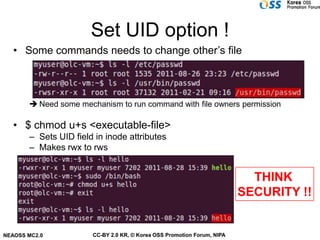
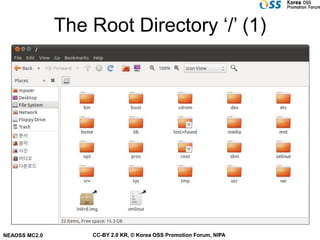
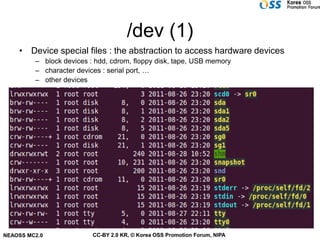
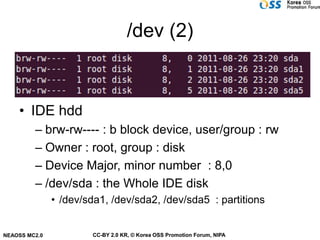
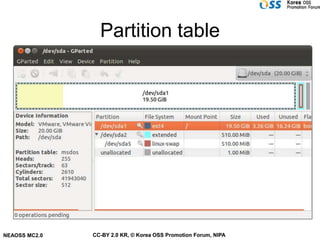
The document discusses Linux file systems and files. Some key points include:
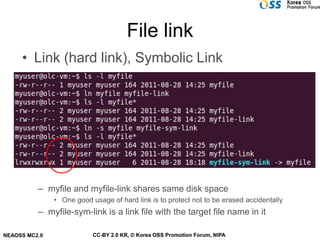
- In Linux, everything is treated as a file with different attributes like regular files, directories, links, and devices.
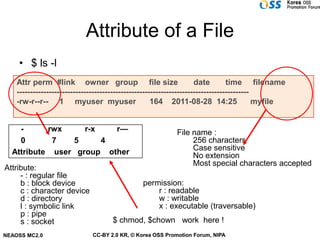
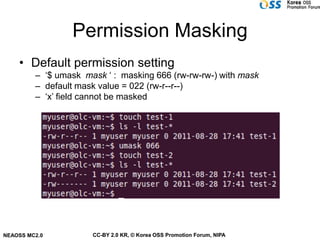
- Files have owners, groups, and permissions that control access for owners, groups, and others.
- There is a predefined directory structure with important directories like /etc, /usr, /sbin, and users' home directories under /home.
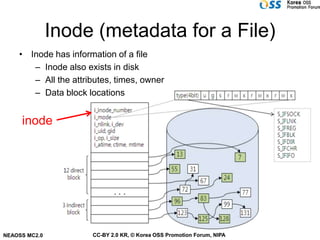
- Inodes store metadata about files like attributes, ownership, and locations of data blocks on the disk.