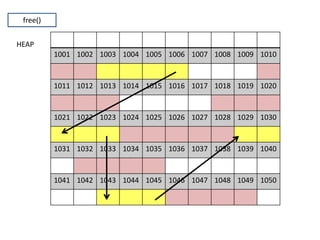
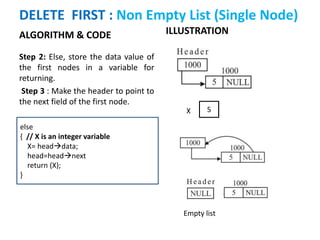
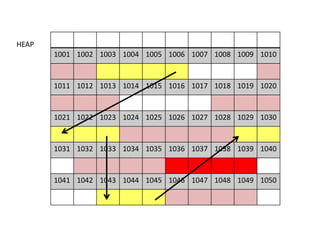
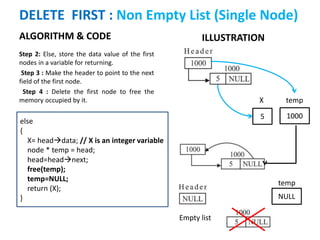
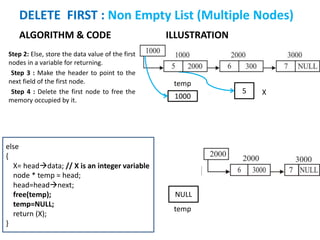
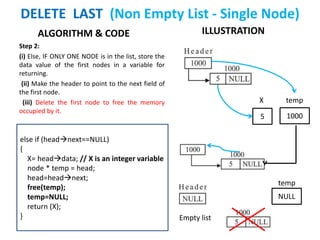
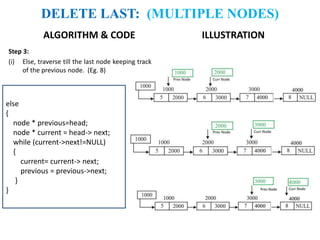
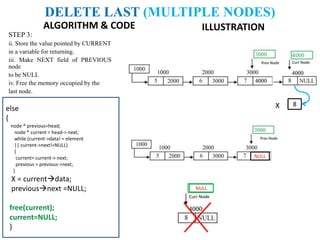
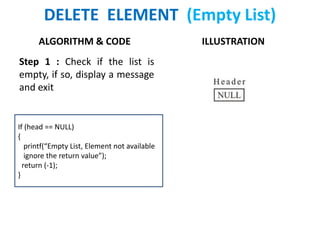
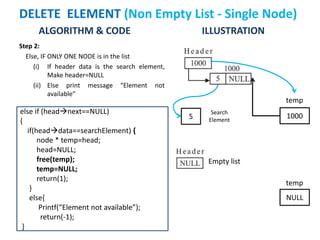
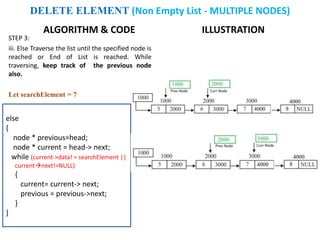
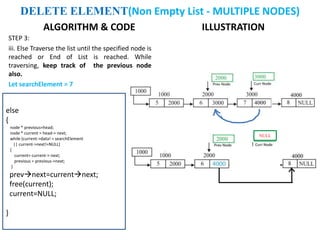
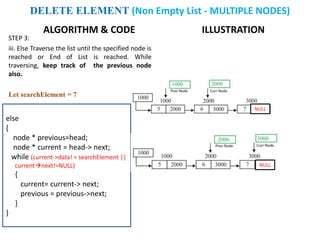
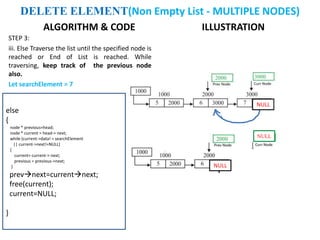
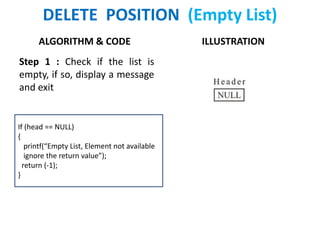
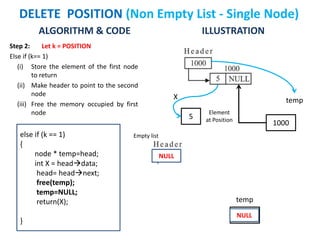
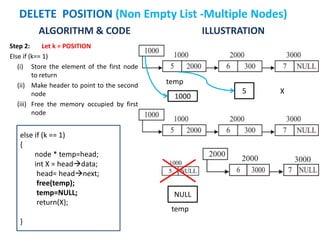
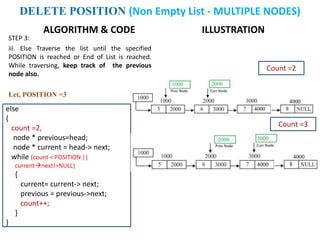
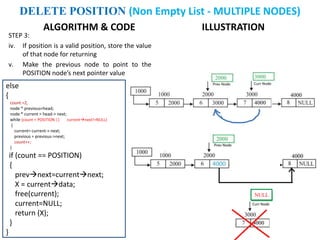
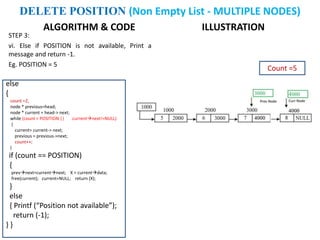
The document discusses various deletion operations on singly linked lists. It provides algorithms and code snippets for deleting the first element, last element, a given element, and an element at a given position in a singly linked list. The algorithms handle both empty lists and non-empty lists with single and multiple nodes. Key steps include checking for empty lists, traversing the list to find the required element or position while tracking the previous node, and updating pointers after deleting the node.