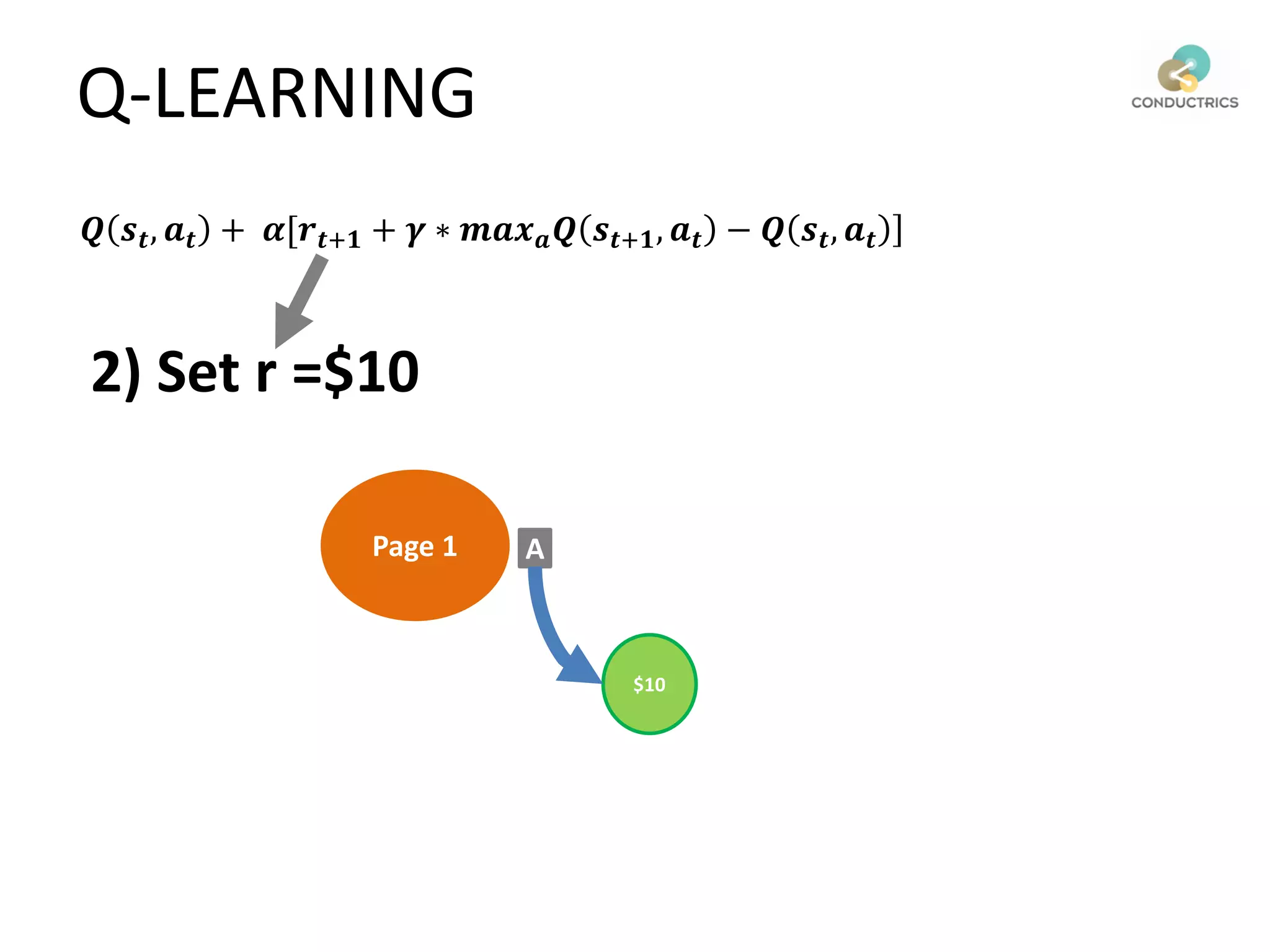

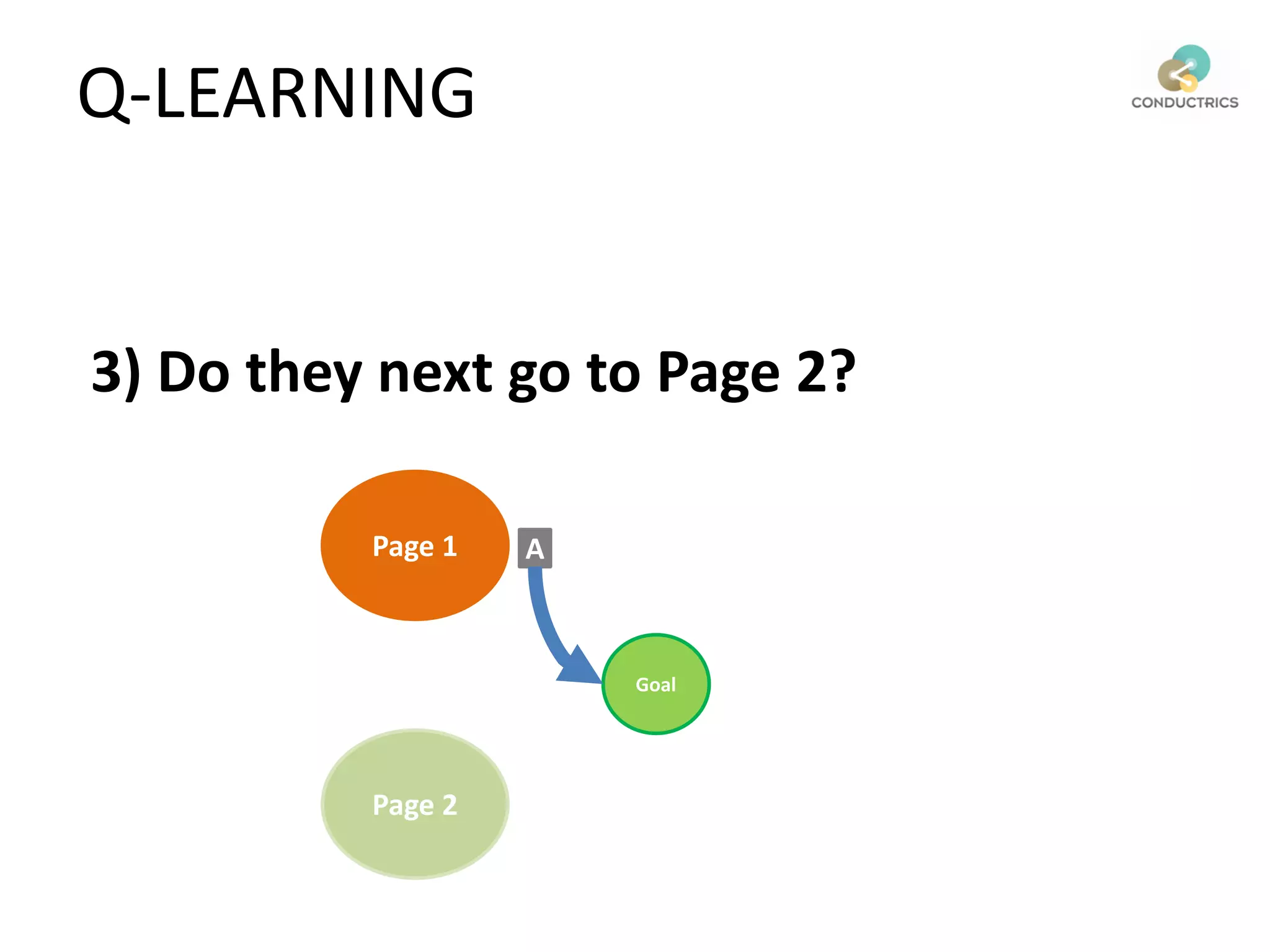




