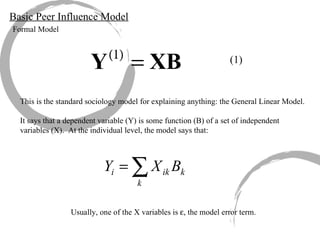
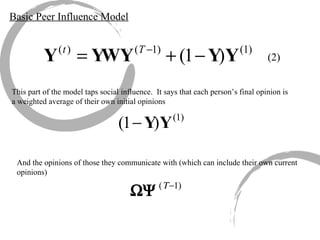
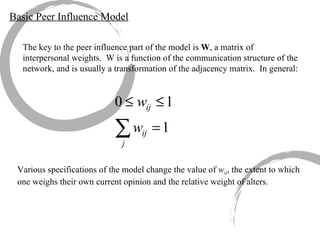
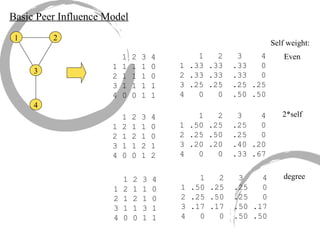
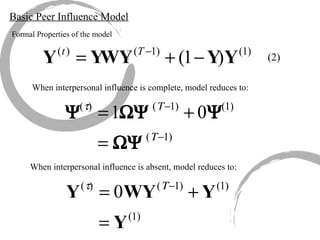
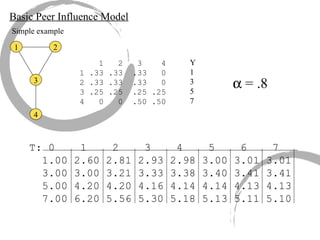
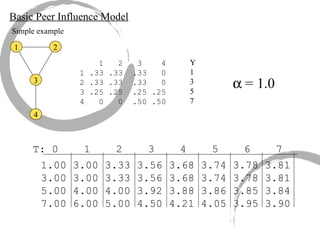
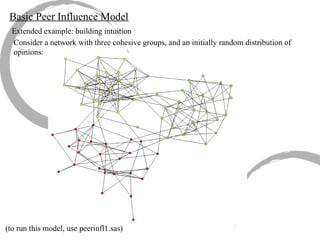
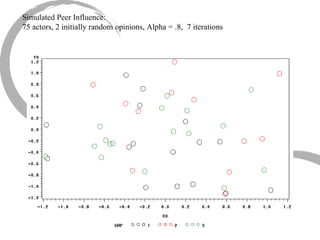
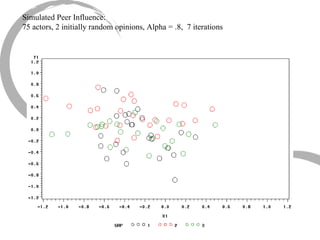
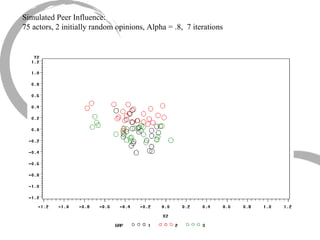
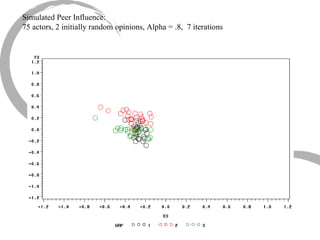
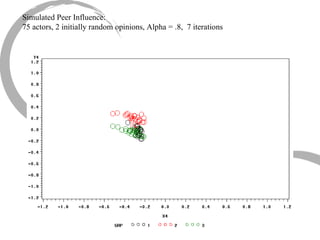
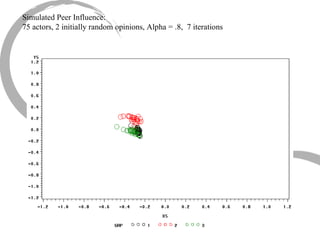
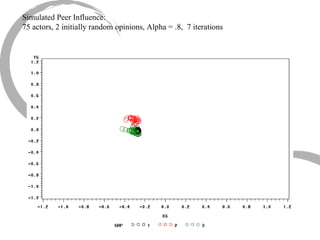
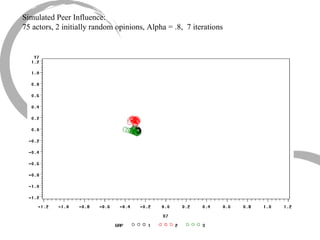
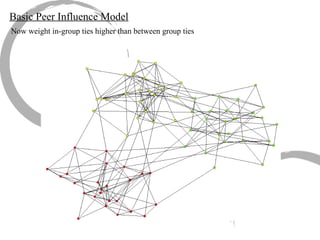
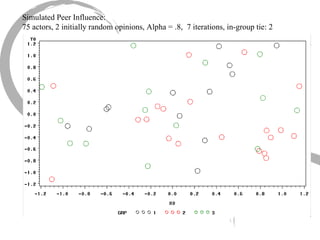
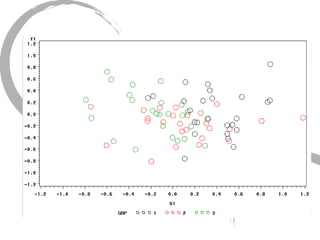
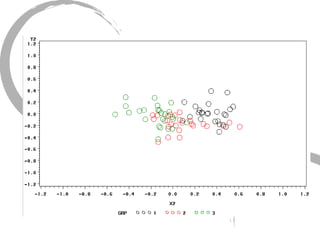
