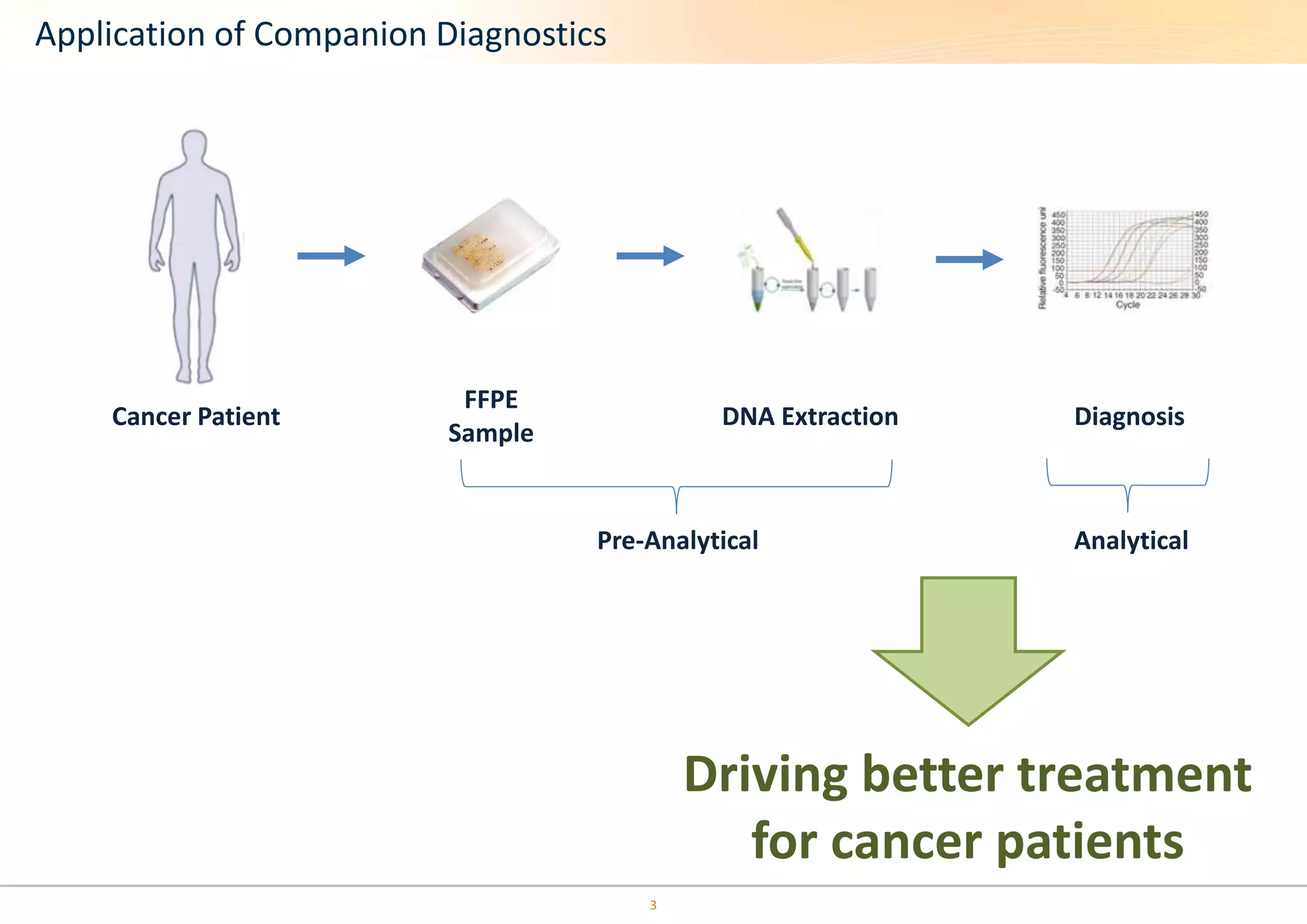
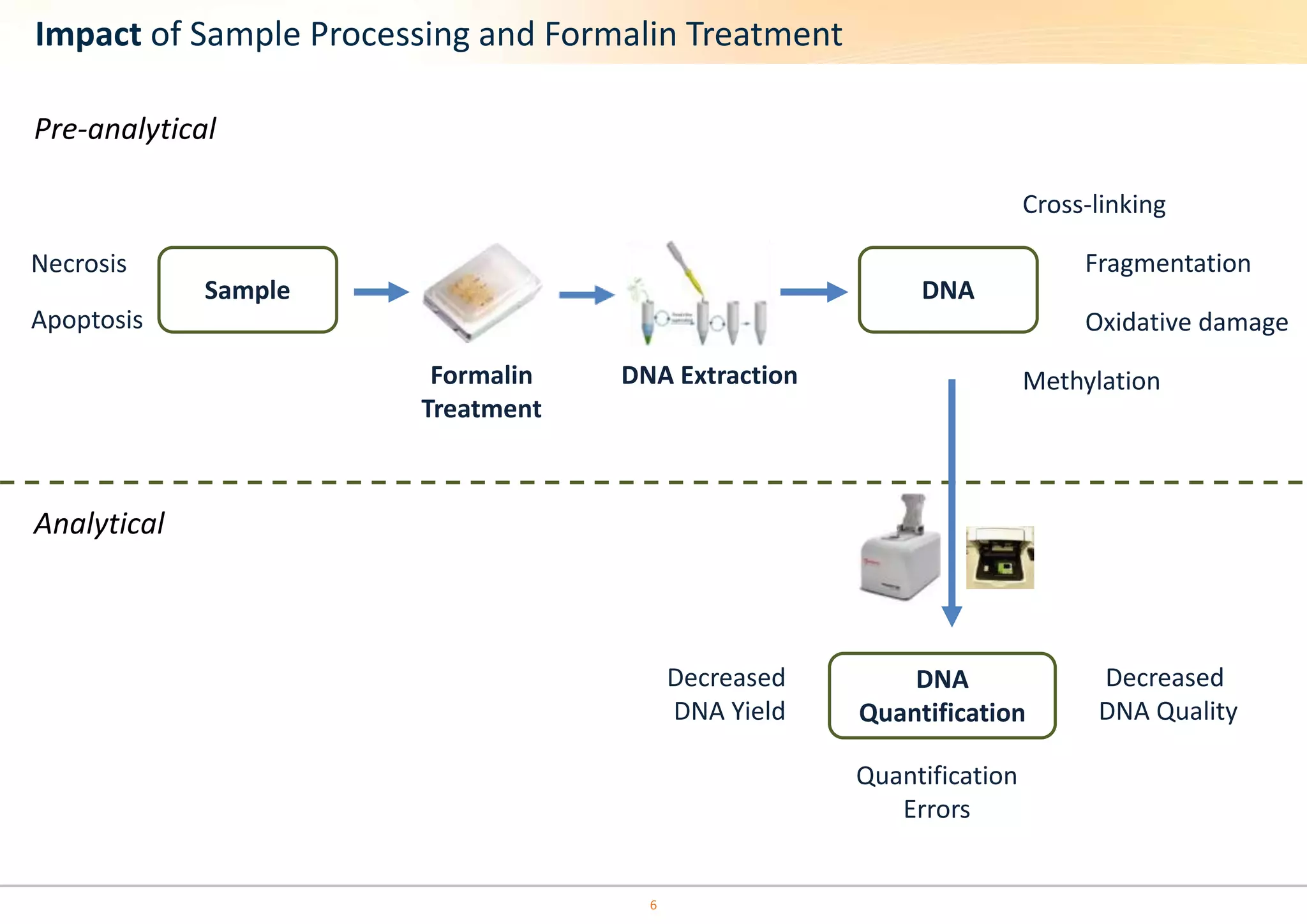
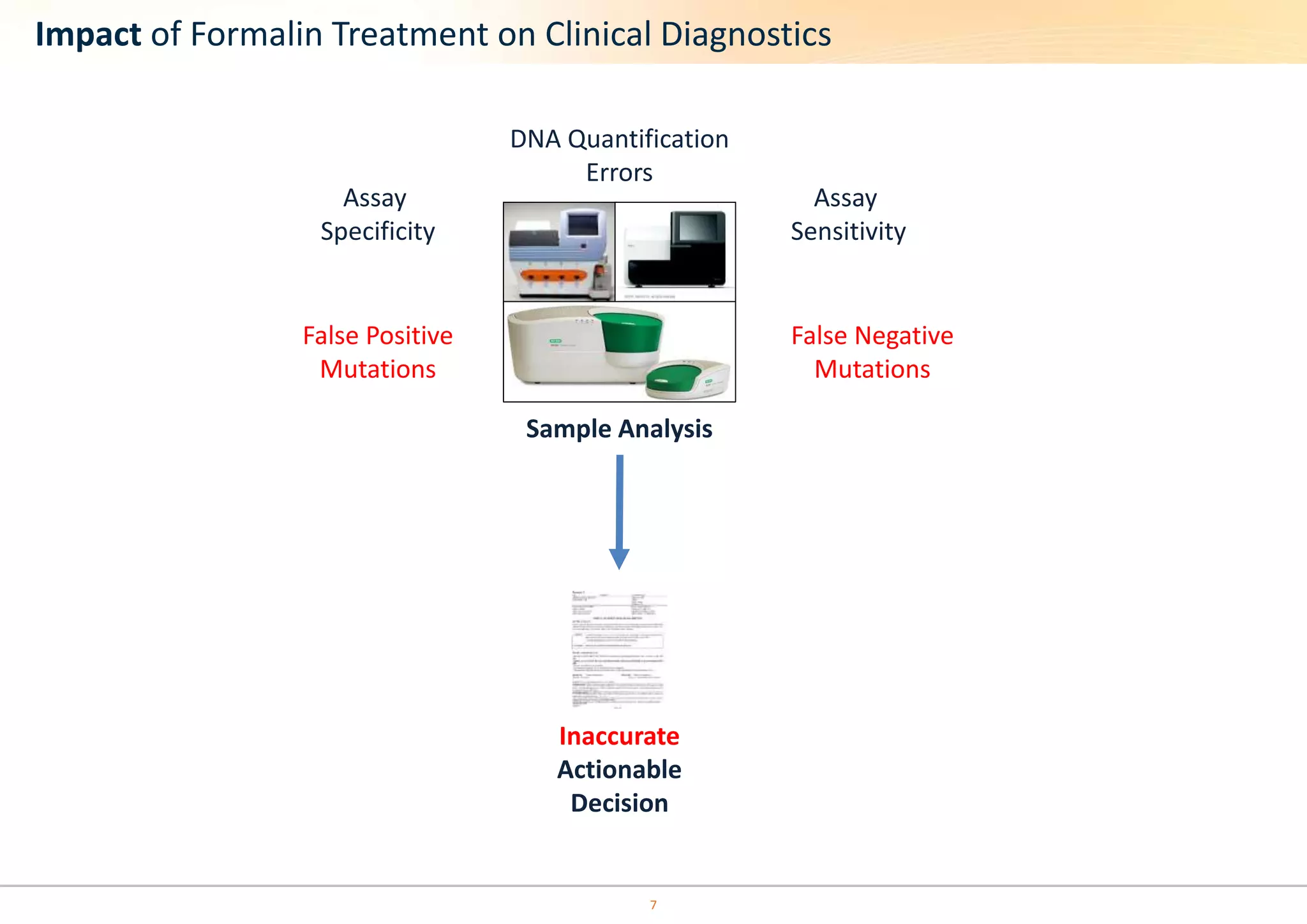
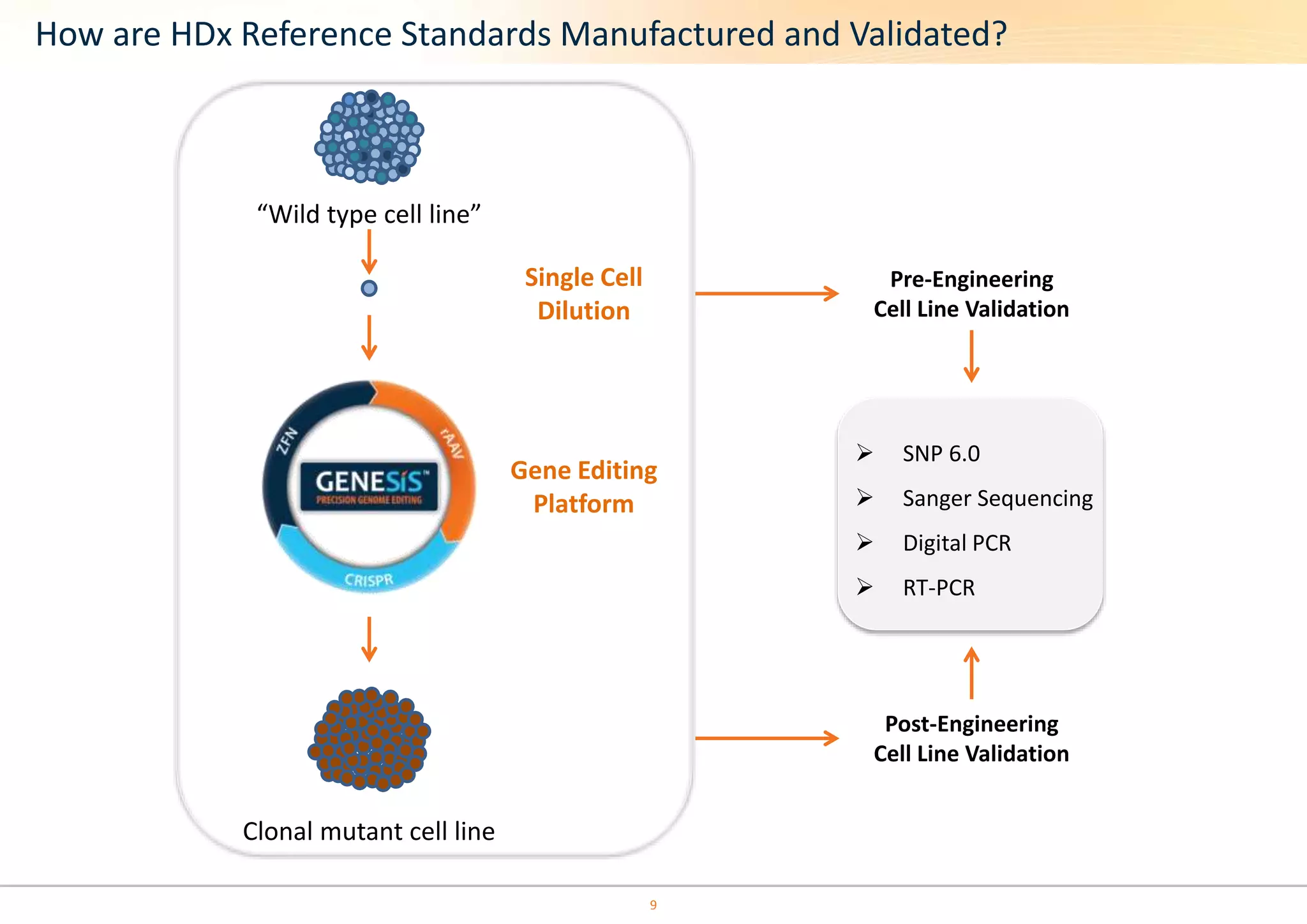
