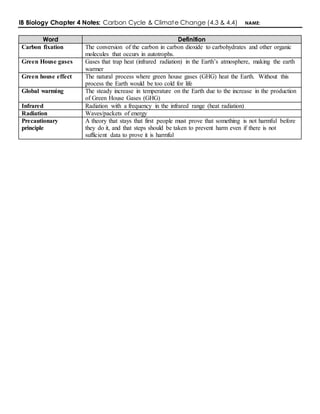
The document covers the carbon cycle and climate change, detailing processes such as carbon fixation, greenhouse gases, and global warming. It explains the roles of autotrophs, anaerobic organisms in methane production, and the formation of fossil fuels and limestone. Additionally, it discusses the impact of greenhouse gases on global temperatures and climate patterns, emphasizing the correlation between rising carbon dioxide levels and climate change linked to human activity.