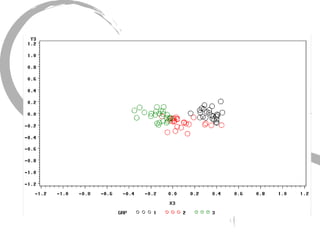
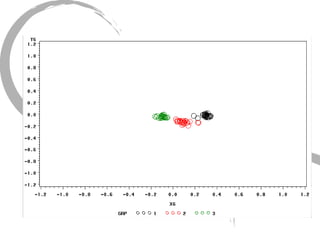
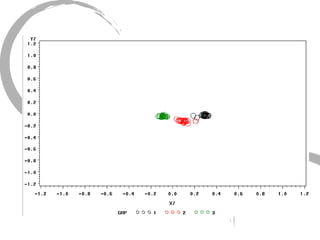
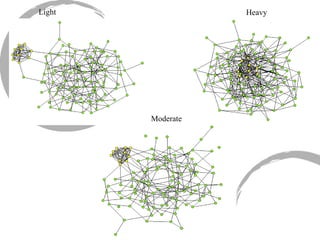
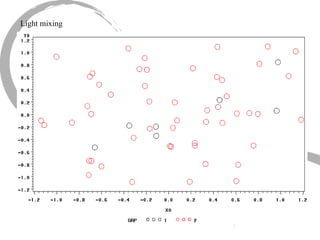
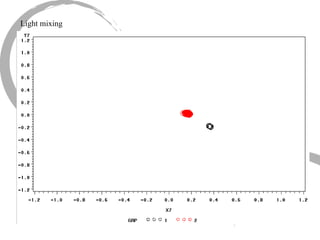
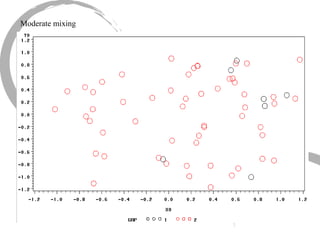
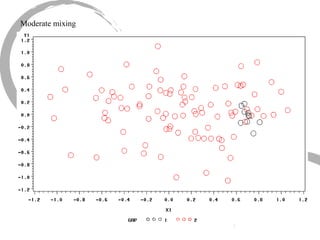
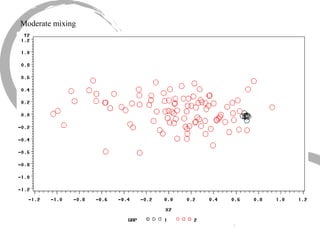
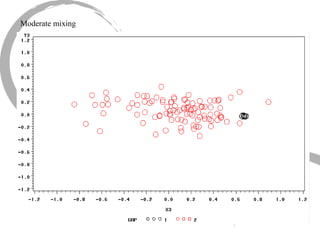
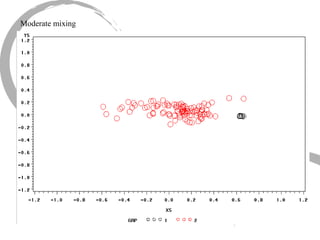
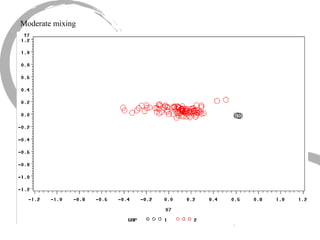
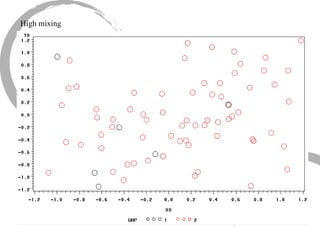
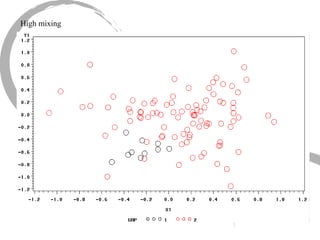
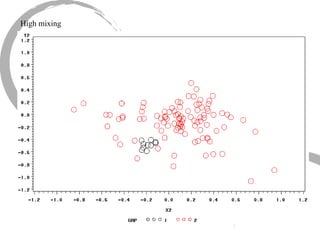
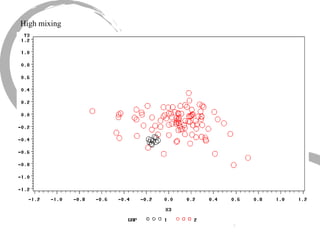
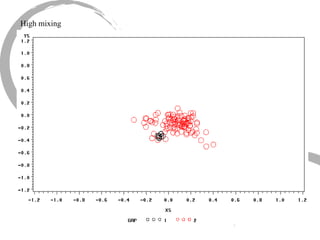
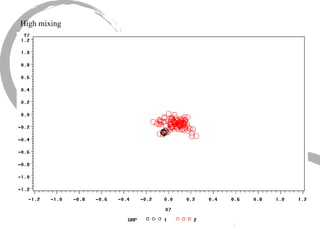
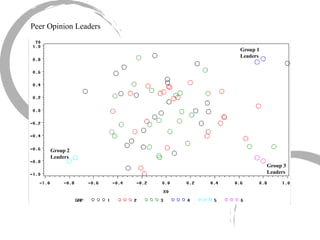
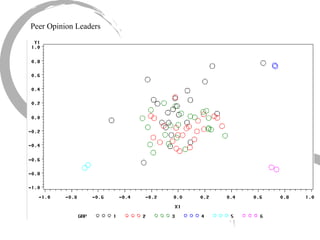