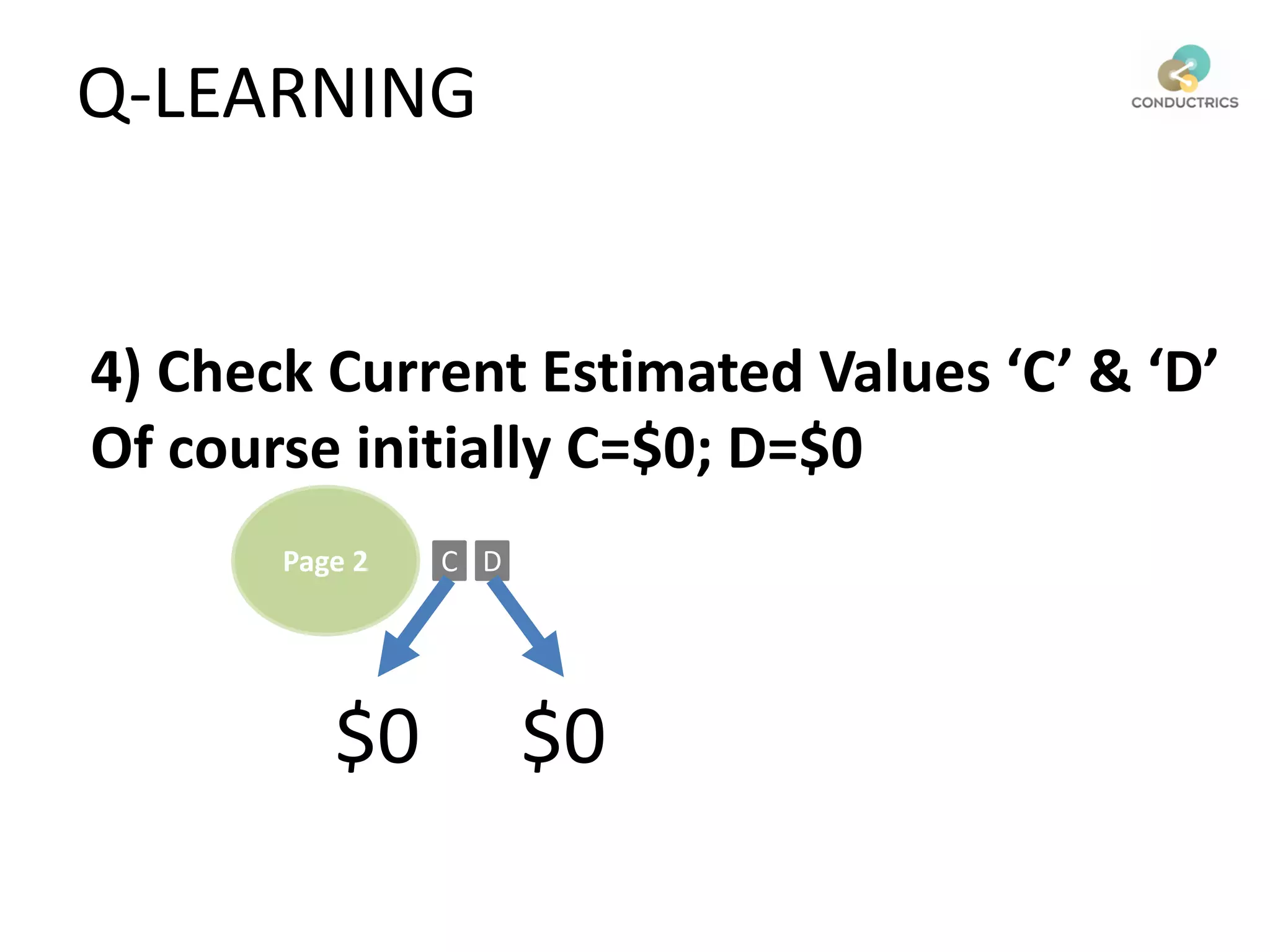
