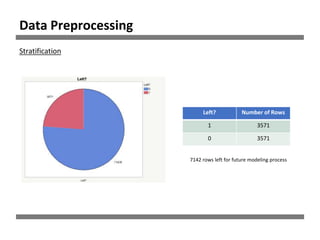
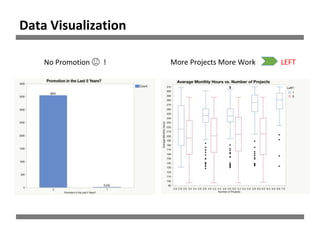
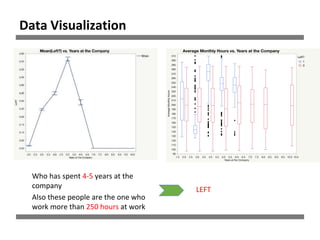
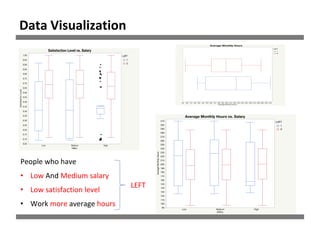
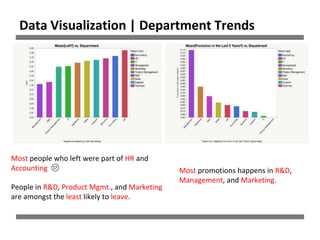
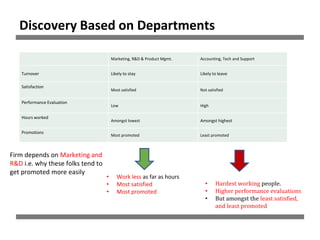
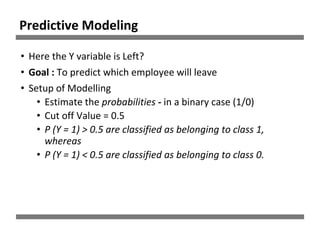
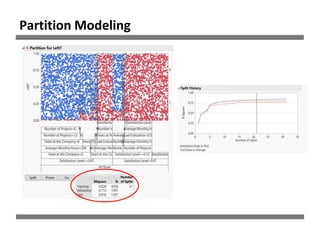
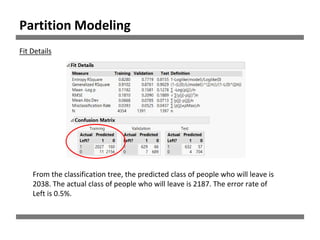
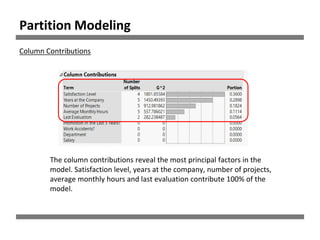
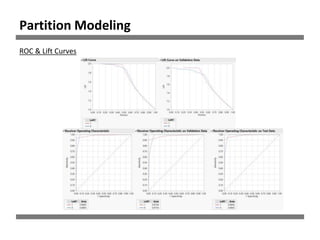
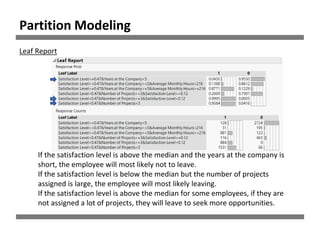
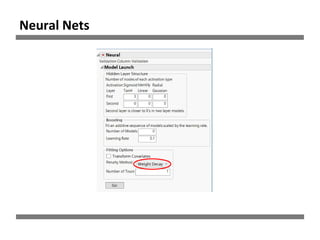
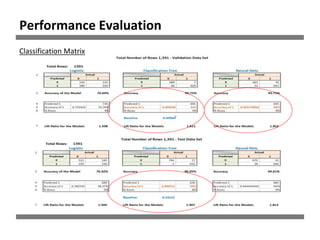
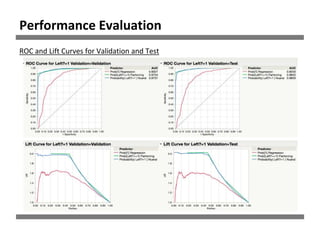
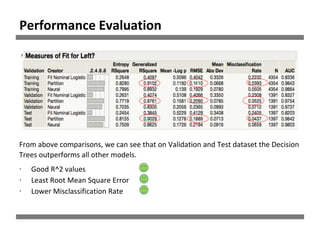
The document discusses a study on human resource analytics focused on predicting employee turnover using various factors such as satisfaction levels, years at the company, and workload. It details data preprocessing, modeling techniques, and findings, indicating that employees with low satisfaction and high project assignment are likely to leave. The study concluded that decision trees outperformed other models in predicting turnover, highlighting key predictors of employee retention.