Colloid solutions like albumin can be used in burn resuscitation after the first 24 hours to decrease edema and volume needs while blunting myocardial depression, but early use risks worsening capillary leak. Hypertonic saline may benefit high-risk burn patients by reducing fluid needs but requires close monitoring and is best used in specialized burn centers given the risks. The safety and efficacy of both colloids and hypertonic saline have been shown in pediatric and geriatric populations if lower tonicity solutions are used.
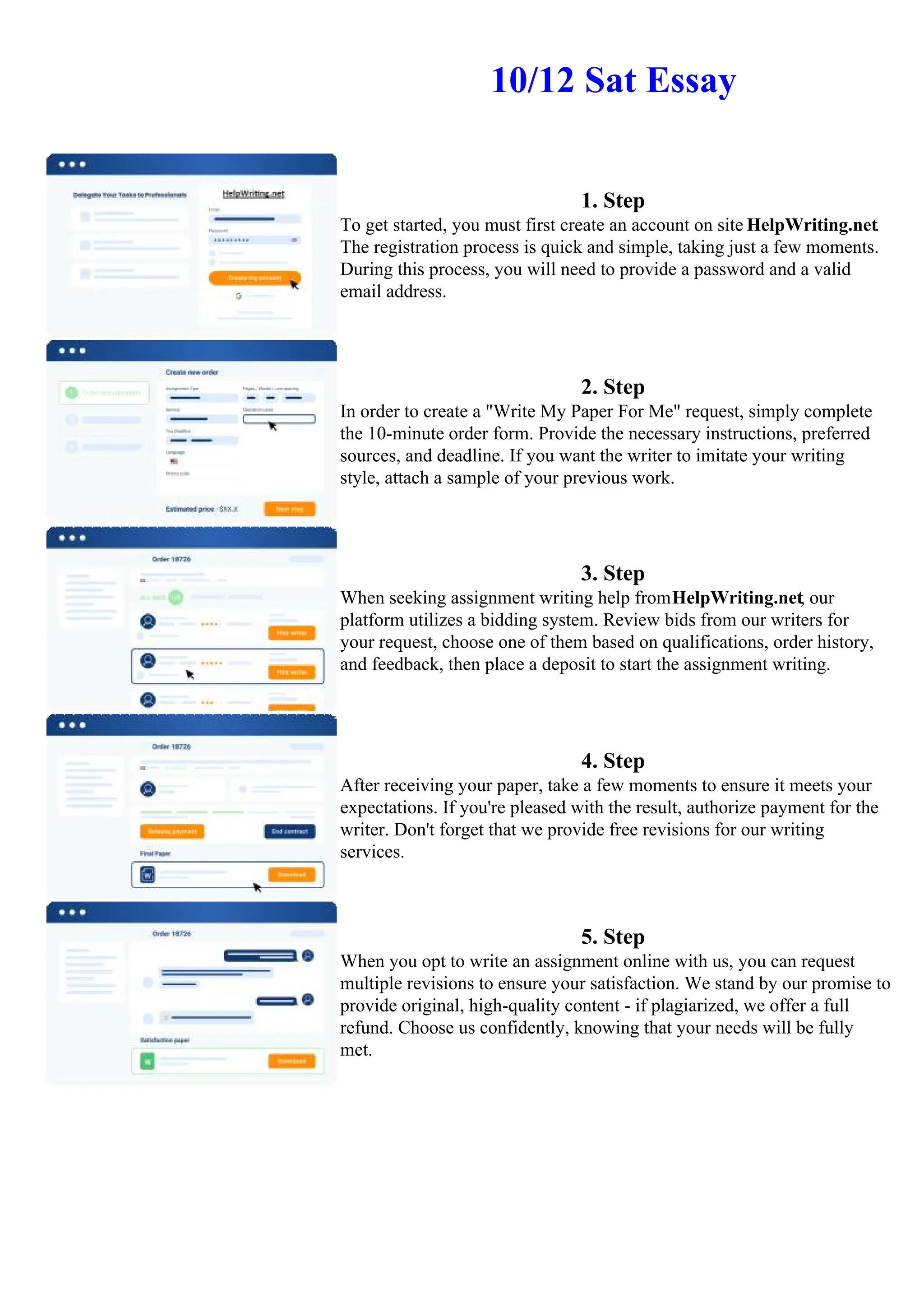

































![Social Problems Of The Troubles In Ireland
Social Problems of the Troubles in Ireland For about 150 years Ireland and neighboring countries
have struggled with social controversy and segregation that has consumed society and its views,
which have been labeled as the Troubles . Ireland has struggled to become peaceful and accept the
ties it has to the United Kingdom. In every country there is hate, wars, and events that cause the
population to raise up arms and try to get their points across, but in Irelandit has lasted a very long
time due to Nationalists versus the government, Catholics versus Protestants, Loyalists versus
Unionists, and many other radicals that believed in something greater than what Ireland was during
certain time periods. Britain played a big role in Irish... Show more content on Helpwriting.net ...
(Personal communication, April 20, 2014)
The IRA is the Irish Republican Army made up of Irish volunteers since 1919. Many of the
volunteers have been involved in street riots, hate crimes, and violence. They are known for
burning homes and shooting civilians. (Coogan, 1993, 4) Throughout 1920 s to the 1990 s
Ireland had some serious problems. New groups kept springing up, creating violence, riots, and
rebellions. Around 1918 the War of Independence had begun and lasted until July 1921.
(Douglas, 1999, 104) On Sunday, November 22 the event that is very well known as Bloody
Sunday occurred. Assassinations and brutal killings took place; the IRA killed fourteen British
officers in Dublin and killed 12 people during a football match. (Douglas, 1999, 105) Ireland s
militia grew tired of the IRA unlawful acts. In the early 1930 s the economic war began due to
land payments owed to Britain. (Douglas, 1999, 118) During this time riots broke out killing 12
people, injuring 600, and driving 2000 people from their homes because of disputes between the
North and the South.(Douglas, 1999, 129) Nationalism has been one of the leading ideals
throughout Ireland s history. In the words of Richard English, It [nationalism] has caused and
fuelled wars; stabilized and destabilized states; defined political and cultural life across the globe .
(2006, 3) Irish nationalism was based upon ancient and primitive foundations. (2006, 20)
... Get more on HelpWriting.net ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1012satessay-240127111001-07ddf95d/85/1012-Sat-Essay-Online-assignment-writing-service-35-320.jpg)



