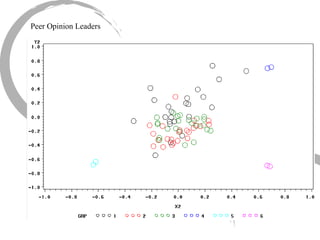
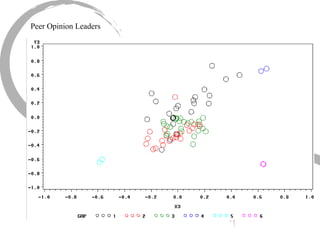
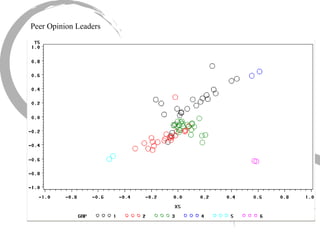
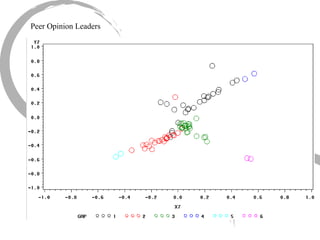
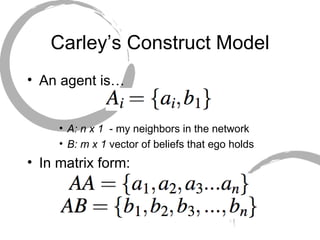
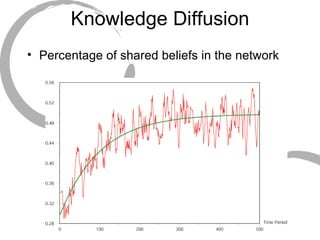
The document discusses how social networks and individual attitudes influence each other through two related processes: social contagion and homophily. Social contagion refers to the diffusion of attributes through a social network based on its structure, while homophily refers to the formation of social networks based on shared attributes among individuals. The document outlines Friedkin's model of social influence, which models how individuals' opinions are shaped both by their own characteristics and by interpersonal influences within their social network over multiple time periods.