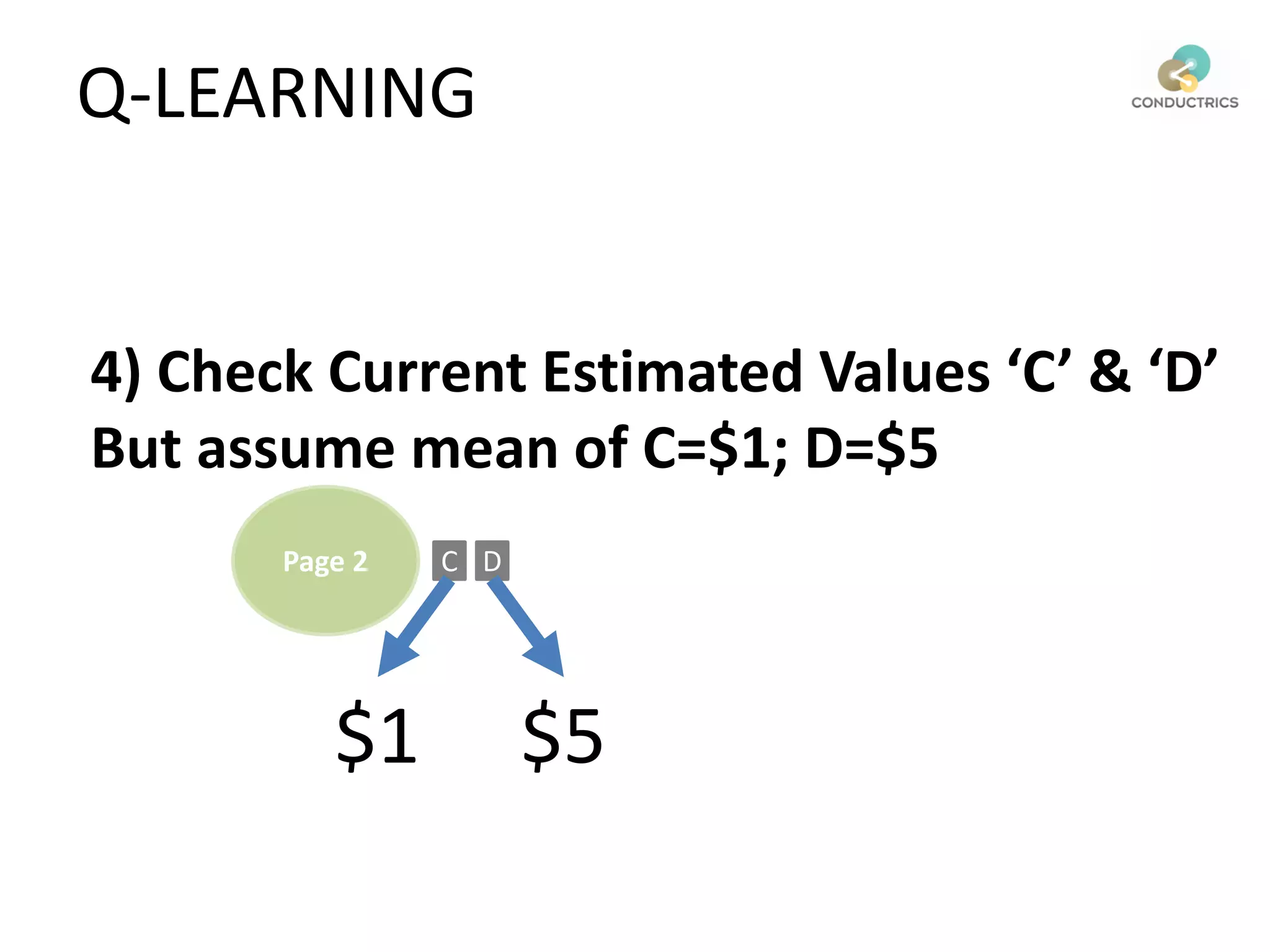
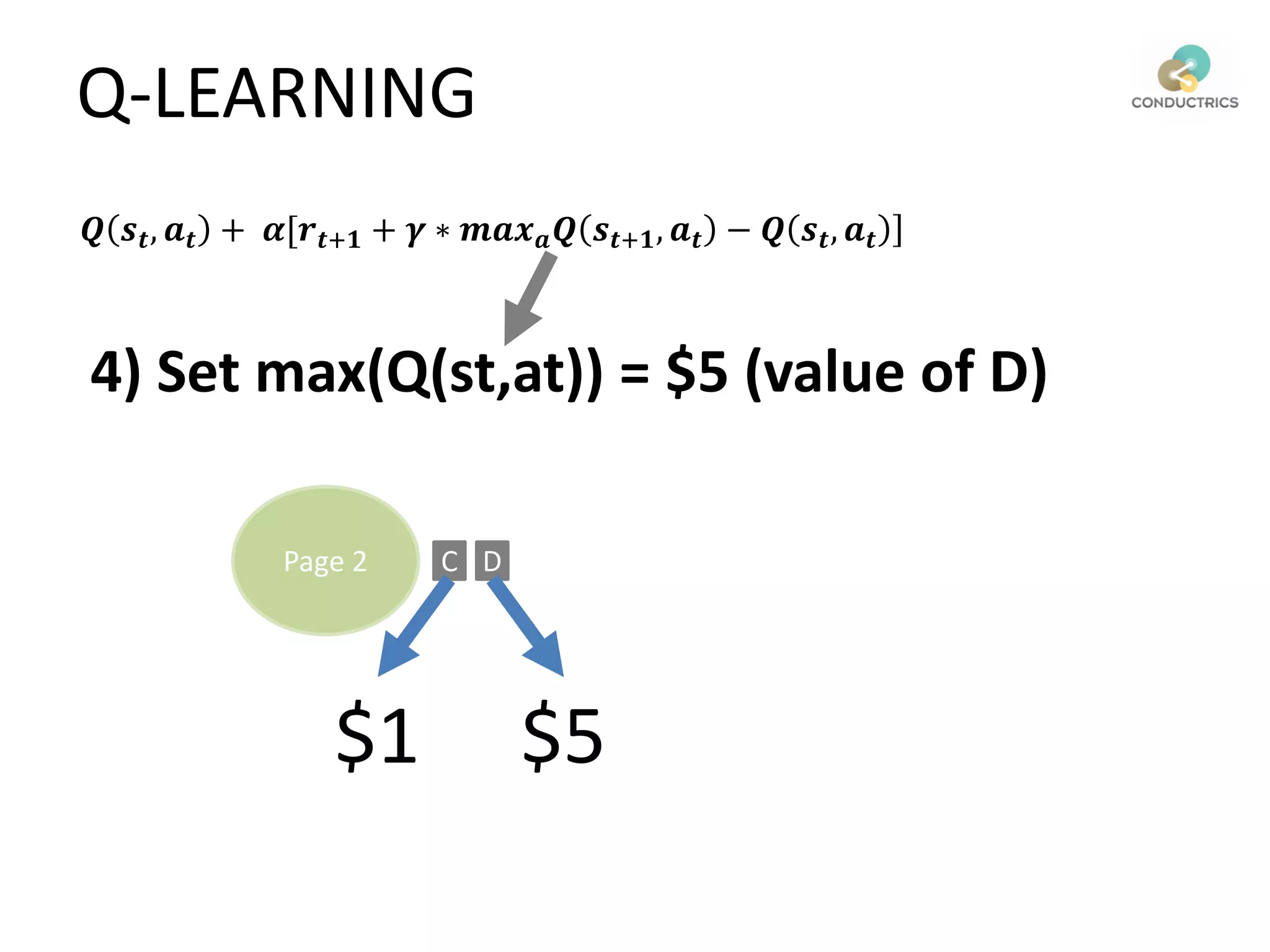