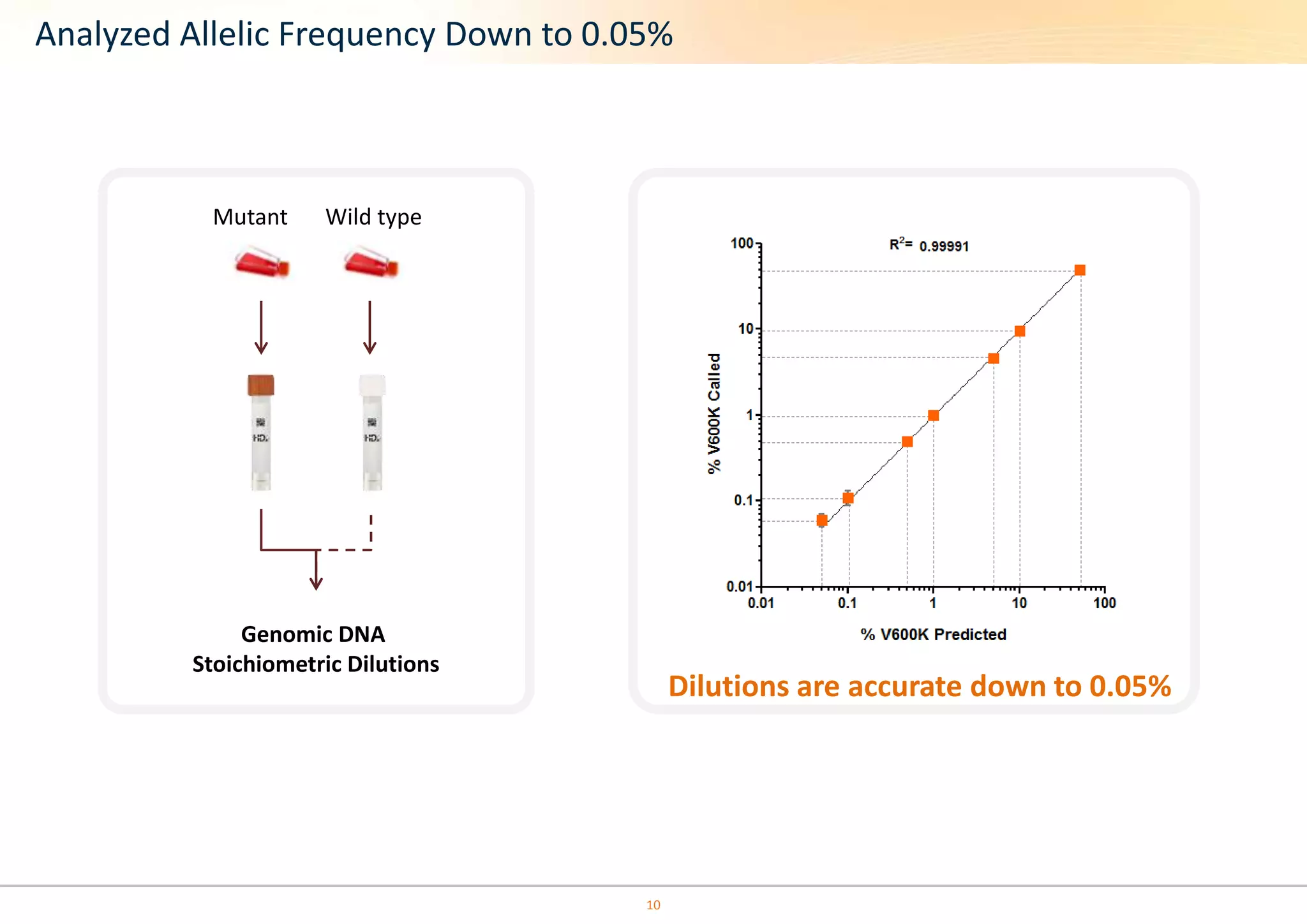
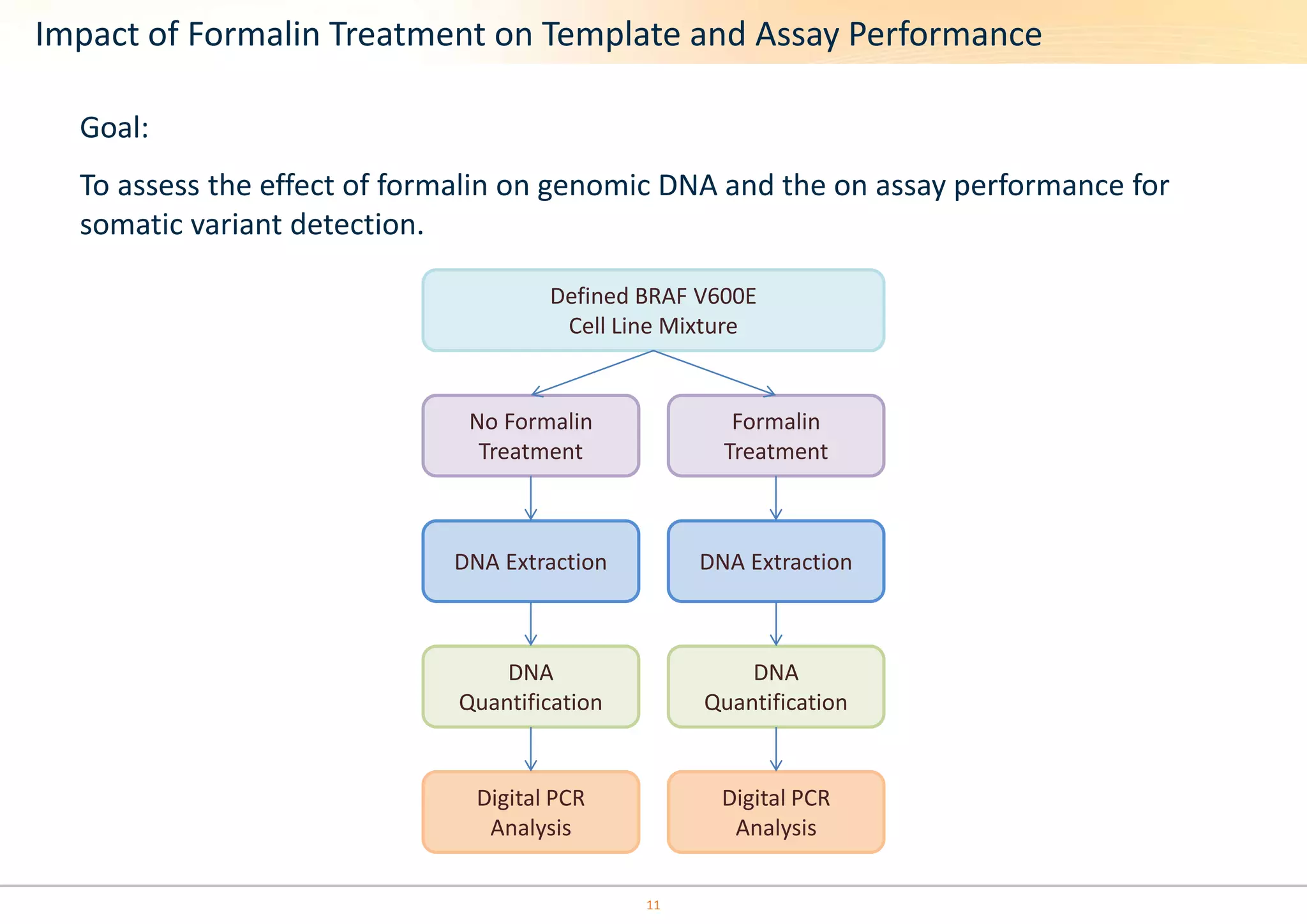
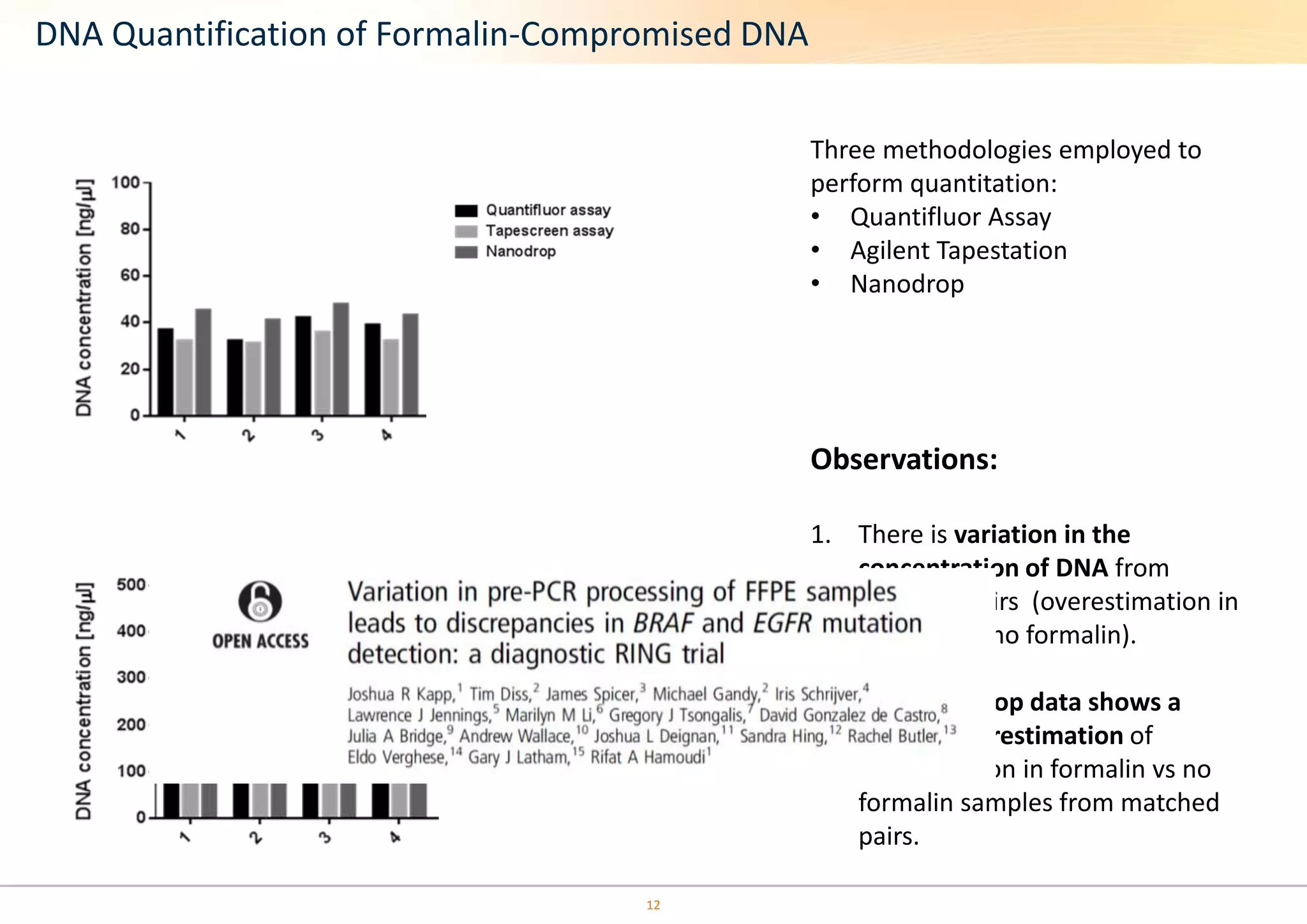
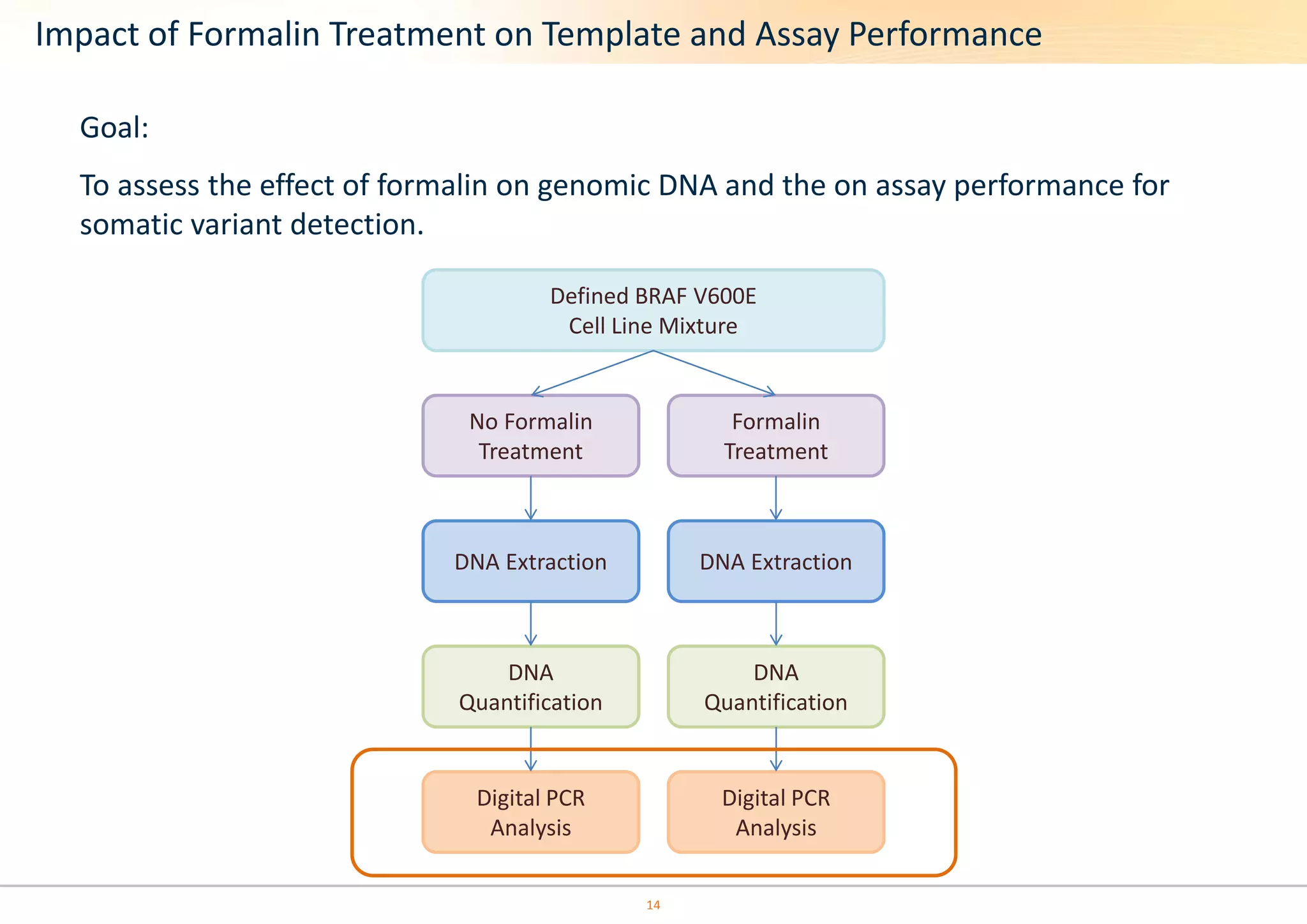
