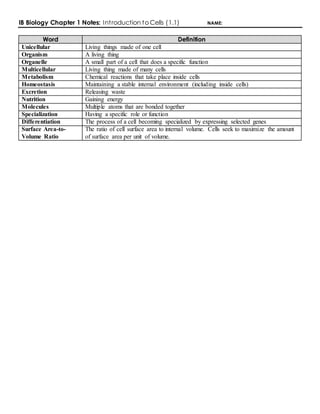
The document covers key concepts in IB Biology related to cells, including definitions of terms such as unicellular and multicellular organisms, organelles, and the principles of metabolism and homeostasis. It discusses the importance of the surface area-to-volume ratio in cell size limitation and outlines cell theory essentials, differentiation, and emergent properties. Additionally, it provides examples of atypical cells and methods for investigating cell structure using light microscopes.