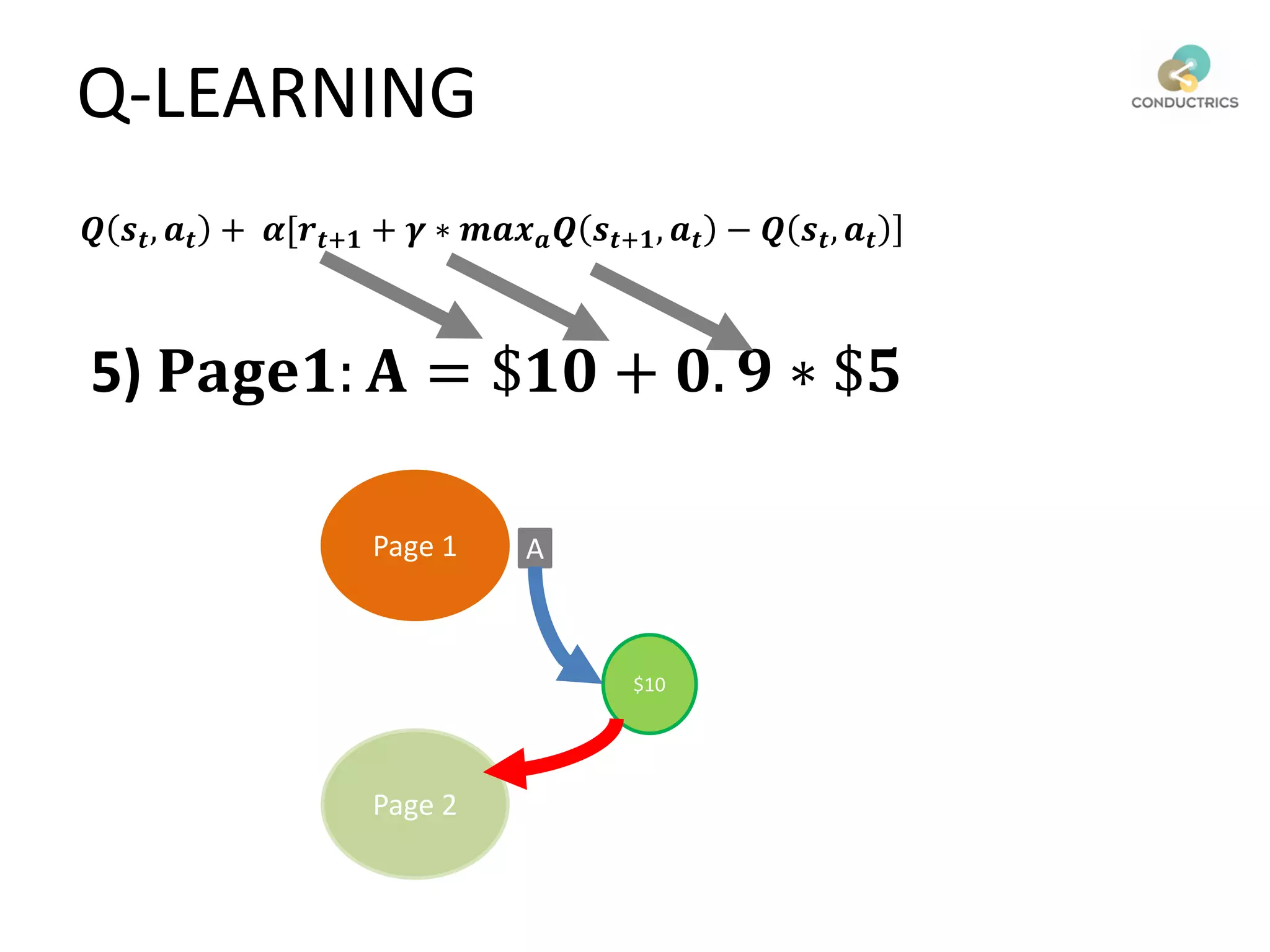






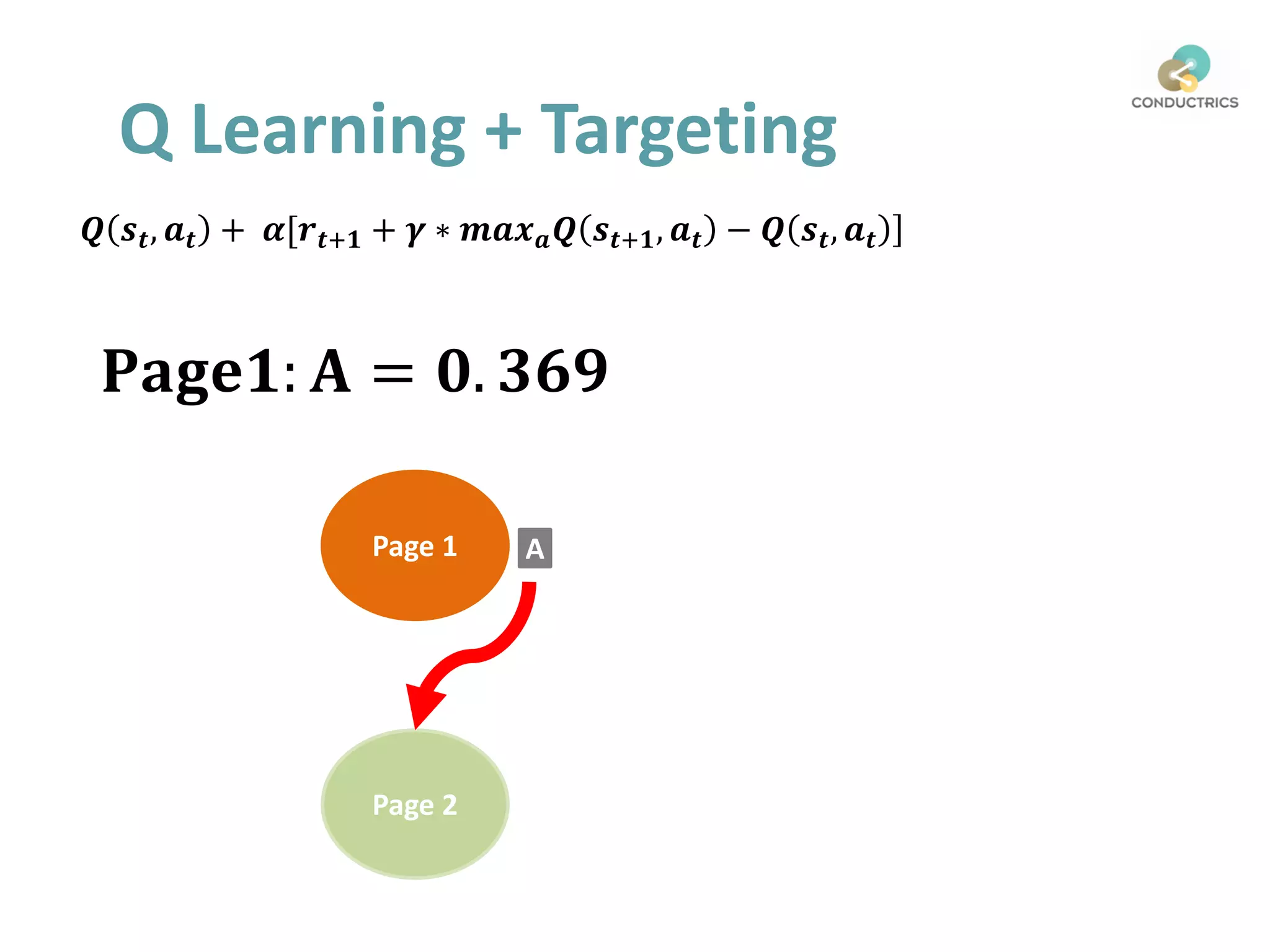
![Attribution calculation depends on [Rural;New]
Page 1
Page 2
A
Q Learning + Targeting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mattgershoff-171101154036/75/Matt-gershoff-84-2048.jpg)