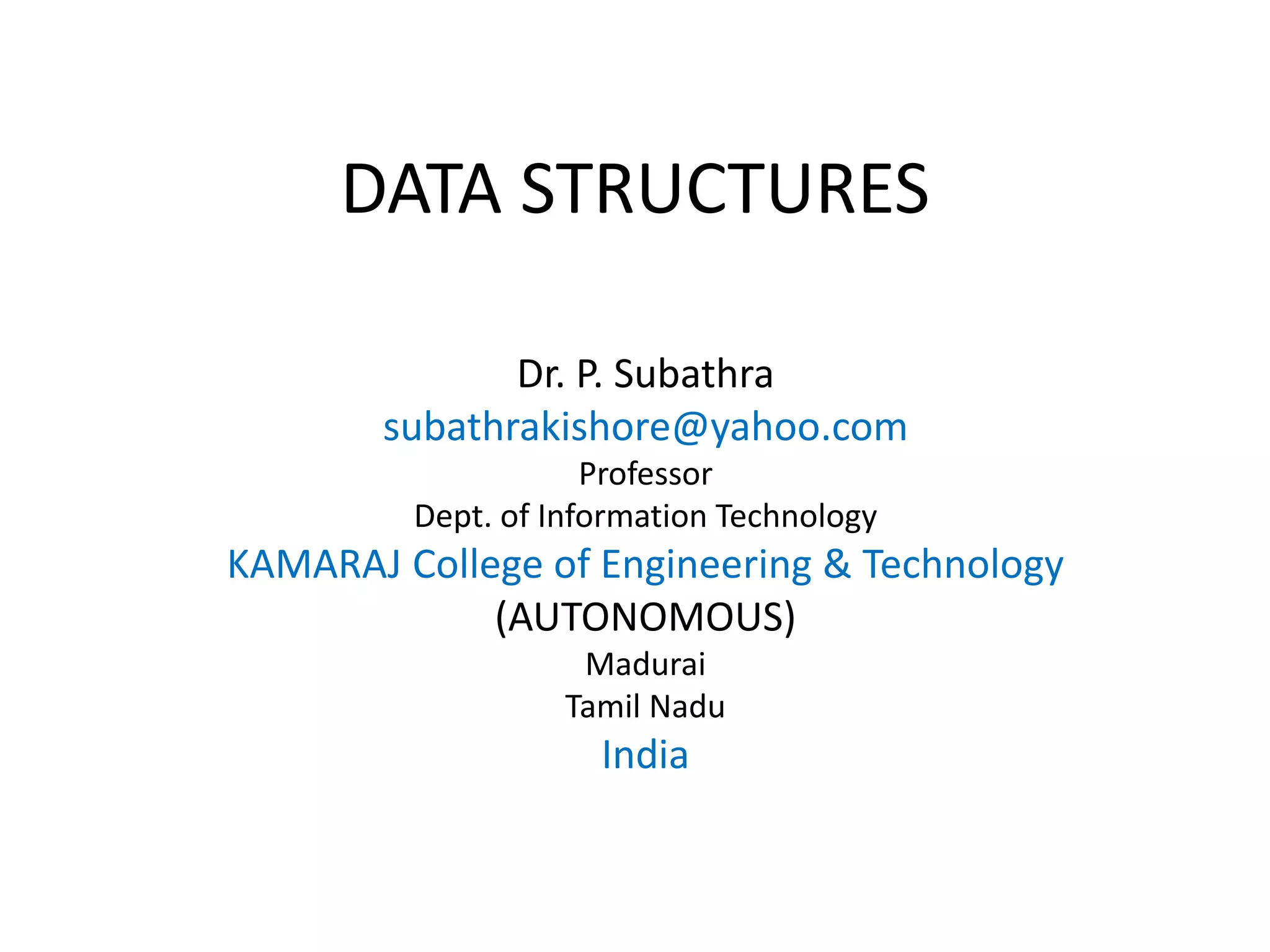
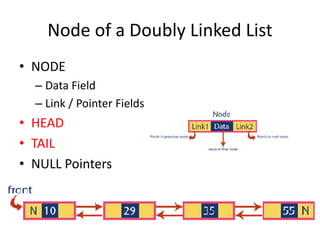
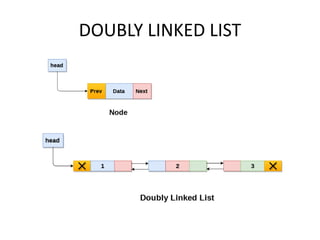
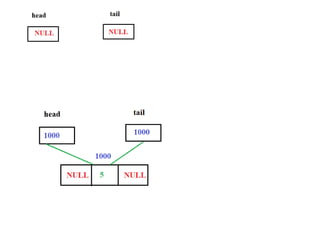
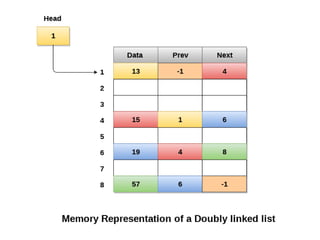
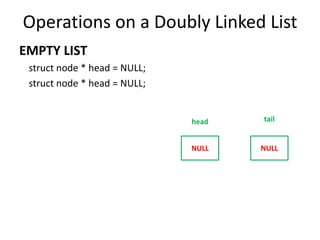
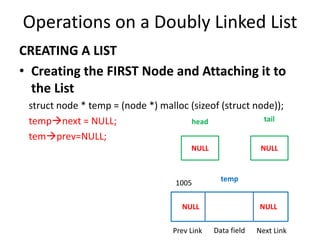
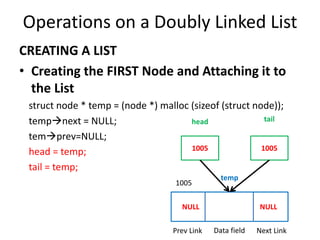
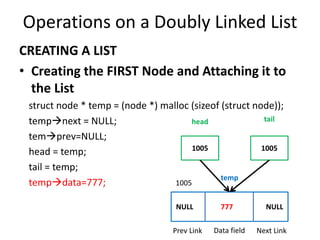
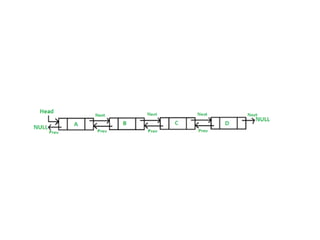
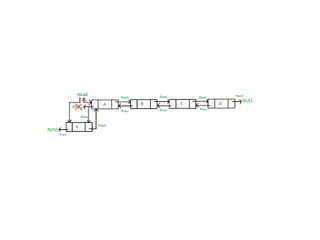
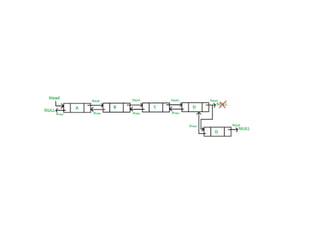
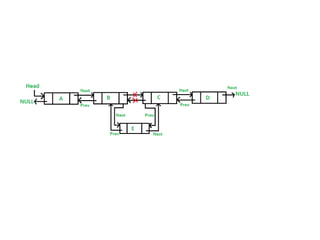
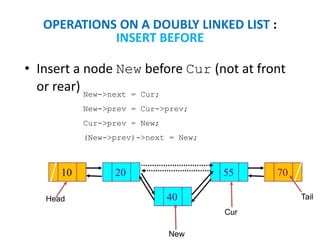
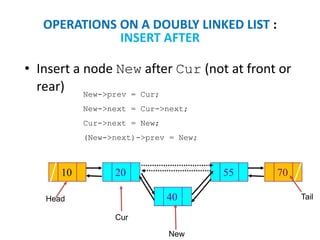
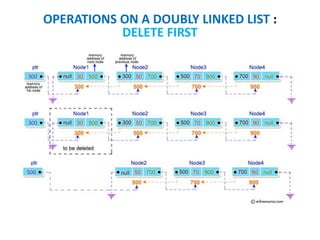
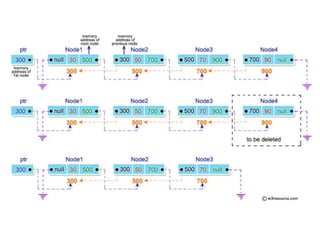
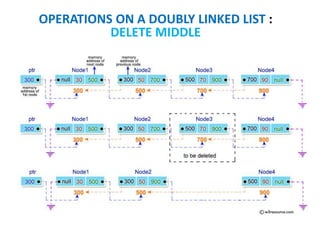
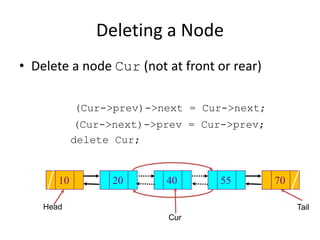
This document discusses doubly linked lists. It begins by explaining some of the limitations of circular singly linked lists, such as the inability to easily traverse backwards. Doubly linked lists are then introduced as a solution, with each node containing pointers to both the next and previous nodes. The key operations on doubly linked lists like insertion at the beginning, end, and middle as well as deletion at the beginning, end, and middle are described algorithmically. Traversal in both the forward and backward directions is also covered. Code examples are provided to demonstrate creating and manipulating doubly linked lists.