Embed presentation
Downloaded 28 times

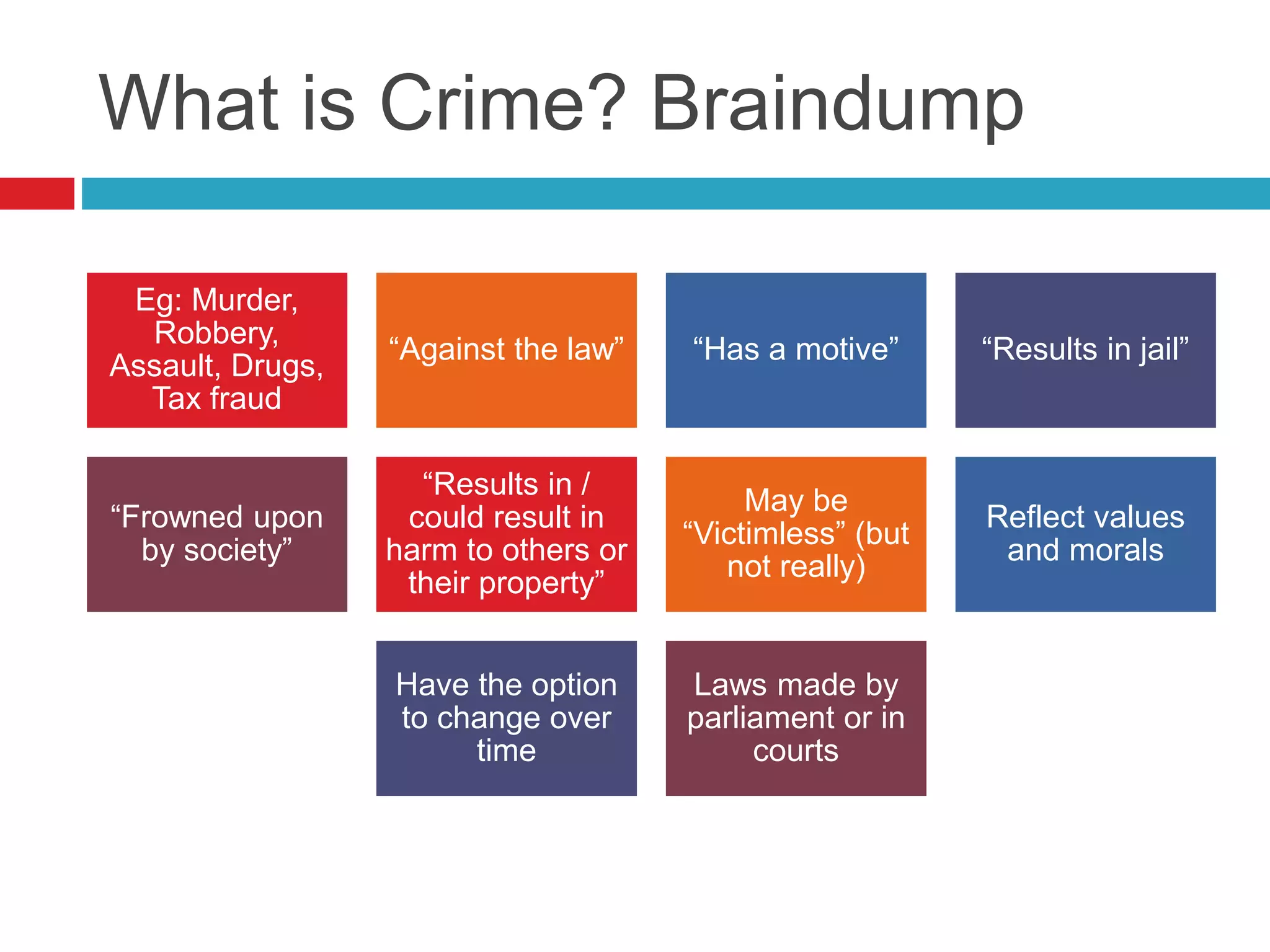





Crime is defined as an act or omission committed against the community that is punishable by the state. What constitutes a crime can vary between jurisdictions and is influenced by a society's values, morals, religion, culture, history, and legal traditions. Sometimes laws need reforming to remove outdated crimes or create new crimes to address changes in society, like computer crimes. The features of criminal law are protecting society, prosecuting crimes against people, the state, or property, where the state takes action against offenders through police prosecution in court under the burden of proof of beyond a reasonable doubt.