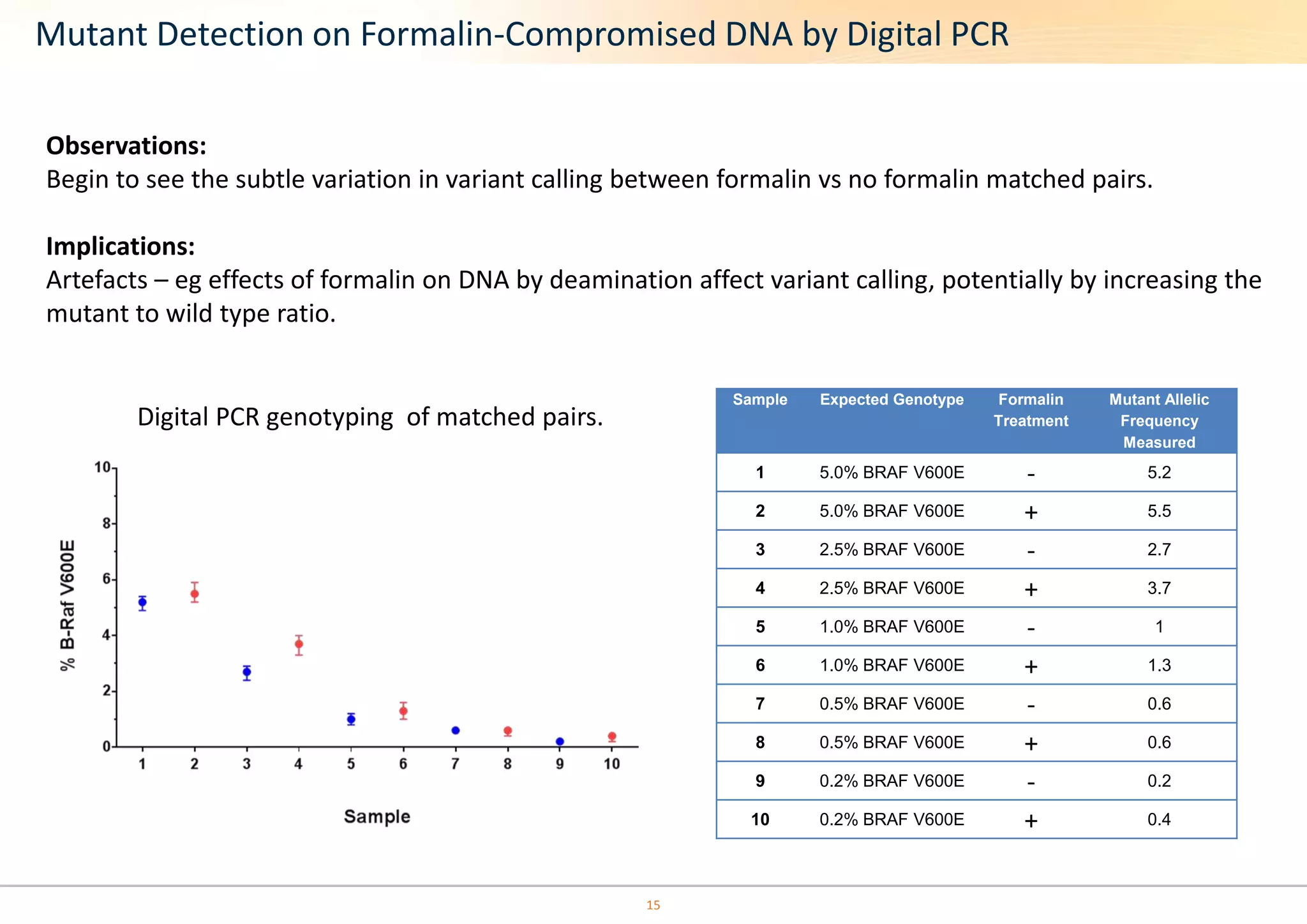
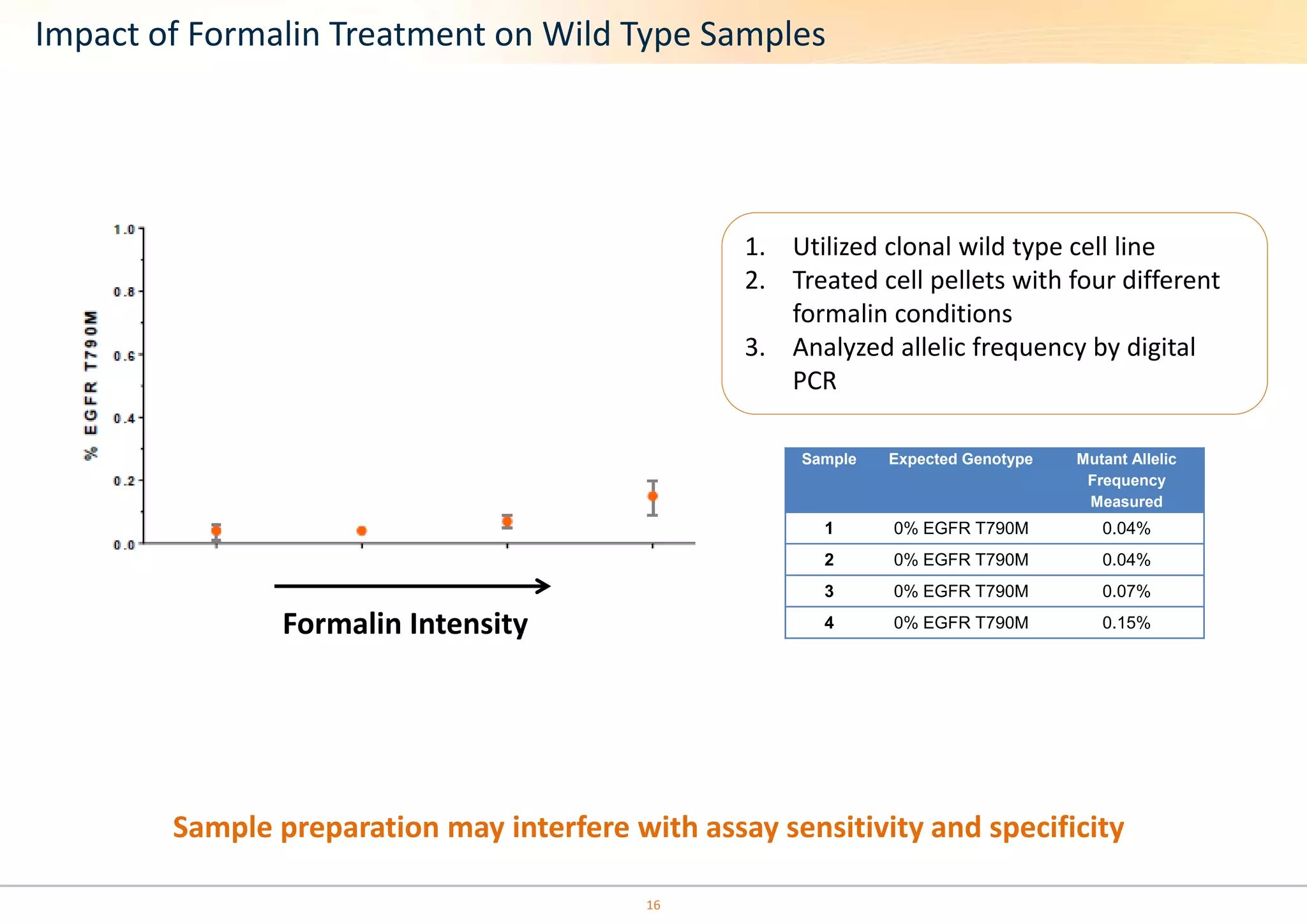
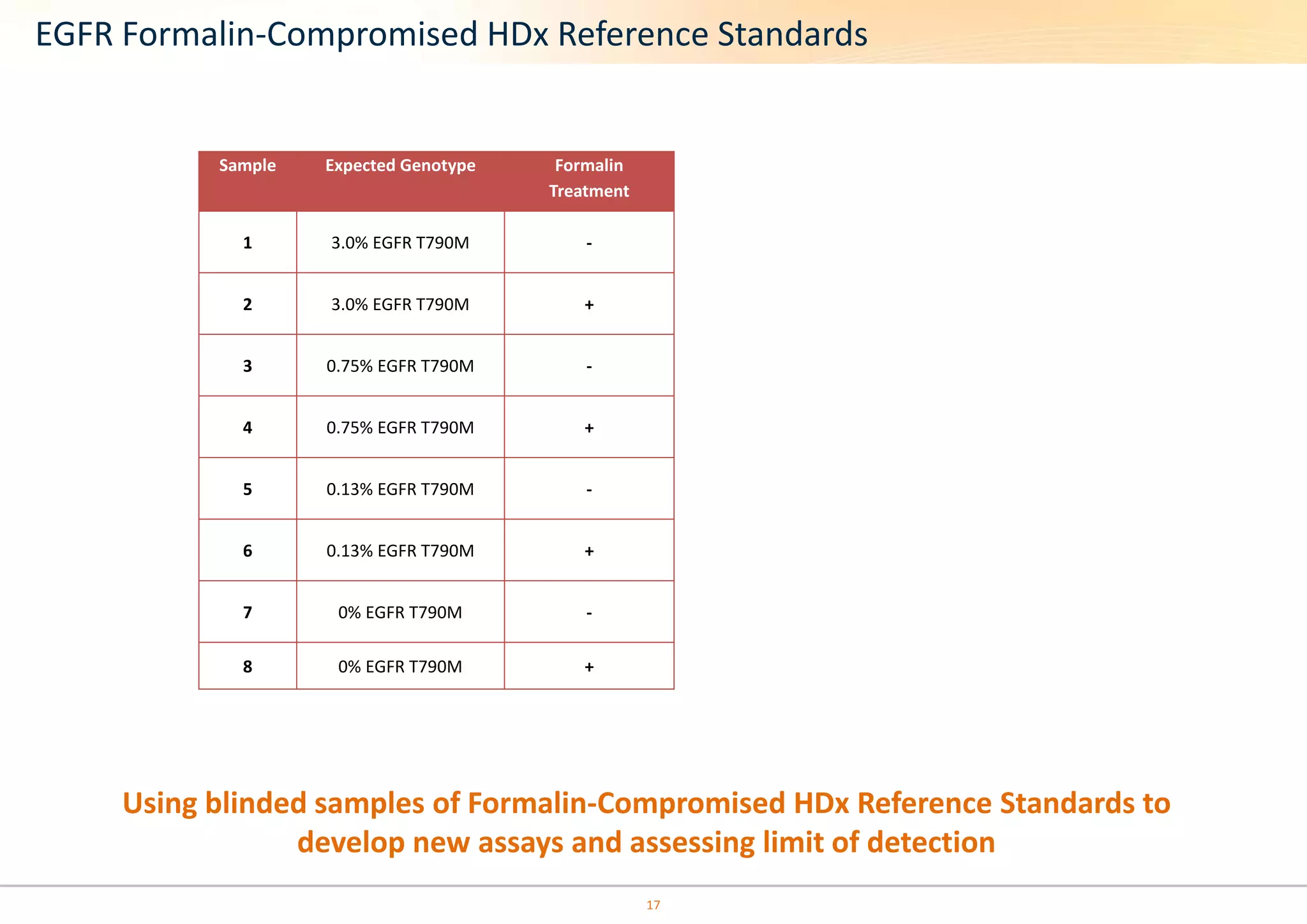
