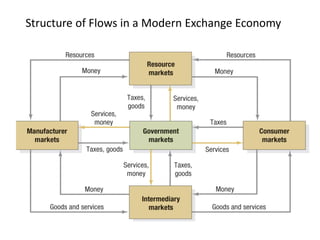
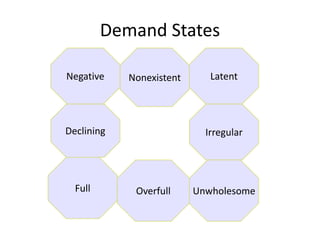
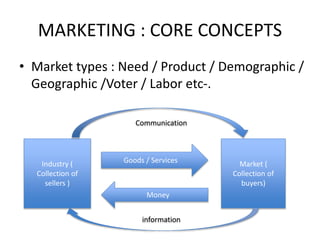
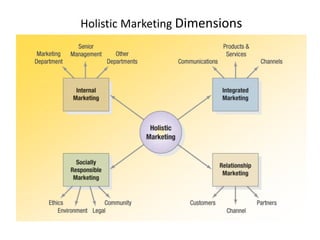
This document discusses core marketing concepts including definitions of marketing, needs, wants, demands, products, markets, and exchange. It outlines different marketing philosophies like the production, product, selling, and marketing concepts. It also discusses societal marketing and how marketing considers social and ethical factors. The functions of marketing management are described as developing strategies and plans, capturing customer insights, connecting with customers, building brands, shaping offerings, delivering value, and creating long-term growth.