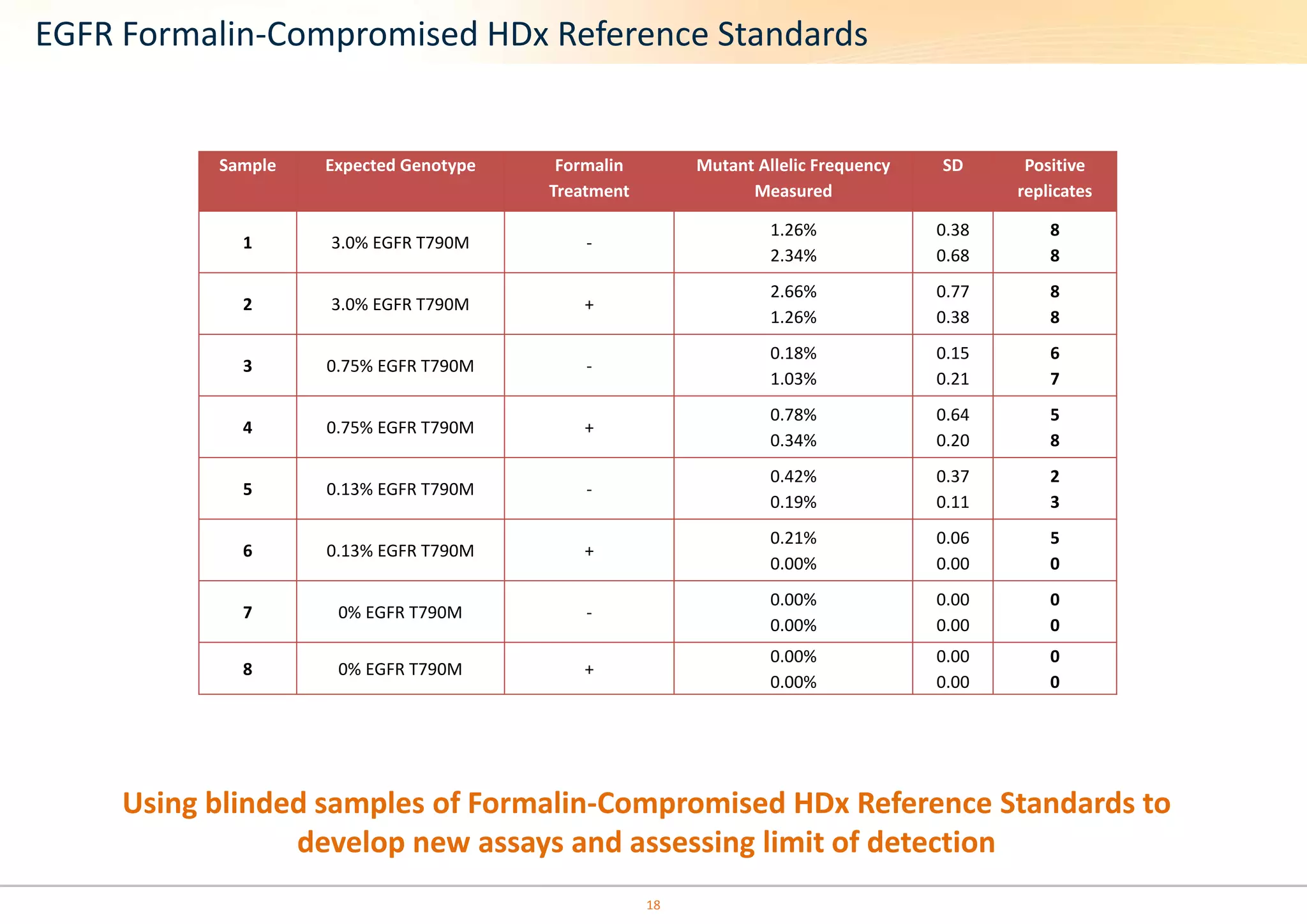
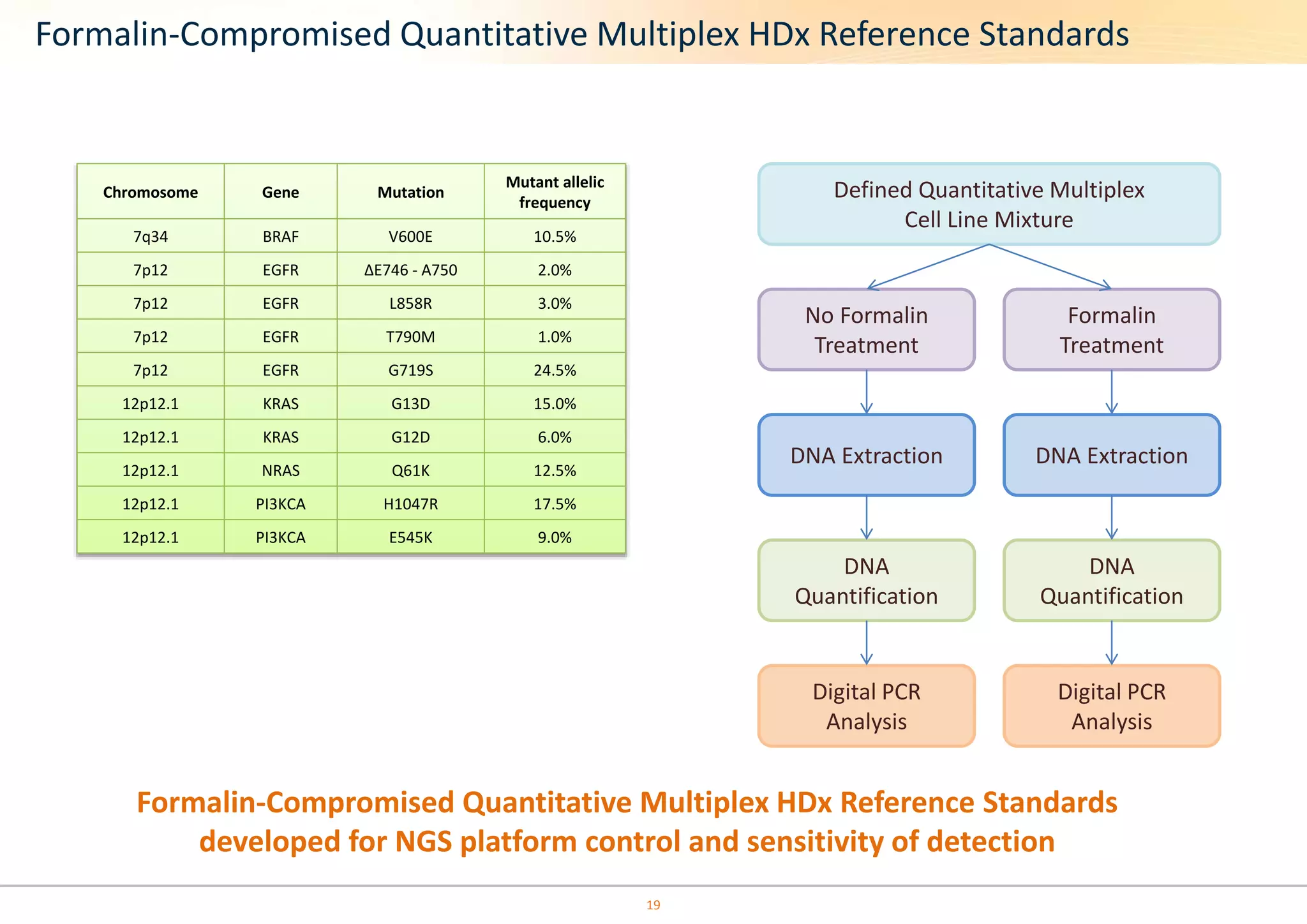
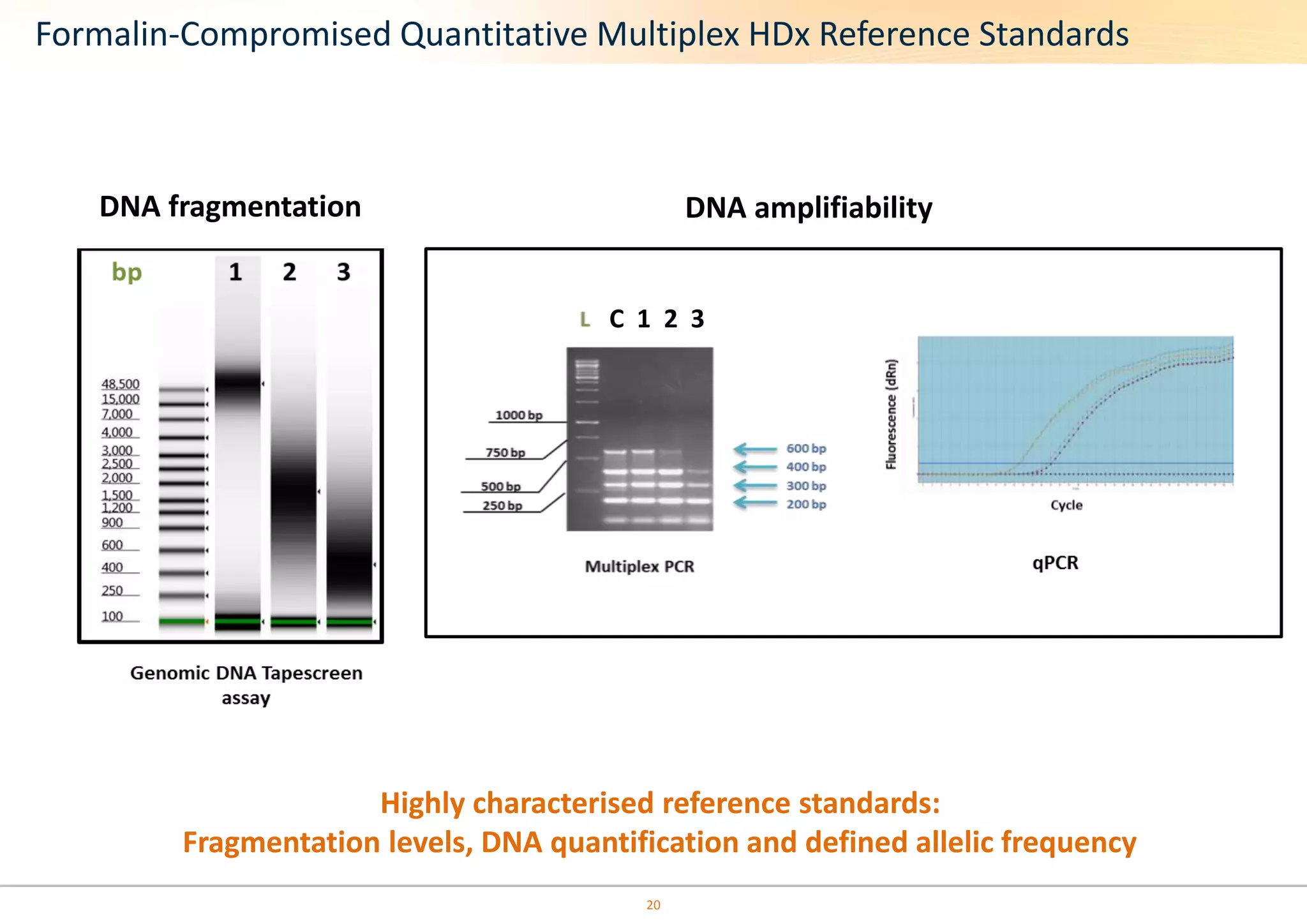
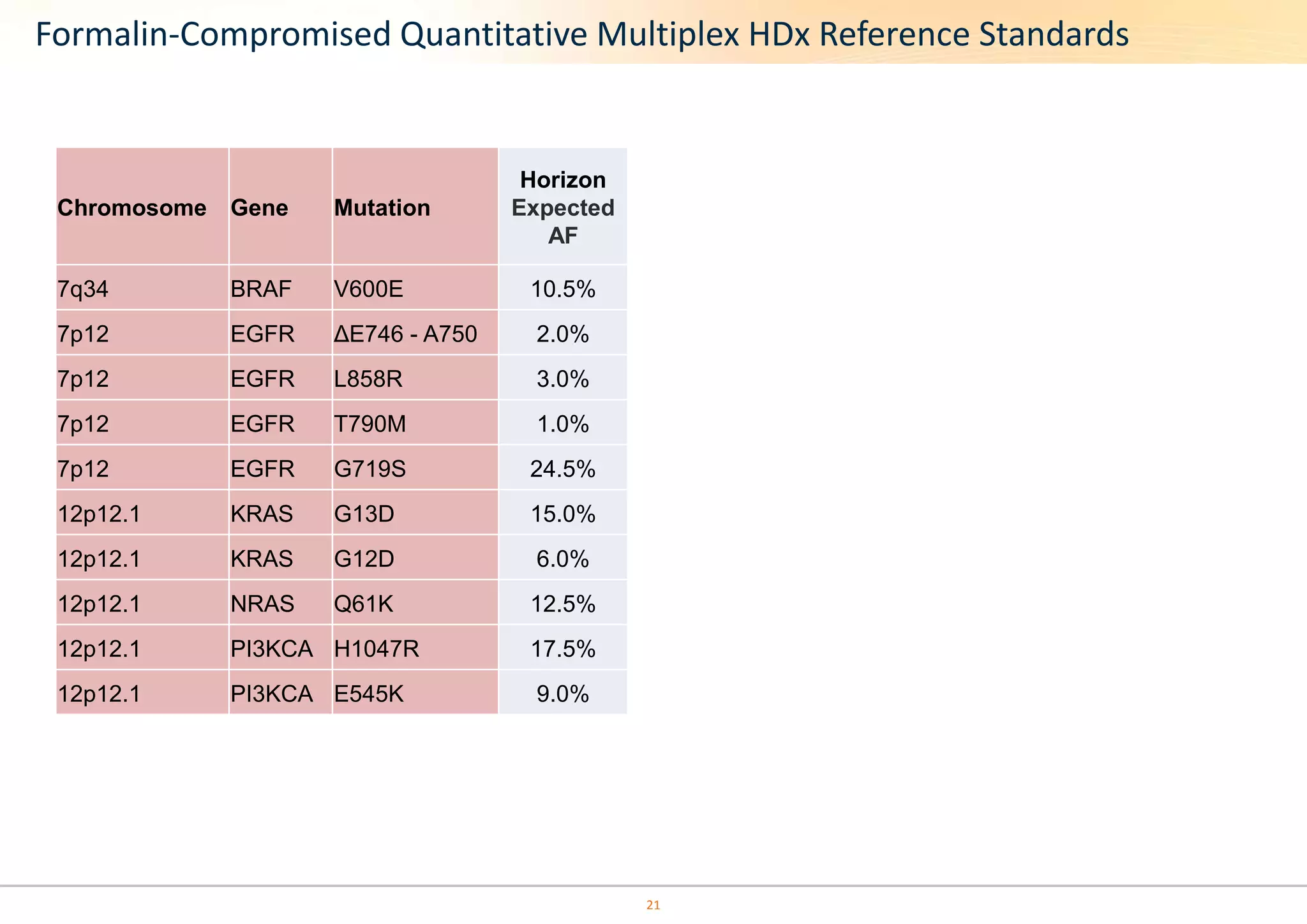
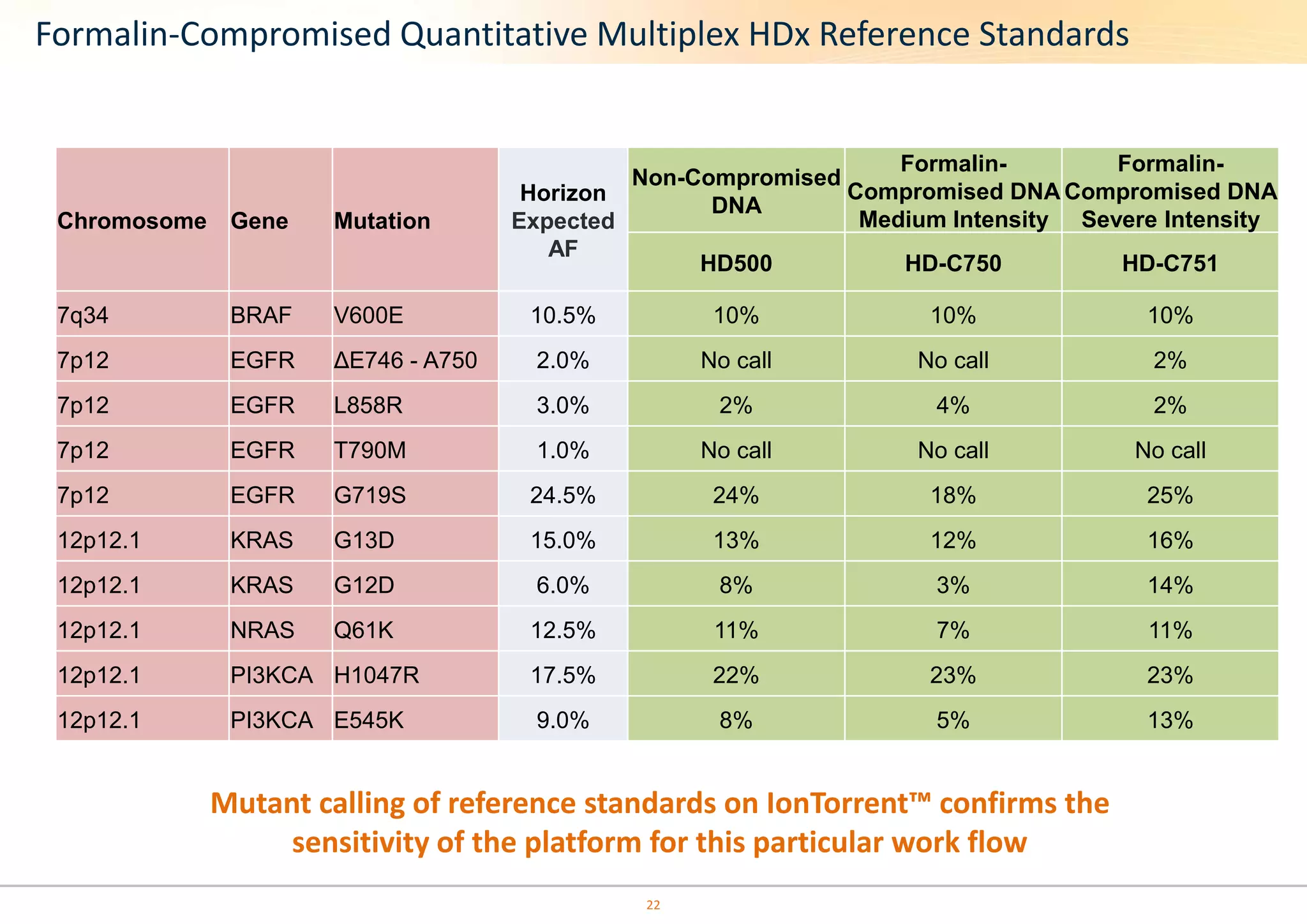
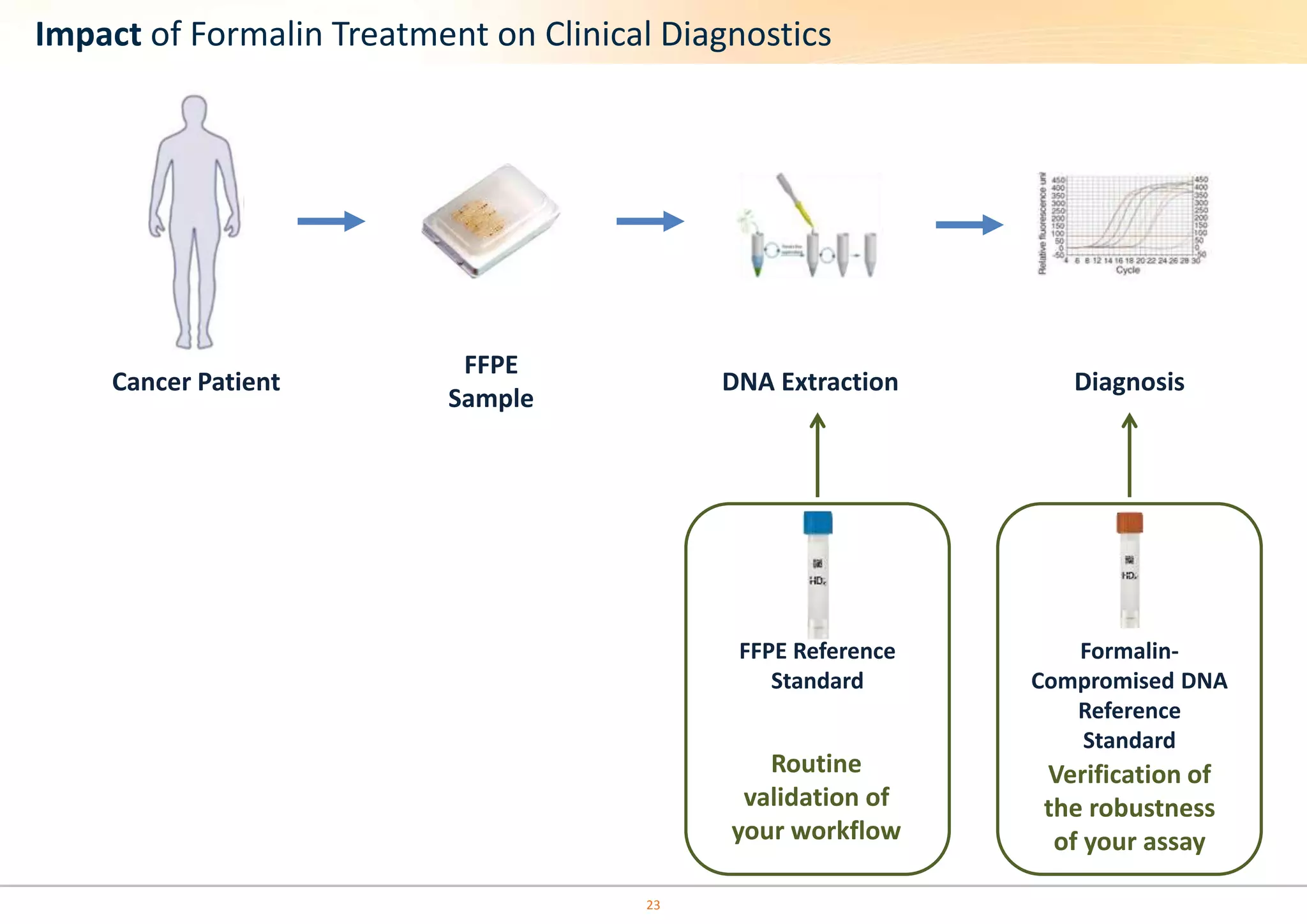
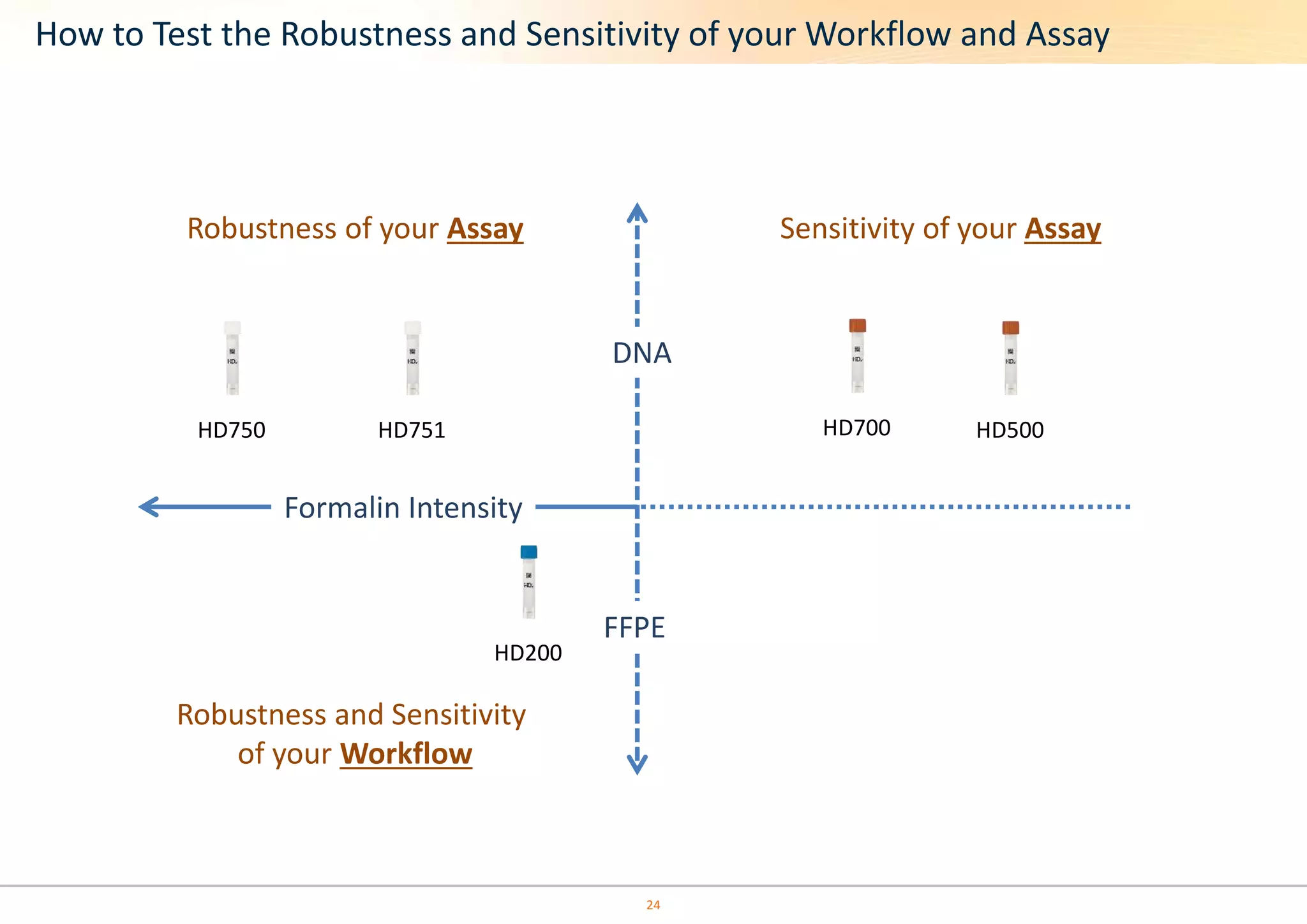
The document discusses the impact of formalin treatment on DNA extraction and clinical diagnostics, highlighting how it affects DNA yield, quality, and assay performance. It presents data on quantification errors, false positives, and false negatives in mutation detection, emphasizing challenges in personalized medicine related to formalin-compromised samples. Researchers at Horizon Diagnostics are developing reference standards to better understand these effects and improve molecular assay reliability.